

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 2034.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160377
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
AN Huiqin1,*, YU Yucai1, YAN Lin1, WU Tingting1, LI Xiaofeng1, HE Xiaoling1, ZHAO Lizhi2, HUANG Weiping3,*
Received:2016-05-26
Online:2016-11-10
Published:2016-10-20
Contact:
AN Huiqin,HUANG Weiping
E-mail:anhuiqinhebei@163.com;hwp914@nankai.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
AN Huiqin, YU Yucai, YAN Lin, WU Tingting, LI Xiaofeng, HE Xiaoling, ZHAO Lizhi, HUANG Weiping. Synthesis of Highly Dispersed Au Nanoparticles Modified N-Doped TiO2 Nanotubes by the Assist of Lysine and Their Photocatalytic Activity†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(11): 2034.
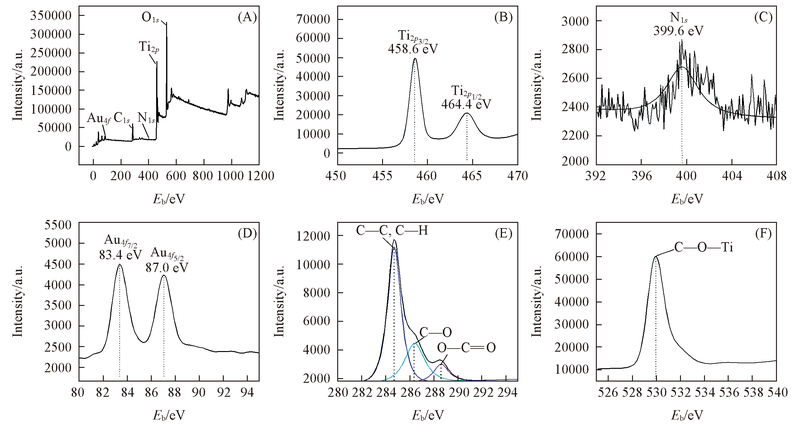
Fig.4 Wide XPS spectrum of Au/N-TiO2 nanotubes with 1.0% N and 3.0% Au loading(A) and high resolution XPS spectra for Ti2p(B), N1s(C), Au4f(D), C1s(E) and O1s(F)
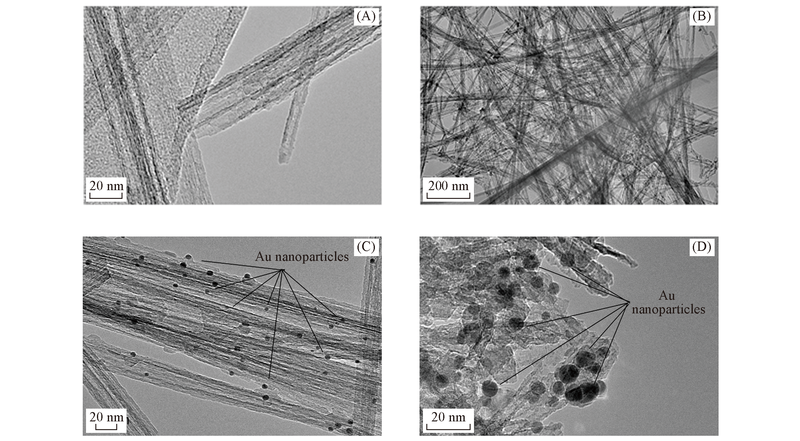
Fig.5 HRTEM(A) and TEM(B) images of 1.0% N-TiO2 nanotubes and HRTEM images of Au/N-TiO2 nanotubes with 1.0% N and 3.0% Au loading in the presence(C) and absence(D) of lysine
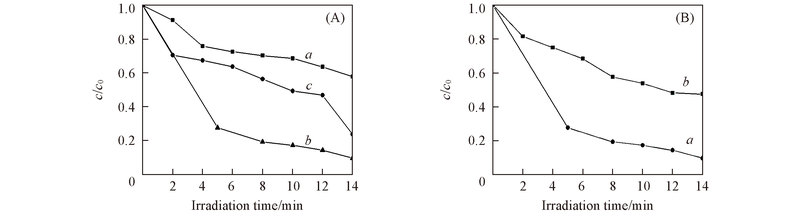
Fig.7 Photocatalytic activity of N-doped TiO2 nanotubes with different N contents(A) and comparison of photocatalytic activities of 1.0% N-doped TiO2 nanotubes(a) and pure TiO2 nanotubes(b)(B) toward MO degradation(A) w(N): a. 0.5%; b. 1.0%; c. 2.0%.
| [1] | Liu, X. , Chen, Y. , Rao S., H. , Pang G., S. , Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2015, 31( 5), 688- 692 |
| [2] | Widchaya, R. , Araya, T. , Ratchaneekorm, W. , Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2014, 30( 1), 149- 156 |
| [3] | Shi Y., K. , Hu X., J. , Zhu B., L. , Zhang S., M. , Huang W., P. , Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2015, 31( 5), 851- 857 |
| [4] | 安会琴, 朱宝林, 吴红艳, 张明, 王淑荣, 张守民, 吴世华, 黄唯平. 高等学校化学学报, 2008, 29(3), 439- 444 |
| An H., Q. , Zhu B., L. , Wu H., Y. , Zhang, M. , Wang S., R. , Zhang S., M. , Wu. S., H. , Huang W., P. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29( 3), 439- 444 ( | |
| [5] | Kasuga, T. , Hiramatsu, M. , Hoson, A. , Sekino, T. , Niihara, K. , Langmuir, 1998, 14( 12), 3160- 3163 |
| [6] | Valentin C., D. , Finazzi, E. , Pacchioni, G. , Selloni, A. , Livraghi, S. , Paganini M., C. , Giamello, E. , Chem. Phys., 2007, 339( 1-3), 44- 56 |
| [7] | Iliev, V. , Tomova, D. , Bilyarska, L. , Tyuliev, G. , J. Mol. Catal. A, 2007, 263( 1/2), 32- 38 |
| [8] | Yu, Y. , Wu H., H. , Zhu B., L. , Wang S., R. , Huang W., P. , Wu S., H. , Zhang S., M. , Catal. Lett., 2008, 121( 1), 165- 171 |
| [9] | Cantau, C. , Pigot, T. , Dupin, J. , Lacombe, S. , J. Photoch. Photobio. A, 2010, 216( 2/3), 201- 208 |
| [10] | Pelaez, M. , de la Cruz A., A. , Stathatos, E. , Falaras, P. , Dionysiou D., D. , Catal. Today, 2009, 144( 1/2), 19- 25 |
| [11] | Zhu B., L. , Li K., R. , Feng Y., F. , Zhang S., M. , Wu S., H. , Huang W., P. , Catal. Lett., 2007, 118( 1), 55- 58 |
| [12] | An H., Q. , He X., L. , Li J., Q. , Zhao L., Z. , Chang, C. , Zhang S., H. , Huang W., P. , New J. Chem., 2015, 39( 6), 4611- 4623 |
| [13] | Iliev, V. , Tomova, D. , Todorovska, R. , Oliver, D. , Petrov, L. , Todorovsky, D. , Uzunova-Bujnova, M. , Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 2006, 313( 2), 115- 121 |
| [14] | An H., Q. , Zhou, J. , Li J., X. , Zhu B., L. , Wang S., R. , Zhang S., M. , Wu S., H. , Huang W., P. , Catal. Commun., 2009, 11( 3), 175- 179 |
| [15] | Hashmi A. S., K. , Hutchings G., J. , Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2006, 45( 47), 7896- 7936 |
| [16] | Wen, D. , Guo S., J. , Zhai J., F. , Deng, L. , Ren, W. , Dong S., J. , J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113( 30), 13023- 13028 |
| [17] | Guo S., J. , Dong S., J. , Wang E., K. , J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113( 14), 5485- 5492 |
| [18] | Zhong Z., Y. , Lin, J. , Teh S., P. , Teo, J. , Dautzenberg F., M. , Adv. Funct. Mater., 2007, 17( 8), 1402- 1408 |
| [19] | Zhang, J. , Liu, X. , Wang, L. , Yang, T. , Guo, X. , Wu, S. , Wang, S. , Zhang, S. , J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115( 13), 5352- 5357 |
| [20] | Zhang, J. , Liu X., H. , Guo X., Z. , Wu S., H. , Wang S., R. , Chem. Eur. J., 2010, 16( 27), 8108- 8116 |
| [21] | Wang Z., P. , Cai W., M. , Hong X., T. , Zhao X., L. , Xu, F. , Cai C., G. , Appl. Catal. B, 2005, 57( 3), 223- 231 |
| [22] | Chen, Y. , Zhang, S. , Yu, Y. , Wu, H. , Wang, S. , Zhu, B. , Huang, W. , Wu, S. , J. Disper. Sci. Technol., 2008, 29( 2), 245- 249 |
| [23] | An H., Q. , Hu X., J. , Zhu B., L. , Song J., J. , Zhao W., L. , Zhang S., M. , Huang W., P. , Mater. Sci.-Poland, 2013, 31( 4), 531- 542 |
| [24] | Sun, L. , Zhao, Z. , Zhou, Y. , Liu, L. , Nanoscale, 2012, 4( 2), 613- 620 |
| [25] | Sathish, M. , Viswanathan, B. , Viswanath R., P. , Gopinath C., S. , Chem. Mater., 2005, 17( 25), 6349- 6353 |
| [26] | Zhao, L. , Chen, X. , Wang, X. , Zhang, Y. , Wei, W. , Sun, Y. , Antonietti, M. , Titirici M., M. , Adv. Mater., 2010, 22( 30), 3317- 3321 |
| [27] | Xiang, Q. , Yu, J. , Jaroniec, M. , Nanoscale, 2011, 3( 9), 3670- 3678 |
| [28] | Wang W., S. , Wang D., H. , Qu W., G. , Lu L., Q. , Xu A., W. , J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116( 37), 19893- 19901 |
| [29] | Yang X., X. , Cao C., D. , Erickson, L. , Hohn, K. , Maghirang, R. , Klabunde, K. , Appl. Catal. B, 2009, 91( 3/4), 657- 662 |
| [30] | Mubeen, S. , Lee, J. , Singh, N. , Kramer, S. , Stucky G., D. , Moskovits, M. , Nat. Nanotechnol., 2013, 8, 247- 251 |
| [31] | McFarland E., W. , Tang, J. , Nature, 2003, 421( 6923), 616- 618 |
| [1] | WU Yaqiang, LIU Siming, JIN Shunjin, YAN Yongqing, WANG Zhao, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Synthesis of Zn-Doped NiCoP Catalyst with Porous Double-layer Nanoarray Structure and Its Electrocatalytic Properties for Hydrogen Evolution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2483. |
| [2] | WANG Yuyao, ZHANG Qiang, YU Jihong. Synthesis of Hierarchical NaX Zeolite and Its CO2 Adsorption Performance † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 616. |
| [3] | YAN Song, ZHANG Chengwu, YUAN Fang, QIN Chuanyu. Synthesis of Nitrogen-doped Carbon Nanotubes and the Performance and Mechanism of PMS Activation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2503. |
| [4] | ZHANG Lutao, ZHOU Guangming, LUO Dan, CHEN Rong. Rapid Detection on Chlortetracycline Residues in Honey by Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1662. |
| [5] | ZHAO Wencai, HAN Lili, PENG Yingjun, WANG Xiaojing, LIU Shengyu, LI Pengfei, HUANG Yibing, CHEN Yuxin. Effect of Basic Amino Acids on the Biological Activity of Helical Antimicrobial Peptide† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 681. |
| [6] | TONG Ti*, ZHAO Yangyang, FU Yilin, SHAN Guiye. Special Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering on Lung Cancer Tissues Based on Au/Cu Nanorods Substrate† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(9): 1536. |
| [7] |
GAO Haiyan, WANG Jingyi, ZHAO Yongnan, CHEN Kunfeng, XUE Dongfeng.
Preparation,Characterization and Gas Sensing Properties of Sn Doped Mo |
| [8] | ZHAO Qi, HE Wanying, DUAN Lijie, ZHANG Yu, YU Shuangjiang, GAO Guanghui. Fabrication and Characterization of Injectable Polysaccharide-polypeptide Hydrogel Based on Schiff’s Base† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(9): 1750. |
| [9] | TENG Xiaobo,ZHANG Chunxia,ZHANG Ying. Synthesis of the Supported Au Polystyrene/poly(acrylic acid) Composite Microspheres and Their pH Regulated Performance† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(8): 1509. |
| [10] | WANG Kai, XU Li, CHEN Hengze, QIAO Huiying, CHEN Chao, ZHANG Ning. Hydrogenation of 4-Nitrophenol over MIL-101 Confinement Au Nanoparticles Catalyst† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(4): 723. |
| [11] | WANG Xiaohui, , LI Xiaotian. TiO2 Nanofibers Embedded with Au and Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Visible-light Photocatalysis† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(5): 976. |
| [12] | JIN Ping, DAI Zhao, GUO Wenjuan, CHEN Guangping. Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles Assemblies with Controllable,Continuous and Discrete Nanostructures† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(5): 844. |
| [13] | WU Liyan, LIU Zhifang, QIN Qing, CAO Yaan, ZHENG Wenjun. Ionic Liquid-assisted Synthesis of Anatase TiO2 Nanotubes and Their UV Light Photocatalytic Activities† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(5): 934. |
| [14] | WANG Qing, LIU Wei, YANG Xiao-Hai, WANG Ke-Min, LIU Pei, HE Lei-Liang. High Sensitive Glutathione and Cysteine Detection by Au Nanoparticles Enhanced Electrochemical Biosensor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(8): 1845. |
| [15] | LIU Xia, LI Rong-Zhuo, LI Lei, LI Wen-Jin, ZHOU Chun-Jiao. Immunoanalysis of E. coli O157: H7 Based on Au Nanoparticles Labelling Antibody Using SPR Biosensor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(6): 1333. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||