

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (7): 1307.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160098
• Organic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YUAN Jie1,4, LIU Qingchuan2, XU Guangcan1,3, LIANG Guangyi1,3,*, XU Bixue1,*( )
)
Received:2016-02-17
Accepted:2016-06-15
Online:2016-07-10
Published:2016-06-15
Contact:
LIANG Guangyi,XU Bixue
E-mail:guangyi_liang@126.com;bixue_xu@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YUAN Jie, LIU Qingchuan, XU Guangcan, LIANG Guangyi, XU Bixue. Synthesis and Anti-HBV Activity Evaluation of the Galactopyranosyl Derivatives of MTS Based on Click Reaction†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(7): 1307.
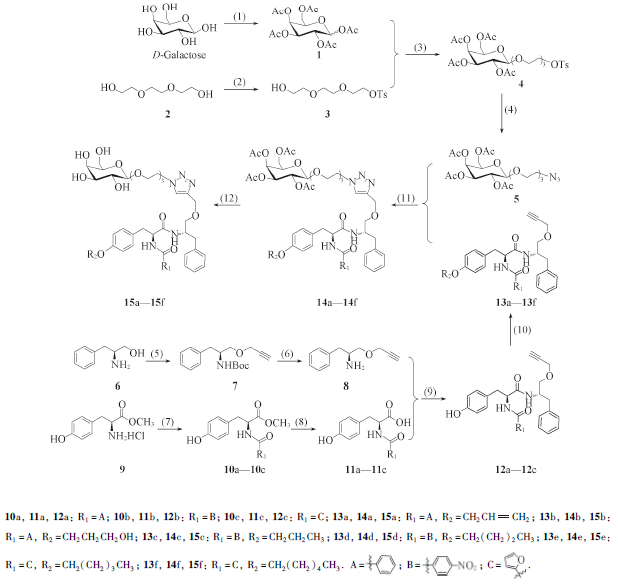
Scheme 1 Synthetic routes of target compounds 15a—15f(1) Ac2O, CH3COONa, 140 ℃; (2) TsCl, pyridine, r. t.; (3) 0.4 nm MS, BF3·Et2O, CH2Cl2, 0 ℃ to r. t.; (4) NaN3, TBAI, DMF, 60 ℃; (5) (a)(Boc)2O, DMF/H2O, r. t.; (b) propargyl bromide(80%, solution in toluene), NaH(60%, dispersion in mineral oil), DMF, 0 ℃ to r. t.; (6) TFA, CH2Cl2, 0 ℃ to r. t.; (7) benzoic acid, 4-nitrobenzoic acid or furoic acid, IBCF, NMM, CH2Cl2/DMF, 0 ℃ to r. t.; (8) 1.0 mol/L NaOH(aq.), DMF, r. t.; (9) IBCF, NMM, CH2Cl2/DMF, 0 ℃ to r. t.; (10) CH3(CH2)5Br, CH3(CH2)4Br, CH3(CH2)3I, CH3(CH2)2I, Br(CH2)3OH or allyl bromide, K2CO3, DMF, r. t.; (11) (+)-sodium L-ascorbate, CuI, DIPEA, DMF/H2O, r. t.; (12) CH3ONa, CH3OH/CH2Cl2, r. t..
| Compd. | Appearance | Yield(%) | m. p./℃ | [α | ESI-MS, m/z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | Pale oil | 72 | |||
| 4 | Pale oil | 73 | 657.0 [M+Na]+ | ||
| 5 | Pale oil | 94 | 544.2 [M+K]+ | ||
| 8 | Pale oil | 37 | |||
| 12a | White solid | 27 | 160—162 | -61.0 | |
| 12b | Yellow solid | 29 | 200—202 | -104.3 | |
| 12c | White solid | 25 | 98—100 | -24.4 | |
| 13a | White solid | 83 | 167—169 | -51.9 | |
| 13b | White solid | 80 | 135—137 | -29.8 | |
| 13c | Yellow solid | 90 | 232—234 | -22.6 | |
| 13d | Yellow solid | 88 | 219—221 | -35.2 | |
| 13e | White solid | 87 | 123—125 | -50.6 | |
| 13f | White solid | 84 | 124—126 | -35.4 | |
| 14a | Pale oil | 93 | -29.1 | 1024.2 [M+Na]+ | |
| 14b | Pale oil | 90 | -29.0 | 1042.3 [M+Na]+ | |
| 14c | Pale oil | 87 | -24.0 | 1071.2 [M+Na]+ | |
| 14d | Pale oil | 92 | -31.6 | 1063.3 [M+H]+ | |
| 14e | Pale oil | 88 | -32.9 | 1022.3 [M+H]+ | |
| 14f | Pale oil | 86 | -35.9 | 1058.3 [M+Na]+ |
Table 1 Appearance, yields, melting points, specific rotation and ESI-MS data for all intermediates*
| Compd. | Appearance | Yield(%) | m. p./℃ | [α | ESI-MS, m/z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | Pale oil | 72 | |||
| 4 | Pale oil | 73 | 657.0 [M+Na]+ | ||
| 5 | Pale oil | 94 | 544.2 [M+K]+ | ||
| 8 | Pale oil | 37 | |||
| 12a | White solid | 27 | 160—162 | -61.0 | |
| 12b | Yellow solid | 29 | 200—202 | -104.3 | |
| 12c | White solid | 25 | 98—100 | -24.4 | |
| 13a | White solid | 83 | 167—169 | -51.9 | |
| 13b | White solid | 80 | 135—137 | -29.8 | |
| 13c | Yellow solid | 90 | 232—234 | -22.6 | |
| 13d | Yellow solid | 88 | 219—221 | -35.2 | |
| 13e | White solid | 87 | 123—125 | -50.6 | |
| 13f | White solid | 84 | 124—126 | -35.4 | |
| 14a | Pale oil | 93 | -29.1 | 1024.2 [M+Na]+ | |
| 14b | Pale oil | 90 | -29.0 | 1042.3 [M+Na]+ | |
| 14c | Pale oil | 87 | -24.0 | 1071.2 [M+Na]+ | |
| 14d | Pale oil | 92 | -31.6 | 1063.3 [M+H]+ | |
| 14e | Pale oil | 88 | -32.9 | 1022.3 [M+H]+ | |
| 14f | Pale oil | 86 | -35.9 | 1058.3 [M+Na]+ |
| Compd. | 1H NMR(CDCl3), δ |
|---|---|
| 3 | 7.80(d, J=8.3 Hz, 2H, ArH, 7.35(d, J=8.0 Hz, 2H, ArH), 4.17(t, J=4.8 Hz, 2H, CH2OH), 3.75—3.68(m, 4H, OCH2×2), 3.63—3.55(m, 6H, OCH2×3), 2.45(s, 3H, CH3) |
| 4 | 7.79(d, J=8.3 Hz, 2H, ArH), 7.34(dd, J=8.6, 0.6 Hz, 2H, ArH), 5.38(dd, J=3.4, 1.0 Hz, 1H, 4d-H), 5.20(dd, J=10.5, 8.0 Hz, 1H, 2d-H), 5.02(dd, J=10.5, 3.4 Hz, 1H, 3d-H), 4.56(d, J=8.0 Hz, 1H, 1d-H), 4.20—4.09(m, 4H, 6d-H, OCH2), 3.98—3.89(m, 2H, 5d-H, OCH2), 3.73(ddd, J=11.0, 7.0, 3.9 Hz, 1H, OCH2), 3.70—3.55(m, 8H, OCH2×4), 2.45(s, 3H, CH3), 2.15(s, 3H, CH3CO), 2.05(s, 3H, CH3CO), 2.05(s, 3H, CH3CO), 1.99(s, 3H, CH3CO) |
| 5 | 5.39(dd, J=3.4, 1.1 Hz, 1H, 4d-H), 5.22(dd, J=10.5, 8.0 Hz, 1H, 2d-H), 5.02(dd, J=10.5, 3.4 Hz, 1H, 3d-H), 4.58(d, J=8.0 Hz, 1H, 1d-H), 4.22—4.10(m, 2H, 6d-H), 4.00—3.89(m, 2H, 5d-H, OCH2), 3.76(ddd, J=11.0, 6.9, 4.0 Hz, 1H, OCH2), 3.70—3.64(m, 8H, OCH2×4), 3.41(t, J=5.0 Hz, 2H, CH2N3), 2.15(s, 3H, CH3CO), 2.07(s, 3H, CH3CO), 2.05(s, 3H, CH3CO), 1.99(s, 3H, CH3CO) |
| 8 | 7.32—7.21(m, 5H, 5c-H—9c-H), 4.17(d, J=1.9 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 3.54(dd, J=9.1, 4.1 Hz, 1H, 1c-H), 3.38(dd, J=8.9, 7.1 Hz, 1H, 1'c-H), 3.29—3.25(m, 1H, 2c-H), 2.81(dd, J=13.5, 5.4 Hz, 1H, 3c-H), 2.58(dd, J=13.3, 8.3 Hz, 1H, 3'c-H), 2.43(t, J=2.4 Hz, 1H, OCH2C≡≡CH) |
Table 2 1H NMR data for intermediates 3—5 and 8*
| Compd. | 1H NMR(CDCl3), δ |
|---|---|
| 3 | 7.80(d, J=8.3 Hz, 2H, ArH, 7.35(d, J=8.0 Hz, 2H, ArH), 4.17(t, J=4.8 Hz, 2H, CH2OH), 3.75—3.68(m, 4H, OCH2×2), 3.63—3.55(m, 6H, OCH2×3), 2.45(s, 3H, CH3) |
| 4 | 7.79(d, J=8.3 Hz, 2H, ArH), 7.34(dd, J=8.6, 0.6 Hz, 2H, ArH), 5.38(dd, J=3.4, 1.0 Hz, 1H, 4d-H), 5.20(dd, J=10.5, 8.0 Hz, 1H, 2d-H), 5.02(dd, J=10.5, 3.4 Hz, 1H, 3d-H), 4.56(d, J=8.0 Hz, 1H, 1d-H), 4.20—4.09(m, 4H, 6d-H, OCH2), 3.98—3.89(m, 2H, 5d-H, OCH2), 3.73(ddd, J=11.0, 7.0, 3.9 Hz, 1H, OCH2), 3.70—3.55(m, 8H, OCH2×4), 2.45(s, 3H, CH3), 2.15(s, 3H, CH3CO), 2.05(s, 3H, CH3CO), 2.05(s, 3H, CH3CO), 1.99(s, 3H, CH3CO) |
| 5 | 5.39(dd, J=3.4, 1.1 Hz, 1H, 4d-H), 5.22(dd, J=10.5, 8.0 Hz, 1H, 2d-H), 5.02(dd, J=10.5, 3.4 Hz, 1H, 3d-H), 4.58(d, J=8.0 Hz, 1H, 1d-H), 4.22—4.10(m, 2H, 6d-H), 4.00—3.89(m, 2H, 5d-H, OCH2), 3.76(ddd, J=11.0, 6.9, 4.0 Hz, 1H, OCH2), 3.70—3.64(m, 8H, OCH2×4), 3.41(t, J=5.0 Hz, 2H, CH2N3), 2.15(s, 3H, CH3CO), 2.07(s, 3H, CH3CO), 2.05(s, 3H, CH3CO), 1.99(s, 3H, CH3CO) |
| 8 | 7.32—7.21(m, 5H, 5c-H—9c-H), 4.17(d, J=1.9 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 3.54(dd, J=9.1, 4.1 Hz, 1H, 1c-H), 3.38(dd, J=8.9, 7.1 Hz, 1H, 1'c-H), 3.29—3.25(m, 1H, 2c-H), 2.81(dd, J=13.5, 5.4 Hz, 1H, 3c-H), 2.58(dd, J=13.3, 8.3 Hz, 1H, 3'c-H), 2.43(t, J=2.4 Hz, 1H, OCH2C≡≡CH) |
| Compd. | 1H NMR(400 MHz), δa | 13C NMR, δb |
|---|---|---|
| 12a | 7.75—7.69(m, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.52(t, J=7.4 Hz, 1H, 5b-H), 7.43(t, J=7.5 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 7.23—7.04(m, 7H, 5a-H, 9a-H, 5c-H—9c-H), 6.69(d, J=8.4 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 4.72(t, J=7.5 Hz, 1H, 2a-H), 4.20—4.13(m, 1H, 2c-H), 4.08(dd, J=8.2, 2.4 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 3.39(dd, J=9.4, 4.7 Hz, 1H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 3.34—3.27(m, 2H, 1c-H), 3.03(dd, J=13.7, 7.1 Hz, 1H, 3a-H), 2.95—2.82(m, 2H, 3'a-H, 3c-H), 2.74(dd, J=13.6, 7.7 Hz, 1H, 3'c-H) | 172.8(C1a), 169.6(C1b), 157.0(C7a), 139.1(C4c), 135.0(C2b), 132.7(C5b), 131.3(2C), 130.3(2C), 129.4(2C), 129.2(2C), 128.8(C4a), 128.2(C3b, C7b), 127.2(C7c), 116.1(C6a, C8a), 80.3(OCH2C≡≡CH), 76.0(OCH2C≡≡CH), 71.0(C1c), 59.0(OCH2·C≡≡CH), 56.6(C2a), 51.6(C2c), 38.2(C3a), 38.0(C3c) |
| 12b | 9.19(s, 1H, OH), 8.80(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.29(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 8.09(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.00(d, J=9.0 Hz, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.23—7.11(m, 5H, 5c-H—9c-H), 7.08(d, J=8.5 Hz, 2H, 5a-H, 9a-H), 6.62(d, J=8.5 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 4.67—4.56(m, 1H, 2a-H), 4.13(d, J=2.4 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 4.11—4.01(m, 1H, 2c-H), 3.49—3.31(m, 3H, OCH2C≡≡CH, 1c-H), 2.91(dd, J=13.8, 4.6 Hz, 1H, 3a-H), 2.86—2.77(m, 2H, 3'a-H, 3c-H), 2.70(dd, J=13.7, 8.2 Hz, 1H, 3'a-H) | 170.8(C1a), 164.4(C1b), 155.7(C7a), 149.0(C5b), 139.7(C4c), 138.4(C2b), 130.1(2C), 129.2(2C), 129.0(2C), 128.2, 128.1(2C), 126.1(C7c), 123.4(C4b, C6b), 114.9(C6a, C8a), 80.2(OCH2C≡≡CH), 77.4(OCH2C≡≡CH), 70.3(C1c), 57.7(OCH2C≡≡CH), 55.3(C2a), 50.0(C2c), 36.6(C3a, C3c) |
| 12c | 9.19(s, 1H, OH), 8.13—8.02(m, 2H, NHCO×2), 7.81(dd, J=1.7, 0.7 Hz, 1H, 5b-H), 7.23—7.10(m, 6H, 3b-H, 5c-H—9c-H), 7.02(d, J=8.5 Hz, 2H, 5a-H, 9a-H), 6.63—6.57(m, 3H, 4b-H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 4.59—4.49(m, 1H, 2a-H), 4.13(d, J=2.4 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 4.08—3.99(m, 1H, 2c-H), 3.48—3.33(m, 3H, OCH2C≡≡CH, 1c-H), 2.89—2.76(m, 3H, 3a-H, 3c-H), 2.69(dd, J=13.7, 8.1 Hz, 1H, 3'c-H) | 170.8(C1a), 157.3, 155.8(C1b, C7a), 147.5(C2b), 145.1(C5b), 138.4(C4c), 130.1(2C), 129.2(2C), 128.1(2C), 128.0, 126.1(C7c), 114.9(C6a, C8a), 113.7, 111.9(C3b, C4b), 80.2(OCH2C≡≡CH), 77.4(OCH2·C≡≡CH), 70.3(C1c), 57.7(OCH2C≡≡CH), 54.2(C2a), 50.0(C2c), 36.7(C3a, C3c) |
| 13a | 8.42(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.04(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 7.80—7.75(m, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.54—7.40(m, 3H, 4b-H—6b-H), 7.27—7.07(m, 7H, 5a-H, 9a-H, 5c-H—9c-H), 6.81(d, J=8.7 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 6.04—5.94(m, 1H, OCH2CH | 171.3(C1a), 166.5(C1b), 156.9(C7a), 138.6(C4c), 134.2(C2b), 134.0(OCH2·CH |
| 13b | 8.41(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.04(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 7.81—7.74(m, 2H, H-3b, 7b-H), 7.54—7.41(m, 3H, 4b-H—6b-H), 7.31—7.02(m, 7H, H-5a, 9a-H, 5c-H—9c-H), 6.79(d, J=8.7 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 4.71—4.54(m, 1H, 2a-H), 4.13(d, J=2.3 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 4.09—4.01(m, 1H, 2c-H), 3.94(t, J=6.4 Hz, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2OH), 3.70—3.24(m, 5H, OCH2CH2CH2OH, OCH2C≡≡CH, 1c-H), 2.97—2.76(m, 3H, 3a-H, 3c-H), 2.74—2.66(m, 1H, 3'c-H), 1.86—1.75(m, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2OH) | 171.2(C1a), 166.3(C1b), 157.3(C7a), 138.5(C4c), 134.2(C2b), 131.4(C5b), 130.3(2C), 130.1(C4a), 129.3(2C), 128.3(2C), 128.3(2C), 127.5(C3b, C7b), 126.2(C7c), 114.1(C6a, C8a), 80.3(OCH2C≡≡CH), 77.4(OCH2C≡≡CH), 70.5(C1c), 64.5(OCH2·CH2CH2OH), 58.6(OCH2CH2CH2OH), 57.8(OCH2C≡≡ CH), 55.2(C2a), 50.1(C2c), 36.7(C3a), 36.6(C3c), 32.2(OCH2CH2CH2OH) |
| 13c | 8.83(d, J=8.2 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.29(d, J=8.4 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 8.12(d, J=8.0 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.00(d, J=8.2 Hz, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.29—7.09(m, 7H, 5a-H, 9a-H, 5c-H—9c-H), 6.79(d, J=8.0 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 4.70—4.59(m, 1H, 2a-H), 4.17—4.02(m, 3H, OCH2C≡≡CH, 2c-H), 3.83(t, J=5.8 Hz, 2H, OCH2CH2CH3), 3.61—3.24(m, 3H, OCH2C≡≡CH, 1c-H), 3.03—2.76(m, 3H, 3a-H, 3c-H), 2.76—2.66(m, 1H, 3'c-H), 1.76—1.59(m, 2H, OCH2CH2CH3), 0.93(t, J=7.1 Hz, 3H, OCH2CH2CH3) | 170.9(C1a), 164.6(C1b), 157.3(C7a), 149.1(C5b), 139.8(C4c), 138.5(C2b), 130.3(2C), 130.0(C4a), 129.3(2C), 129.0(C3b, C7b), 128.3(2C), 126.2(C7c), 123.6(C4b, C6b), 114.1(C6a, C8a), 80.3(OCH2·C≡≡CH), 77.4(OCH2C≡≡CH), 70.4(C1c), 69.0(OCH2CH2CH3), 57.8(OCH2C≡≡CH), 55.4(C2a), 50.1(C2c), 36.7(C3a), 36.7(C3c), 22.2(OCH2CH2CH3), 10.6(OCH2CH2CH3) |
| 13d | 8.83(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.29(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 8.12(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.00(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, H-3b, 7b-H), 7.25—7.10(m, 7H, 5a-H, 9a-H, 5c-H—9c-H), | 170.8(C1a), 164.6(C1b), 157.3(C7a), 149.1(C5b), 140.0(C4c), 138.5(C2b), 130.3(2C), 129.8(C4a), 129.3(2C), 129.0(2C), |
| 13d | 6.79(d, J=8.7 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 4.68—4.60(m, 1H, 2a-H), 4.13(d, J=2.4 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 4.10—4.03(m, 1H, 2c-H), 3.87(t, J=6.5 Hz, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2CH3), 3.55—3.27(m, 3H, OCH2C≡≡CH, 1c-H), 3.00—2.79(m, 3H, 3a-H, 3c-H), 2.75—2.67(m, 1H, 3'c-H), 1.68—1.58(m, 2H, OCH2CH2·CH2CH3), 1.45—1.32(m, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2CH3), 0.89(t, J=7.4 Hz, 3H, OCH2CH2CH2CH3) | 128.2(2C), 126.2(C7c), 123.5(C4b, C6b), 114.1(C6a, C8a), 80.3(OCH2C≡≡CH), 77.3(OCH2C≡≡CH), 70.4(C1c), 67.0(OCH2·CH2CH2CH3), 57.8(OCH2C≡≡CH), 55.3(C2a), 50.0(C2c), 36.7(C3a), 36.6(C3c), 30.9(OCH2CH2CH2CH3), 18.8(OCH2CH2·CH2CH3), 13.8(OCH2CH2CH2CH3) |
| 13e | 8.14(d, J=8.6 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.09(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 7.80(dd, J=1.7, 0.8 Hz, 1H, 5b-H), 7.22—7.08(m, 8H, 3b-H, 5a-H, 9a-H, 5c-H—9c-H), 6.76(d, J=8.7 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 6.60(dd, J=3.5, 1.8 Hz, 1H, 4b-H), 4.60—4.52(m, 1H, 2a-H), 4.12(d, J=2.3 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 4.09—4.00(m, 1H, 2c-H), 3.86(t, J=6.5 Hz, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 3.59—3.31(m, 3H, OCH2C≡≡CH, 1c-H), 2.92—2.76(m, 3H, 3a-H, 3c-H), 2.73—2.64(m, 1H, 3'c-H), 1.70—1.61(m, 2H, OCH2·CH2CH2CH2CH3), 1.41—1.25(m, 4H, OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 0.86(t, J=7.1 Hz, 3H, OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3) | 170.9(C1a), 157.5, 157.4(C1b, C7a), 147.5(C2b), 145.3(C5b), 138.5(C4c), 130.3(2C), 129.7(C4a), 129.4(2C), 128.3(2C), 126.3(C7c), 114.1(C6a, C8a), 114.0, 112.1(C3b, C4b), 80.3(OCH2C≡≡CH), 77.5(OCH2C≡≡CH), 70.5(C1c), 67.4(OCH2·CH2CH2CH2CH3), 57.9(OCH2C≡≡CH), 54.3(C2a), 50.1(C2c), 36.8(C3a), 36.7(C3c), 28.6(OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 27.9(OCH2·CH2CH2CH2CH3), 22.1(OCH2CH2CH2CH2·CH3), 14.1(OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3) |
| 13f | 8.14(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.09(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 7.81(dd, J=1.7, 0.8 Hz, 1H, 5b-H), 7.29—7.05(m, 8H, 3b-H, 5a-H, 9a-H, 5c-H—9c-H), 6.76(d, J=8.7 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 6.60(dd, J=3.5, 1.8 Hz, 1H, 4b-H), 4.61—4.52(m, 1H, 2a-H), 4.13(d, J=2.3 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 4.09—3.99(m, 1H, 2c-H), 3.86(t, J=6.5 Hz, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 3.61—3.27(m, 3H, OCH2C≡≡CH, 1c-H), 2.94—2.76(m, 3H, 3a-H, 3c-H), 2.74—2.63(m, 1H, 3'c-H), 1.71—1.58(m, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 1.42—1.32(m, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2·CH2CH2CH3), 1.32—1.21(m, 4H, OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 0.85(t, J=7.0 Hz, 3H, OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3) | 170.8(C1a), 157.5, 157.3(C1b, C7a), 147.5(C2b), 145.3(C5b), 138.5(C4c), 130.3(2C), 129.6(C4a), 129.3(2C), 128.3(2C), 126.2(C7c), 114.1(C6a, C8a), 113.9, 112.0,(C3b, C4b), 80.3(OCH2C≡≡CH), 77.4(OCH2C≡≡CH), 70.4(C1c), 67.4(OCH2·CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 57.8(OCH2C≡≡CH), 54.2(C2a), 50.1(C2c), 36.7(C3a), 36.7(C3c), 31.1(OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3),28.8(OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 25.4(OCH2·CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 22.2(OCH2CH2CH2·CH2CH2CH3), 14.1(OCH2CH2CH2CH2·CH2CH3) |
| 14a | 7.72(d, J=7.7 Hz, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.69(s, 1H, OCH2C | 170.6, 170.4, 170.3, 170.2, 170.0(C1a, CH3CO×4), 167.0(C1b), 157.7(C7a), 144.6(OCH2C |
| Compd. | 1H NMR(400 MHz), δa | 13C NMR, δb |
| 14b | 7.77—7.74(m, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.65(s, 1H, OCH2C | 170.6, 170.4, 170.3, 170.1, 169.6(C1a, CH3CO×4), 166.9(C1b), 158.0(C7a), 144.7(OCH2C |
| 14c | 8.27(d, J=8.8 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 7.90(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.69(s, 1H, OCH2C | 170.6, 170.4, 170.3, 169.9, 169.6(C1a, CH3CO×4), 164.9(C1b), 158.4(C7a), 149.8(C5b), 144.5(OCH2C |
| 14d | 8.27(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 7.90(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.69(s, 1H, OCH2C | 170.6, 170.4, 170.3, 169.9, 169.6(C1a, CH3CO×4), 164.9(C1b), 158.4(C7a), 149.8(C5b), 144.5(OCH2C |
| 14e | 7.68(s, 1H, OCH2C | 170.4, 170.2, 170.2, 169.8, 169.4(C1a, CH3CO×4), 158.0, 157.8(C1b, C7a), 147.3(C2b), 144.4, 144.2(C5b, OCH2C |
| 14f | 7.67(s, 1H, OCH2C | 170.5, 170.4, 170.3, 170.0, 169.6(C1a, CH3CO×4), 158.2, 158.0(C1b, C7a), 147.5(C2b), 144.6, 144.4(C5b, OCH2C |
Table 3 1H NMR and 13C NMR data for intermediates 12a—12c, 13a—13f and 14a—14f
| Compd. | 1H NMR(400 MHz), δa | 13C NMR, δb |
|---|---|---|
| 12a | 7.75—7.69(m, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.52(t, J=7.4 Hz, 1H, 5b-H), 7.43(t, J=7.5 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 7.23—7.04(m, 7H, 5a-H, 9a-H, 5c-H—9c-H), 6.69(d, J=8.4 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 4.72(t, J=7.5 Hz, 1H, 2a-H), 4.20—4.13(m, 1H, 2c-H), 4.08(dd, J=8.2, 2.4 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 3.39(dd, J=9.4, 4.7 Hz, 1H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 3.34—3.27(m, 2H, 1c-H), 3.03(dd, J=13.7, 7.1 Hz, 1H, 3a-H), 2.95—2.82(m, 2H, 3'a-H, 3c-H), 2.74(dd, J=13.6, 7.7 Hz, 1H, 3'c-H) | 172.8(C1a), 169.6(C1b), 157.0(C7a), 139.1(C4c), 135.0(C2b), 132.7(C5b), 131.3(2C), 130.3(2C), 129.4(2C), 129.2(2C), 128.8(C4a), 128.2(C3b, C7b), 127.2(C7c), 116.1(C6a, C8a), 80.3(OCH2C≡≡CH), 76.0(OCH2C≡≡CH), 71.0(C1c), 59.0(OCH2·C≡≡CH), 56.6(C2a), 51.6(C2c), 38.2(C3a), 38.0(C3c) |
| 12b | 9.19(s, 1H, OH), 8.80(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.29(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 8.09(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.00(d, J=9.0 Hz, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.23—7.11(m, 5H, 5c-H—9c-H), 7.08(d, J=8.5 Hz, 2H, 5a-H, 9a-H), 6.62(d, J=8.5 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 4.67—4.56(m, 1H, 2a-H), 4.13(d, J=2.4 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 4.11—4.01(m, 1H, 2c-H), 3.49—3.31(m, 3H, OCH2C≡≡CH, 1c-H), 2.91(dd, J=13.8, 4.6 Hz, 1H, 3a-H), 2.86—2.77(m, 2H, 3'a-H, 3c-H), 2.70(dd, J=13.7, 8.2 Hz, 1H, 3'a-H) | 170.8(C1a), 164.4(C1b), 155.7(C7a), 149.0(C5b), 139.7(C4c), 138.4(C2b), 130.1(2C), 129.2(2C), 129.0(2C), 128.2, 128.1(2C), 126.1(C7c), 123.4(C4b, C6b), 114.9(C6a, C8a), 80.2(OCH2C≡≡CH), 77.4(OCH2C≡≡CH), 70.3(C1c), 57.7(OCH2C≡≡CH), 55.3(C2a), 50.0(C2c), 36.6(C3a, C3c) |
| 12c | 9.19(s, 1H, OH), 8.13—8.02(m, 2H, NHCO×2), 7.81(dd, J=1.7, 0.7 Hz, 1H, 5b-H), 7.23—7.10(m, 6H, 3b-H, 5c-H—9c-H), 7.02(d, J=8.5 Hz, 2H, 5a-H, 9a-H), 6.63—6.57(m, 3H, 4b-H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 4.59—4.49(m, 1H, 2a-H), 4.13(d, J=2.4 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 4.08—3.99(m, 1H, 2c-H), 3.48—3.33(m, 3H, OCH2C≡≡CH, 1c-H), 2.89—2.76(m, 3H, 3a-H, 3c-H), 2.69(dd, J=13.7, 8.1 Hz, 1H, 3'c-H) | 170.8(C1a), 157.3, 155.8(C1b, C7a), 147.5(C2b), 145.1(C5b), 138.4(C4c), 130.1(2C), 129.2(2C), 128.1(2C), 128.0, 126.1(C7c), 114.9(C6a, C8a), 113.7, 111.9(C3b, C4b), 80.2(OCH2C≡≡CH), 77.4(OCH2·C≡≡CH), 70.3(C1c), 57.7(OCH2C≡≡CH), 54.2(C2a), 50.0(C2c), 36.7(C3a, C3c) |
| 13a | 8.42(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.04(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 7.80—7.75(m, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.54—7.40(m, 3H, 4b-H—6b-H), 7.27—7.07(m, 7H, 5a-H, 9a-H, 5c-H—9c-H), 6.81(d, J=8.7 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 6.04—5.94(m, 1H, OCH2CH | 171.3(C1a), 166.5(C1b), 156.9(C7a), 138.6(C4c), 134.2(C2b), 134.0(OCH2·CH |
| 13b | 8.41(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.04(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 7.81—7.74(m, 2H, H-3b, 7b-H), 7.54—7.41(m, 3H, 4b-H—6b-H), 7.31—7.02(m, 7H, H-5a, 9a-H, 5c-H—9c-H), 6.79(d, J=8.7 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 4.71—4.54(m, 1H, 2a-H), 4.13(d, J=2.3 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 4.09—4.01(m, 1H, 2c-H), 3.94(t, J=6.4 Hz, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2OH), 3.70—3.24(m, 5H, OCH2CH2CH2OH, OCH2C≡≡CH, 1c-H), 2.97—2.76(m, 3H, 3a-H, 3c-H), 2.74—2.66(m, 1H, 3'c-H), 1.86—1.75(m, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2OH) | 171.2(C1a), 166.3(C1b), 157.3(C7a), 138.5(C4c), 134.2(C2b), 131.4(C5b), 130.3(2C), 130.1(C4a), 129.3(2C), 128.3(2C), 128.3(2C), 127.5(C3b, C7b), 126.2(C7c), 114.1(C6a, C8a), 80.3(OCH2C≡≡CH), 77.4(OCH2C≡≡CH), 70.5(C1c), 64.5(OCH2·CH2CH2OH), 58.6(OCH2CH2CH2OH), 57.8(OCH2C≡≡ CH), 55.2(C2a), 50.1(C2c), 36.7(C3a), 36.6(C3c), 32.2(OCH2CH2CH2OH) |
| 13c | 8.83(d, J=8.2 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.29(d, J=8.4 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 8.12(d, J=8.0 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.00(d, J=8.2 Hz, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.29—7.09(m, 7H, 5a-H, 9a-H, 5c-H—9c-H), 6.79(d, J=8.0 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 4.70—4.59(m, 1H, 2a-H), 4.17—4.02(m, 3H, OCH2C≡≡CH, 2c-H), 3.83(t, J=5.8 Hz, 2H, OCH2CH2CH3), 3.61—3.24(m, 3H, OCH2C≡≡CH, 1c-H), 3.03—2.76(m, 3H, 3a-H, 3c-H), 2.76—2.66(m, 1H, 3'c-H), 1.76—1.59(m, 2H, OCH2CH2CH3), 0.93(t, J=7.1 Hz, 3H, OCH2CH2CH3) | 170.9(C1a), 164.6(C1b), 157.3(C7a), 149.1(C5b), 139.8(C4c), 138.5(C2b), 130.3(2C), 130.0(C4a), 129.3(2C), 129.0(C3b, C7b), 128.3(2C), 126.2(C7c), 123.6(C4b, C6b), 114.1(C6a, C8a), 80.3(OCH2·C≡≡CH), 77.4(OCH2C≡≡CH), 70.4(C1c), 69.0(OCH2CH2CH3), 57.8(OCH2C≡≡CH), 55.4(C2a), 50.1(C2c), 36.7(C3a), 36.7(C3c), 22.2(OCH2CH2CH3), 10.6(OCH2CH2CH3) |
| 13d | 8.83(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.29(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 8.12(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.00(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, H-3b, 7b-H), 7.25—7.10(m, 7H, 5a-H, 9a-H, 5c-H—9c-H), | 170.8(C1a), 164.6(C1b), 157.3(C7a), 149.1(C5b), 140.0(C4c), 138.5(C2b), 130.3(2C), 129.8(C4a), 129.3(2C), 129.0(2C), |
| 13d | 6.79(d, J=8.7 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 4.68—4.60(m, 1H, 2a-H), 4.13(d, J=2.4 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 4.10—4.03(m, 1H, 2c-H), 3.87(t, J=6.5 Hz, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2CH3), 3.55—3.27(m, 3H, OCH2C≡≡CH, 1c-H), 3.00—2.79(m, 3H, 3a-H, 3c-H), 2.75—2.67(m, 1H, 3'c-H), 1.68—1.58(m, 2H, OCH2CH2·CH2CH3), 1.45—1.32(m, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2CH3), 0.89(t, J=7.4 Hz, 3H, OCH2CH2CH2CH3) | 128.2(2C), 126.2(C7c), 123.5(C4b, C6b), 114.1(C6a, C8a), 80.3(OCH2C≡≡CH), 77.3(OCH2C≡≡CH), 70.4(C1c), 67.0(OCH2·CH2CH2CH3), 57.8(OCH2C≡≡CH), 55.3(C2a), 50.0(C2c), 36.7(C3a), 36.6(C3c), 30.9(OCH2CH2CH2CH3), 18.8(OCH2CH2·CH2CH3), 13.8(OCH2CH2CH2CH3) |
| 13e | 8.14(d, J=8.6 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.09(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 7.80(dd, J=1.7, 0.8 Hz, 1H, 5b-H), 7.22—7.08(m, 8H, 3b-H, 5a-H, 9a-H, 5c-H—9c-H), 6.76(d, J=8.7 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 6.60(dd, J=3.5, 1.8 Hz, 1H, 4b-H), 4.60—4.52(m, 1H, 2a-H), 4.12(d, J=2.3 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 4.09—4.00(m, 1H, 2c-H), 3.86(t, J=6.5 Hz, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 3.59—3.31(m, 3H, OCH2C≡≡CH, 1c-H), 2.92—2.76(m, 3H, 3a-H, 3c-H), 2.73—2.64(m, 1H, 3'c-H), 1.70—1.61(m, 2H, OCH2·CH2CH2CH2CH3), 1.41—1.25(m, 4H, OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 0.86(t, J=7.1 Hz, 3H, OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3) | 170.9(C1a), 157.5, 157.4(C1b, C7a), 147.5(C2b), 145.3(C5b), 138.5(C4c), 130.3(2C), 129.7(C4a), 129.4(2C), 128.3(2C), 126.3(C7c), 114.1(C6a, C8a), 114.0, 112.1(C3b, C4b), 80.3(OCH2C≡≡CH), 77.5(OCH2C≡≡CH), 70.5(C1c), 67.4(OCH2·CH2CH2CH2CH3), 57.9(OCH2C≡≡CH), 54.3(C2a), 50.1(C2c), 36.8(C3a), 36.7(C3c), 28.6(OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 27.9(OCH2·CH2CH2CH2CH3), 22.1(OCH2CH2CH2CH2·CH3), 14.1(OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3) |
| 13f | 8.14(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.09(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 7.81(dd, J=1.7, 0.8 Hz, 1H, 5b-H), 7.29—7.05(m, 8H, 3b-H, 5a-H, 9a-H, 5c-H—9c-H), 6.76(d, J=8.7 Hz, 2H, 6a-H, 8a-H), 6.60(dd, J=3.5, 1.8 Hz, 1H, 4b-H), 4.61—4.52(m, 1H, 2a-H), 4.13(d, J=2.3 Hz, 2H, OCH2C≡≡CH), 4.09—3.99(m, 1H, 2c-H), 3.86(t, J=6.5 Hz, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 3.61—3.27(m, 3H, OCH2C≡≡CH, 1c-H), 2.94—2.76(m, 3H, 3a-H, 3c-H), 2.74—2.63(m, 1H, 3'c-H), 1.71—1.58(m, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 1.42—1.32(m, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2·CH2CH2CH3), 1.32—1.21(m, 4H, OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 0.85(t, J=7.0 Hz, 3H, OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3) | 170.8(C1a), 157.5, 157.3(C1b, C7a), 147.5(C2b), 145.3(C5b), 138.5(C4c), 130.3(2C), 129.6(C4a), 129.3(2C), 128.3(2C), 126.2(C7c), 114.1(C6a, C8a), 113.9, 112.0,(C3b, C4b), 80.3(OCH2C≡≡CH), 77.4(OCH2C≡≡CH), 70.4(C1c), 67.4(OCH2·CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 57.8(OCH2C≡≡CH), 54.2(C2a), 50.1(C2c), 36.7(C3a), 36.7(C3c), 31.1(OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3),28.8(OCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 25.4(OCH2·CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3), 22.2(OCH2CH2CH2·CH2CH2CH3), 14.1(OCH2CH2CH2CH2·CH2CH3) |
| 14a | 7.72(d, J=7.7 Hz, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.69(s, 1H, OCH2C | 170.6, 170.4, 170.3, 170.2, 170.0(C1a, CH3CO×4), 167.0(C1b), 157.7(C7a), 144.6(OCH2C |
| Compd. | 1H NMR(400 MHz), δa | 13C NMR, δb |
| 14b | 7.77—7.74(m, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.65(s, 1H, OCH2C | 170.6, 170.4, 170.3, 170.1, 169.6(C1a, CH3CO×4), 166.9(C1b), 158.0(C7a), 144.7(OCH2C |
| 14c | 8.27(d, J=8.8 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 7.90(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.69(s, 1H, OCH2C | 170.6, 170.4, 170.3, 169.9, 169.6(C1a, CH3CO×4), 164.9(C1b), 158.4(C7a), 149.8(C5b), 144.5(OCH2C |
| 14d | 8.27(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 7.90(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, 3b-H, 7b-H), 7.69(s, 1H, OCH2C | 170.6, 170.4, 170.3, 169.9, 169.6(C1a, CH3CO×4), 164.9(C1b), 158.4(C7a), 149.8(C5b), 144.5(OCH2C |
| 14e | 7.68(s, 1H, OCH2C | 170.4, 170.2, 170.2, 169.8, 169.4(C1a, CH3CO×4), 158.0, 157.8(C1b, C7a), 147.3(C2b), 144.4, 144.2(C5b, OCH2C |
| 14f | 7.67(s, 1H, OCH2C | 170.5, 170.4, 170.3, 170.0, 169.6(C1a, CH3CO×4), 158.2, 158.0(C1b, C7a), 147.5(C2b), 144.6, 144.4(C5b, OCH2C |
| Compd. | Appearance | Yield(%) | [α | HRMS(calcd.), m/z |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15a | Pale oil | 92 | -26.1 | 856.3751(856.3745) [M+Na]+ |
| 15b | Pale oil | 95 | -24.0 | 874.3842(874.3851) [M+Na]+ |
| 15c | Pale oil | 90 | -16.0 | 903.3759(903.3752) [M+Na]+ |
| 15d | Pale oil | 95 | -29.9 | 917.3917(917.3909) [M+Na]+ |
| 15e | Pale oil | 86 | -32.0 | 854.4193(854.4188) [M+H]+ |
| 15f | Pale oil | 85 | -40.0 | 890.4172(890.4164) [M+Na]+ |
Table 4 Appearance, yields, specific rotation and HRMS data for target compounds 15a—15f
| Compd. | Appearance | Yield(%) | [α | HRMS(calcd.), m/z |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15a | Pale oil | 92 | -26.1 | 856.3751(856.3745) [M+Na]+ |
| 15b | Pale oil | 95 | -24.0 | 874.3842(874.3851) [M+Na]+ |
| 15c | Pale oil | 90 | -16.0 | 903.3759(903.3752) [M+Na]+ |
| 15d | Pale oil | 95 | -29.9 | 917.3917(917.3909) [M+Na]+ |
| 15e | Pale oil | 86 | -32.0 | 854.4193(854.4188) [M+H]+ |
| 15f | Pale oil | 85 | -40.0 | 890.4172(890.4164) [M+Na]+ |
| Compd. | 1H NMR(400 MHz), δ | 13C NMR(101 MHz), δ |
|---|---|---|
| 15a | 7.97(s, 1H, OCH2C | 173.1(C1a), 169.8(C1b), 158.9(C7a), 145.6(OCH2C |
| 15b | 7.98(s, 1H, OCH2C | 173.1(C1a), 169.8(C1b), 159.4(C7a), 145.6(OCH2C |
| 15c | 8.81(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.28(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 8.11(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.04(s, 1H, OCH2·C | 170.9(C1a), 164.7(C1b), 157.3(C7a), 149.2(C5b), 143.8(OCH2C |
| 15d | 8.80(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.28(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 8.09(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.04(s, 1H, OCH2·C | 170.9(C1a), 164.6(C1b), 157.3(C7a), 149.1(C5b), 143.8(OCH2C |
| 15e | 7.99(s, 1H, OCH2C | 172.7(C1a), 160.1(C1b), 159.4(C7a), 148.5(C2b), 146.5(C5b), 145.5(OCH2C |
| 15f | 7.99(s, 1H, OCH2C | 172.7(C1a), 160.1(C1b), 159.4(C7a), 148.5(C2b), 146.5(C5b), 145.5(OCH2C |
Table 5 1H NMR and 13C NMR data for target compounds 15a—15f*
| Compd. | 1H NMR(400 MHz), δ | 13C NMR(101 MHz), δ |
|---|---|---|
| 15a | 7.97(s, 1H, OCH2C | 173.1(C1a), 169.8(C1b), 158.9(C7a), 145.6(OCH2C |
| 15b | 7.98(s, 1H, OCH2C | 173.1(C1a), 169.8(C1b), 159.4(C7a), 145.6(OCH2C |
| 15c | 8.81(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.28(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 8.11(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.04(s, 1H, OCH2·C | 170.9(C1a), 164.7(C1b), 157.3(C7a), 149.2(C5b), 143.8(OCH2C |
| 15d | 8.80(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.28(d, J=8.9 Hz, 2H, 4b-H, 6b-H), 8.09(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.04(s, 1H, OCH2·C | 170.9(C1a), 164.6(C1b), 157.3(C7a), 149.1(C5b), 143.8(OCH2C |
| 15e | 7.99(s, 1H, OCH2C | 172.7(C1a), 160.1(C1b), 159.4(C7a), 148.5(C2b), 146.5(C5b), 145.5(OCH2C |
| 15f | 7.99(s, 1H, OCH2C | 172.7(C1a), 160.1(C1b), 159.4(C7a), 148.5(C2b), 146.5(C5b), 145.5(OCH2C |
| [1] | Lozano R., Naghavi M., Foreman K., Lim S., Shibuya K. J., Aboyans V., Lancet,2012, 380(9859), 2095—2128 |
| [2] | Goulis I., Karatapanis S., Akriviadis E., Deutsch M., Dalekos G. N., Raptopoulou-Gigi M., Mimidis K., Germanidis G., Drakoulis C., Triantos C., Zintzaras E., Bakalos G., Papatheodoridis G., Liver Int., 2015, 35(5), 1540—1548 |
| [3] | Liang G. P., Hu Z. X., Liu Q. C., Huang Z. M., Zhang J. X., Liang G. Y., Xu B. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2014, 35(11), 2353—2359(梁光平, 胡占兴, 刘青川, 黄正明, 张建新, 梁光义, 徐必学. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(11), 2353—2359) |
| [4] | Qiu J. Y., Xu B. X., Huang Z. M., Pan W. D., Cao P. X., Liu C. X., Hao X. J., Song B. A., Liang G. Y., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2011, 19(18), 5352—5360 |
| [5] | Qiu J. Y., Huang Z. M., Pan W. D., Cao P. X., Liang G. Y., J. Chin. Pharm. Univ., 2012, 43(5), 390—394(邱净英, 黄正明, 潘卫东, 曹佩雪, 梁光义. 中国药科大学学报, 2012, 43(5), 390—394) |
| [6] | Liang G. P., Cao P. X., Yang X. X., Huang Z. M., Liu Q. C., Liang G. Y., Xu B. X., Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2014, 34(5), 973—979(梁光平, 曹佩雪, 杨秀虾, 黄正明, 刘青川, 梁光义, 徐必学. 有机化学, 2014, 34(5), 973—979) |
| [7] | Spiess M., Biochem., 1990, 29(43), 10009—10018 |
| [8] | Ding J. X., Xiao C. S., Li Y., Cheng Y. L., Wang N. N., He C. L., Zhuang X. L., Zhu X. J., Chen X. S., J. Control. Release,2013, 169(3), 193—203 |
| [9] | Wang Y. Q., Su J., Cai W. W., Lu P., Yuan L. F., Jin T., Chen S. Y., Sheng J., Drug. Des. Devel. Ther., 2013, 7(3), 211—221 |
| [10] | Naicker K., Ariatti M., Singh M., Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,2014, 122, 482—490 |
| [11] | Tao Y. F., He J. L., Zhang M. Z., Hao Y., Liu J., Ni P. H., Polym. Chem., 2014, 5(10), 3443—3452 |
| [12] | Yuan J., Liu Q. C., Xu G. C., Hu Z. X., Liang G. P., Huang Z. M., Liu C. X., Liang G. Y., Xu B. X., Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2015, 35(10), 2176—2183(袁洁, 刘青川, 徐广灿, 胡占兴, 梁光平, 黄正明, 刘昌孝, 梁光义, 徐必学. 有机化学, 2015, 35(10), 2176—2183) |
| [13] | Khorev O., Stokmaier D., Schwardt O., Cutting B., Ernst B., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2008, 16(9), 5216—5231 |
| [14] | LaBell R. Y., Jacobsen N. E., Gervay-Hague J., O’Brian D. F., Bioconjugate Chem., 2002, 13(1), 143—149 |
| [15] | Percec V., Leowanawat P., Sun H. J., Kulikov O., Nusbaum C. D., Tran T. M., Bertin A., Wilson D. A., Peterca M., Zhang S. D., Kamat N. P., Vargo K., Moock D., Johnston E. D., Hammer D. A., Pochan D. J., Chen Y. X., Chabre Y. M., Shiao T. C., Bergeron-Blerk M., André S., Roy R., Gabius H. J., Heiney P. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(24), 9055—9077 |
| [16] | Zhang S. D., Moussodia R. O., Sun H. J., Leowanawat P., Muncan A., Nusbaum C. D., Chelling K. M., Heiney P. A., Klein M. L., André S., Roy R., Gabius H. J., Percec V., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(41), 10899—10903 |
| [17] | Zhao J., Xuan L. N., Zhao H. C., Cheng J., Fu X. Y., Jing F. M., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2014, 30(5), 764—769 |
| [18] | LiY. D., Mao W. T., Fan Z. J., Fang Z., Ji X. T., Zong G. N., Li F. Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2014, 30(3), 390—395 |
| [19] | Salameh B. A., Cumpstey I., Sundin A., Leffler H., Nilsson U. J., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2010, 18(14), 5367—5378 |
| [20] | Zhang S. S., Wan J., Li X. M., Li C. L., Xu L. Z., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2007, 23(1), 120—124 |
| [21] | Johansson J. R., Lincoln P., Nordén B., Kann N., J. Org. Chem.2011, 76(7), 2355—2359 |
| [22] | Mishra K. B., Tiwari V. K., J. Org. Chem., 2014, 79(12), 5752—5762 |
| [23] | Li L. F., Chang K. C., Zhou Y. M., Shieh B., Ponder J., Abraham A. D., Ali H., Snow A., Mark Petrash J., LaBarbera D. V., J. Med. Chem., 2014, 57(1), 71—77 |
| [24] | Cai M.S., Li Z. J., Carbohydrate Chemistry: Fundamentals, Reactions, Synthesis, Isolation and Structure, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2006, 370—373 |
| (蔡孟深, 李中军. 糖化学—基础、 反应、 合成、 分离及结构, 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2006, 370—373) |
| [1] | WANG Ruhan, JIA Shunhan, WU Limin, SUN Xiaofu, HAN Buxing. CO2-involved Electrochemical C—N Coupling into Value-added Chemicals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220395. |
| [2] | LI Yidi, TIAN Xiaochun, LI Junpeng, CHEN Lixiang, ZHAO Feng. Electron Transfer on the Semiconductor-microbe Interface and Its Environmental Application [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220089. |
| [3] | JIN Xiangyuan, ZHANG Libing, SUN Xiaofu, HAN Buxing. Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction over Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220035. |
| [4] | DOU Shuzhen, WANG Zhongshun, LYU Nan. Improving the Detection Performance of Surface-assisted Laser Desorption/ionization Mass Spectrometry by Silicon Nanostructures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1156. |
| [5] | MA Yanrong, JIANG Shengnan, JIN Yan. Sensitive and Electrochemical Detection of Telomerase Activity Based on the Signal Amplification of Strand Displacement Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 745. |
| [6] | YANG Pengfei, SHI Yuping, ZHANG Yanfeng. Large-scale Syntheses and Versatile Applications of Two-dimensional Metal Dichalcogenides [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 504. |
| [7] | HAN Juntian,CUI Yaoxing,SU Zhijun,WU Yi,CHEN Liuping,XU Junhui. Two-Electron Storage Viologen for Aqueous Organic Redox Flow Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1035. |
| [8] | LIU Lu,WU Hanyue,LI Jing,SHE Lan. Tuning Microstructures of Iron-Nickel Alloy Catalysts for Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1083. |
| [9] | LI Zhenhua, SHI Run, ZHAO Jiaqi, ZHANG Tierui. Research Progress of Photo-driven C1 Conversion to Value-added Chemicals † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 604. |
| [10] | HAN Fangjie, DAI Mengjiao, LIANG Zhishan, SONG Zhongqian, HAN Dongxue, NIU Li. Research Progress of Photoelectrochemical Technology Applied in Antioxidant Analysis † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 591. |
| [11] | WANG Xinghuo,TANG Jun,YANG Yingwei. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles-Based Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems Gated by Polymers † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 28. |
| [12] | FAN Hui, JIN Baokang. Investigation on Electrochemical Capture of CO2 by Quinone Derivatives Based on in situ FTIR Spectroelectrochemistry † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1847. |
| [13] | QIAO Xuejiao, LI Dan, CHENG Longjiu, JIN Baokang. Mechanism of Electrochemical Capture of CO2 via Redox Cycle of 2-Amino-3-chloro-1,4-naphthoquinone in BMIMBF4 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1606. |
| [14] | MA Yucong, FAN Baomin, WANG Manman, YANG Biao, HAO Hua, SUN Hui, ZHANG Huijuan. Two-step Preparation of Trazodone and Its Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism for Carbon Steel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1706. |
| [15] | LIU Shufeng,QIU Haiyan,JIANG Tao,ZHANG Yehua,ZHAO Yun,CHENG Hanwen,CHEN Yong. Ion Transfer Behavior of Protonated Phenazopyridine at the Liquid/Liquid Interface Modified by Functionalized Hybrid Mesoporous Silica Membrane† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 973. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||