

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (6): 1189.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160063
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
BU Honghong1, JIAO Yanni2, LAN Wenjun1, ZHUANG Xiaoli1, DAI Xiaonan1,*( ), LI Tianduo1,*(
), LI Tianduo1,*( )
)
Received:2016-01-24
Online:2016-06-10
Published:2016-05-04
Contact:
DAI Xiaonan,LI Tianduo
E-mail:sddxn@163.com;litianduo@163.com
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
BU Honghong, JIAO Yanni, LAN Wenjun, ZHUANG Xiaoli, DAI Xiaonan, LI Tianduo. Rheological Properties of GuHCl/Type Ⅰ Collagen Dispersions†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6): 1189.
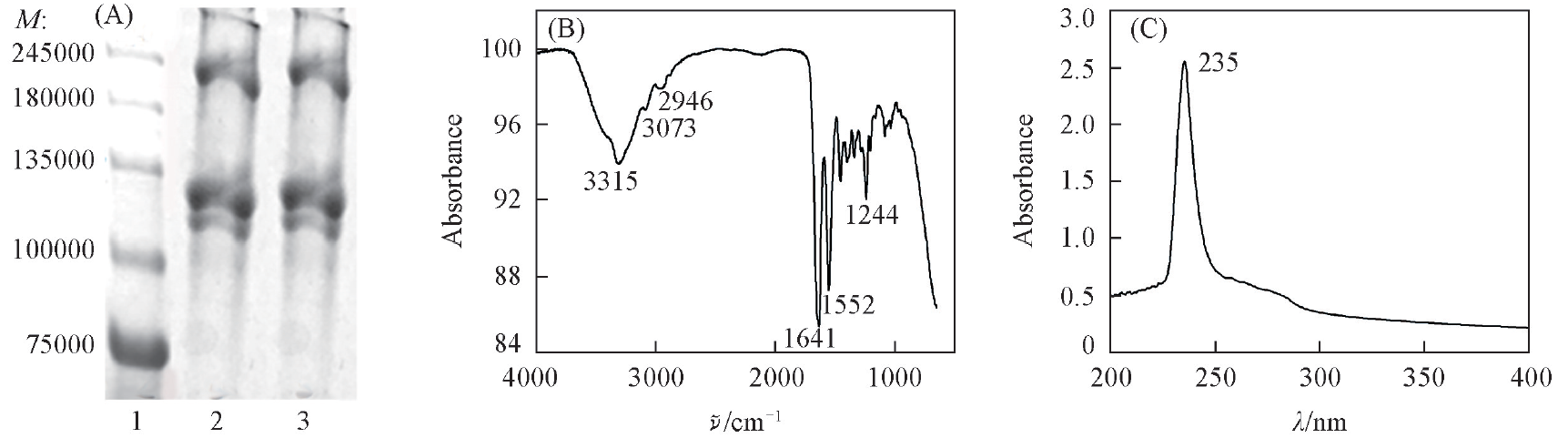
Fig.1 Protein patterns(A), FTIR(B) and UV-Vis(C) spectra of pig skin collagenLane 1 represents the protein molecular weight marker; Lane 2, 3 represent pig skin collagen.
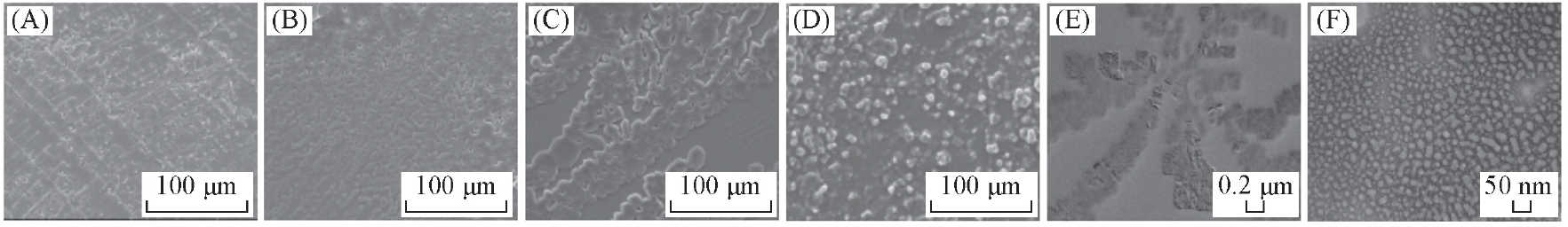
Fig.2 SEM(A—D)and TEM(E, F) images of GuHCl/collagen dispersions(A) 0.1 mg/mL collagen; (B) 0.1 mg/mL collagen+0.5 mol/L GuHCl; (C) 0.1 mg/mL collagen+1.0 mol/L GuHCl;(D) 0.1 mg/mL collagen+4.0 mol/L GuHCl; (E) 0.1 mg/mL collagen; (F) 0.1 mg/mL collagen+4.0 mol/L GuHCl.
| System | Power-law equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Collagen | τ=0.544 D0.49 | 0.9957 |
| Collagen+1.0 mol/L GuHCl | τ=0.073 D0.68 | 0.9952 |
| Collagen+2.0 mol/L GuHCl | τ=0.003 D0.92 | 0.9961 |
| Collagen+4.0 mol/L GuHCl | τ=0.002 D0.95 | 0.9936 |
| Collagen+6.0 mol/L GuHCl | τ=0.001 D0.96 | 0.9967 |
Table 1 Power-law equation and R2 of GuHCl/collagen dispersions at different GuHCl concentrations
| System | Power-law equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Collagen | τ=0.544 D0.49 | 0.9957 |
| Collagen+1.0 mol/L GuHCl | τ=0.073 D0.68 | 0.9952 |
| Collagen+2.0 mol/L GuHCl | τ=0.003 D0.92 | 0.9961 |
| Collagen+4.0 mol/L GuHCl | τ=0.002 D0.95 | 0.9936 |
| Collagen+6.0 mol/L GuHCl | τ=0.001 D0.96 | 0.9967 |
| Time/h | Power-law equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | τ=0.128 D0.61 | 0.9946 |
| 12 | τ=0.073 D0.68 | 0.9952 |
| 24 | τ=0.045 D0.77 | 0.9969 |
| 48 | τ=0.002 D0.95 | 0.9980 |
Table 2 Power-law equation and R2 of GuHCl/collagen dispersions at different GuHCl(1.0 mol/L) function time
| Time/h | Power-law equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | τ=0.128 D0.61 | 0.9946 |
| 12 | τ=0.073 D0.68 | 0.9952 |
| 24 | τ=0.045 D0.77 | 0.9969 |
| 48 | τ=0.002 D0.95 | 0.9980 |
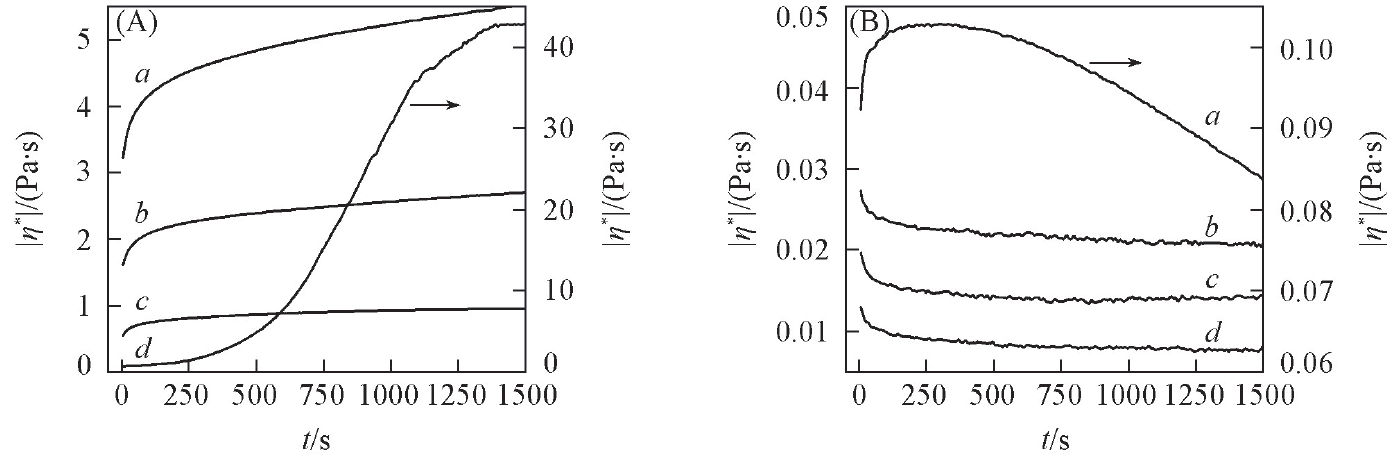
Fig.5 Effect of GuHCl concentration on the thixotropy of collagen dispersions under oscillatory shear experimentsc(GuHCl)/(mol·L-1): (A) a. 0.25; b. 0.5; c. 0.75; d. 0. (B) a. 1.0; b. 2.0; c. 4.0; d. 6.0.
| [1] | Doublet B., Van Der Rest M., J. Biol. Chem., 1991, 266, 6853—6858 |
| [2] | Friess W., Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 1998, 45, 113—136 |
| [3] | Blair H. C., Zaidi M., Schlesinger P. H., Biochem. J., 2002, 354, 329—341 |
| [4] | Brekken R. A., Sage E. H., Matrix Biology, 2000, 19, 569—580 |
| [5] | Kadler K., Pretein Profile., 1995, 2, 491—519 |
| [6] | Meaney M. M., Rice K., Wright R. J., Spector M., J. Orthop., Res., 2003, 21, 238—244 |
| [7] | Usha R., Ramasami T., Themochimica Acta, 2004, 409, 201—206 |
| [8] | Sionkowska A., Kaminska A., Inter. J. Biol. Macromolecules, 1999, 24, 337—340 |
| [9] | McClain P. E., Wiley E. R., J. Biol. Chem., 1972, 247(3), 692—697 |
| [10] | Wang F., Tang K. Y., Pan H. B., China Leather, 2011, 40(7), 30—33 |
| (王芳, 汤克勇, 潘洪波. 中国皮革, 2011, 40(7), 30—33) | |
| [11] | Péterfi T., Arch. Entwicklungsmech. Organ., 1927, 112, 660—695(Péterfi T., Wilhelm Roux’ Archiv für Entwicklungsmechanik der Organismen, 1927,112, 660—695) |
| [12] | Dai X. N., Hou W. G., Duan H. D., Ni P., Colloid Surf. A, 2007, 295, 139—145 |
| [13] | Chen Y., Ye R., Wang Y., Int. J. Food Sci. Tech., 2015, 50, 186—193 |
| [14] | Zhang M., Liu W., Li G., Food Chemistry, 2009, 115, 826—831 |
| [15] | Abraham L. C., Zuena E., Perez B., Kaplan D. L., Journal of Biomedical Materials Research B, 2008, 87, 264—285 |
| [16] | Forgacs G., Newman S. A., Hinner B., Maier C. W., Sackmann E., Biophysical Journal, 2003, 84, 1272—1280 |
| [17] | Kadler K. E., Hojima Y., Prockop D. J., J. Biol. Chem., 1987, 262, 15696—15701 |
| [18] | Yan M. Y., Li B. F., Zhao X., Food Chemistry, 2010, 122, 1333—1337 |
| [19] | Shi X. Y., Ma W. Y., Biomaterials, 2001, 22, 1627—1634 |
| [20] | Wu K., Liu W. T., Li G. Y., Spectrochimica Acta A, 2013, 102, 186—193 |
| [21] | Liu A. J., Chen Y., Jia Y. L., Zhang G. R., Process Biochemistry, 2007, 42, 54—59 |
| [22] | Dai X. N., Hou W. G., Li S. P., Wang X. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2001, 22(9), 1578—1580 |
| (戴肖南, 侯万国, 李淑萍, 王新芳. 高等学校化学学报, 2001, 22(9), 1578—1580) |
| [1] | HAN Yixiu, WU Dianguo, LI Hongpu, YIN Hongyao, MEI Yongjun, FENG Yujun, ZHONG Zuqin. Interactions Between Hydrophobic Associating Poly(sodium acrylate) and a Zwitterionic Surfactant in Non-aqueous Media and Low Temperature Environment [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2056. |
| [2] | LIU Guomin, LU Tiancheng, JI Xuan, JIA Wenyuan, LI Yalong, ZHAO Yian, LUO Yungang. Preparation and Osteogenic Induction Activity of CBD-BMP2-MP/PLGA 3D Printed Composite Scaffolds† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1552. |
| [3] | GUO Zhenhao, GUI Qifeng, ZHANG Bo, REN Shuaizhen, ZHANG Shupeng, LI Xinzhong, REN Tianrui. Application of Polycarboxylate and Naphthalenesulfonate Dispersants in High Concentration Suspension Concentrate† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1278. |
| [4] | CUI Guolian, DAN Nianhua, DAN Weihua. Preparation and Characterization of Novel Dopamine-based Bioadhesive Hydrogels† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(2): 318. |
| [5] | WANG Yifu, DONG Jinxin, WANG Jilin, WANG Lulu, FENG Ruijiang. Ordered Self-assembly of Gemini Molecules in Mesoporous Silica Channels Constructing Normal Micelles to Assist the Migration of OH-† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(1): 141. |
| [6] | SUN Hui, YU Qingsong, YANG Biao, XU Guozhi. Surface Hydrophilic Modification of Poly(ether ether ketone) and Immobilization of Collagen† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6): 1154. |
| [7] | ZHI Zijian, ZOU Mingming, LI Shan, CHEN Jianle, YE Xingqian, CHEN Shiguo. Rheological and Structural Characterization of Pectin Polysaccharides from Citrus Pulp† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6): 1175. |
| [8] | LIU Yangjian, RUAN Yingbo, ZHANG Baoqing, QIAO Xin, LIU Chenyang. Tuning of Ionic Interaction and Rheological Properties of Nanoscale Ionic Materials† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(4): 767. |
| [9] | CHEN Lamei, CAO Jie, YE Lin, ZHANG Aiying, FENG Zengguo. Preparation of Multi-functional Wound Dressing with Core-shell Nanofibers via Co-axial Electrospinning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(3): 600. |
| [10] | WANG Dong, HAN Na, ZHANG Xingxiang, WANG Lejun, WANG Ning, LI Wei, YU Wanyong, LI Zhinan. Preparation and Characterization of Cellulose Propionate-g-diethylene Glycol Hexadecyl Ether Solid-solid Phase Change Material† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(6): 1221. |
| [11] | ZHANG Huanhuan, XU Donghua, GUAN Dongbo, YAO Weiguo, SHI Tongfei. Rheological Properties of Two-component Silicon Rubber During Cross-linking by Addition Reaction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(4): 788. |
| [12] | ZHANG Xia, ZHOU Hao, YANG Yuhong, HUANG Yufang, CHEN Xin. Oxidized Cellulose Enhanced Collagen Hydrogels† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 2040. |
| [13] | ZENG Qinghui, LI Na, TIAN Ye, WU Di, ZHAO Yaowu, LI Lihua, ZHOU Changren. Effects of Collagen Films with Liquid Crystal-liked Ordered Structure on Adhesion, Proliferation and Differentiation of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(8): 1658. |
| [14] | XU Hai-Tao, LI Jing, LIANG Hong-Bo, XIONG Lei, GAO Ge. Synthesis and Properties of Fluorine-Containing Electron Beam Curing Polyurethane Acrylate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(04): 823. |
| [15] | LÜ Shao-Yi, SHAO Zi-Qiang, ZHANG Zhen-Ling, WANG Fei-Jun, WANG Wen-Jun. Rheological Properties of New Stimuli-responsive Energetic Gels [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(02): 409. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||