

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (10): 1709.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170132
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Yuxiang1,*( ), LIU Yicheng1, ZHAO Min1, YUAN Hongming3, YAO Pingping1, HUANG Yan1, NI Chaoying2,*(
), LIU Yicheng1, ZHAO Min1, YUAN Hongming3, YAO Pingping1, HUANG Yan1, NI Chaoying2,*( )
)
Received:2017-03-07
Online:2017-10-10
Published:2017-09-22
Contact:
YANG Yuxiang,NI Chaoying
E-mail:yxyang@ecust.edu.cn;cni@udel.edu
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YANG Yuxiang, LIU Yicheng, ZHAO Min, YUAN Hongming, YAO Pingping, HUANG Yan, NI Chaoying. Thermal Reduation Preparation of Co2+/Dy3+ Doped Cubic Fe3O4 and Their Magnetic Targeting Retention†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1709.
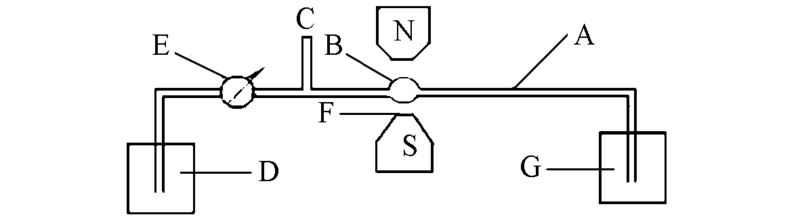
Fig.2 Experimental chart of magnetic targetingA. Pipeline; B. simulated perivascular tumor tissue; C. entrance for magnetic fluid of iron oxide; D. distilled water; E. constant flow pump; F. medical pulse magnetic field; G. beaker used to collect the outgoing solution.
| (hkl) | dtheoretical/nm | dmeasured/nm | I/I0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (111) | 0.48399 | 0.48439 | 8.9606 |
| (220) | 0.29638 | 0.29700 | 35.1254 |
| (311) | 0.25276 | 0.25355 | 100 |
| (222) | 0.24200 | 0.24212 | 11.8279 |
| (400) | 0.20958 | 0.20869 | 17.9211 |
| (422) | 0.17112 | 0.17037 | 12.1864 |
| (511) | 0.16113 | 0.16016 | 25.8064 |
| (440) | 0.14819 | 0.14684 | 29.0322 |
| (620) | 0.13255 | 0.13209 | 4.6595 |
| (622) | 0.12638 | 0.12732 | 7.8853 |
| (444) | 0.12100 | 0.12123 | 4.6595 |
Table 1 Experimental data and calculated results of PXRD of Fe3O4(cubic system)
| (hkl) | dtheoretical/nm | dmeasured/nm | I/I0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (111) | 0.48399 | 0.48439 | 8.9606 |
| (220) | 0.29638 | 0.29700 | 35.1254 |
| (311) | 0.25276 | 0.25355 | 100 |
| (222) | 0.24200 | 0.24212 | 11.8279 |
| (400) | 0.20958 | 0.20869 | 17.9211 |
| (422) | 0.17112 | 0.17037 | 12.1864 |
| (511) | 0.16113 | 0.16016 | 25.8064 |
| (440) | 0.14819 | 0.14684 | 29.0322 |
| (620) | 0.13255 | 0.13209 | 4.6595 |
| (622) | 0.12638 | 0.12732 | 7.8853 |
| (444) | 0.12100 | 0.12123 | 4.6595 |
| CoxFe3-xO4 | DyxFe3-xO4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | a/nm | 105Relative error | x | a/nm | 105Relative error |
| 0.06 | 0.8421 | 9.2211 | 0.05 | 0.8386 | 7.4738 |
| 0.14 | 0.8379 | 9.9783 | 0.13 | 0.8362 | 0.9782 |
| 0.29 | 0.8397 | 8.6385 | 0.28 | 0.8355 | 1.9035 |
| 0.44 | 0.8409 | 9.0054 | 0.43 | 0.8357 | 5.2441 |
| 0.58 | 0.8390 | 8.4927 | 0.53 | 2.498* | 0.1300 |
Table 2 Results for rietveld analysis of PXRD of CoxFe3-xO4 and DyyFe3-yO4*
| CoxFe3-xO4 | DyxFe3-xO4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | a/nm | 105Relative error | x | a/nm | 105Relative error |
| 0.06 | 0.8421 | 9.2211 | 0.05 | 0.8386 | 7.4738 |
| 0.14 | 0.8379 | 9.9783 | 0.13 | 0.8362 | 0.9782 |
| 0.29 | 0.8397 | 8.6385 | 0.28 | 0.8355 | 1.9035 |
| 0.44 | 0.8409 | 9.0054 | 0.43 | 0.8357 | 5.2441 |
| 0.58 | 0.8390 | 8.4927 | 0.53 | 2.498* | 0.1300 |
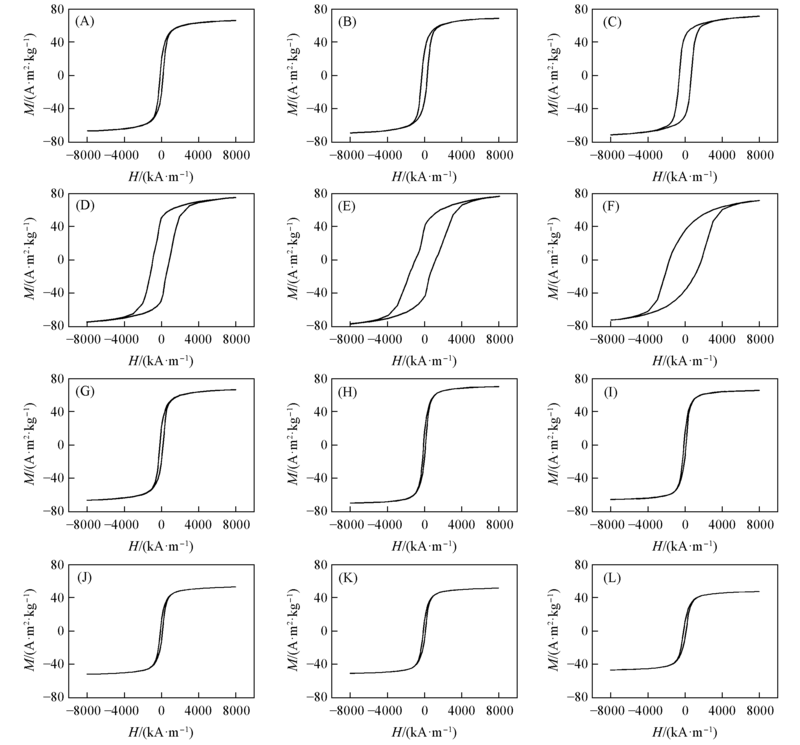
Fig.7 Magnetization hysteresis curves of CoxFe3-xO4(A—F) and DyxFe3-xO4(G—I)(A)—(F) x=0, 0.06, 0.14, 0.29, 0.44, 0.58; (G)—(L) x=0, 0.05, 0.13, 0.28, 0.43, 0.53.
| CoxFe3-xO4 | DyxFe3-xO4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | Ms/(A·m2·kg-1) | Mr/(A·m2·kg-1) | Hc/(kA·m-1) | x | Ms/(A·m2·kg-1) | Mr/(A·m2·kg-1) | Hc/(kA·m-1) |
| 0 | 66.36 | 20.26 | 183.9 | 0 | 66.36 | 20.26 | 183.9 |
| 0.06 | 68.99 | 30.76 | 307.8 | 0.05 | 70.21 | 17.13 | 147.8 |
| 0.14 | 71.50 | 47.71 | 663.4 | 0.13 | 65.62 | 14.73 | 105.7 |
| 0.29 | 75.08 | 49.74 | 897.5 | 0.28 | 52.25 | 13.22 | 132.2 |
| 0.44 | 76.65 | 42.57 | 1097.5 | 0.43 | 50.88 | 12.04 | 121.3 |
| 0.58 | 72.14 | 36.21 | 1746.2 | 0.53 | 47.28 | 9.61 | 113.4 |
Table 3 Magnetic parameters of CoxFe3-xO4 and DyxFe3-xO4
| CoxFe3-xO4 | DyxFe3-xO4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | Ms/(A·m2·kg-1) | Mr/(A·m2·kg-1) | Hc/(kA·m-1) | x | Ms/(A·m2·kg-1) | Mr/(A·m2·kg-1) | Hc/(kA·m-1) |
| 0 | 66.36 | 20.26 | 183.9 | 0 | 66.36 | 20.26 | 183.9 |
| 0.06 | 68.99 | 30.76 | 307.8 | 0.05 | 70.21 | 17.13 | 147.8 |
| 0.14 | 71.50 | 47.71 | 663.4 | 0.13 | 65.62 | 14.73 | 105.7 |
| 0.29 | 75.08 | 49.74 | 897.5 | 0.28 | 52.25 | 13.22 | 132.2 |
| 0.44 | 76.65 | 42.57 | 1097.5 | 0.43 | 50.88 | 12.04 | 121.3 |
| 0.58 | 72.14 | 36.21 | 1746.2 | 0.53 | 47.28 | 9.61 | 113.4 |
| Sample | Spacing/cm | Pulsed field voltage(V/Hz) | Magnetic peak/mT | Concentration after retention/(g·L-1) | Retention rate(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dy0.05Fe2.95O4 | 2 | 500/2 | 269 | 0.0230 | 80.7 |
| 2 | 600/2 | 290 | 0.0202 | 81.2 | |
| 2 | 700/2 | 350 | 0.0504 | 81.8 | |
| Co0.44Fe2.56O4 | 2 | 500/2 | 249 | 0.0230 | 92.7 |
| 2 | 600/2 | 271 | 0.0202 | 93.6 | |
| 2 | 700/2 | 346 | 0.0050 | 98.4 | |
| 10 | 500/2 | 55.5 | 0.1115 | 64.6 | |
| 10 | 600/2 | 79.2 | 0.1055 | 66.5 | |
| 10 | 700/2 | 96.3 | 0.1008 | 68.0 | |
| USPIO[ | 2 | 500/2 | 279 | 0.0430 | 76.8 |
| 2 | 600/2 | 378 | 0.0422 | 77.2 | |
| 2 | 700/2 | 433 | 0.0408 | 78.0 | |
| 10 | 500/2 | 53 | 0.0591 | 41.0 |
Table 4 Retention situation under different conditions
| Sample | Spacing/cm | Pulsed field voltage(V/Hz) | Magnetic peak/mT | Concentration after retention/(g·L-1) | Retention rate(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dy0.05Fe2.95O4 | 2 | 500/2 | 269 | 0.0230 | 80.7 |
| 2 | 600/2 | 290 | 0.0202 | 81.2 | |
| 2 | 700/2 | 350 | 0.0504 | 81.8 | |
| Co0.44Fe2.56O4 | 2 | 500/2 | 249 | 0.0230 | 92.7 |
| 2 | 600/2 | 271 | 0.0202 | 93.6 | |
| 2 | 700/2 | 346 | 0.0050 | 98.4 | |
| 10 | 500/2 | 55.5 | 0.1115 | 64.6 | |
| 10 | 600/2 | 79.2 | 0.1055 | 66.5 | |
| 10 | 700/2 | 96.3 | 0.1008 | 68.0 | |
| USPIO[ | 2 | 500/2 | 279 | 0.0430 | 76.8 |
| 2 | 600/2 | 378 | 0.0422 | 77.2 | |
| 2 | 700/2 | 433 | 0.0408 | 78.0 | |
| 10 | 500/2 | 53 | 0.0591 | 41.0 |
| [1] | Faraji M., Yamini Y., Rezaee M., J. Iran Chem. Soc., 2010, 7(1), 1—37 |
| [2] | Sun S. H., Zeng H., Robinson D. B., Raoux S., Rice P. M., Wang S. X., Li G. X., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 273—279 |
| [3] | Wei G. Y., Zhang J. W., Li A. W., Liu L. Q., Yang H., Wang J. P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2015, 36(5), 838—843 |
| (魏光耀, 张佳伟, 李爱武, 刘连庆, 杨海, 王继萍. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(5), 838—843) | |
| [4] | Knoll A., Lyakhova K. S., Horvat A., Krausch G., Sevink G. J. A., Zvelindovsky A. V., Magerle R., Nat. Mater., 2004, 3(3), 886—891 |
| [5] | Frey N. A., Peng S., Cheng K., Sun S. H., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 40(49), 2532—2542 |
| [6] | Matsuoka F., Shinkai M., Honda H., Kubo T., Sugita T., Kobayashi T., Bio. Med. Cent., 2004, 2(1), 1—6 |
| [7] | Bergemann C., Schulte D. M., Oster J., Brassard L., Lübbe A. S., J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1999, 194, 45—52 |
| [8] | Goodwin S., Peterson C., Hoh C., Bittner C. J., J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1999, 194, 132—139 |
| [9] | Davis S. M., Zaera F., Somorjai G. A., J. Catal., 1984, 85(1), 206—223 |
| [10] | Gratton S. E., Ropp P. A., Pohlhaus P. D., Luft J. C., Madden V. J., Napier M. E., Desimone J. M., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2008, 105(33), 11613—11618 |
| [11] | Geng B. Y., Ma J. Z., You J. H., Cryst. Growth Des., 2008, 8(5), 1443—1447 |
| [12] | Gao G. H., Liu X. H., Shi R. G., Zhou K. C., Shi Y. G., Ma R. Z., Muromachi E. T., Qiu G. Z., Cryst. Growth Des., 2010, 10(7), 2888—2894 |
| [13] | Zhao L., Zhang H. J., Xing Y., Song S. Y., Yu S. Y., Shi W. D., Guo X. M., Yang J. H., Lei Y. Q., Cao F., Chem. Mater., 2007, 20(1), 198—204 |
| [14] | Abbas M., Takahashi M., Kim C. G., J. Nanopart Res., 2013, 15, 1354—1366 |
| [15] | Uheida A., Salazar A. G., Björkman E., Björkman E., J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2006, 298(2), 501—507 |
| [16] | Makromol K., Tsuda K., Takaki M., Makromol. Chem. Rapid Commun., 1990, 11(5), 223—227 |
| [17] | Ayyub P., Multani M., Barma M., Palkar V. R., Vijayaraghavan R. J., Phys. C: Solid State Phys., 2000, 21(21), 2229—2245 |
| [18] | Xu R. R., Pang W. Q., Inorg. Syn. Prep. Chem., High Education Press, Beijing, 2001, 24—26 |
| (徐如人, 庞文琴. 无机合成与制备化学, 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2001, 24—26) | |
| [19] | Meng J. H., Yang G. Q., Yan L. M., Wang X. Y., Dyes Pigm., 2005, 66(2), 109—113 |
| [20] | Ding Y., Morber J. R., Snyder R. L., Wang Z. L., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2007, 17(7), 1172—1178 |
| [21] | Zhu Y. H., Li C. Z., Acta Chim. Sinica,1997, 55, 998—1003 |
| (朱以华, 李春忠. 化学学报, 1997, 55, 998—1003) | |
| [22] | Shannon R. D., Acta Cryst., 1976, 32(5), 751—767 |
| [23] | Zhang M. S., Sun J. J., Chen J., Inorg. Mater., 2012, 27(11), 1174—1178 |
| (张茂润, 孙静静, 陈静. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(11), 1174—1178) | |
| [24] | Zhang S. X., Wang J., Wang D. L., Ma Y. W., Mater. Lett., 2009, 63(21), 1820—1822 |
| [25] | Zhao H. T., Wang Q., Liu R. P., Ma R. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2016, 37(4), 613—618 |
| (赵海涛, 王俏, 刘瑞萍, 马瑞廷. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(4), 613—618) | |
| [26] | Hou Y. H., Huang Y. L., Liu Z. W., Zeng D. C., Acta Phys. Sin., 2015, 64(3), 446—451 |
| (侯育花, 黄有林, 刘仲武, 曾德长. 物理学报, 2015, 64(3), 446—451) | |
| [27] | Chen J. M., A New Way to Prepare Ferrite Powder by Wet Method, National Defence Industry Press, Beijing, 2001 |
| (陈俊明. 湿法制备铁氧体磁粉的新途径. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2001) | |
| [28] | Yang Y. X., Zhang L. P., Liang X. J., Chin. J. Inorg. Chem., 2010, 26(4), 668—676 |
| (杨宇翔, 张莉苹, 梁晓娟. 无机化学学报, 2010, 26(4), 668—676) | |
| [29] | Tripathy D., Adeyeye A. O., Boothroyd C. B., J. Appl. Phys., 2007, 101(1), 013904 |
| [30] | Borisova N. M., Gorshenkov M. V., Khovailo V. V., Phys. Solid State,2014, 56(7), 1334—1337 |
| [31] | Deepak F. L., Bañobre L. M., Carbó A. E., J. Phys. Chem. C,2015, 119(21), 11947—11957 |
| [32] | Huan W. W., Cheng C., Yang Y. X., J. Nanosci. Nanotechno., 2012, 12(6), 4621—4634 |
| [33] | Ayyappan S., Mahadevan S., Chandramohan P., J. Phys. Chem. C,2010, 114(14), 6334—6341 |
| [34] | Han X. Y., Yao P. P., Cheng C., Yuan H. M., Yang Y. X., Ni C. Y., J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2017, 17(1), 1—17 |
| [1] | CHENG Qian, YANG Bolong, WU Wenyi, XIANG Zhonghua. S-doped Fe-N-C as Catalysts for Highly Reactive Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220341. |
| [2] | SONG Youwei, AN Jiangwei, WANG Zheng, WANG Xuhui, QUAN Yanhong, REN Jun, ZHAO Jinxian. Effects of Ag,Zn,Pd-doping on Catalytic Performance of Copper Catalyst for Selective Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Oxalate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20210842. |
| [3] | SUN Xuefeng, RENAGUL Abdurahman, YANG Tongsheng, YANG Qianting. Synthesis and Luminescence Properties of Cr,In Co-doped Small Size MgGa2O4 Near-infrared Persistent Luminescence Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210850. |
| [4] | WANG Zumin, MENG Cheng, YU Ranbo. Doping Regulation in Transition Metal Phosphides for Hydrogen Evolution Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220544. |
| [5] | HONG Yangyu, XING Hongzhu, BING Qiming, GAO Xuwen, QI Bin, CHEN Yakun, SU Tan, ZOU Bo. Synthesis and Fluorescence Properties of Novel Ce3+-doped Manganese Phosphite Open-framework Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2725. |
| [6] | WU Yaqiang, LIU Siming, JIN Shunjin, YAN Yongqing, WANG Zhao, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Synthesis of Zn-Doped NiCoP Catalyst with Porous Double-layer Nanoarray Structure and Its Electrocatalytic Properties for Hydrogen Evolution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2483. |
| [7] | CHEN Mingsu, ZHANG Huiru, ZHANG Qi, LIU Jiaqin, WU Yucheng. First-principles Study on the Catalytic Effect of Co,P co-Doped MoS2 in Lithium-sulfur Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2540. |
| [8] | CHEN Xiaoyu, YU Ranbo. Research Progress on Doping of Molybdenum Disulfide and Hydrogen Evolution Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 475. |
| [9] | MA Jun, ZHONG Yang, ZHANG Shanshan, HUANG Yijun, ZHANG Lipeng, LI Yaping, SUN Xiaoming, XIA Zhenhai. Design and Theoretical Calculation of Heteroatoms Doped Graphdiyne Towards Efficiently Catalyzing Oxygen Reduction and Evolution Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 624. |
| [10] | YAO Mingcai, YANG Qiang, MENG Jian, LIU Xiaojuan. Effect of Zn2+ Substituting Ga3+ on Structure and Photocatalytic Properties of Wurtzite β-CuGa1-xZnxO2 with Unequal Doping [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3561. |
| [11] | ZHU Yuxin, OUYANG Jie, SONG Yanhua, TANG Sheng, CUI Yanjuan. Preparation of Boron and Iodine co-Doped Carbon Nitride and Its Performance in Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution from Water† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1645. |
| [12] | ZHAO Guoqing, YUAN Zhao, WANG Lian, GUO Zhuo. Preparation of Ni2P/N, S co-Doped Reduced Graphene Oxide Composites and Their Electrocatalytic Properties for Hydrogen Evolution† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1575. |
| [13] | HUANG Jialing,LIU Fengjiao,WANG Tingting,LIU Cuie,ZHENG Fengying,WANG Zhenhong,LI Shunxing. Nitrogen and Sulfur co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Accurate Detection of pH in Gastric Juice† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1513. |
| [14] | CHENG Shifu,HU Hao,CHEN Bihua,WU Haihong,GAO Guohua,HE Mingyuan. Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Porous Carbons Prepared from Binary Ionic Liquids † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1048. |
| [15] | WANG Xia, LIU Yanji, JIA Yongfeng, JI Lei, HU Quanli, DUAN Limei, LIU Jinghai. Preparative Chemistry of N-containing Porous Carbon Nanofibers for Capacity Improvement in Lithium-sulfur Battery † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 829. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||