

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (12): 20220476.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220476
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Xiwen1, CHENG Chaoqun1, CHENG Yuan1, ZHAO Sheng1, WEI Hui1,2( )
)
Received:2022-04-11
Online:2022-12-10
Published:2022-08-24
Contact:
WEI Hui
E-mail:weihui@nju.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
CHEN Xiwen, CHENG Chaoqun, CHENG Yuan, ZHAO Sheng, WEI Hui. CeO2@montmorillonite Nanozyme for Crohn’s Disease Therapy[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(12): 20220476.
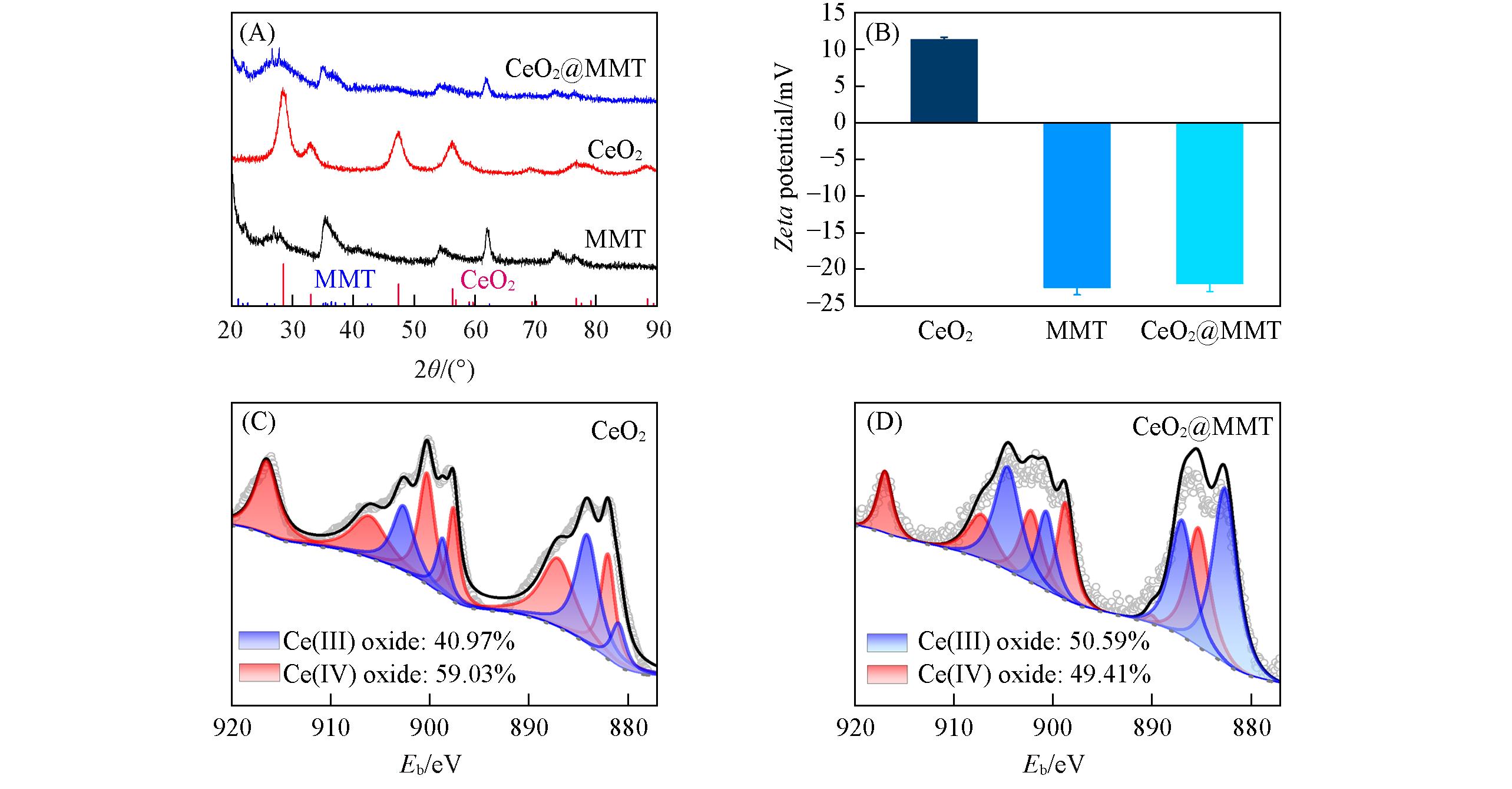
Fig.4 XRD patterns(A), zeta potentials(B) and XPS spectra(C, D) of CeO2,MMT and CeO2@MMT(B) Data are presented as mean±standard error of the mean(n=3).
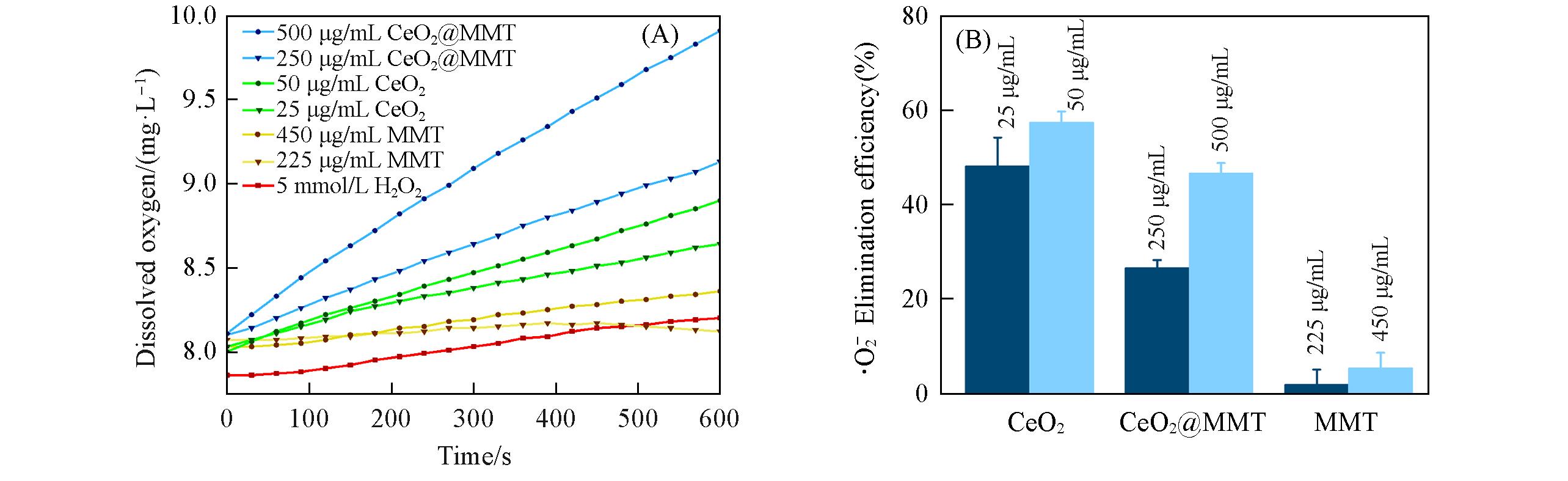
Fig.5 ROS scavenging activity of CeO2@MMT(A) CAT-like activity test. Typical kinetic curves of oxygen generation from the decomposition of H2O2 in the presence of indicated materials recorded every 30 s for 10 min. (B) SOD-like activity and •O2‒ scavenging rates of indicated materials. Data are presented as mean±standard error of the mean(n=4).
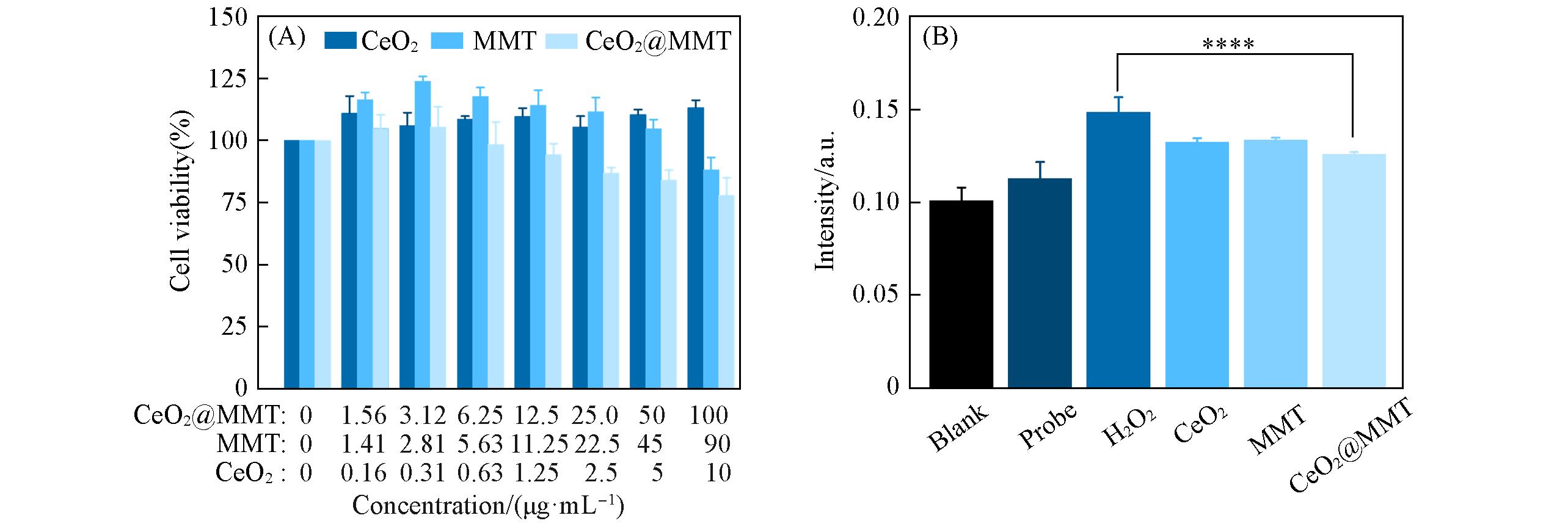
Fig.6 Cell viability after incubation with indicated materials for 24 h(A) and ROS level of RAW264.7 macrophages pretreated with indicated materials under H2O2(100 μmol/L) stimulation(B)Data are presented as mean±standard error of the mean(n=5). ****P < 0.0001 compared to the H2O2 group.
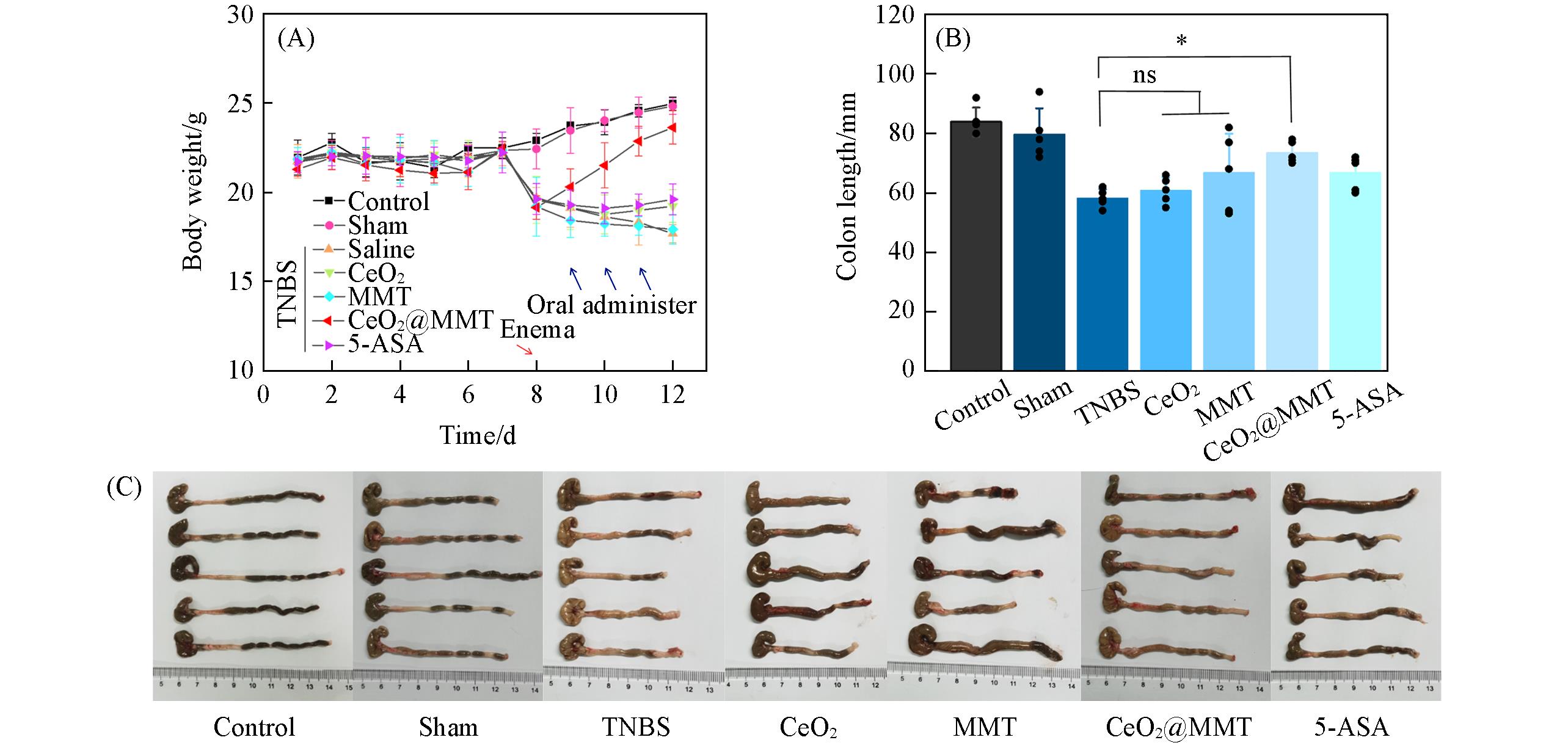
Fig.8 Weight change and colon length statistics of different groups of mice(A) The curves of weight changes of mice in different treatment groups; statistics(B) and photos(C) of colon length of mice in different treatment groups on day 12. Data are presented as mean±standard error of the mean(n=5). *P < 0.05 compared to the TNBS group.
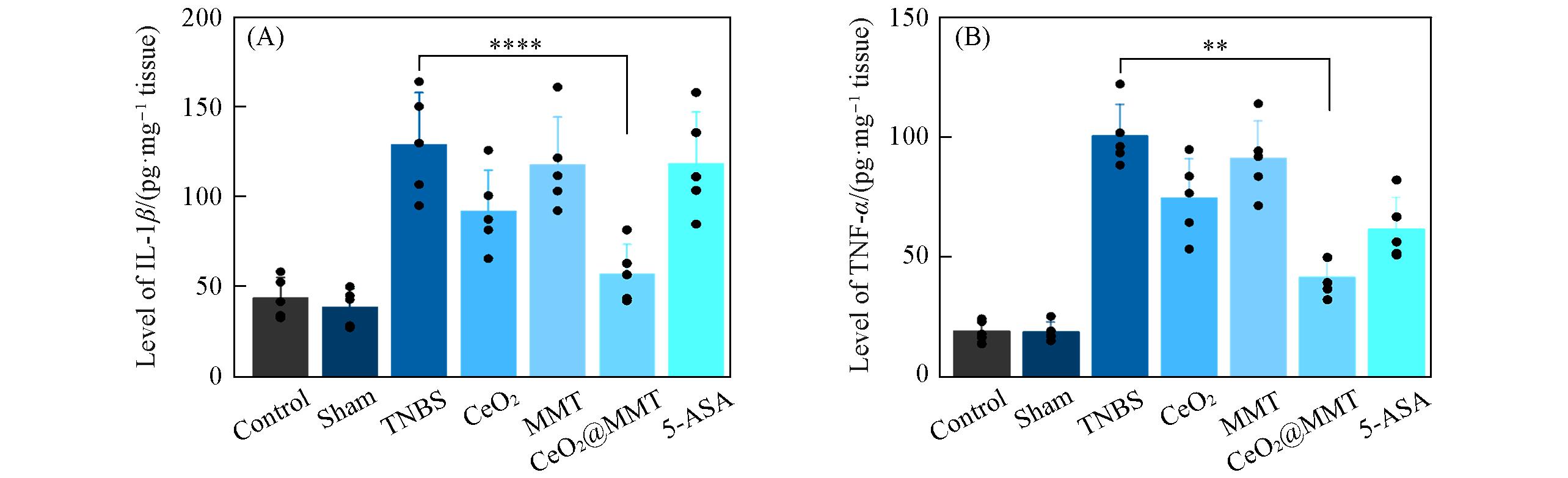
Fig.10 Local concentrations of the proinflammatory cytokines IL⁃1β(A) and TNF⁃α(B) in colon homogenate of different groups of mice on the 12th dayData are presented as mean±standard error of the mean(n = 5). **** P < 0.0001 and ** P < 0.01, comparison between TNBS group and CeO2@MMT group.
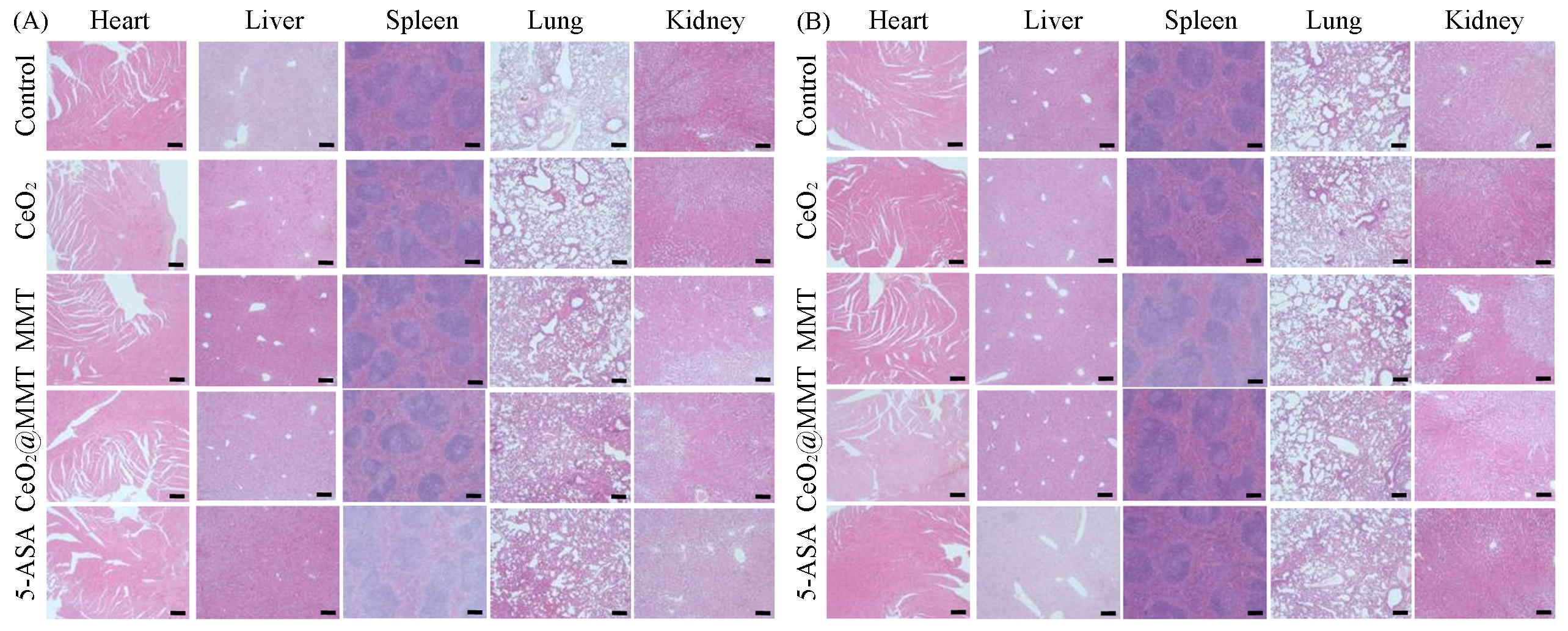
Fig.11 Pathological sections(H&E staining) of the heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney of different groups of mice after 7 d(A) and 30 d(B) of administration
| 1 | Torres J., Mehandru S., Colombel J. F., Peyrin⁃Biroulet L., Lancet, 2017, 389, 1741―1755 |
| 2 | Ungaro R., Mehandru S., Allen P. B., Peyrin⁃Biroulet L., Colombel J. F., Lancet, 2017, 389, 1756―1770 |
| 3 | Kaplan G. G., Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol., 2015, 12, 720―727 |
| 4 | Nagao⁃Kitamoto H., Kitamoto S., Kamada N., Cancer Metastasis Rev., 2022, 1―16 |
| 5 | Bernstein C. N., Fried M., Krabshuis J. H., Cohen H., Eliakim R., Fedail S., Gearry R., Goh K. L., Hamid S., Khan A. G., LeMair A. W., Malfertheiner, Qin O., Rey J. F., Sood A., Steinwurz F., Thomsen O. O., Thomson A., Watermeyer G., Inflamm. Bowel Dis., 2010, 16, 112―124 |
| 6 | Wilson D. S., Dalmasso G., Wang L., Sitaraman S. V., Merlin D., Murthy N., Nat. Mater., 2010, 9, 923―928 |
| 7 | Chapkin R. S., Kamen B. A., Callaway E. S., Davidson L. A., George N. I., Wang N., Lupton J. R., Finnell R. H., J. Nutr. Biochem., 2009, 20, 649―655 |
| 8 | Lautenschlager C., Schmidt C., Fischer D., Stallmach A., Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 2014, 71, 58―76 |
| 9 | Farkas S., Hornung M., Sattler C., Anthuber M., Gunthert U., Herfarth H., Schlitt H. J., Geissler E. K., Wittig B. M., Clin. Exp. Immunol., 2005, 142, 260―267 |
| 10 | Zhang S., Ermann J., Succi M. D., Zhou A., Hamilton M. J., Cao B., Korzenik J. R., Glickman J. N., Vemula P. K., Glimcher L. H., Traverso G., Langer R., Karp J. M., Sci. Transl. Med., 2015, 7, 300ra128 |
| 11 | Roessner A., Kuester D., Malfertheiner P., Schneider S., Pathol. Res. Pract., 2008, 204, 511―524 |
| 12 | Poli G., Free Radic. Biol. Med., 2002, 33, 301―302 |
| 13 | Zhang Q., Tao H., Lin Y., Hu Y., An H., Zhang D., Feng S., Hu H., Wang R., Li X., Zhang J., Biomaterials, 2016, 105, 206―221 |
| 14 | Wei H., Wang E., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42, 6060―6093 |
| 15 | Bao X., Zhao J., Sun J., Hu M., Yang X., ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 8882―8892 |
| 16 | Li S., Shang L., Xu B., Wang S., Gu K., Wu Q., Sun Y., Zhang Q., Yang H., Zhang F., Gu L., Zhang T., Liu H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 12624―12631 |
| 17 | Li Y., He X., Yin J., Ma Y., Zhang P., Li J., Ding Y., Zhang J., Zhao Y., Chai Z., Zhang Z., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 1832―1835 |
| 18 | Xi J., Zhang R., Wang L., Xu W., Liang Q., Li J., Jiang J., Yang Y., Yan X., Fan K., Gao L., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31, 2007130 |
| 19 | Zhang Y., Wang F., Liu C., Wang Z., Kang L., Huang Y., Dong K., Ren J., Qu X., ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 651―661 |
| 20 | Zhao S., Li Y., Liu Q., Li S., Cheng Y., Cheng C., Sun Z., Du Y., Butch C. J., Wei H., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 2004692―2004706 |
| 21 | Korsvik C., Patil S., Seal S., Self W. T., Chem. Commun.(Camb.), 2007, 10, 1056―1058 |
| 22 | Reed K., Cormack A., Kulkarni A., Mayton M., Sayle D., Klaessig F., Stadler B., ChemInform, 2015, 46, 390―405 |
| 23 | Ivanov V. K., Shcherbakov A. B., Usatenko A. V., Russ. Chem. Rev., 2009, 78, 855―871 |
| 24 | Heckert E. G., Karakoti A. S., Seal S., Self W. T., Biomaterials, 2008, 29, 2705―2709 |
| 25 | Deshpande S., Patil S., Kuchibhatla S. V. N. T., Seal S., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2005, 87, 3113―3115 |
| 26 | Liu Y., Cheng Y., Zhang H., Zhou M., Yu Y., Lin S., Jiang B., Zhao X., Miao L., Wei C., Liu Q., Lin Y., Du Y., Butch C. J., Wei H., Sci. Adv., 2020, 6, eabb2695 |
| 27 | Wirtz S., Popp V., Kindermann M., Gerlach K., Weigmann B., Fichtner⁃Feigl S., Neurath M. F., Nat. Protoc., 2017, 12, 1295 |
| 28 | Neurath M., Fuss I., Strober W. Int. Rev. Immunol., 2000, 19, 51―62 |
| [1] | CHEN Jiamin, QU Xiaozhang, QI Guohua, XU Weiqing, JIN Yongdong, XU Shuping. SERS Nanoprobe for the Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species in Cells Produced by Electrostimulus [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220033. |
| [2] | LI Ao, LI Lingxuan, ZUO Cuicui, CHEN Chuankai, FAN Yifan, BU Yifan, LIN Hongyu, GAO Jinhao. Boronate-based 19F NMR/MRI Molecular Probe for Activatable Deep-tissue Imaging of Reactive Oxygen Species [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(12): 20220545. |
| [3] | XU Huan, KE Lyu, TANG Mengke, SHANG Han, XU Wenxuan, ZHANG Zilin, FU Yanan, HAN Guangdong, CUI Jinsheng, YANG Haoran, GAO Jiefeng, ZHANG Shenghui, HE Xinjian. In⁃situ Liquid Exfoliation of Montmorillonite Nanosheets in Poly(lactic acid) to Resist Oxygen Permeation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220316. |
| [4] | SHAO Wenhui, HU Xin, SHANG Jing, LIN Feng, JIN Liming, QUAN Chunshan, ZHANG Yanmei, LI Jun. Design, Synthesis and Photocatalytic Antibacterial Mechanism of Ag-AgVO3/BiVO4 Composite as a High-efficient and Broad-spectral Antibacterial Agent [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220132. |
| [5] | ZHANG Jihua,WANG Chao,ZAO Weitao,LI Li,LIU Xiaoyan,YANG Yuan,WANG Hao. Preparation of High-performance Montmorillonite/hydrogenated Butadiene-acrylonitrile Rubber by Using Electrostatic Interfaces [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 803. |
| [6] | LUAN Jingde, LIU Yawei, ZHANG Chengyu, KE Xin. Synchronization Capture of Zn2+ and p-Nitrophenyl Phenol on Montmorillonite Composites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 270. |
| [7] | LI Tingting, ZHAO Lele, WANG Ruili, ZHANG Shuqiu. Preparation and in vitro Release of Ketoprofen/acid-montmorillonite† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 722. |
| [8] | LI Xingjian,JU Yunpeng,CHANG Degong,ZHANG Yiheng. Preparation and Properties of Flame Retardant Waterborne Polyurethane Nanocomposites via Click Reaction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(8): 1580. |
| [9] | LUO Yanling, LIU Yajun. Role of Superoxide in Bioluminescence† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(1): 24. |
| [10] | RAN Shi-Ya, XU Yuan-Yuan, GUO Zheng-Hong, FANG Zheng-Ping. Synergistic Flame Retardant of Acid or Alkali-treated Montmrillonite/Phosphate Flame Retardant in PC/ABS Blends [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(2): 467. |
| [11] | SHAN Xue-Ying, TAI Qi-Long, HU Yuan, SONG Lei, LU Siu-Ming. Preparation and Property of Inherent Flame Retardant Polystyrene/Clay Nanocomposites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(10): 2431. |
| [12] | ZHU Zhi-Jie, LIU Qiong, CHEN Ping, XU Xu, NI Jia-Zuan, YANG Si-Lin, SONG Yun. Seleno-polymannuronate Synthesis and Resistance to Oxidation and Apoptosis in Alzheimer’s Disease Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(1): 115. |
| [13] | DUAN Shu-E, ZHAI Yun-Hui, QU Ying-Juan, MA Ming-Yang. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Silver-histidine Complex Doped Montmorillonite Antibacterial Agent [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(12): 2617. |
| [14] | LI Chen, YANG Zheng, SHE Meng-Yao, YIN Wen-Ting, LI Jian-Li*, ZHAO Gui-Fang, SHI Zhen. Recent Progress in Superoxide Dismutase Mimics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(9): 2046. |
| [15] | YE Ling*, ZHANG Jing-Yang. Chelate Regulatory ζ-potentials of Montmorilloniteand Its Adsorption Capacity for Cr(Ⅲ) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(12): 2478. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||