

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 1280.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180694
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Dongwei, TIAN Runsai, LIU Zhenjiang, FENG Yuanyuan, DING Hongyu, FENG Jijun( )
)
Received:2018-10-16
Online:2019-06-10
Published:2019-03-27
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
MA Dongwei,TIAN Runsai,LIU Zhenjiang,FENG Yuanyuan,DING Hongyu,FENG Jijun. Microwave-assisted Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Na-Doped Cathode Materials Li2-xNaxMnSiO4/C†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1280.
| Sample | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN0 | 0.63037 | 0.53828 | 0.49806 | 0.16900 |
| CN9 | 0.63080 | 0.53825 | 0.49942 | 0.16956 |
Table 1 Cell parameters of CN0 and CN9 samples
| Sample | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN0 | 0.63037 | 0.53828 | 0.49806 | 0.16900 |
| CN9 | 0.63080 | 0.53825 | 0.49942 | 0.16956 |
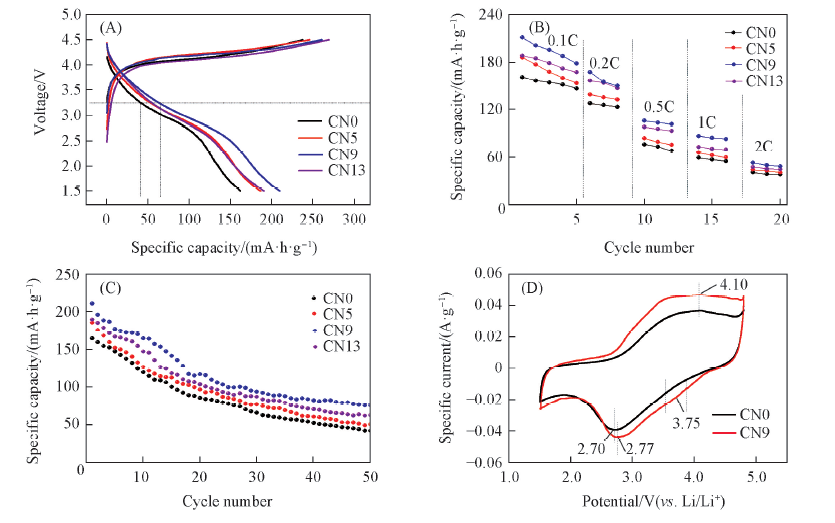
Fig.6 Initial charge-discharge curves(A), rate performances(B) and cycle performances(C) of CN0, CN5, CN9, CN13 samples and CV curves of CN0 and CN9 samples scanned at 0.1 mV/s after five cycles(D)
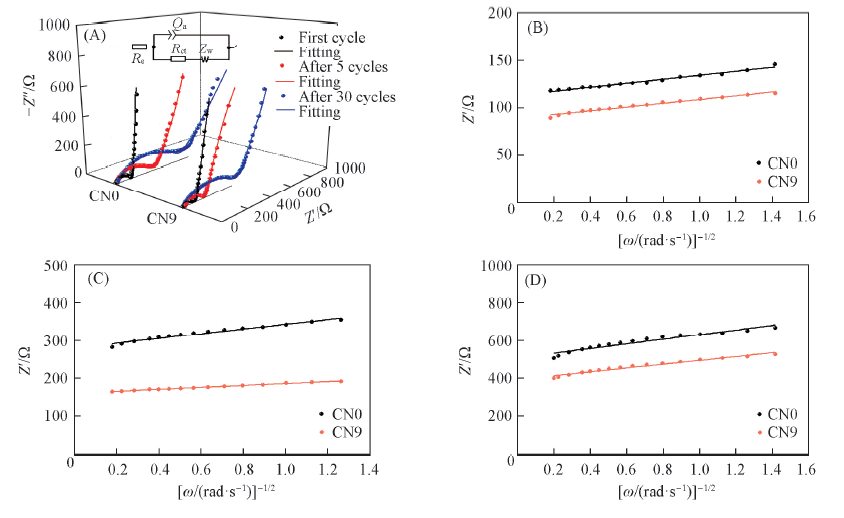
Fig.7 Nyquist plots and equivalent circuit(inset)(A) and relationship between Z’ and ω-1/2 in low-frequency region(B—D) of CN0 and CN9 at room temperature The solid line represents the fitted results. (B) First cycle; (C) after 5 cycles; (D) after 30 cycles.
| Sample | Re/W | Rct/W | σw/(cm2·s-1/2) | 1013 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First cycle | After 5 cycls | After 30 cycls | First cycle | After 5 cycls | After 30 cycls | First cycle | After 5 cycls | After 30 cycls | First cycle | After 5 cycls | After 30 cycls | |
| CN0 | 2.12 | 2.70 | 13.99 | 111.60 | 269.00 | 489.00 | 21.17 | 63.36 | 124.32 | 3.37 | 0.38 | 0.10 |
| CN9 | 2.60 | 4.24 | 3.07 | 79.00 | 165.10 | 400.20 | 19.79 | 25.73 | 101.39 | 3.82 | 2.28 | 0.15 |
Table 2 EIS fitting results of CN0 and CN9 samples
| Sample | Re/W | Rct/W | σw/(cm2·s-1/2) | 1013 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First cycle | After 5 cycls | After 30 cycls | First cycle | After 5 cycls | After 30 cycls | First cycle | After 5 cycls | After 30 cycls | First cycle | After 5 cycls | After 30 cycls | |
| CN0 | 2.12 | 2.70 | 13.99 | 111.60 | 269.00 | 489.00 | 21.17 | 63.36 | 124.32 | 3.37 | 0.38 | 0.10 |
| CN9 | 2.60 | 4.24 | 3.07 | 79.00 | 165.10 | 400.20 | 19.79 | 25.73 | 101.39 | 3.82 | 2.28 | 0.15 |
| [1] | Tang Y., Zhang Y., Li W., Ma B., Chen X., Chem. Soc. Rev.,2015, 44, 5926-5940 |
| [2] | Darcovich K., Henquin E. R., Kenney B., Davidson I. J., Saldanha N., Beausoleil-Morrison I., Appl. Energy,2013, 111, 853-861 |
| [3] | Ye D. L., Sun C. H., Chen Y., Ozawa K., Hulicova-Jurcakova D., Zou J., Wang L. Z., Nano Research,2015, 8(3), 808-820 |
| [4] | Dominko R., Bele M., Kokalj A., Gaberscek M., Jamnik J., J. Power Sources,2008, 184, 462-468 |
| [5] | Choi J. W., Aurbach D., Nat. Rev. Mater.,2016, 1(4), 16013-16029 |
| [6] | Hwang C., Kim T., Noh Y., Cha W., Shim J., Kwak K., Ok K. M., Lee K. K., Mater. Lett.,2016, 164, 270-273 |
| [7] | Wang Y. C., Zhao S. X., Zhai P. Y., Li F., Nan C. W., J. Alloys Compd.,2014, 614, 271-276 |
| [8] | Armand M., Tarascon J. M., Dompablo M. E., Electrochem. Commun.,2011, 13, 1047-1050 |
| [9] | Yang X. F., Yang J. H., Zaghib K., Trudeau M., Ying J., Nano Energy,2015, 12, 305-313 |
| [10] | Xie M., Luo R., Chen R. J., Wu F., Zhao T. L., Wang Q. Y., Li L., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces,2015, 7, 10779-10784 |
| [11] | Qiu S., Pu X. J., Ai X. P., Yang H. X., Chen Z. X., Cao Y. L., Electrochimica Acta,2018, 291, 124-131 |
| [12] | Chen Z. X., Qiu S., Cao Y. L., Qian J. F., Ai X. P., Xie K., Hong X. B., Yang H. X., J. Mater. Chem. A,2013, 1, 4988-4992 |
| [13] | Swietoslawski M., Molenda M., Furczon K., Dziembaj R., J. Power Sources,2013, 244, 510-514 |
| [14] | Zhu J. T., Tang H. Q., Tang Z. Y., Ma C. X., J. Alloys Compd.,2015, 633, 194-200 |
| [15] | Zhu J. T., Tang Z. Y., Tang H. Q., Xu Q., Zhang X. H., J. Electroanal. Chem.,2016, 761, 37-45 |
| [16] | Wu T. T., Lai C. Y., Xu Q. J., Mater. Lett.,2017, 186, 293-297 |
| [17] | Cheng H. M., Zhao S. X., Wu X., Zhao J. W., Wei L., Nan C. W., Appl. Surf. Sci.,2018, 433, 1067-1074 |
| [18] | Jia M. Z., Wang H. Y., Chen Y. Z., Ma C. L., Acta Phys. Sin.,2016, 65, 057101 |
| (嘉明珍, 王红艳, 陈元正, 马存良.物理学报, 2016, 65, 057101) | |
| [19] | Zhang X., Zhou Y. P., Luo B., Zhu H. C., Chu W., Huang K. M., Nano-Micro Lett.,2018, 10(1), 13 |
| [20] | Zhang Z. J., Wang Y. X., Chou S. L., Li H. J., Liu H. K., Wang J. Z., J. Power Sources,2015, 280, 107-113 |
| [21] | Lee C. L., Lee H. Y., Tseng K. H., Hong P. K., Jou C. J. G., Environ. Chem. Lett.,2011, 9, 355-359 |
| [22] | Lee C. L., Jou C. J. G., Environ Eng Sci.,2011, 28, 191-195 |
| [23] | Jou C. J. G., Hsieh S. C., Lee C. L., Lin C., Huang H. W., J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng.,2010, 41, 216-220 |
| [24] | Dominko R., Arcon I., Kodre A., Hanzel D., Gaberscek M., J. Power Sources.,2009, 189, 51-58 |
| [25] | Zhang S., Deng C., Liu F. L., Wu Q., Zhang M., Meng F. L., Gao H., J. Electroanal. Chem.,2013, 689, 88-95 |
| [26] | Dean J., Lange’s Handbook of Chemistry, Translated by Shang J. F., Cao S. J., Xin W. M., Zheng F. Y., Lu X. M., Lin C. Q., Science Press, Beijing, 1991, 117-120 |
| (Dean J.著, 尚久方,操时杰,辛无名,郑飞勇,陆晓明,林长青译.兰氏化学手册, 北京: 科学出版社, 1991, 117-120) | |
| [27] | Kuang B. Y., Dou Y. K., Wang Z. H., Ning M. Q., Jin H. B., Guo D. Y., Cao M. S., Fang X. Y., Zhao Y. J., Li J. B., Applied Surface Science,2018, 445, 383-390 |
| [28] | Liu N., He Z. X., Zhang X. B., Jiang Y. Q., Li Y. H., Zhu J., Meng W., Dai L., Wang L., Ceramics International,2017, 43, 11481-11487 |
| [29] | Chen Y. X., Ni D., Yang X. W., Liu C. C., Yin J. L., Cai K. F., Electrochimica Acta,2018, 278, 114-123 |
| [30] | Qu L., Luo D., Fang S. H., Liu Y., Yang L., Hirano S. I., Yang C. C., J. Power Sources,2016, 307, 69-76 |
| [31] | Hwang C., Kim T., Shim J., Kwak K., Ok K., Lee K., J. Power Sources,2015, 294, 522-529 |
| [1] | ZHANG Shiyu, HE Runhe, LI Yongbing, WEI Shijun, ZHANG Xingxiang. Fabrication of Lithium-sulfur Battery Cathode with Radiation Crosslinked Low Molecular Weight of Polyacrylonitrile and the Mechanism of Sulfur Storage [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210632. |
| [2] | GAO Xiaole, WANG Jiaxin, LI Zhifang, LI Yanchun, YANG Donghua. Synthesis of NiOx-ZSM-5 Composite Materials and Its Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Performance in Microbial Electrolysis Cell [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2886. |
| [3] | BAO Junquan, ZHENG Shibing, YUAN Xuming, SHI Jinqiang, SUN Tianjiang, LIANG Jing. An Organic Salt PTO(KPD)2 with Enhanced Performance as a Cathode Material in Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2911. |
| [4] | WANG Yimeng, LIU Kai, WANG Baoguo. Coating Strategies of Ni-rich Layered Cathode in LIBs [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1514. |
| [5] | ZHANG Huishuang, GAO Yanxiao, WANG Qiuxian, LI Xiangnan, LIU Wenfeng, YANG Shuting. High-low Temperature Properties of Ni-rich LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 Cathode Material by Hydrothermal Synthesis with CTAB Assisted [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 819. |
| [6] | LU Di,ZHENG Chunman,CHEN Yufang,LI Yujie,ZHANG Hongmei. Synthesis of Li-rich Layers/Spinel/Carbon Composite Cathode Materials with Phenol Formaldehyde Resin and Its Electrochemical Performance† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1684. |
| [7] | LI Xin, CHEN Liang, MA Xiaotao, ZHANG Ding, XU Shoudong, ZHOU Xianxian, DUAN Donghong, LIU Shibin. Preparation of V2O3 Hollow Spheres for Lithium Sulfur Batteries † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1972. |
| [8] | YANG Jinge, LI Yujie, LU Di, CHEN Yufang, SUN Weiwei, ZHENG Chunman. Morphology Control and Lithium Storage Performance of Micro/nano Li-rich Cathode Material† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1495. |
| [9] | YAO Fengnan,LI Yu,FENG Wei. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Carbon-coated FeF2 Nanocomposite† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1418. |
| [10] |
CHEN Hong,DU Yonghui,ZHANG Xin,LIU Wenyan,ZHOU Xiaoming.
Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of Poly(3-hexylthiophene)-coated Lithium-rich Layered Cathode Material Li1.18Ni0.15Co0.15Mn0.52 |
| [11] | Jian LIU,Haihui DU,Tianjiang SUN,Qingshun NIAN,Haixia LI,Zhanliang TAO. Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of Calcium Bronze/Carbon Nanotubes Composites † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2526. |
| [12] | LUO Man, JIANG Wenquan, HAN Xue, GUO Ronggui, LI Tao, YU Limin. Synthesis and Characterization of Full Concentration-gradient LiNi0.643Co0.055Mn0.302O2 Cathode Material for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(1): 148. |
| [13] | WANG Kun, HUANG Mengyi, ZHANG Xiaosong, HUANG Junjie, DENG Xiang, LIU Changlu. Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2@C Composite† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(1): 141. |
| [14] | ZHANG Dong, LI Tingting, QIU Hailong, WEI Yingjin, WANG Chunzhong, CHEN Gang, YUE Huijuan. Preparation and Characterization of N-doped Li2FeSiO4/C Cathode Materials for Lithium Ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(9): 1633. |
| [15] | ZHENG Zhuo, WU Zhenguo, XIANG Wei, HUA Weibo, GUO Xiaodong. Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Na+-stabilized Layered LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 Cathode Material for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8): 1458. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||