

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 306.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180597
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ABUDUHEIREMU Awati, ZHANG Dedong, HALIDAN Maimaiti*( )
)
Received:2018-08-27
Online:2019-02-10
Published:2018-11-05
Contact:
HALIDAN Maimaiti
E-mail:m15899160730@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ABUDUHEIREMU Awati,ZHANG Dedong,HALIDAN Maimaiti. Preparation and CO2 Reduction Performance of Composite Photocatalyst Based on Aminated Coal-based Carbon Dots†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 306.
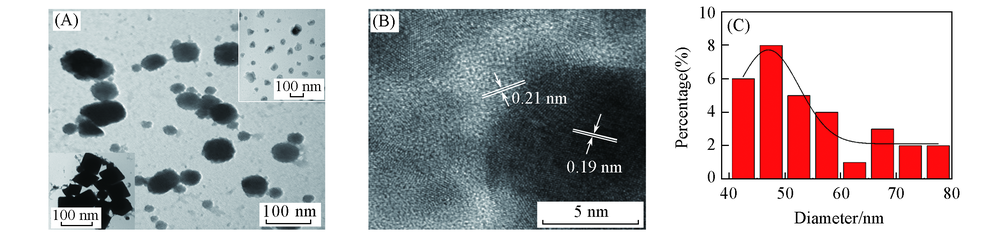
Fig.2 TEM(A) and HRTEM(B) images and particle distribution(C) of Cu2O/NH2-CDsThe insets in (A): TEM images of Cu2O(lower left corner) and NH2-CDs(upper right corner).
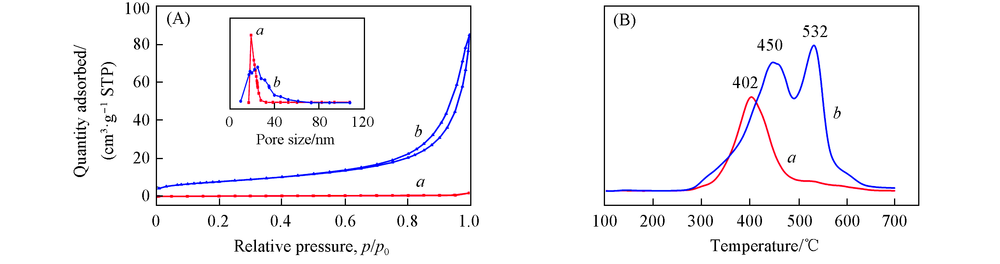
Fig.6 N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and corresponding BJH pore size distributions(inset)(A) and CO2-TPD profiles(B) of Cu2O(a) and Cu2O/NH2-CDs(b)
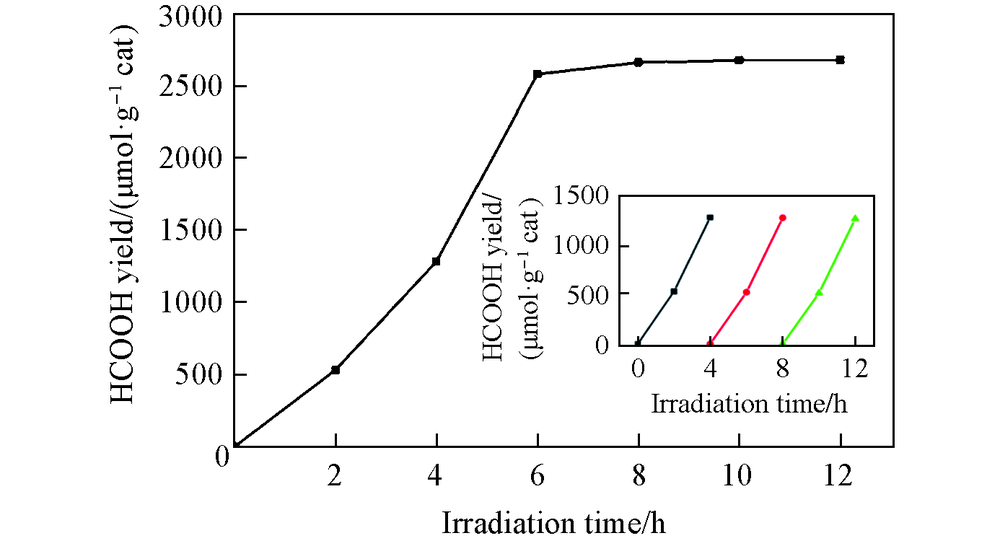
Fig.9 HCOOH yield changed with irradiation time with sample CP3 as catalystInset is the long-term time curve of recovered sample CP3 for photocatalysis of CO2(with solution being replaced and photocatalyst being recovered every 4 h).
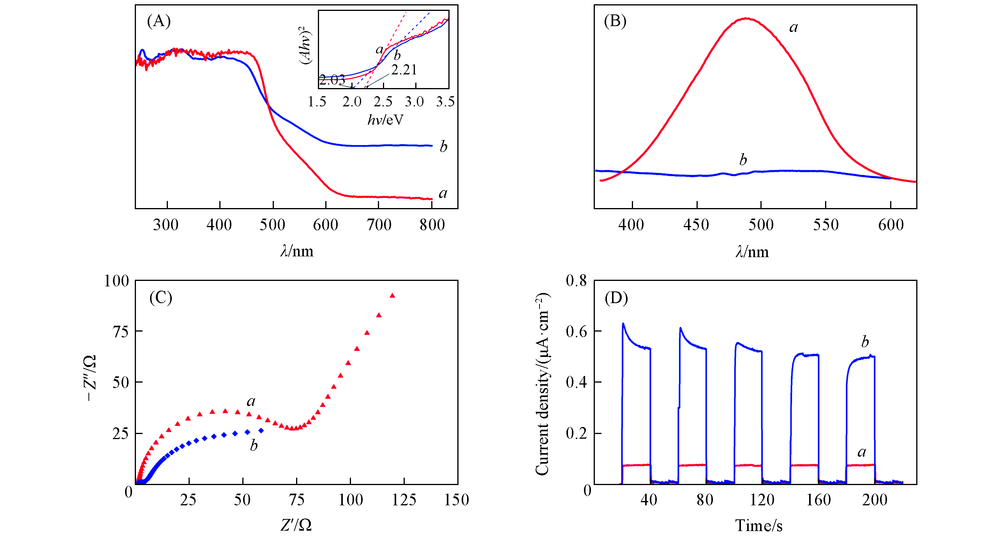
Fig.10 DR UV-Vis spectra and the calculation of band gap(inset)(A), FL spectra(B), Nyquist plots(C) and transient photocurrent responses(D) of Cu2O(a) and Cu2O/NH2-CDs(b)
| [1] | Nahar S., Zain M. F. M., Kadhum A. A. H., Hasan H. A., Hasan M. R., Materials(Basel), 2017, 10(6), 629-655 |
| [2] | Indrakanti V. P., Kubicki J. D., Schobert H. H., Fuel Process. Technol.,2011, 92(4), 805-811 |
| [3] | Habisreutinger S. N., Schmidt-Mende L., Stolarczyk J. K., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.,2013, 52(29), 7372-7408 |
| [4] | Yamazaki Y., Takeda H., Ishitani O., J. Photochem. Photobio. C: Photochem. Rev.,2015, 25, 106-137 |
| [5] | Ran J., Jaroniec M., Qiao S. Z., Adv. Mater.,2018, 30(7), 1704649-1704680 |
| [6] | Kumar B., Llorente M., Froehlich J., Dang T., Sathrum A., Kubiak C. P., Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem.,2012, 63, 541-569 |
| [7] | Yu L., Li G., Zhang X., Ba X., Shi G., Li Y., Wong P. K., Yu J. C., Yu Y., ACS Catalysis,2016, 6(10), 6444-6454 |
| [8] | Ba X., Yan L. L., Huang S., Yu J., Xia X. J., Yu Y., J. Phys. Chem. C,2014, 118(42), 24467-24478 |
| [9] | Wang A., Li X., Zhao Y., Wu W., Chen J., Meng H., Powder Technol.,2014, 261, 42-48 |
| [10] | Yu L., Xiong L., Yu Y., J. Phys. Chem. C,2015, 119(40), 22803-22811 |
| [11] | McShane C. M., Choi K. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2009, 131(7), 2561-2569 |
| [12] | Lin C. Y., Lai Y. H., Mersch D., Reisner E., Chem. Sci.,2012, 3(12), 3482-3487 |
| [13] | Yin G., Nishikawa M., Nosaka Y., Srinivasan N., Atarashi D., Sakai E., Miyauchi M., ACS Nano,2015, 9(2), 2111-2119 |
| [14] | Sato S., Morikawa T., Saeki S., Kajino T., Motohiro T., Angew. Chem.,2010, 122(30), 5227-5231 |
| [15] | Suzuki T. M., Nakamura T., Saeki S., Matsuoka Y., Tanaka H., Yano K., Kajino T., Morikawa T., J. Mater. Chem.,2012, 22(47), 24584-24590 |
| [16] | Ye R., Xiang C., Lin J., Peng Z., Huang K., Yan Z., Cook N. P., Samuel E. L., Hwang C. C., Ruan G., Ceriotti G., Raji A. R., Marti A. A., Tour J. M., Nat. Commun.,2013, 4(2943), 1-6 |
| [17] | Hu C., Yu C., Li M., Wang X., Yang J., Zhao Z., Eychmuller A., Sun Y. P., Qiu J., Small,2014, 10(23), 4926-4933 |
| [18] | Hu S., Wei Z., Chang Q., Trinchi A., Yang J., Appl. Surf. Sci.,2016, 378, 402-407 |
| [19] | Shan Z., Wu J., Xu F., Huang F. Q., Ding H., J. Phys. Chem. C,2008, 112(39), 15423-15428 |
| [20] | Zhang D. D., Maimaiti H., Awati A., Yisilamu G., Sun F. C., Wang M., Chem. Phys. Lett.,2018, 700, 27-35 |
| [21] | Li Y., Zhang W., Shen X., Peng P., Xiong L., Yu Y., Chinese J. Catal.,2015, 36(12), 2229-2236 |
| [22] | Zhang Y. F., Maimaiti H., Zhang B., RSC Adv.,2017, 7(5), 2842-2850 |
| [23] | Li Z., Zhu L., Wu W., Wang S., Qiang L., Appl. Catal. B: Environ.,2016, 192, 277-285 |
| [24] | Khan M. A., Wahab Y., Muhammad R., Tahir M., Sakrani S., Appl. Surf. Sci.,2018, 435, 718-732 |
| [25] | Krishna Sadhanala H., Maddegalla A., Nanda K. K., New J. Chem.,2017, 41(22), 13742-13746 |
| [26] | Liu L., Qi Y., Hu J., An W., Lin S., Liang Y., Cui W., Mater. Lett.,2015, 158, 278-281 |
| [27] | Huang C., Ye W., Liu Q., Qiu X., ACS Appl. Mater. Interface,2014, 6(16), 14469-14476 |
| [28] | Guo Y., Wang H., Ma X., Jin J., Ji W., Wang X., Song W., Zhao B., He C., ACS Appl. Mater. Interface,2017, 9(22), 19074-19081 |
| [29] | Ms S., Sankararaman S., J. Mater. Sci. Nanotechnol.,2017, 5(1), 104-110 |
| [30] | Wang M. X., Guo Z., Huang Z. H., Kang F., Catal. Commun.,2015, 62, 83-88 |
| [31] | Ishizaki T., Wada Y., Chiba S., Kumagai S., Lee H., Serizawa A., Li O. L., Panomsuwan G., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.,2016, 18(31), 21843-21851 |
| [32] | Yang J., Li Z., Zhao C., Wang Y., Liu X., Mater. Res. Bull.,2014, 60, 530-536 |
| [33] | Tulumello D., Cooper G., Koprinarov I., Hitchcock A. P., Rightor E. G., Mitchell G. E., Rozeveld S., Meyers G. F., Stokich T. M., J. Phys. Chem. B,2005, 109(13), 6343-6354 |
| [34] | Zhang T., Li C., Gu Y., Yan X., Zheng B., Li Y., Liu H., Lu N., Zhang Z., Feng G., Talanta,2017, 165, 143-151 |
| [35] | Bian S., Shen C., Qian Y., Liu J., Xi F., Dong X., Sens. Actua. B: Chem.,2017, 242, 231-237 |
| [36] | Wuang S. C., Neoh K. G., Kang E. T., Pack D. W., Leckband D. E., Adv. Funct. Mater.,2006, 16(13), 1723-1730 |
| [37] | Yang Y. T., Yang X. X., Wang Y. T., Luo J., Zhang F., Yang W. J., Chen J. H., Fuel,2018, 219, 166-175 |
| [38] | Ma Y., Li X., Yang Z., Xu S., Zhang W., Su Y., Hu N., Lu W., Feng J., Zhang Y., Langmuir,2016, 32(37), 9418-9427 |
| [39] | Jin J., Yu J., Guo D., Cui C., Ho W., Small,2015, 11(39), 5262-5271 |
| [40] | Witoon T., Kachaban N., Donphai W., Kidkhunthod P., Faungnawakij K., Chareonpanich M., Limtrakul J., Energy Convers. Manage.,2016, 118, 21-31 |
| [41] | Hsu H. C., Shown I., Wei H. Y., Chang Y. C., Du H. Y., Lin Y. G., Tseng C. A., Wang C. H., Chen L. C., Lin Y. C., Chen K. H., Nanoscale,2013, 5(1), 262-268 |
| [42] | Wang F., Chen P., Feng Y., Xie Z., Liu Y., Su Y., Zhang Q., Wang Y., Yao K., Lv W., Liu G., Appl. Catal. B: Environ.,2017, 207, 103-113 |
| [43] | Ong W. J., Tan L. L., Chai S. P., Yong S. T., Dalton Trans.,2015, 44(3), 1249-1257 |
| [44] | Li M., Wang M., Zhu L., Li Y., Yan Z., Shen Z., Cao X., Appl. Catal. B: Environ.,2018, 231, 269-276 |
| [1] | WANG Zhipeng,NIU Zhuzhu,BAN Lijun,HAO Quanai,ZHANG Hongxi,LI Haitao,ZHAO Yongxiang. Formaldehyde Ethynylation Reaction over Cu2O Supported on TiO2 with Different Phases† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 334. |
| [2] | XIAO Biyuan,QIU Jiangyuan,QIN Fanghong,WAN Ting,XU Yaqun,NONG Xiaohui,HUANG Zaiyin. Study on Particle Size Effect on Adsorption Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Cubic Nano-Cu2O † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2214. |
| [3] | LI Ru, YU Liangmin, YAN Xuefeng, JIANG Tao. Morphology-controlled Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Cu2O/ZnO Microstructures† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(2): 267. |
| [4] | GUO Lanlei, LI Jing, ZHU Yangwen, MA Baodong, XU Zhicheng, WANG Wuning, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Lu. Interaction Forces Between Simulated Mini Liquid Droplets of Emulsions† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(2): 361. |
| [5] | HE Xu, LIU Xiaoqiang, HE Bing, WANG Hanguang, LIU Xudong, TIAN Zhiyue, CHU Wei, XUE Ying. Coalbed Methane Adsorption on Al-, Si-, P- and S-containing Coal Models Predicted by Density Functional Theory† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1786. |
| [6] | JIANG Guangce, LIN Xiongchao, ZHANG Shengjuan, WANG Zhongqi, WANG Yonggang, CHEN Qiang, ZHU Yufei. Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Direct Coal Liquefaction Residue Basing on Hansen Solubility Parameters† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(3): 544. |
| [7] | HE Yitao, WANG Luxiang, JIA Dianzeng, ZHAO Hongyang. Coal-based Carbon Nanofibers Prepared byElectrospinning for Supercapacitor† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(1): 157. |
| [8] | ZOU Zhiming, LI Zhanwei, FU Cuiliu, SUN Zhaoyan, AN Lijia. Arrested Coalescence of Droplets in PBD/PDMS Blends† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(2): 421. |
| [9] | WANG Rong, SHI Zhan-Hua, CAI Fang-Gong, YANG Feng, JIA Yong-Fang, LI Ying, CHENG Cui-Hua, ZHAO Yong. Surface Photovoltage Properties of Deep Level in ZnO/Cu2O Heterojunction Films [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(04): 768. |
| [10] | JIANG Zhi-Liang*, ZHANG Yu-Lan, LIANG Ai-Hui, WEI Li-Li, WANG Su-Mei. Immunonanogold Catalytic-Cu2O Particle Resonance Scattering Spectral Determination of Trace α-Fetoprotein [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(6): 1109. |
| [11] | LI Zhong*, WEN Chun-Mei, WANG Rui-Yu, ZHENG Hua-Yan, XIE Ke-Chang. Chloride-free Cu2O/AC Catalyst Prepared by Pyrolysis of Copper Acetate and Catalytic Oxycarbonylation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(10): 2024. |
| [12] | LIN Yi1, CAI Wen-Sheng1,2*, SHAO Xue-Guang2. Improved Tight-binding Monte Carlo Method and Its Application in Carbon Nanopeapod [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(9): 1751. |
| [13] | XU Ling, ZHU Guang-Shan, CHU Bin, SHI Chun-Feng, GAN Mei-Na, XIE Ya-Ru, SHEN Qi-Hui, WANG Run-Wei, QIU Shi-Lun. Synthesis and Characterization of a New Type of Mesoporous SAPO [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2005, 26(9): 1585. |
| [14] | QIU Jin, YANG Ru, JIANG Nan, LI Min. Synthesis of High Ordered SiO2 Microwires with Bamboo Charcoals as the Template [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2005, 26(6): 1010. |
| [15] | LI Dong Tao, LI Wen, SUN Qing Lei, LI Bao Qing . A Study on Hydrogen Bond in Coal Macerals with In situ Diffuse Reflectance FTIR by Using a New Experimental Method [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2003, 24(4): 703. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||