

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (9): 2105.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170823
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles
ZHANG Rongrong1, YUAN Guangming1,2, LUO Weihua1,2,*( )
)
Received:2017-12-15
Online:2018-09-07
Published:2018-06-26
Contact:
LUO Weihua
E-mail:lwh6803@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHANG Rongrong,YUAN Guangming,LUO Weihua. Synthesis, Characterization and Gas Adsorption Properties of Hypercrosslinked Polymers Based on Carbazoles Containing Aldehyde or Ketone Groups†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2105.
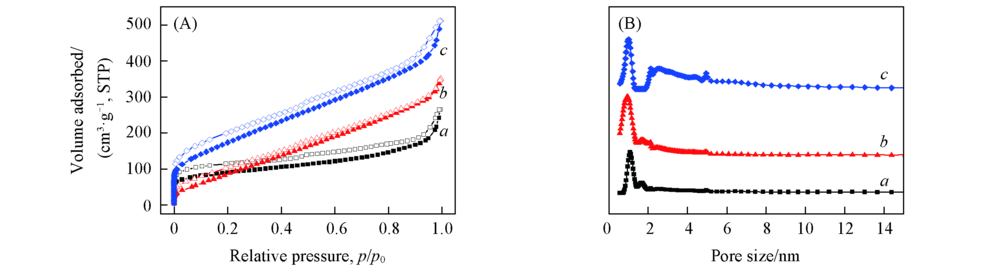
Fig.6 Nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms of HPP-2(a), HPP-3(b) and HPP-4(c) measured at 77 K(A) and the PSD profiles of HPP-2(a), HPP-3(b) and HPP-4(c) calculated by NLDFT(B)The adsorption and desorption branches are labeled with solid and open symbols, respectively.
| Polymer | CO2 uptakee(%) | CH4 uptakee(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPP-2 | 330 | 200 | 0.21 | 0.98 | 6.90 | 1.10 |
| HPP-3 | 420 | 250 | 0.39 | 0.96 | 8.30 | 1.30 |
| HPP-4 | 660 | 470 | 0.68 | 1.07 | 9.80 | 1.60 |
Table 1 Porosity properties and gas uptake capacities of polymers HPP-2—HPP-4
| Polymer | CO2 uptakee(%) | CH4 uptakee(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPP-2 | 330 | 200 | 0.21 | 0.98 | 6.90 | 1.10 |
| HPP-3 | 420 | 250 | 0.39 | 0.96 | 8.30 | 1.30 |
| HPP-4 | 660 | 470 | 0.68 | 1.07 | 9.80 | 1.60 |
| [1] | Zhou Y. M., Kong X. Z., Han H., Jiang X. B., Zhu X. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(3), 495—502 |
| (周亚梅, 孔祥正, 韩慧, 姜绪宝, 朱晓丽. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(3), 495—502) | |
| [2] | Xu S., Luo Y., Tan B., Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2013, 34(6), 471—484 |
| [3] | Guan Y. W., Ben T., Zhang D. L., Xu J., Pei C. Y., Zhu L. K., Lu C. J., Meng F. X., Deng F., Qiu S. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(10), 2152—2157 |
| (关有为, 贲腾, 张大梁, 徐君, 裴翠颖, 朱良奎, 逯春晶, 孟凡星, 邓风, 裘式纶. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(10), 2152—2157) | |
| [4] | Wood C. D., Tan B., Trewin A., Niu H., Bradshaw D., Rosseinsky M. J., Khimyak Y. Z., Campbell N. L., Kirk R., Stöckel E., Cooper A. I., Chem. Mater., 2007, 19(8), 2034—2048 |
| [5] | Tsyurupa M. P., Davankov V. A., React. Funct. Polym., 2006, 66(7), 768—779 |
| [6] | Sidorov S. N., Bronstein L. M., Davankov V. A., Tsyurupa M. P., Solodovnikov S. P., Valetsky P. M., Chem. Mater., 1999, 11(11), 3210—3215 |
| [7] | Molla R. A., Bhanja P., Ghosh K., Islam S. S., Bhaumik A., Islam S. M., Chem. Cat. Chem., 2017, 9(11), 1939—1946 |
| [8] | Mane S., Ponrathnam S., Chavan N., Ind. Eng. Chem.Res., 2015, 54(27), 6893—6901 |
| [9] | Geetanjali, Singh R., Chauhan S. M. S., J. Braz. Chem. Soc., 2006, 17(2), 421—425 |
| [10] | Fan S. H., Yang J., Wei T., Zhang J., Zhang N., Chai M. Q., Jin X. Y., Wu H., Talanta, 2016, 160, 713—720 |
| [11] | Luo Y., Li B., Wang W., Wu K., Tan B., Adv. Mater., 2012, 24(42), 5703—5707 |
| [12] | Zhi Y. F., Li K., Xia H., Xue M., Mu Y., Liu X. M., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(18), 8697—8704 |
| [13] | Wang W. J., Zhou M., Yuan D. Q., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(4), 1334—1347 |
| [14] | Zhu J. H., Chen Q., Sui Z. Y., Pan L., Yu J., Han B. H., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2(38), 16181—16189 |
| [15] | Li Z.P., Li H., Xia H., Chem. Eur. J., 2015, 21(48), 17355—17362 |
| [16] | Zhu X., Ding S., Abney C. W., Browning K. L., Sacci R. L., Veith G. M., Tian C. C., Dai S., Chem. Commun., 2017, 53(54), 7645—7648 |
| [17] | Tan L. X., Tan B. E., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46(11), 3322—3356 |
| [18] | Das S., Heasman P., Ben T., Qiu S.L., Chem. Rev., 2017, 117(3), 1515—1563 |
| [19] | Luo Y., Zhang S., Ma Y., Wang W., Tan B., Polym. Chem., 2013, 4(4), 1126—1131 |
| [20] | Pan L., Chen Q., Zhu J. H., Yu J. G., He Y. J., Han B. H., Polym. Chem., 2015, 6(13), 2478—2487 |
| [21] | Liu H., Li S., Yang H. Y., Liu S. H., Chen L. Y., Tang Z. W., Fu R. W., Wu D. C., Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(27), 1700723 |
| [22] | Chen Q., Luo M., Hammershoj P., Zhou D., Han Y., Laursen B. W., Yan C. G., Han B. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(14), 6084—6087 |
| [23] | Cao Q., Chen Q., Han B. H., Acta Chim. Sinica, 2015, 73(6), 541—556 |
| [24] | Chen Q., Liu D. P., Luo M., Feng L. J., Zhao Y. C., Han B. H., Small, 2014, 10(2), 308—315 |
| [25] | Chen Q., Liu D. P., Zhu J. H., Han B. H., Macromolecules, 2014, 47(17), 5926—5931 |
| [26] | Luo J., Zhang X., Zhang J., ACS Catal., 2015, 5(4), 2250—2254 |
| [27] | Pan L., Xu M. Y., Feng L. J., Chen Q., He Y. J., Han B. H., Polym. Chem., 2016, 7(12), 2299—2307 |
| [28] | Feng L. J., Chen Q., Zhu J. H., Liu D. P., Zhao Y. C., Han B. H., Polym. Chem., 2014, 5(8), 3081—3088 |
| [29] | Liu J., Chen Q., Sun Y. N., Xu M. Y., Liu W., Han B. H., RSC Adv., 2016, 6(54), 48543—48549 |
| [30] | Su C. L., Tandiana R., Tian B. B., Sengupta A., Tang W., Su J., Loh K. P., ACS Catal., 2016, 6(6), 3594—3599 |
| [31] | Bheemireddy S. R., Hautzinger M. P., Li T., Lee B., Plunkett K. N., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(16), 5801—5807 |
| [32] | Liu J., Liu Y. F., Jiang X. W., Luo Y. L., Lyu Y. O., Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2017, 250, 203—209 |
| [33] | Yang X., Yu M., Zhao Y., Zhang C., Wang X., Jiang J.X., RSC Advance, 2014, 4(105), 61051—61055 |
| [1] | ZHANG Chi, SUN Fuxing, ZHU Guangshan. Synthesis, N2 Adsorption and Mixed-matrix Membrane Performance of Bimetal Isostructural CAU-21 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210578. |
| [2] | WANG Longjie, FAN Hongchuan, QIN Yu, CAO Qiue, ZHENG Liyan. Research Progress of Metal-organic Frameworks in the Field of Chemical Separation and Analysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1167. |
| [3] | ZHANG Danwei, WANG Hui, LI Zhanting. Water-soluble Regular Three-dimensional Supramolecular and Covalent Organic Polymers † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1139. |
| [4] | LIN Weiguo,SUN Weihang,QU Zongkai,FENG Xiaolei,RONG Junfeng,CHEN Xu,YANG Wensheng. Preparation and Performance of Nano-porous Si/Graphite/C Composite Microspheres as Anode Material for Li-ion Batteries† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1216. |
| [5] | YAN Tingting,XING Guolong,BEN Teng,QIU Shilun. Influence of Building Blocks on Gas Adsorption Performance of Porous Aromatic Frameworks† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5): 1072. |
| [6] | LIU Xuewu,CHEN Shuhua,ZHAN Shiping. Experimental Study and Theoretical Phase Diagram Calculation for Polystyrene Membranes Prepared by Supercritical CO2-induced Phase Inversion† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(8): 1573. |
| [7] | CHEN Siru, XUE Ming, PAN Ying, XU Dan, QIU Shilun. Synthesis, Characterization and Gas Adsorption Properties of Two New Porous Metal-organic Gels† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(5): 815. |
| [8] | LIU Jiu-Gui, JIANG Li-Zhong, ZHAN Jia-Yu, WU De-Zhen, JIN Ri-Guang. Preparation, Structure and Properties of Porous Polyimide Films via PAA/PU Alloy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(1): 178. |
| [9] | WANG Shu-Mei, GAO Guang-Hua, YU Yang-Xin, WANG Xiao-Lin. Molecular Simulation of Equilibrium Adsorption of Nitrogen and Oxygen both in Slit Pore and on Membrane Surface [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2005, 26(11): 2113. |
| [10] | DU Zhong-Jie, ZHANG Chen, LI Hang-Quan . Preparation of Polystyrene/Divinylbenzene Porous Materials via Reverse Concentrated Emulsion Pathway [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2002, 23(8): 1614. |
| [11] | PENG Qi-Jun, XU Ling, SUN Pei-Dong, YANG Li, QIAN Yong . The Dynamic Simulation of Chromatographic Separation of Citric Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2001, 22(3): 385. |
| [12] | DAI Min-Guang, YANG Su, JIANG Mao-Xiu. Studies on Binary Gas Solid Adsorption(Ⅲ)──Acetone-n-hexane,Toluene-n-hexane,Benzene-n-hexane,n-Pentane-n-hexane Adsorption on Silylanization Silica Gel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1996, 17(2): 202. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||