

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 558.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170602
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Chenghuan, TAN Yinle, GUO Zhaoxia*( ), YU Jian*(
), YU Jian*( )
)
Received:2017-09-06
Online:2018-03-10
Published:2017-12-13
Contact:
GUO Zhaoxia,YU Jian
E-mail:guozx@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn;yujian03@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HUANG Chenghuan, TAN Yinle, GUO Zhaoxia, YU Jian. Diffusion and Polymerization Behavior of Styrene in Polyethylene Pellets of Different Molecular Structures†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(3): 558.
| PE | Tm/℃ | ΔHm/(J·g-1) | Xc(%) | Tc/℃ | ΔHc/(J·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE | 129.3 | 169.4 | 62.7 | 115.0 | 156.2 |
| LDPE | 107.7 | 88.1 | 32.6 | 92.8 | 80.6 |
| LLDPE | 126.9 | 145.5 | 53.9 | 112.7 | 140.3 |
Table 1 Measurement of the crystallinity of different PEs
| PE | Tm/℃ | ΔHm/(J·g-1) | Xc(%) | Tc/℃ | ΔHc/(J·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE | 129.3 | 169.4 | 62.7 | 115.0 | 156.2 |
| LDPE | 107.7 | 88.1 | 32.6 | 92.8 | 80.6 |
| LLDPE | 126.9 | 145.5 | 53.9 | 112.7 | 140.3 |
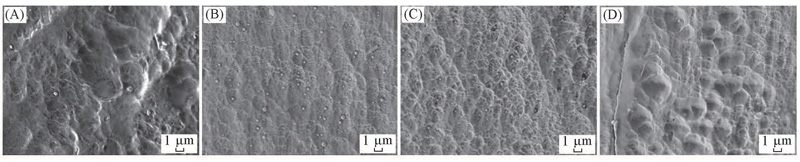
Fig.2 FESEM images of the cross-section of HDPE and HDPE/PS nanoalloy pellets(A) HDPE; (B) surface of HDPE/PS; (C) mid-depth from the surface to the center of HDPE/PS; (D) center of HDPE/PS.
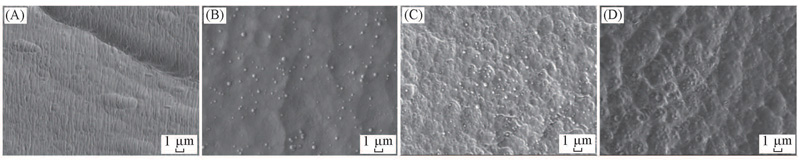
Fig.3 FESEM images of the cross-section of LDPE(A) and LDPE/PS(B—D) nanoalloy pellets(A) LDPE; (B) surface of LDPE/PS; (C) mid-depth from the surface to the center of LDPE/PS; (D) center of LDPE/PS.
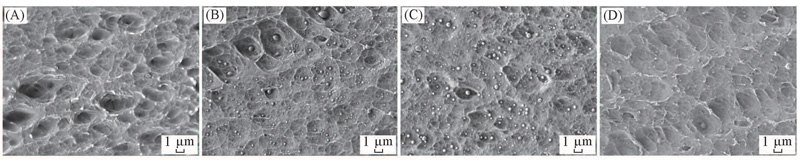
Fig.4 FESEM images of the cross-section of LLDPE and LLDPE/PS nanoalloy pellets(A) LLDPE; (B) surface of LLDPE/PS; (C) mid-depth from the surface to the center of LLDPE/PS; (D) center of LLDPE/PS.
| PE/PS | PS content(%) | Graft ratio(%) | Peak area ratio of PS/PE |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE/PS | 16.0 | 1.20 | 0.03 |
| LDPE/PS | 19.3 | 5.63 | 0.14 |
| LLDPE/PS | 18.1 | 4.85 | 0.12 |
Table 2 Graft ratio and peak area ratio of PE/PS nanoblends
| PE/PS | PS content(%) | Graft ratio(%) | Peak area ratio of PS/PE |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE/PS | 16.0 | 1.20 | 0.03 |
| LDPE/PS | 19.3 | 5.63 | 0.14 |
| LLDPE/PS | 18.1 | 4.85 | 0.12 |
| System | Young’s modulus/MPa | Tensile strength/MPa | Elongation at break(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE | 1006.3±65.3 | 21.3±0.5 | 29.0±4.0 |
| HDPE/PS | 1134.1±38.4 | 24.6±0.3 | 54.1±0.3 |
| LDPE | 140.9±2.6 | 10.2±0.2 | 113.1±3.9 |
| LDPE/PS | 205.6±3.8 | 11.5±0.1 | 106.7±2.5 |
| LLDPE | 334.9±6.4 | 16.3±0.4 | 450.1±7.7 |
| LLDPE/PS | 434.7±14.1 | 18.5±0.3 | 454.5±0.1 |
Table 3 Mechanical properties of PE and PE/PS injection-molded bar
| System | Young’s modulus/MPa | Tensile strength/MPa | Elongation at break(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE | 1006.3±65.3 | 21.3±0.5 | 29.0±4.0 |
| HDPE/PS | 1134.1±38.4 | 24.6±0.3 | 54.1±0.3 |
| LDPE | 140.9±2.6 | 10.2±0.2 | 113.1±3.9 |
| LDPE/PS | 205.6±3.8 | 11.5±0.1 | 106.7±2.5 |
| LLDPE | 334.9±6.4 | 16.3±0.4 | 450.1±7.7 |
| LLDPE/PS | 434.7±14.1 | 18.5±0.3 | 454.5±0.1 |
| [1] | Xing Z., Wang M. H., Du G. H., Xiao T. Q., Liu W. H., Dou Q., Wu G. Z., J. Supercrit. Fluids, 2013, 82, 50—55 |
| [2] | Xu S. A., Tjong S. C., Polym. J., 2000, 32(3), 208—214 |
| [3] | Wu L. Y., Zhu J. J., Liao X., Ni K., Zhang Q. W., An Z., Yang Q., Li G. X., Polym. Int., 2015, 64(7), 892—899 |
| [4] | Kim T. Y., Kim D. M., Kim W. J., Lee T. H., Suh K. S., J. Polym. Sci. B: Polym. Phys., 2004, 42(15), 2813—2820 |
| [5] | Aghjeh M. K. R., Khodabandelou M., Khezrefaridi M., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2009, 114(4), 2235—2245 |
| [6] | Bureau M. N., El Kadi H., Denault J., Dickson J. I., Polym. Eng. Sci., 1997, 37(2), 377—390 |
| [7] | Stary Z., Fortelny I., Krulis Z., Slouf M., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2008, 107(1), 174—186 |
| [8] | George T. S., Krishnan A., Joseph N., Anjana R., George K. E., Polym. Compos., 2012, 33(9), 1465—1472 |
| [9] | Fortelny I., Michalkova D., Hromadkova J., Lednicky F., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2001, 81(3), 570—580 |
| [10] | Fortelny I., Mikesova J., Hromadkova J., Hasova V., Horak Z., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2003, 90(9), 2303—2309 |
| [11] | Fortelny I., Slouf M., Hlavata D., Sikora A., Compos. Interfaces, 2006, 13(8/9), 783—799 |
| [12] | Michalkova D., Pospisil J., Fortelny I., Slouf M., Krulis Z., J. Vinyl Addit. Technol., 2006, 12(2), 58—65 |
| [13] | Fortelny I., Slouf M., Sikora A., Hlavata D., Hasova V., Mikesova J., Jacob C., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2006, 100(4), 2803—2816 |
| [14] | Stary Z., Krulis Z., Hromadkova J., Slouf M., Kotek J., Fortelny I., Int. Polym. Process., 2006, 21(3), 222—229 |
| [15] | Xie H. Q., Liu D. G., Xie D., Guan J. G., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2006, 99(4), 1887—1894 |
| [16] | Michalkova D., Pospisil J., Fortelny I., Hromadkova J., Lednicky F., Schmidt P., Krulis Z., Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2009, 94(9), 1486—1493 |
| [17] | Chirawithayaboon A., Kiatkamjornwong S., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2004, 91(2), 742—755 |
| [18] | Bartczak Z., Galeski A., Pluta M., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2000, 76(12), 1746—1761 |
| [19] | Chan S. H., Lin Y. Y., Ting C., Macromolecules, 2003, 36(24), 8910—8912 |
| [20] | Lebovitz A. H., Khait K., Torkelson J. M., Polymer, 2003, 44(1), 199—206 |
| [21] | Lebovitz A. H., Khait K., Torkelson J. M., Macromolecules, 2002, 35(23), 8672—8675 |
| [22] | Furgiuele N., Lebovitz A. H., Khait K., Torkelson J. M., Macromolecules, 2000, 33(2), 225—228 |
| [23] | Watkins J. J., McCarthy T. J., Macromolecules, 1994, 27(17), 4845—4847 |
| [24] | Kung E., Lesser A. J., McCarthy T. J., Macromolecules, 1998, 31(13), 4160—4169 |
| [25] | Yao X. R., Yu J., Guo Z. X., Polymer, 2011, 52(3), 667—675 |
| [26] | Yao X. R., Wang L., Guo Z. X., Yu J., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2013, 127(2), 1092—1097 |
| [27] | Yao X. R., Chen F., Guo Z. X., Yu J., Chin. Chem. Lett., 2012, 23(6), 753—756 |
| [28] | Qiu H. Y., Chen F., Guo Z. X., Yu J., Chin. J. Polym. Sci., 2015, 33(10), 1380—1388 |
| [29] | Chen F., Guo Z. X., Yu J., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2016, 133(37), DOI: 10.1002/app. 43934 |
| [30] | Chen F., Guo Z. X., Yu J., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2016, 133(38), DOI: 10.1002/app. 43983 |
| [31] | Chen F., Guo Z. X., Yu J., Chin. Chem. Lett., 2016, 27(10), 1641—1643 |
| [32] | Wang W. J., Huang C. H., Guo Z. X., Yu J., Chin. J. Polym. Sci., 2017, 35(8), 939—949 |
| [33] | Yao X. R., Guo Z. X., Yu J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(11), 2573—2578 |
| (姚雪容, 郭朝霞, 于建.高等学校化学学报,2012, 33(11), 2573—2578) | |
| [34] | Huang C. H., Chen F., Guo Z. X., Yu J., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2017, 134(10), DOI: 10.1002/app. 44554 |
| [35] | Chen F., Yao X.R., Guo Z. X., Yu J.,Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2016, (12), 1717—1723 |
| (陈放, 姚雪容, 郭朝霞, 于建. 高分子学报, 2016, (12), 1717—1723) | |
| [36] | Kong Y., Hay J. N., Polymer, 2002, 43(14), 3873—3878 |
| [37] | Nunes L. C. S., Dias F. W. R., Mattos H. S. D. C., Polymer Testing, 2011, 30(7), 791—796 |
| [38] | Zhang X. M., Elkoun S., Ajji A., Huneault M. A., Polymer, 2004, 45(1), 217—229 |
| [1] | LI Wei, LUO Piao, HUANG Lianzhan, CUI Zhiming. Lithium Polystyrene Sulfonate Based Interfacial Protective Layer for Lithium Metal Anodes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220166. |
| [2] | JI Fa, LIU Ling, YU Linling, SUN Yan. Effects of Muco-inert and Acid-sensitive Modification on Mucosal Penetration of Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20210837. |
| [3] | ZHAO Sheng, HUO Zhipeng, ZHONG Guoqiang, ZHANG Hong, HU Liqun. Preparation of Modified Gadolinium/Boron/Polyethylene Nanocomposite and Its Radiation Shielding Performance for Neutron and Gamma-ray [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220039. |
| [4] | LIU Qingqing, WANG Pu, WANG Yongshuai, ZHAO Man, DONG Huanli. Synthesis and Topochemical Polymerization Study of Naphthalene/perylene Imides Substituted Diacetylene Derivatives [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220091. |
| [5] | MA Yukun, JIN Hui, REN Chuanli, LI Zhibo. Ring-opening Polymerization of Cyclic Esters Using Recyclable Polystyrene Supported Urea-Base Binary Catalyst [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2968. |
| [6] | ZHANG Wanbin, WANG Yanmeng, WANG Shaowu, TONG Xin, HAN Xiaoqian, ZHANG Ce, ZHANG Guanghua, ZHU Xiuzhong. Synthesis of Poly(allyl glycidyl ether) Bearing Alkyl Functional Side Groups and Its Plasticizing and Antistatic Effects for PVC [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2961. |
| [7] | LI Haibo, XIAO Changfa, JIANG Long, HUANG Yun, DAN Yi. Copolymerization of Methyl Acrylate and 1-Octene Catalyzed by the Loaded Aluminum Chloride on MCM-41 Molecular Sieve [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2974. |
| [8] | LIU Simei, LIU Weihua, LU Manli, ZHANG Wenli, SHEN Rongfang, WANG Mouhua. Evolution of the Radicals in γ-Rays Irradiated Medical Grade Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2602. |
| [9] | LIU Xiaojin, LI Ting, WANG Yang, DONG Weifu. Preparation of Terpolymer Microspheres with Broad Band UV-blocking Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1965. |
| [10] | YANG Lincan, LENG Xuefei, HAN Li, LI Chao, ZHANG Songbo, LEI Lan, MA Hongwei, LI Yang. Synthesis of α,ω⁃End Alkynyl-functionalized Styrene-isoprene-styrene Polymer Based on Di-lithium Method [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 866. |
| [11] | LI Rongye, NI Yunxia, LIU Dandan, LI Zhi, CHENG Yuxin, XIA Mingxin, FU Xiaohui. Synthesis and Characterization of Thermoresponsive Polypeptide/polypeptoid Block Copolymers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 850. |
| [12] | XU Xiaozhou, LIU Yi, HE Minhui, MO Song, LAN Bangwei, ZHAI Lei, FAN Lin. Effect of Copolymerization Structure and Molecular Weight on Melt Fluidity and Thermal Properties of Thermoplastic Polyimide Resins [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 919. |
| [13] | DU Xinyao, WANG Wei, LIN Yu, WU Guozhang. Synthesis and Optical Properties of Polycarbonates Copolymerized with Bisphenol Fluorene Moiety [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3765. |
| [14] | KUANG Xiaojun, YI Jingwei, FANG Xiaoxia, LAI Dongmei, XU Hong. Preparation of Water-soluble Coumarin Fluorescent Substrate and Its Application in Droplet Based Digital Detection [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3537. |
| [15] | LI Chen, LI Yuesheng. Living Ring-opening Polymerization of O-Carboxyanhydrides Catalyzed by Pyridine Derivatives [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3203. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||