

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (9): 1678.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170053
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YOU Yanwei, XIAO Changfa*( ), WANG Chun, HUANG Qinglin, CHEN Mingxing, HUANG Yan
), WANG Chun, HUANG Qinglin, CHEN Mingxing, HUANG Yan
Received:2017-01-20
Online:2017-09-10
Published:2017-08-17
Contact:
XIAO Changfa
E-mail:cfxiao@tjpu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YOU Yanwei, XIAO Changfa, WANG Chun, HUANG Qinglin, CHEN Mingxing, HUANG Yan. Preparation and Properties of Poly(tetrafluoroethylene-co-hexafluoropropylene) Hollow Fiber Membranes†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(9): 1678.
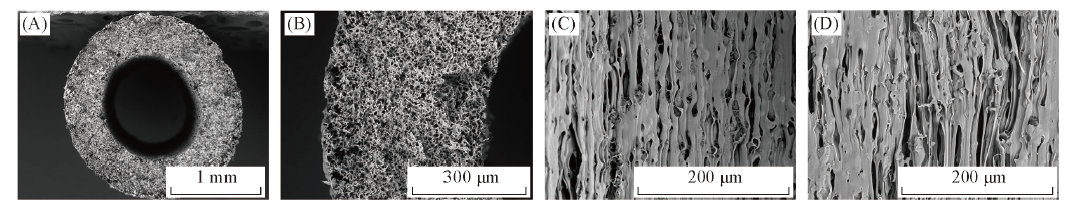
Fig.3 Morphologies of untreated FEP hollow fiber membranes(M0)(A) Cross section; (B) partial enlargement of cross section; (C) inner surface; (D) outer surface.
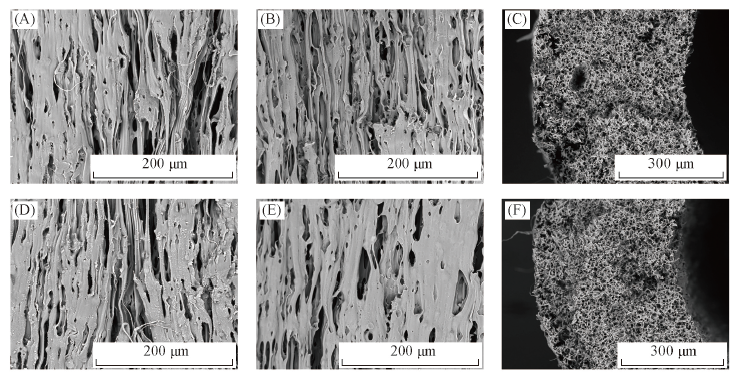
Fig.5 SEM images of FEP hollow fiber membranes immersed by 25% NaOH for 30 d(sample N3, A—C) and 60 d(sample N4, D—F)(A) and (D) Outer surface; (B) and (E) inner surface; (C) and (F) cross section.
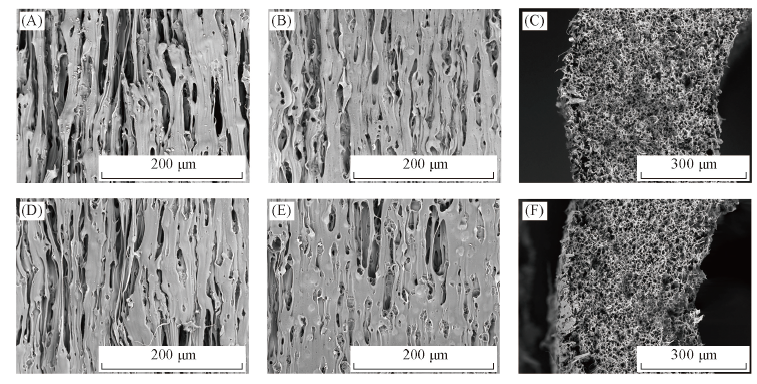
Fig.6 SEM images of FEP hollow fiber membranes immersed in 10%(A—C) and 25%(D—F) H2SO4 for 30 d (A, D) Outer surface; (B, E) inner surface; (C, F) cross section.
| Sample | Pore diametermin/μm | Pore diameteravg/μm |
|---|---|---|
| M0 | 0.3289 | 0.5468 |
| N2 | 0.7896 | 1.0970 |
| N4 | 0.9913 | 1.3591 |
| H2 | 0.8533 | 1.1844 |
| H4 | 1.1164 | 1.5201 |
Table 1 Minimum and average pore diameter of FEP hollow fiber membranes
| Sample | Pore diametermin/μm | Pore diameteravg/μm |
|---|---|---|
| M0 | 0.3289 | 0.5468 |
| N2 | 0.7896 | 1.0970 |
| N4 | 0.9913 | 1.3591 |
| H2 | 0.8533 | 1.1844 |
| H4 | 1.1164 | 1.5201 |
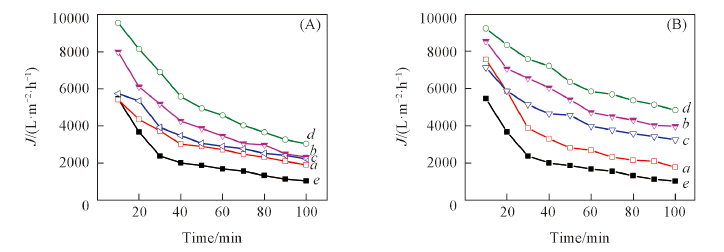
Fig.15 Pure water flux of FEP hollow fiber membranes after NaOH(A)/H2SO4(B) treatment (A) a. N1; b. N2; c. N3; d. N4; e. M0. (B) a. H1; b. H2; c. H3; d. H4; e. M0.
| Sample | Stress/MPa | Strain(%) | Stress retention ratio(%) | Sample | Stress/MPa | Strain(%) | Stress retention ratio(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | 5.01 | 44.5 | 100 | PVDF-0 | 4.98 | 84.3 | 100 |
| N4 | 4.35 | 12.2 | 86.8 | PVDF-H | 3.11 | 30.9 | 62.4 |
| H4 | 4.05 | 12.2 | 80.8 | PVDF-N | 1.9 | |
Table 2 Mechanical properties of hollow fiber membranes
| Sample | Stress/MPa | Strain(%) | Stress retention ratio(%) | Sample | Stress/MPa | Strain(%) | Stress retention ratio(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | 5.01 | 44.5 | 100 | PVDF-0 | 4.98 | 84.3 | 100 |
| N4 | 4.35 | 12.2 | 86.8 | PVDF-H | 3.11 | 30.9 | 62.4 |
| H4 | 4.05 | 12.2 | 80.8 | PVDF-N | 1.9 | |
| [1] | Lloyd D. R., Kinzer K. E., Tseng H. S., Journal of Membrane Science, 1990, 52(3), 239—261 |
| [2] | Zhou L. Z., Wang X., Cheng X. W., Long Y. C., Ping Z. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2005, 26(3), 567—570 |
| (周立志, 王星, 程晓维, 龙英才, 平郑骅.高等学校化学学报,2005, 26(3), 567—570 | |
| [3] | Park S. Y., Chung J. W., Kwak S. Y., Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 491, 1—9 |
| [4] | Ma Y. G., Yang M. L., Lin D. H., Shen J. C., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 1990, 11(11), 1307—1309 |
| [5] | Huang Q. L., Xiao C. F., Hu X. Y., Journal of Materials Science, 2010, 45(24), 6569—6573 |
| [6] | Takagi Y., Lee J. C., Yagi S. I., Yamane H., Wano T., Kitagawa D., El Salmawy A., Polymer,2011, 52(18), 4099—4105 |
| [7] | Zhou T., Yao Y. Y., Xiang R. L., Wu Y. R., Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 453, 402—408 |
| [8] | Huang Y., Huang Q. L., Liu H., Zhang C. X., You Y. W., Li N. N., Xiao C. F., Journal of Membrane Science, 2017, 523, 317—326 |
| [9] | Yang X.S., An S. L.,Tianjin Textile Science & Technology, 2013, (2), 40—42 |
| (杨兴胜, 安树林. 天津纺织科技, 2013, (2), 40—42) | |
| [10] | Miao Z.Q., Xiao C. F., Huang Q. L.,Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2012, (12), 1423—1428 |
| (苗中青, 肖长发, 黄庆林. 高分子学报, 2012, (12), 1423—1428) | |
| [11] | Gupta B., Muzyyan N., Saxena S., Grover N., Alam S., Radiation Physics and Chemistry,2008, 77(1), 42—48 |
| [12] | Park Y. W., Tasaka S., Inagaki N., Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2002, 83(6), 1258—1267 |
| [13] | Danks T. N., Slade R. C. T., Varcoe J. R., Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2002, 12(12), 3371—3373 |
| [14] | Wu Y. J., Huang Q. L., Xiao C. F., Chen K. K., Li X. F., Li N. N., Desalination,2014, 353, 118—124 |
| [15] | Chen K. K., Xiao C. F., Huang Q. L., Liu H., Liu H. L., Wu Y. J., Liu Z., Desalination,2015, 375, 24—32 |
| [16] | Wu Y. J., Xiao C. F., Huang Q. L., Chen K. K., Chinese Journal of Materials Research,2014, 28(5), 353—361 |
| (吴艳杰, 肖长发, 黄庆林, 陈凯凯.材料研究学报,2014, 28(5), 353—361) | |
| [17] | Jiang Z. H., Guo Z. G., Jia Z., Xiao C. F., An S. L., e-Polymers,2016, 16(2), 171—176 |
| [18] | Huang Q. L., Xiao C. F., Hu X. Y., Li X. F., Desalination,2011, 277(1), 187—192 |
| [19] | Nasef M. M., Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2000, 68(2), 231—238 |
| [20] | Singh N., Husson S. M., Zdyrko B. Luzinov I., Journal of Membrane Science, 2005, 262(1), 81—90 |
| [21] | Zhao W. K., Zhou L., Liu C., Hu L., Fang Y. L., Masato K., Acta Chimica Sinica, 2003, 61(5), 699—704 |
| (赵文宽, 周磊, 刘昌, 胡翎, 方佑龄, 木内正人, 化学学报, 2003, 61(5), 699—704) | |
| [22] | Liu C. S., Jiang W. Q., Guan Z. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(5), 1175—1180 |
| (刘传生, 蒋文曲, 管自生.高等学校化学学报,2011, 32(5), 1175—1180) | |
| [23] | Zhang H.F., Huang Q. L., Xiao C. F., Liu H. L., Chen K. K., Wang C.,Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2015, (9), 1078—1084 |
| (张海芬, 黄庆林, 肖长发, 刘海亮, 陈凯凯, 王纯. 高分子学报, 2015, (9), 1078—1084) | |
| [24] | Li H. J., Cao Y. M., Yang L. S., Yuan Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2005, 26(10), 1890—1895 |
| (李红剑, 曹义鸣, 杨林松, 袁权.高等学校化学学报,2005, 26(10), 1890—1895) | |
| [25] | Wang X. L., Pan X. H., Zhang Y. P., China Water and Wastewater,2013, 29(17), 89—92 |
| (王旭亮, 潘献辉, 张艳萍.中国给水排水,2013, 29(17), 89—92) |
| [1] | GAO Yifei, XIAO Changfa, JI Dawei, HUANG Yangzheng. Preparation of PVDF Hollow Fiber Membranes via Melt Spinning-stretching Method and Its Oil-water Separation Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2065. |
| [2] | HAN Na, LI Huihui, LI Chuanbao, ZHANG Xingxiang, LI Wei, WANG Dong. Synthesis and Properties of Melt Processable Acrylonitrile-N-vinylimidazole Copolymers and Fiber† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 2073. |
| [3] | PEI Cui-Ying, QU Feng-Yu*. Preparation and Characterization of Hydroxyl Functional Compound with Covalent Organic Framework [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(6): 1234. |
| [4] | LIU Yu-Hai, LI Hui-Zhen, LIU Xi, HU Li-Ping, YANG Zhan-Lan, XU Yi-Zhuang, .... Rheological Behavior of Isotactic Polypropylene(iPP) Melts in Supercooling State [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(8): 1671. |
| [5] | LI Yong-Guo, LIU Hong, WANG Zheng-Tao, HU Zhi-Bi. Multi-components Comprehensive Evaluation on Chemical Stability of Fermented Red Yeast Rice [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(1): 35. |
| [6] | YANG Jia-Zhen, JIN Yi, CAO Ying-Hua, SUN Li-Xian, TAN Zhi-Cheng . Studies on Electrochemical Stability of Room Temperature Ionic Liquids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(9): 1733. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||