

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (9): 1701.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170015
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles
WU Jing1, GUO Jing1,2,*( ), ZHANG Sen1,2, GONG Yumei1,2, ZHANG Hong1,2
), ZHANG Sen1,2, GONG Yumei1,2, ZHANG Hong1,2
Received:2017-01-05
Online:2017-09-10
Published:2017-05-19
Contact:
GUO Jing
E-mail:guojing8161@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WU Jing, GUO Jing, ZHANG Sen, GONG Yumei, ZHANG Hong. Correlativity of Characterization for Sodium Alginate/Antarctic Krill Protein by Salt Concentration†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(9): 1701.
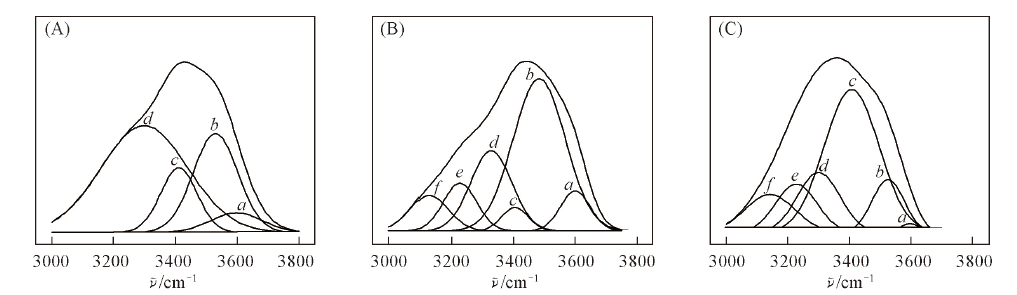
Fig.6 Gauss fitting of SA(A) and SA/AKP[c(NaCl)=0(B), 1 g/L(C)] composite fiber a. —OH; b. OH…π; c. OH…OH; d. OH…O(etheric); e. OH annular polymer; f. OH…N.
| Sample | Hydrogen bond type | Peak area | Proportion(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium alginate | Free hydroxyl | —OH | 3598 | 7.34 | 5.8 |
| Intermolecular hydrogen bonds | OH…π | 3530 | 33.09 | 26.1 | |
| OH…O(etheric) | 3300 | 68.75 | 54.2 | ||
| SA/AKP composite fiber | Intramolecular hydrogen bonds | OH…OH | 3411 | 17.62 | 13.9 |
| without salt | Free hydroxyl | —OH | 3600 | 10.22 | 7.5 |
| Intermolecular hydrogen bonds | OH…π | 3484 | 68.09 | 49.7 | |
| OH…O(etheric) | 3328 | 28.29 | 20.6 | ||
| OH…N | 3129 | 11.46 | 8.4 | ||
| Salt concentration of 2 g/L | Intramolecular hydrogen bonds | OH…OH | 3406 | 5.35 | 3.9 |
| SA/APK composite fiber | OH cyclic polymer | 3228 | 13.66 | 9.9 | |
| Free hydroxyl | —OH | 3597 | 12.14 | 1.2 | |
| Intermolecular hydrogen bonds | OH…π | 3526 | 106.28 | 10.5 | |
| OH…O(etheric) | 3300 | 160.36 | 15.8 | ||
| OH…N | 3143 | 121.24 | 11.9 | ||
| Intramolecular hydrogen bonds | OH…OH | 3408 | 488.72 | 48.1 | |
| OH cyclic polymer | 3228 | 126.41 | 12.5 | ||
Table 1 Fitting results of various hydrogen bond types
| Sample | Hydrogen bond type | Peak area | Proportion(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium alginate | Free hydroxyl | —OH | 3598 | 7.34 | 5.8 |
| Intermolecular hydrogen bonds | OH…π | 3530 | 33.09 | 26.1 | |
| OH…O(etheric) | 3300 | 68.75 | 54.2 | ||
| SA/AKP composite fiber | Intramolecular hydrogen bonds | OH…OH | 3411 | 17.62 | 13.9 |
| without salt | Free hydroxyl | —OH | 3600 | 10.22 | 7.5 |
| Intermolecular hydrogen bonds | OH…π | 3484 | 68.09 | 49.7 | |
| OH…O(etheric) | 3328 | 28.29 | 20.6 | ||
| OH…N | 3129 | 11.46 | 8.4 | ||
| Salt concentration of 2 g/L | Intramolecular hydrogen bonds | OH…OH | 3406 | 5.35 | 3.9 |
| SA/APK composite fiber | OH cyclic polymer | 3228 | 13.66 | 9.9 | |
| Free hydroxyl | —OH | 3597 | 12.14 | 1.2 | |
| Intermolecular hydrogen bonds | OH…π | 3526 | 106.28 | 10.5 | |
| OH…O(etheric) | 3300 | 160.36 | 15.8 | ||
| OH…N | 3143 | 121.24 | 11.9 | ||
| Intramolecular hydrogen bonds | OH…OH | 3408 | 488.72 | 48.1 | |
| OH cyclic polymer | 3228 | 126.41 | 12.5 | ||
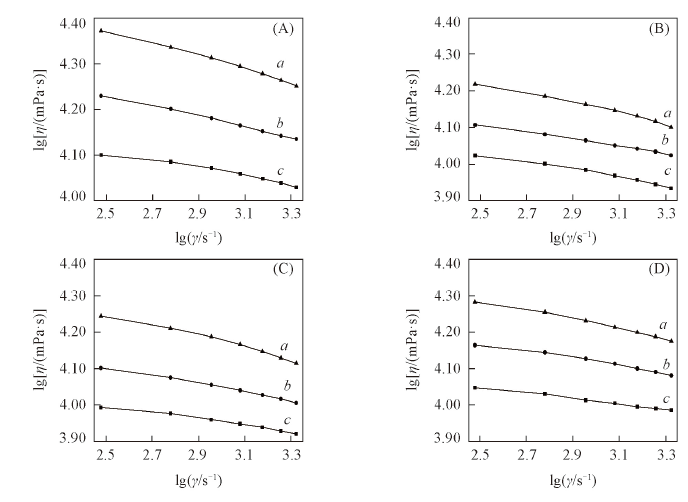
Fig.7 Curves of shear rate and viscosity of SA/APK composite material with different salt concentrations c(NaCl)/(g·L-1): (A) 0; (B) 1; (C) 2; (D) 3. a. 30 ℃; b. 40 ℃; c. 50 ℃.
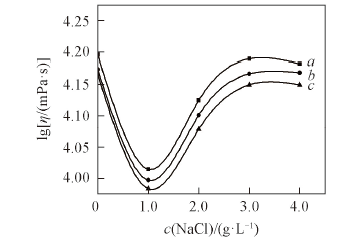
Fig.9 Relationship between salt concentration and viscosity SA/APK composite material with different shear ratesShear rate/s-1: a. 1200; b. 1800; c. 2400.
| [1] | Dangelico R. M., Pontrandolfo P., Pujari D., Journal of Product Innovation Management,2013, 30(4), 642—658 |
| [2] | Zhao X. H., Li Q., Ma X. M., Xiong Z., Quan F. Y., Xia Y. Z., RSC Advances, 2015, 5(61), 49534—49540 |
| [3] | Bendtsen S. T., Wei M., Journal of Materials Chemistry B,2015, 3(15), 3081—3090 |
| [4] | Khan F., Ahmad S. R., Macromolecular Bioscience, 2013, 13(4), 395—421 |
| [5] | Pannier A. K., Soltmann U., Soltmann B., Altenburger R., Schmitt-Jansen M., Journal of Materials Chemistry B,2014, 2(45), 7896—7909 |
| [6] | Ahn S. Y., Mun C. H., Lee S. H., RSC Advances, 2015, 5(20), 15172—15181 |
| [7] | Gigliotti J. C., Davenport M. P., Beamer S. K., Tou J. C., Jaczynski J., Food Chemistry, 2011, 125(3), 1028—1036 |
| [8] | Liu Q., Huang H. L., Li M. N., Wang Q., Zhou D. Y., Ru W., Chinese Journal of Polar Research,2015, 27(1), 31—37 |
| (刘勤, 黄洪亮, 李励年, 王茜, 周雨思, 阮雯.极地研究,2015, 27(1), 31—37) | |
| [9] | Bax M. L., Aubry L., Ferreira C., Daudin J. D., Gatellier P., Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry ,2012, 60(10), 2569—2576 |
| [10] | Feng D. N., Yuan Y., Su X. F., Zhu X. L., Wang Y. H., Food Research and Development,2015, 36(8), 5—7 |
| (冯迪娜, 袁玥, 苏学锋, 朱晓丽, 王元好.食品研究与开发,2015, 36(8), 5—7) | |
| [11] | Yang L. J., Guo J., Liu M. Z., Zhang S., Guan F. C., Mou S. Y., Qi S. W., Li S. L., Journal of Functional Materials, 2016, 47(2), 2084—2088 |
| (杨利军, 郭静, 刘孟竹, 张森, 管福成, 牟思阳, 齐善威, 李圣林.功能材料,2016, 47(2), 2084—2088) | |
| [12] | Yang L. J., Guo J., Li S. L., Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2016, 33(7), 1524—1530 |
| (杨利军, 郭静, 李圣林.复合材料学报,2016, 33(7), 1524—1530) | |
| [13] | Yang L. J., Guo J., Yu Y., An Q. D., Wang L. Y., Li S. L., Huang X. L., Mu S. Y., Qi S. W., Carbohydrate Polymers, 2016, 142, 275—281 |
| [14] | Park M., Lee D., Hyun J., Carbohydrate Polymers, 2015, 116, 223—228 |
| [15] | Shen W., Hsieh L. Y., Carbohydrate Polymers, 2014, 102(1), 893—900 |
| [16] | Li J., Journal of Jinzhong University, 2011, 28(3), 30—32 |
| (李军.晋中学院学报,2011, 28(3), 30—32 | |
| [17] | Khalifa M., Mahendran A., Anandhan S., RSC Advances, 2016, 6, 114052—114060 |
| [18] | Lan A., Li X. D., Tang J. W., Zhang Y., Yu M. H., Journal of Donghua University (Natural Science), 2016, 42(1), 18—23 |
| (兰嫒, 李欣达, 唐静文, 张玥, 余木火.东华大学学报自然科学版,2016, 42(1), 18—23) | |
| [19] | Li X. D., Lan A., Tang J. W., Yang Y. P., He X. Y., Lu S. Y., Zhang Y., Yu M. H., Journal of Materials Science & Engineering,2015, 33(4), 474—478 |
| (李欣达, 兰嫒, 唐静文, 杨燕平, 何小云, 陆帅羽, 张玥, 余木火.材料科学与工程学报,2015, 33(4), 474—478) |
| [1] | CHANG Sihui, CHEN Tao, ZHAO Liming, QIU Yongjun. Thermal Degradation Mechanism of Bio-based Polybutylactam Plasticized by Ionic Liquids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220353. |
| [2] | LIU Simei, LIU Weihua, LU Manli, ZHANG Wenli, SHEN Rongfang, WANG Mouhua. Evolution of the Radicals in γ-Rays Irradiated Medical Grade Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2602. |
| [3] | LIU Xiaojin, LI Ting, WANG Yang, DONG Weifu. Preparation of Terpolymer Microspheres with Broad Band UV-blocking Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1965. |
| [4] | LI Rongye, NI Yunxia, LIU Dandan, LI Zhi, CHENG Yuxin, XIA Mingxin, FU Xiaohui. Synthesis and Characterization of Thermoresponsive Polypeptide/polypeptoid Block Copolymers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 850. |
| [5] | GAO Naiwei, MA Qiang, HE Yonglin, WANG Yapei. Green Electronic Devices Based on Ionic Liquids † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 901. |
| [6] | Minwen JIANG,Chenhui YIN,Sheng LI,Xiaoli LI. Synthesis of DOPO-based Cyclotriphosphazene Macromolecule Flame Retardant and Its Performance in Flame-retarded Epoxy Resin † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2615. |
| [7] | MENG Xiufeng,ZHAI Zhiwei,GUO Aijun. Self-assembled Monolayers for Controllable Adhesion of DOPA† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2245. |
| [8] | YAN Huiqiong, CHEN Xiuqiong, LI Jiacheng, FENG Yuhong, WU Jianbo, LIN Qiang, SHI Zaifeng, WANG Xianghui. Synthesis of Amidic Alginate Derivatives Modified Silica Nanoparticles via Ugi Multicomponent Reaction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5): 1018. |
| [9] | LIU Yajie, ZHANG Peng, DU Jianwei, WANG Youxiang. pH-Responsive PEGylated Gene Delivery System† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5): 1003. |
| [10] | CHENG Yong, LI Xiaohu, LIU Weihua, WU Guozhong, WANG Mouhua. Decay of Free Radicals in Polycarbosilane Induced by γ-Rays Irradiation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(3): 595. |
| [11] | MA Lili, SHAO Jun, YANG Chenguang, TANG Zhaohui, CHEN Xuesi. Synthesis and Property of PDLA-PBS-PDLA Tri-block Copolymer† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(11): 2329. |
| [12] | WANG Jingyun, Fu Xue, BAO Yongming. Cationization of Inulin via Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization for Gene Delivery† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(10): 2124. |
| [13] | KONG Yunna, LI Wenyu, DU Jianwei, TANG Jianguo, HU Qiaoling, WANG Youxiang. Stimulus-responsive Diselenide-crosslinked Polyethyleneimine as Gene Vector† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(4): 881. |
| [14] | YAN Hui-Qiong, LI Jia-Cheng, FENG Yu-Hong, HU Wen-Tao, LIU Ruo-Lin, LIN Qiang. Stability and Release Properties of Drug-loaded Pickering Emulsions by the Modified Sodium Alginate Activated SiO2 Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(9): 2164. |
| [15] | REN Yuan-Lin, XIN Peng-Yue, SU Qian, CHENG Bo-Wen. Preparation and Properties of Halogen-free Fire Retardant Acrylonitrile Copolymer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(9): 2216. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||