

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (6): 966.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160878
• Special Articles of China International Conference on Electrospinning(CICE 2016) • Previous Articles Next Articles
SONG Qingsong, ZHANG Jingnan, LIU Yong*( )
)
Received:2016-12-05
Online:2017-06-10
Published:2017-04-26
Contact:
LIU Yong
E-mail:yongsd@iccas.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
SONG Qingsong, ZHANG Jingnan, LIU Yong. Mesoscale Simulation of a Melt Electrospinning Jet in a Periodically Changing Electric Field[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(6): 966.
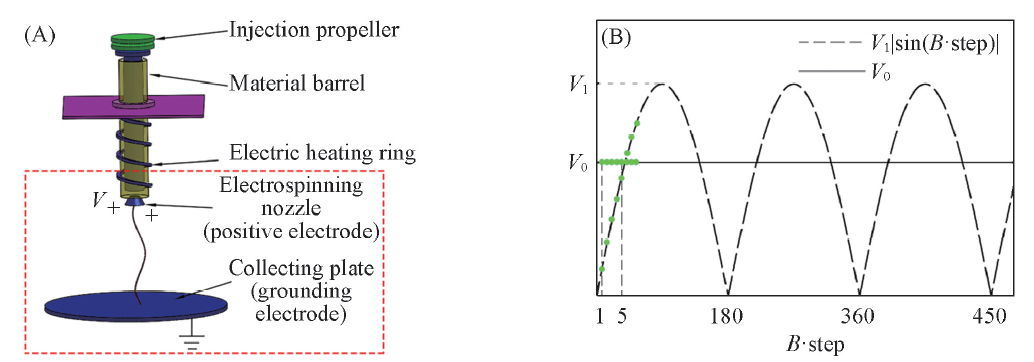
Fig.1 Electrospinning device and voltage format(A) Schematic diagram of a common stable field electrospinning device; (B) positive voltage changes with an increase in steps: the stable electric field is V0 (solid line); the absolute sine wave electric field(ASWEF) is changing as V1|sin(B·step)|. B=1 in this picture(dotted line).
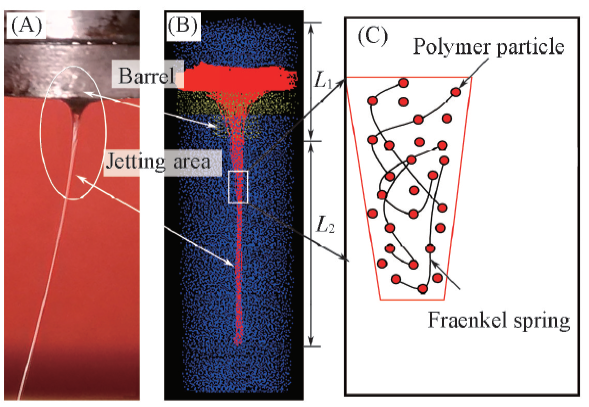
Fig.2 Modeling systems corresponding to the jetting process(A) Experimental system; (B) simulation system; (C) schematic representation of the molecular chains in a polymer jet.
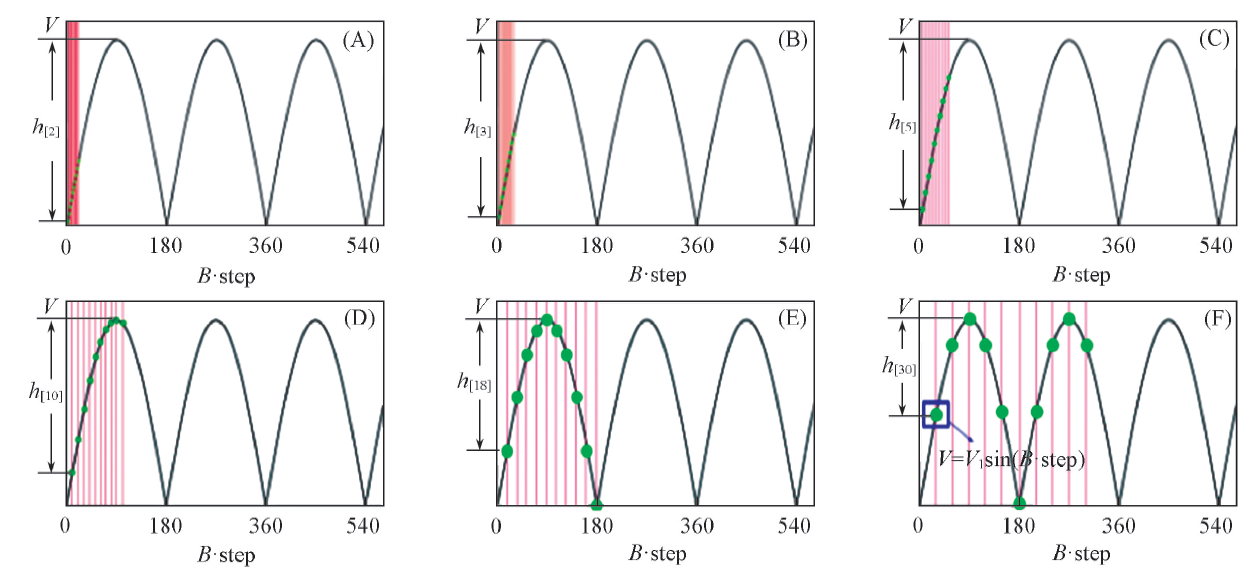
Fig.5 Changes in positive voltage at different control frequencies in an ASWEFGreen dots represent the voltage at certain steps, with each green dot and red line corresponding to one step.(A) B=2; (B) B=3; (C) B=5; (D) B=10; (E) B=18; (F) B=30.
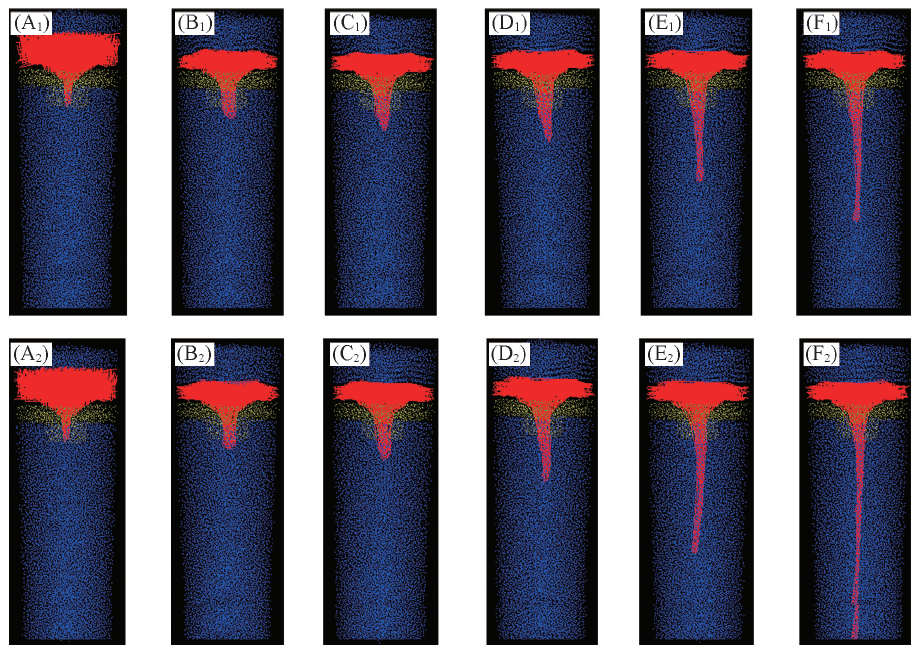
Fig.6 Falling process of a jetting fiber at various calculation steps in a stable electric field(A1—F1) and an ASWEF at B=2(A2—F2) Step: (A1, A2) 10; (B1, B2) 1010; (C1, C2) 2010; (D1, D2) 3010; (E1, E2) 4010; (F1, F2) 4440.
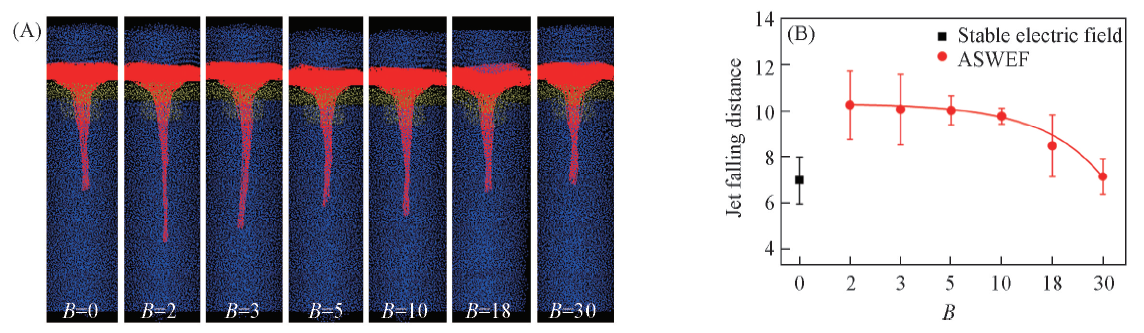
Fig.7 Snapshots of a falling jet(A) and the corresponding falling distances(B) under ASWEF conditions at different control frequencies after 4000 steps Control frequency 0 corresponds to a stable electric field.
| [1] | Fong H., Reneker D.H., J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polm. Phys., 1999, 37, 34—88 |
| [2] | Kim J.S., Reneker D. H., Polym. Eng. Sci., 1999, 39, 8—49 |
| [3] | Strutt J. W., Rayleigh L., Proc. London. Math. Soc., 1879, 10, 4—13 |
| [4] | Brown T.D., Dalton P. D., Hutmacher D. W., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2016, 56, 116—166 |
| [5] | Brown T.D., Dalton P. D., Hutmacher D. W., Adv. Mater., 2011, 23, 5651—5657 |
| [6] | Kim J., Lee S.H., Park S. J., Lee Y. S., Res. Chem. Intermed., 2014, 40, 2571—2581 |
| [7] | Mazalevska O., Struszczyk M.H., Krucinska L., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2013, 129, 779—792 |
| [8] | Zhou H.J., Green T. B., Joo Y. L., Polymer, 2006, 47, 7497—7505 |
| [9] | Zhao F.W., Liu Y., Yuan H. L., Yang W. M., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2012, 125, 2652—2658 |
| [10] | Liu Y., Liu Z.X., Deng L., Wang K. J., Yang W. M., Mater. Sci. Forum., 2013, 745, 407—411 |
| [11] | Zeng J., Chen X.S., Xu X. Y., Liang Q. Z., Bian X. C., Yang L. X., Jing X. B., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2003, 89, 1085—1092 |
| [12] | Liu Y., Zhao F.W., Zhang C., Zhang J. M., Yang W. M., J. Serb. Chem. Soc., 2012, 77, 1071—1082 |
| [13] | Lin K., Chua K.N., Christopherson G. T., Lim S., Mao H. Q., Polymer, 2007, 48, 6384—6394 |
| [14] | Urszula S., Corinne A.S., Colin R. W., J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 22935—22941 |
| [15] | Zhao F.W., Liu Y., Ding Y. M., Yan H., Xie P. C., Yang W. M., Key Eng. Mater., 2012, 501, 32—36 |
| [16] | Liu Y., Deng R.J., Hao M. F., Yan H., Yang W. M., Polym. Eng. Sci., 2010, 50, 2074—2078 |
| [17] | Malakhov S.N., Khomenko A. Y., Belousov S. I., Prazdnichnyi A. M., Chvalun S. N., Shepelev A. D., Budyka A. K., Fibre. Chem., 2009, 41, 355—359 |
| [18] | Deng R.J., Liu Y., Ding Y. M., Xie P. C., Luo L., Yang W. M., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2009, 114, 166—175 |
| [19] | Qu J.P., Zeng G. S., He H. Z., Jin G., Cao X. W., CIESC Journal, 2006, 57, 414—423 |
| [20] | Qu J. P., Zhang N., Yu X. P., Zhang G. Z., Liu S. R., Tian B., Liu L. M., Adv. Polym. Tech., 2013, 32, 21336-1—12 |
| [21] | Zeng G.S., Qu J. P., Polym. Compos., 2008, 29, 1252—1257 |
| [22] | Wan Y.Q., He J. H., Wu Y., Yu J. Y., Mater. Lett., 2006, 60, 3296—3300 |
| [23] | Xie G., Wang Y., Han X.T., Gong Y., Wang J. P., Zhang J. M., Deng D. P., Liu Y., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2016, 55, 7116—7123 |
| [24] | Liu Y., Wang X., Yan H., Guan C.F., Yang W. M., J. Mater. Sci., 2011, 46, 7877—7882 |
| [25] | Wang X., Liu Y., Zhang C., An Y., He X.T., Yang W. M., J. Nanosci. Nanotechno., 2013, 13, 4680—4685 |
| [26] | Wang X., Liu Y., Yan H., Guan C.F., Yang W. M., CIESC Journal, 2012, 63, 320—324 |
| [27] | Li X.H., Liu Y., Peng H., Ma X. J., Fong H., Mater. Lett., 2016, 176, 194—198 |
| [28] | Camposeo A., Greenfeld I., Tantussi F., Moffa M., Fuso F., Allegrini M., Zussman E., Macromolecules, 2014, 47, 4704—4710 |
| [29] | Catalani L.H., Collins G., Jaffe M., Macromolecules, 2007, 40, 1693—1697 |
| [30] | Reneker D.H., Yarin A. L., Fong H., Koombhongse S., J. Appl. Phys., 2000, 87, 4531—4547 |
| [31] | Liu Y., An Y., Yan H., Guan C.F., Yang W. M., J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys., 2010, 48, 2484—2489 |
| [32] | Barua B., Saha M. C., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2015, 132, 41918-1—11 |
| [33] | Wang H.L., Zheng G. F., Sun D. H., Adv. Mater. Res., 2009, 60, 456—460 |
| [34] | Zhong Y.Y., Zheng G. F., Sun D. H., Adv. Mater. Res., 2009, 60, 465—469 |
| [35] | Zhu S. Q., Yu H., Chen Y. M., Zhu M. F., J. Nanomater., 2012, 12, 525419-1—8 |
| [36] | Zhmayev E., Cho D., Joo Y.L., Polymer, 2010, 51, 4140—4144 |
| [37] | Wan Y.Q., He J. H., Wu Y., Yu J. Y., Mater. Lett., 2006, 60, 3296—3300 |
| [38] | Duan H.W., Design of High-Voltage Electrospinning Machine and Optimizing of Electrostatic Field, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, 2008 |
| [39] | Liu Y., Li X.H., Ramakrishna S., J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys., 2014, 52, 946—952 |
| [40] | Badieyan S.S., J. Polym. Eng., 2015, 35, 587—596 |
| [41] | Reneker D.H., Yarin A. L., Polymer, 2008, 49, 2387—2425 |
| [42] | Greenfeld I., Zussman E., J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys., 2013, 51, 1377—1391 |
| [43] | Jungst T., Muerza-Cascante M.L., Brown T. D., Standfest M., Hutmacher D. W., Groll J., Dalton P. D., Polym. Int., 2015, 64, 1086—1095 |
| [44] | Mayuri P.V., Ramesh P., J. Mater. Sci., 2016, 51, 2739—2746 |
| [45] | Hohman M.M., Shin M., Rutledge G., Brenner M. P., Phys. Fluids, 2001, 13, 2221—2236 |
| [46] | Zhmayev E., Cho D., Joo Y.L., Polymer, 2010, 51, 274—290 |
| [47] | Li J.L., J. Electrostat., 2007, 65, 750—757 |
| [48] | Malakhov S.N., Khomenko A. Y., Belousov S. I., Prazdnichnyi A. M., Chvalun S. N., Shepelev A. D., Budyka A. K., Fibre Chem., 2009, 41, 355—359 |
| [1] | TANG Yuanhui, LI Chunyu, LIN Yakai, ZHANG Chunhui, LIU Ze, YU Lixin, WANG Haihui, WANG Xiaolin. Dissipative Particle Dynamics Simulation of the Effect of Polymer Chain Rigidity on Membranes Formation by Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation Process [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220169. |
| [2] | GAO Yifei, XIAO Changfa, JI Dawei, HUANG Yangzheng. Preparation of PVDF Hollow Fiber Membranes via Melt Spinning-stretching Method and Its Oil-water Separation Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2065. |
| [3] | LUO Dajun, SHAO Huiju, JIN Jinbo, XIE Gaoyi, CUI Zhenyu, YU Jie, QIN Shuhao. Preparation of Hydrophilic Polypropylene/Polyvinyl Butyral Hollow Fiber Membranes by Melt-spinning-stretching† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1838. |
| [4] | LI Ren, ZHAO Jianwei, HOU Jin, HE Yuanyuan, CHENG Na. Effect of the Convex and the Concave Microstructures in the Metallic Nanowires on the Initial Deformation Behavior† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(3): 514. |
| [5] | RONG Jingjing,MA Lan,ZHU Youliang,HUANG Yineng,SUN Zhaoyan. Simulation of Perforated Lamelar Structures of Diblock Copolymer Induced by Surface Patterns† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(12): 2805. |
| [6] | WANG Li, WANG Chu, ZHOU Jian. Dissipative Particle Dynamics Simulations on the pH-responsive Gating of Block Copolymer Brush Modified Nanopores† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(1): 85. |
| [7] | WANG Wei, XU Jiali, LIN Yuanfei, LI Xueyu, MENG Lingpu, LI Liangbin. Effect of Hot Stretching on the Structure of Polypropylene Microporous Membranes with in situ Small Angle X-Ray Scattering† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 2128. |
| [8] | XU Fanhua, HENG Xiao, REN Jianxue, ZHOU Hengwei. Simulation Study of the Phase Separation and Self-assembly of Nanoparticles Coated with Ligands† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6): 1115. |
| [9] | LIU Linlin, YANG Zhongzhi. Self-assembly Morphological Control of Block Copolymers Simulated via the Combination of Dissipative Particle Dynamics and ABEEM Polarizable Force Field† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(11): 2179. |
| [10] | LI Gen, WANG Rui, WANG Feng, LIANG Ningning, ZHU Zhiguo, ZHANG Xiuqin, YANG Mingshu. Preparation and Characterization of TiO2 Nanorods/SiO2@TiO2 Core Shell Particles and Its Application in PLLA† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 2024. |
| [11] | LIU Xiaohan, GUO Hongxia. Dissipative Particle Dynamics Simulation of the Phase Behavior of T-shaped Ternary Amphiphiles Possessing Long Rod-like Mesogens† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(2): 440. |
| [12] | XIE Yu, LÜ Zhong-Yuan, SUN Zhao-Yan, AN Li-Jia. Dissipative Particle Dynamics Simulation Study on the Micellization and Gelation Behavior of PEO-PPO-PEO Solution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(6): 1454. |
| [13] | XIONG Zu-Jiang, ZHANG Xiu-Qin, LIU Guo-Ming, ZHAO Ying, WANG Rui, WANG Du-Jin. Crystallization and Tensile Behavior of Poly(L-lactide)/ Poly(ethylene oxide) Blend [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(5): 1288. |
| [14] | XUE Yao-Hong, ZHAO Yi-Wu, FAN Jing-Tao, HAN Cheng, JIANG Zhen-Gang, YANG Hua-Min, LIU Hong. Computer Simulation of Phase Separation in Binary Polymer Brush Systems [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(1): 242. |
| [15] | LI Yan-Chun, LIU Hong, HUANG Xu-Ri*, SUN Chia-Chung. Dissipative Particle Dynamics Study of Homopolymer Adsorb on Micelle in Non-equilibrium State [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(8): 1845. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||