

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 376.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160553
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Hui, XIA Di, YUAN Yaxian*( ), XU Minmin, YAO Jianlin
), XU Minmin, YAO Jianlin
Received:2016-07-29
Online:2017-03-10
Published:2017-02-23
Contact:
YUAN Yaxian
E-mail:yuanyaxian@suda.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
CHEN Hui, XIA Di, YUAN Yaxian, XU Minmin, YAO Jianlin. Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopic Investigation of PAHs at a PDMS-Au Composite Substrate†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(3): 376.
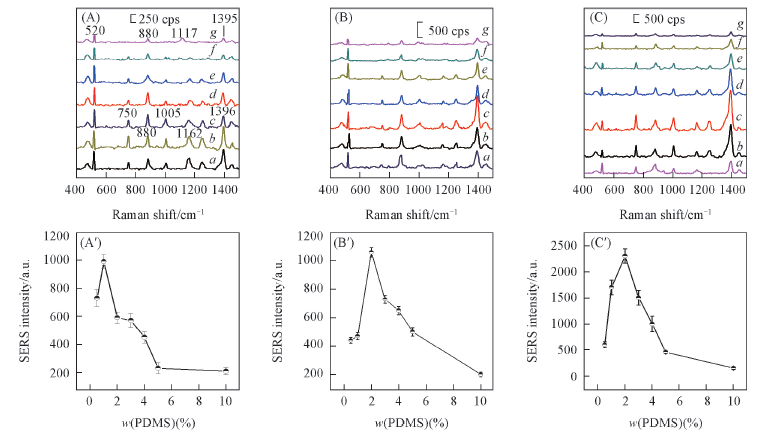
Fig.1 SERS spectra of the anthracene on composite substrate(A—C) and relationships between SERS intensity of anthracene at 1396 cm-1 and concentration of PDMS(A'—C') w(PDMS): a. 0.5%; b. 1%; c. 2%; d. 3%; e. 4%; f. 5%; g. 10%. Solvent: (A), (A') THF; (B), (B') n-hexane; (C), (C') tert butanol.
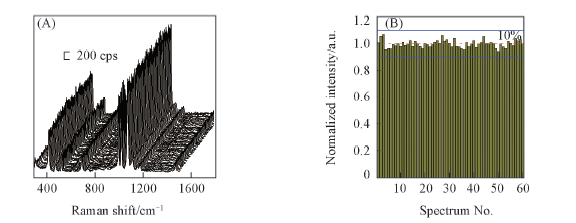
Fig.2 SERS spectra of TP from 60 random spots(A) and SERS intensity distribution of the band at 1027 cm-1(B) The red dashed line is the average intensity of all SERS spectra and the ±10% intensity variation were represented by the solid blue line.
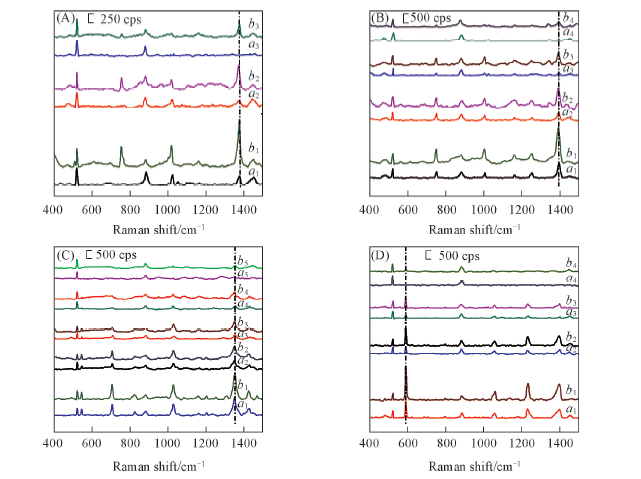
Fig.4 SERS spectra of different PAHs adsorbed on Au MLF(a) and PDMS-Au composite substrates(b) with different concentrations (A) Naphthalene; (B) anthracene; (C) phenanthrene; (D) pyrene. PAHs concentration/(mol·L-1): a1, b1. 10-4; a2, b2. 10-5; a3, b3. 10-6; a4, b4. 10-7; a5, b5. 10-8.
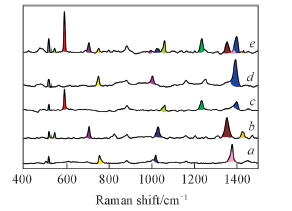
Fig.5 SERS spectra of different PAHs with the concentration of 10-4 mol/L a. Naphthalene; b. phenanthrene; c. pyrene; d. anthracene; e. mixture solution.
| [1] | Ding Y. S., Trommel J. S., Yan X. J., Ashley D., Watson C. H., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2005, 39(2), 471—478 |
| [2] | Conney A. H., Cancer Res., 1982, 42(12), 4875—4917 |
| [3] | Sirimanne S. R., Barr J. R., Patterson D. G., Ma L., Anal. Chem., 1996, 68(9), 1556—1560 |
| [4] | Takada H., Onda T., Ogura N., Environ. Sci. Technol., 1990, 24(8), 1179—1186 |
| [5] | Sander L. C., Wise S. A., Anal. Chem., 1987, 59(18), 2309—2313 |
| [6] | Nie S. M., Dadoo R., Zare R. N., Anal. Chem., 1993, 65(24), 3571—3575 |
| [7] | Schmidt H., Bich H. N., Pfannkuche J., Amann H., Kronfeldt H. D., Kowalewska G., Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2004, 49(3), 229—234 |
| [8] | Yang Y. A., Xu S. P., Wang Y. Y., Qi G. H., Xu W. Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(2), 254—259 |
| (杨永安, 徐抒平, 王昱扬, 齐国华, 徐蔚青. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(2), 254—259) | |
| [9] | Kneipp J., Li X. T., Sherwood M., Panne U., Kneipp H., Stockman M. I., Kneipp K., Anal. Chem., 2008, 80(11), 4247—4251 |
| [10] | Jones C. L., Bantz K. C., Haynes C. L., Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2009, 394, 303—311 |
| [11] | Costa J. C. S., Sant’Ana A. C., Corio P., Temperini M. L. A., Talanta,2006, 70(5), 1011—1016 |
| [12] | Du J. J., Jing C. Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(36), 17829—17835 |
| [13] | Gu X. F., Tian S., Zhou Q., Adkins J., Gu Z. M., Li X. W., Zheng J. W., RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 25989—25996 |
| [14] | Liu C. C., Zhang X. L., Li L. M., Cui J. C., Shi Y. E., Wang L., Zhan J. H., Analyst,2015, 140, 4668—4675 |
| [15] | Guerrini L., Garcia-Ramos J. V., Domingo C., Sanchez-Cortes S., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009, 11, 1787—1793 |
| [16] | Xie Y. F., Wang X., Han X. X., Song W., Ruan W. D., Liu J. Q., Zhao B., Ozaki Y., J. Raman Spectrosc., 2011, 42(5), 945—950 |
| [17] | Lai Y. C., Cui J. C., Jiang X. H., Zhu S., Zhan J. H., Analyst,2013, 138, 2598—2603 |
| [18] | Xu J. W., Du J. J., Jing C. Y., Zhang Y. L., Cui J. L., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 6891—6897 |
| [19] | Wang X., Hao W. M., Zhang H., Pan Y. C., Kang Y., Zhang X. F., Zou M. Q., Tong P. J., Du Y. P., Spectrochim. Acta Part A, 2015, 139, 214—221 |
| [20] | Naeimi M., Karkhaneh A., Barzin J., Khorasani M. T., Ghaffarieh A., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2013, 127(5), 3940—3947 |
| [21] | Menéndez J. C. F., Sánchez M. L. F., Uría J. E. S., Martínez E. F., Sanz-Medel A., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2000, 415, 9—20 |
| [22] | Lamotte M., de Violet P. F., Garrigues P., Hardy M., Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2002, 372, 169—173 |
| [23] | Gupta R., Kulkarni G. U., Chem. Sus. Chem., 2011, 4, 737—743 |
| [24] | Qian C., Guo Q. H., Xu M. M., Yuan Y. X., Yao J. L., RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 53306—53312 |
| [25] | Frens G., Kolloid Z., Nat. Phys. Sci., 1973, 241, 20—22 |
| [26] | Bra<inline-formula><mml:math xmlns:mml=" |
| [27] | Abel L., Thangawng R. S., Ruoff M. A., Glucksberg M. R., Biomed. Microdevices, 2007, 9(4), 587—595 |
| [28] | Koschwanez J. H., Carlson R. H., Medrum D. R., PLoS One.2009, 4(2), e4572 |
| [29] | Shinohara H., Yamakita Y., Ohno K., J. Mol. Struct., 1998, 442, 221—234 |
| [30] | Frank J. J., Edwars G. M., Spectrochimica Acta Part A, 2007, 68, 1065—1069 |
| [1] | WANG Hong, SAN Khin Nyein Ei, FANG Yun, ZHANG Xinyu, FAN Ye. Pickering Emulsion Stabilization and Interfacial Catalytic Oxidation by Janus Nano-Au [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220105. |
| [2] | XIA Dacheng, ZHOU Rui, TU Bo, CAI Zhiwei, GAO Nan, JI Xiaoxu, CHANG Gang, REN Xiaoming, HE Yunbin. Fabrication of Ag/Au Nanowires Array as a SERS Substrate for High-sensitivity Malachite Green Detection [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210731. |
| [3] | DENG Hongri, CAO Xiaomei, WANG Jingbo, LI Xiangyuan. Rate Rules for Hydrogen Abstraction Reactions of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Unsaturated Radicals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210563. |
| [4] | ZHANG Tao, SHAO Liang, ZHANG Menghui, MA Zhonglei, LI Xiaoqiang, MA Jianzhong. Preparation and Properties of Bifunctional Polydimethysiloxane/Copper Nanowire Composite Films [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220359. |
| [5] | LI Congcong, LIU Minghao, HAN Jiarui, ZHU Jingxuan, HAN Weiwei, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study of the Catalytic Activity of VmoLac Non-specific Substrates Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2518. |
| [6] | HU Haocheng, LI Wenli, ZHANG Jianing, LIU Yubo. Extraction, Structure Characterization and Biological Activities of Oligosaccharides from Auricularia heimuer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2465. |
| [7] | XI Jing, CHEN Na, YANG Yanbing, YUAN Quan. Recent Progress in Controlled Synthesis of Persistent Luminescence Nanomaterials for Diagnosis Applications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3247. |
| [8] | TANG Wentao, LI Shengkai, WANG Shen, CHEN Long, CHEN Zhuo. Laser-mediated Enrichment Based Surface Enhanced Raman Analysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3054. |
| [9] | WANG Binyu, LI Li, LI Jing, JIN Keyan, ZHANG Shaoqing, ZHANG Jianan, YAN Wenfu. Recent Progresses on the Synthesis of Zeolites from the Industrial Solid Wastes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 40. |
| [10] | ZHANG Kaixiang, LIU Junjie, SONG Qiaoli, WANG Danyu, SHI Jinjin, ZHANG Haiyue, LI Jinghong. Multifunctional DNA Nanoflowers for Autophagy Inhibition and Enhanced Antitumor Chemotherapy† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1461. |
| [11] | JIN Xin, FENG Xilan, LIU Dapeng, SU Yutong, ZHANG Zheng, ZHANG Yu. Auto-redox Strategy for the Synthesis of Co3O4/CeO2 Nanocomposites and Their Structural Optimization Towards Catalytic CO Oxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 652. |
| [12] | WANG Nan,YAO Kaisheng,ZHAO Chenchen,LI Tianjin,LU Weiwei. Ionic Liquid-assisted Synthesis of AuPd Nanosponges and Their Catalytic Performance † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 62. |
| [13] | WU Ting,CHEN Mengyao,XIAO Kaixia,ZHOU Yanmei,ZHANG Qingyou. Highly Selective Topological Index of Chemical Bonds and Its Applications† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1158. |
| [14] | QI Qi,LU Bingxin,CHE Yuping,WANG Yang,ZHAI Jin. Bimetallic Multi-core Nanoparticles with Dual SiO2 Layer Au@SiO2@Ag@SiO2 for the Detection of Glucose† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 887. |
| [15] | Yanjie LI,Ensi WANG,Xiaowei SHAO,Xingmin ZHANG,Shengxiu NIU,Lijuan YANG,Yi WU. Synthesis and Biological Activity in vitro of Imidazo[4,5-c]quinoline Derivatives † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2502. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||