

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 2236.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160426
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YAN Haixu1,2, YANG Meini1,2, ZENG Hao1,2, PU Hongting3, LIN Rui1,2,*( )
)
Received:2016-06-13
Online:2016-12-10
Published:2016-11-22
Contact:
LIN Rui
E-mail:ruilin@tongji.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YAN Haixu, YANG Meini, ZENG Hao, PU Hongting, LIN Rui. Effect of Acid-treatment of Graphitized Carbon Supports on Performance of Fuel Cell Catalysts†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(12): 2236.
| Sample | Half-peak width/cm-1 | ID/IG | I2D/IG | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | G | 2D | ||||||
| XC-72 CB | 260.3 | 84.1 | 898.9 | 3.72 | 0.85 | |||
| GCB | 45.7 | 58.3 | 48.6 | 0.64 | 1.39 | |||
Table 1 Raman spectroscopy data of XC-72 CB before and after 1700 ℃ treatment
| Sample | Half-peak width/cm-1 | ID/IG | I2D/IG | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | G | 2D | ||||||
| XC-72 CB | 260.3 | 84.1 | 898.9 | 3.72 | 0.85 | |||
| GCB | 45.7 | 58.3 | 48.6 | 0.64 | 1.39 | |||
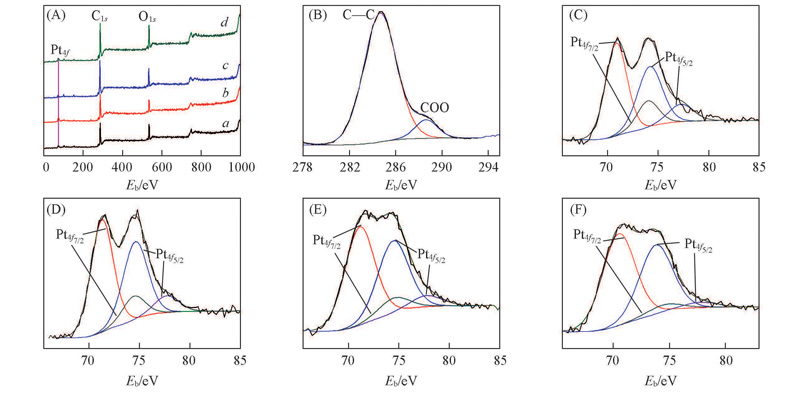
Fig.9 Full scan XPS spectra of the four catalysts(A), C1s XPS spectra of Pt/OGCB catalyst(B) and Pt4f XPS spectra of Pt/GCB(C), Pt/HNO3-GCB(D), Pt/H2SO4-GCB(E) and Pt/OGCB(F) catalyst(A) a. Pt/GCB; b. Pt/HNO3-GCB; c. Pt/H2SO4-GCB; d. Pt/OGCB.
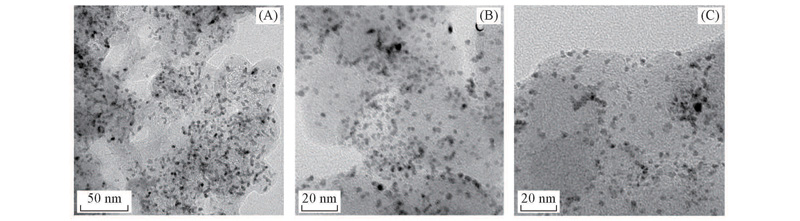
Fig.12 TEM images of Pt/OGCB catalysts and Pt/C(JM) after 5000 cycles accelerated durability tests(A) Pt/OGCB(after 5000 cycles); (B) Pt/C(JM)(fresh); (C) Pt/C(JM)(after 5000 cycles).
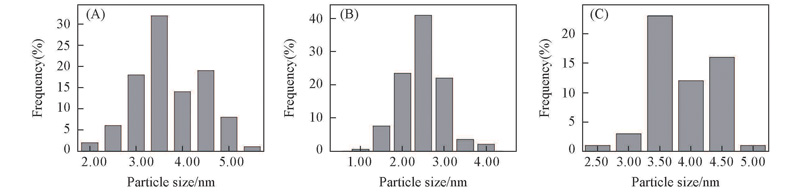
Fig.13 Prticle size distribution of Pt/OGCB catalysts and Pt/C(JM) after 5000 cycles accelerated durability tests(A) Pt/OGCB(after 5000 cycles); (B) Pt/C(JM)(fresh); (C) Pt/C(JM)(after 5000 cycles).
| [1] | Chen K. C., Ji M. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5), 989—995 |
| (陈康成, 纪梦蝶. 高等学校化学学报,2016, 37(5), 989—995) | |
| [2] | Huang Z., Lin R., Tang W. C., Ma J. X., Chin. J. Power Sources, 2014, 38(1), 174—177 |
| (黄真, 林瑞, 唐文超, 马建新. 电源技术,2014, 38(1), 174—177) | |
| [3] | Smimova A., Dong X., Hara H., Vasiliev A., Sammes N., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2005, 30(2), 149—159 |
| [4] | Kim J., Lee J., Tak Y., J. Power Sources, 2009, 192(2), 674—678 |
| [5] | Sasaki K., Shao M., Adzic R., Dissolution and Stabilization of Platinum in Oxygen Cathodes, Springer, New York, 2009, 7—27 |
| [6] | Bruijn F. A. D., Dam V. A. T., Janssen G. J. M., Fuel Cells, 2008, 8(1), 3—22 |
| [7] | Zhang L., Lin R., Huang Z., Fan R.J.,J. Fuel Chem. Technol., 2015, (3), 352—359 |
| (张路, 林瑞, 黄真, 范仁杰. 燃料化学学报, 2015, (3), 352—359) | |
| [8] | Lei M., Liang C., Wang Y., Huang K., Ye C., Liu G., Wang W., Jin S., Zhang R., Fan D., Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 113, 366—372 |
| [9] | Zhang Y., Pan Y., Liu J., Wang G. L., Cao D. X., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2015, 31(1), 117—122 |
| [10] | Su F., Zeng J., Bao X., Yu Y., And J. Y. L., Zhao X. S., Chem. Mater., 2005, 117(15), 3960—3967 |
| [11] | Yang M.N., Lin R., Fan R. J., Zhao T. T., Zeng H., Acta Phy-Chim. Sin., 2015, 31, 2131—2138 |
| (杨美妮, 林瑞, 范仁杰, 赵天天, 曾浩. 物理化学学报,2015, 31(11), 2131—2138) | |
| [12] | Wang C. G., Pan X., Zhang L., Zhu M. K., Li D. K., Diao L. B., Li W. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(2), 368—374 |
| (王存国, 潘璇, 张雷, 朱孟康, 李德凯, 刁玲博, 李伟彦. 高等学校化学学报,2015, 36(2), 368—374) | |
| [13] | Sevilla M., Fuertes A. B., Carbon, 2006, 44(3), 468—474 |
| [14] | Wang X., Hsing I. M., Yue P. L., J. Power Sources, 2001, 96(2), 282—287 |
| [15] | Meyers J. P., Darling R. M., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2005, 153(8), A1432—A1442 |
| [16] | Meng Q., Bai J., Guo S., Chunping L. I., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2015, 31(6), 1072—1077 |
| [17] | Zhao X., Hayashi A., Noda Z., Kimijima K. I., Yagi I., Sasaki K., Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 97(5), 33—41 |
| [18] | Mench M.M., Kumbur E. C., Veziroglu T. N., Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Degradation, Academic Press, New York, 2011, 443—460 |
| [19] | Yano H., Kataoka M., Yamashita H., Uchida H., Watanabe M., Langmuir, 2007, 23(11), 6438—6445 |
| [20] | Hara M., Lee M., Liu C. H., Chen B. H., Yamashita Y., Uchida M., Uchida H., Watanabe M., Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 70(6), 171—181 |
| [21] | Yano H., Akiyama T., Bele P., Uchida H., Watanabe M., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12(15), 3806—3814 |
| [22] | Kim J. Y., Lee S., Kim T. Y., Kim H. T., Electrochim. Acta, 2014, 134(21), 418—425 |
| [23] | Liang C., Dai S., Guiochon G., Anal. Chem., 2003, 75(18), 4904—4912 |
| [24] | Bragg W. L., Proc. Carnbridge Philos. Soc., 1913, 17, 43—57 |
| [25] | Saito T., Matsushige K., Tanaka K., Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter, 2002, 323(1), 280—283 |
| [26] | Chiang Y. C., Ciou J. R., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(11), 6826—6831 |
| [27] | Kim T. W., Park I. S., Ryoo R., Angew. Chem., 2003, 115(36), 4511—4515 |
| [28] | Li L. X., Feng L., New Carbon Mater., 2011, 26(3), 224—228 |
| [1] | QIU Xinsheng, WU Qin, SHI Daxin, ZHANG Yaoyuan, CHEN Kangcheng, LI Hansheng. Preparation and High Temperature Fuel Cell Performance of Ionic Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyimides for Proton Exchange Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220140. |
| [2] | GAO Zhongnan, GUO Lihong, ZHAO Dongyue, LI Xingang. Effect of A Site-deficiency on the Structure and Catalytic Oxidation Activity of the La-Sr-Co-O Perovskite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2869. |
| [3] | LIU Jiaming,FU Kailin,ZHANG Ze,GUO Wei,PAN Mu. Ultra-low Pt Loading Cathodic Catalyst Layer Prepared on Textured Gas Diffusion Layer by Magnetron Sputtering Method for Hydrogen-oxygen Fuel Cells† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 542. |
| [4] | KANG Huan, LI Shang, LIU Chang, GUO Wei, PAN Mu. Synthesis of Ordered Mesoporous Fe-N-C-PANI Catalyst via Self-assembly and Its Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity in Acid Medium [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8): 1423. |
| [5] | LIU Ziyi, XU Miaojun, WANG Qi, LI Bin. Preparation and Properties of Flame Retardant Cotton Fabric by Surface Chemical Grafted Modification [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8): 1477. |
| [6] | ZHAO Li, YU Dongni, DAI Weili, WU Guangjun, LI Landong, GUAN Naijia. Catalytic Performance of Micro-/micro-mesoporous H-ZSM-5 Zeolites for Alkylation of Toluene with Methanol† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1834. |
| [7] | LIU Ming, TIAN Ying, FU Jie, XU Hongfeng. Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Polyaniline Film Formed on Acid-activated Stainless Steel 316L† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(12): 2228. |
| [8] | LI Shang, LI Pei, ZHAO Wei, KANG Huan, PAN Mu. Graphene-supported Fe-N/C Composite Catalyst for Oxygen Reduction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1737. |
| [9] | GAO Chuanhui, GUO Fangrong, WANG Xiaohong, ZHANG Xinhua, WANG Chuanxing, WU Yumin. Synthesis of a Novel Polyester Plasticizer and Its Plasticizing Effect in Poly(vinylchloride)† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(8): 1634. |
| [10] | HUANG Qinghong, ZOU Liangliang, ZHOU Yi, ZOU Zhiqing, ZHANG Xiaogang, YANG Hui. Electrocatalytic Performance of Highly Loaded PtNi Intermetallic Nanoparticles for Oxygen Reduction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 1961. |
| [11] | HU Qing-Ping, PAN Jing, ZHUANG Lin, LU Jun-Tao. Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Completely Based on Pd-alloy Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(1): 170. |
| [12] | HE Wei, ZOU Liang-Liang, ZHOU Yi, LU Xiang-Jun, LI Yuan, ZHANG Xiao-Gang, YANG Hui. In-situ Synthesis of Pt Nanoparticles on Graphene Nanosheets and Its Electrocatalysis for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(01): 133. |
| [13] | WANG Zhe*, GAO Hong-Cheng, ZHAO Cheng-Ji, CHANG Hong, ZHANG Hui-Xuan, NA Hui. Preparation and Behaviors of Sulfonated Poly (arylene ether ketone Sulfone)s /ZrO2 Composite Proton Exchange Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(8): 1884. |
| [14] | WANG Gui-Ling1, WANG Jing1, CAO Dian-Xue1*, TANG Yong-Fu1, L Yan-Zhuo1, LU Tian-Hong2, XING Wei2. Performance of Electrochemical Oxidation of Carbon in Molten Carbonates [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(9): 1829. |
| [15] | YANG Dai-Jun1,2, MA Jian-Xin1,3*, MA Xiao-Wei3, ZHOU Wei1,3, XU Lin4, WU Min-Zhong4, WAN Gang1. Effects of SO2 on Cathode Performance of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(4): 731. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||