

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (5): 912.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150817
• Organic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Nan1, CHENG Xiaoheng2, ZHENG Jimin1,*( ), CHEN Guangju1, JIA Zongchao3
), CHEN Guangju1, JIA Zongchao3
Received:2015-10-23
Online:2016-05-10
Published:2016-04-18
Contact:
ZHENG Jimin
E-mail:jimin_z@bnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Nan, CHENG Xiaoheng, ZHENG Jimin, CHEN Guangju, JIA Zongchao. Expression and Purification of DEPTOR and Its Interaction with mTOR-TRD2†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5): 912.
| Primer name | Sequence(5' to 3') |
|---|---|
| FAT foward primer | CTGCTGGGTGAGAGAGCT |
| FAT reverse primer | AGACTTAGAAGCCACTGTCAGT |
| TRD2 forward primer | ATCCAGGCTACCTGGTATGA |
| TRD2 reverse primer | CTTGTCCCCGAGCGAC |
Table 1 FAT domain and TRD2 subdomain PCR primer sequence
| Primer name | Sequence(5' to 3') |
|---|---|
| FAT foward primer | CTGCTGGGTGAGAGAGCT |
| FAT reverse primer | AGACTTAGAAGCCACTGTCAGT |
| TRD2 forward primer | ATCCAGGCTACCTGGTATGA |
| TRD2 reverse primer | CTTGTCCCCGAGCGAC |
| Primer name | Sequence(5' to 3') |
|---|---|
| DEPTOR foward primer | GCTTGGTACCGAGCTCGG |
| DEPTOR reverse primer | ATGGTGATGGTGATGATG |
| DEPTOR-G270P-forward | GGCAGCAGCCCCTACTTCAGCAGCAGCCCCACCC |
| DEPTOR-G270P-reverse | TGAAGTAGGGGCTGCTGCCACAGCTGCTCATGCTGCTTCT |
Table 2 DEPTOR PCR Primer and G270P Mutation Primer Sequence
| Primer name | Sequence(5' to 3') |
|---|---|
| DEPTOR foward primer | GCTTGGTACCGAGCTCGG |
| DEPTOR reverse primer | ATGGTGATGGTGATGATG |
| DEPTOR-G270P-forward | GGCAGCAGCCCCTACTTCAGCAGCAGCCCCACCC |
| DEPTOR-G270P-reverse | TGAAGTAGGGGCTGCTGCCACAGCTGCTCATGCTGCTTCT |
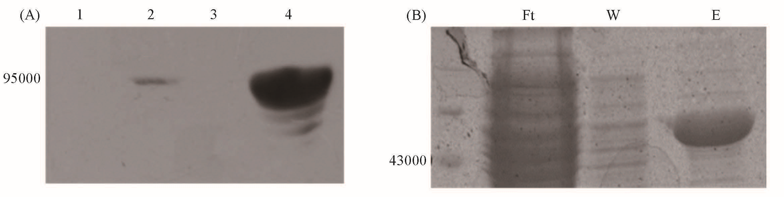
Fig.2 FAT domain and subdomain expression assay in E.coli(A) FAT-GST fusion protein in JM109 expression assay by Western-Blot, lane 1: negative control (incubate without adding IPTG), lane 2: whole-cell-extract after induced by 1 mmol/L IPTG, lanes 3, 4: supernatant/pellet of whole-cell-extract lysate. (B) MBP fusion TRD2 protein in BL21(DE3) expression assay by SDS-PAGE(Ft: flow-through; W: wash; E: eluted protein).
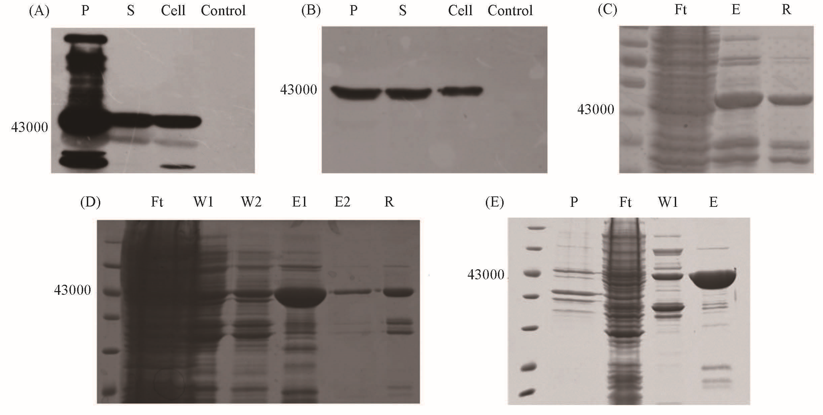
Fig.3 DEPTOR expression assay in E.coliAll the lanes are samples from each purification step, respectively. (A) DEPTOR-His wild-type expression assay by Western-Blot in BL21(DE3); (B) DEPTOR-His wild-type expression assay by Western-Blot in arctic express; (C) DEPTOR-His wild-type expression assay by SDS-PAGE in BL21(DE3); (D) DEPTOR-His G270P expression assay by SDS-PAGE; (E) DEPTOR-His G270P expression assay by SDS-PAGE with glycerol(10%, volume fraction) in purification buffer. P: pellet; S: supernatant; Cell: whole-cell-extract; Control: cell without induced by IPTG; Ft: flow-through; W1, W2: wash; E, E1 and E2: eluted protein; R: resin after elution.
| Secondary structure | Percentage of secondary structure(%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 180—260 nm | 185—260 nm | 190—260 nm | 195—260 nm | 200—260 nm | 205—260 nm | |
| α-Helix | 29.1 | 28.8 | 28.8 | 27.8 | 26.7 | 27.6 |
| Antiparallel β-strand | 14.2 | 14.6 | 15.0 | 13.4 | 11.0 | 9.4 |
| Parallel β-strand | 9.1 | 9.0 | 8.9 | 9.8 | 10.5 | 10.9 |
| β-Turns | 18.3 | 18.3 | 18.2 | 18.1 | 18.4 | 17.8 |
| Coiled-coil | 31.8 | 32.2 | 31.8 | 33.6 | 35.9 | 37.7 |
| Total | 102.4 | 102.9 | 102.8 | 102.7 | 102.5 | 103.3 |
Table 3 Percentage of secondary structure in DEPTOR-wt*
| Secondary structure | Percentage of secondary structure(%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 180—260 nm | 185—260 nm | 190—260 nm | 195—260 nm | 200—260 nm | 205—260 nm | |
| α-Helix | 29.1 | 28.8 | 28.8 | 27.8 | 26.7 | 27.6 |
| Antiparallel β-strand | 14.2 | 14.6 | 15.0 | 13.4 | 11.0 | 9.4 |
| Parallel β-strand | 9.1 | 9.0 | 8.9 | 9.8 | 10.5 | 10.9 |
| β-Turns | 18.3 | 18.3 | 18.2 | 18.1 | 18.4 | 17.8 |
| Coiled-coil | 31.8 | 32.2 | 31.8 | 33.6 | 35.9 | 37.7 |
| Total | 102.4 | 102.9 | 102.8 | 102.7 | 102.5 | 103.3 |
| Secondary structure | Percentage of secondary structure(%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 180—260 nm | 185—260 nm | 190—260 nm | 195—260 nm | 200—260 nm | 205—260 nm | |
| α-Helix | 28.8 | 29.4 | 29.3 | 28.6 | 28.0 | 29.4 |
| Antiparallel β-strand | 14.9 | 14.2 | 14.7 | 12.9 | 10.5 | 8.8 |
| Parallel β-strand | 9.1 | 8.8 | 8.7 | 9.5 | 10.0 | 10.3 |
| β-Turns | 18.4 | 18.2 | 18.1 | 17.9 | 18.1 | 17.4 |
| Coiled-coil | 31.0 | 31.2 | 31.0 | 32.6 | 34.7 | 36.2 |
| Total | 102.2 | 101.8 | 101.9 | 101.6 | 101.3 | 102.1 |
Table 4 Percentage of secondary structure in DEPTOR-G270P*
| Secondary structure | Percentage of secondary structure(%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 180—260 nm | 185—260 nm | 190—260 nm | 195—260 nm | 200—260 nm | 205—260 nm | |
| α-Helix | 28.8 | 29.4 | 29.3 | 28.6 | 28.0 | 29.4 |
| Antiparallel β-strand | 14.9 | 14.2 | 14.7 | 12.9 | 10.5 | 8.8 |
| Parallel β-strand | 9.1 | 8.8 | 8.7 | 9.5 | 10.0 | 10.3 |
| β-Turns | 18.4 | 18.2 | 18.1 | 17.9 | 18.1 | 17.4 |
| Coiled-coil | 31.0 | 31.2 | 31.0 | 32.6 | 34.7 | 36.2 |
| Total | 102.2 | 101.8 | 101.9 | 101.6 | 101.3 | 102.1 |
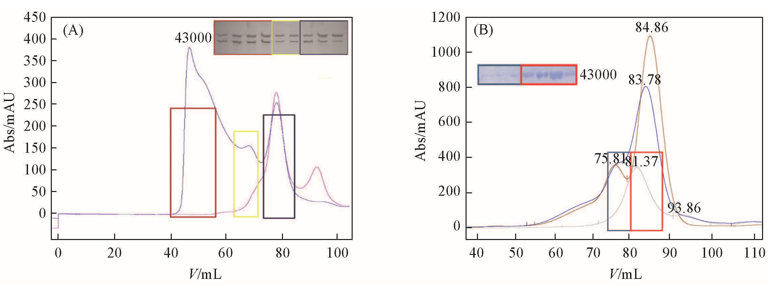
Fig.5 Interaction assay of MBP-TRD2 and DEPTOR(A) MBP-TRD2 and DEPTOR co-purification by gel-filtration (Hi-Load S200) in 20 mmol/L Tris, pH=8.0 and 150 mmol/L NaCl; (B) MBP and DEPTOR co-purification by gel-filtration in the same condition as a negative control. Samples of the putative complexes are picked and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. In each figure, x-axis indicates the elution volume which reflects molecular mass of the protein and y-axis indicates the absorption value which is in direct proportion to protein concentration.
| [1] | Wang J. B., Jiang Y., Liang H., Li P., Xiao H. J., Ji J., Xiang W., Shi J. F., Fan Y. G., Li L., Wang D., Deng S. S., Chen W. Q., Wei W. Q., Qiao Y. L., Boffetta P., Ann.Oncol., 2001, 23(11), 2983—2989 |
| [2] | Qiao Y. L., Chin. J.Oncol., 2009, 34(7), 483—485 |
| [3] | Wei K. R., Liang Z. H., Liu J., Wang Y. N., Chinese Journal of Medical History, 2012, 42(1), 21—25 |
| (魏矿荣, 梁智恒, 刘静, 王亚娜. 中华医史杂志, 2012, 42(1), 21—25) | |
| [4] | Fan W. H., Zhang L. H., Zhang Z. L., Guo J. F., Ren A. M., Ge P. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(7), 1731—1738 |
| (范文海, 张丽红, 张子龙, 郭景富, 任爱民, 葛鹏飞. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(7), 1731—1738) | |
| [5] | Peterson T. R., Laplante M., Thoreen C. C., Sancak Y., Kang S. A., Kuehl W. M., Gray N. S., Sabatini D. M., Cell, 2009, 137(5), 873—886 |
| [6] | Fingar D. C., Salama S., Tsou C., Harlow E., Belnis J., GenesDev., 2002, 16(12), 1472—1487 |
| [7] | Gera J., Lichtenstein A., LeukLymphoma, 2011, 52(10), 1857—1866 |
| [8] | Lu M., Wang J., Elves H., Pearce D., J. Biol.Chem., 2011, 286(35), 30647—30654 |
| [9] | Chen J., Zheng X. F., Brown E. J., Scheriber S. L., Proc. Natl. Acad.Sci., 1995, 92(11), 4947—4951 |
| [10] | Yang H., Rudge D. G., Koos J. D., Vaidialingam B., Yang H. J., Pavletich N. P., Nature,2013, 497(7448), 217—223 |
| [11] | Dames S. A., J. Biol.Chem., 2010, 285(10), 7766—7775 |
| [12] | Hardt M., Chantaravisoot N., Tamanoi F., Genes toCells, 2011, 16(2), 141—151 |
| [13] | Sturgill T. W., Hall M. N., ACS Chem.Biol., 2009, 4(12), 999—1015 |
| [14] | Bakkenist C. J., Kastan M. B., Nature,2003, 421(6922), 499—506 |
| [15] | Mehtab P., Mohammed M. A., Akhtar A., Mahboob A., Chem. Res. ChineseUniversities, 2014, 30(1), 55—62 |
| [16] | Imamura S., Kishi S., Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol., 2005, 37(5), 1105—1116 |
| [17] | Tanaka A., Weinel S., Nagy N., O’Driscoll M., Lai-Cheong J. E., Kulp-Shorten C. L., Knable A., Carpenter G., Fisher S. A., Hiragun M., Yanase Y., Hide M., Callen J., McGrath J. A., Am. J. Hum.Genet., 2012, 90(3), 511—517 |
| [18] | Jiang X., Sun Y., Chen S., Roy K., Price B. D., J. Biol.Chem., 2006, 281(23), 15741—15746 |
| [19] | Rivera-Calzada A., Maman J. D., Spagnolo L., Pearl L. H., Llorca O., Structure, 2005, 13(2), 243—255 |
| [20] | de la Rubia J., Such E., LeukLymphoma, 2010, 51(11), 1960—1961 |
| [21] | Tsai W. B., Chung Y. M., Takahashi Y., Xu Z., Hu M. C., Nat. Cell.Biol., 2008, 10(4), 460—467 |
| [22] | Kazi A. A., Hong-Brown L., Lang S. M., Lang C. H., Mol.Med., 2011, 17(9), 925—936 |
| [23] | Zhang X. Y., Deng D. J., Tan J. J., He Y., Li C. H., Wang C. X., Chem. Res. ChineseUniversities, 2014, 30(2), 297—305 |
| [1] | TANG Yujing, HU Min, WANG Xia, WANG Qigang. Advances in Enzyme-load Nanocatalytic Systems for Disease Treatment [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220640. |
| [2] | CHANG Liying, LING Xinyu, CHEN Heqi, WANG Xue, LIU Tao. Application of Gene Editing in Mitochondrial Diseases [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(Album-4): 20220363. |
| [3] | CAO Shujie, LI Hongjun, GUAN Wenli, REN Mengtian, ZHOU Chuanzheng. Progress on the Stereocontrolled Synthesis of Phosphorothioate Oligonucleotides [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(Album-4): 20220304. |
| [4] | XU Yongbin, FENG Shuaixia, CHEN Jie, GONG Hua, SHI Songshan, WANG Huijun, WANG Shunchun. Structural Characterization of a Homogeneous Polysaccharide Isolated From the Flower of Carthamus tinctorius L. and Its Inhibitory Activity on HepG2 Proliferation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220600. |
| [5] | WU Yushuai, SHANG Yingxu, JIANG Qiao, DING Baoquan. Research Progress of Controllable Self-assembled DNA Origami Structure as Drug Carrier [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220179. |
| [6] | LIU Wenting, LIU Liuyi, ZHU Bochen, MAO Zongwan. Progress on the Recognition, Complex Structure and Intracellular Detection of Nucleic Acid G-quadruplex [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220419. |
| [7] | HU Yucan, CAO Zhaohui, ZHENG Linggang, SHEN Juntao, ZHAO Wei, DAI Lei. Application of CRISPR-Cas Technologies in Microbiome Engineering [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220362. |
| [8] | FANG Xin, ZHAO Ruiqi, MO Jing, WANG Yafen, WENG Xiaocheng. Sequencing Methods for Detection of Nucleic Acid Epigenetic Modifications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220342. |
| [9] | ZHANG Kaisong, WANG Shaoru, ZHANG Yutong, TIAN Tian. Study of Epigenetic Modifications of Nucleic Acids Based on Supramolecular Chemistry [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220335. |
| [10] | ZHU Kai, LI Jie, WU Xiaoyi, HU Weiwei, WU Dongmei, YU Chengxiao, GE Zhiwei, YE Xingqian, CHEN Shiguo. Combined PGC-Triple-Tof-MS Enables the Separation, Identification of Sugar Beet Pectin Derived Oligomers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220023. |
| [11] | FU Jun, WU Meichan, WANG Shuzhen, SHAO Xiuli, HE Feng. Antifungal Mechanism of Fubaiju Essential Oil According to Labeling Method [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3657. |
| [12] | ZHAO Zhuo, WANG Xueqiang. Investigations upon the Bioconjugation-based Construction Technologies and Applications of Aptamer-drug Conjugates [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3367. |
| [13] | CHEN Wang, HU Daihua, LIU Gege. Synthesis of Ursodeoxycholic Acid from Dehydroiso-androsterone 3-Acetate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2782. |
| [14] | HU Haocheng, LI Wenli, ZHANG Jianing, LIU Yubo. Extraction, Structure Characterization and Biological Activities of Oligosaccharides from Auricularia heimuer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2465. |
| [15] | YANG Yiran, YAO Hua, YAN Jianghong, SUN Zhiheng, ZHANG Yu, FANG Xueqing, LI Xuwen, JIN Yon⁃Ri. Chemical Constituents of New Steroidal Saponins from Allium chinense G. Don [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1742. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||