

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 167.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150567
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Ziliang1,2, LI Qi1, XUE Yanhu1, JI Xiangling1,*( ), BO Shuqin1, LIU Yonggang1,*(
), BO Shuqin1, LIU Yonggang1,*( )
)
Received:2015-07-20
Online:2016-01-10
Published:2015-10-21
Contact:
JI Xiangling,LIU Yonggang
E-mail:xlji@ciac.ac.cn;yonggang@ciac.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHAO Ziliang, LI Qi, XUE Yanhu, JI Xiangling, BO Shuqin, LIU Yonggang. Composition and Molecular Weight Determination of Aqueous Two-phase System by Quantitative Size Exclusion Chromatography†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(1): 167.
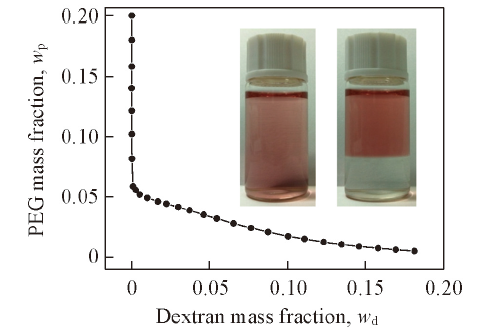
Fig.1 Cloud point curve of the aqueous solution of dextran and PEG at (25±1) ℃ obtained by titration ^The homogeneous solution in the left vial has a composition in the one-phase region, the right one shows phase separation in the two-phase region. Au nanoparticles are dispersed in water and added to the mixed solution to enhance the color contrast.
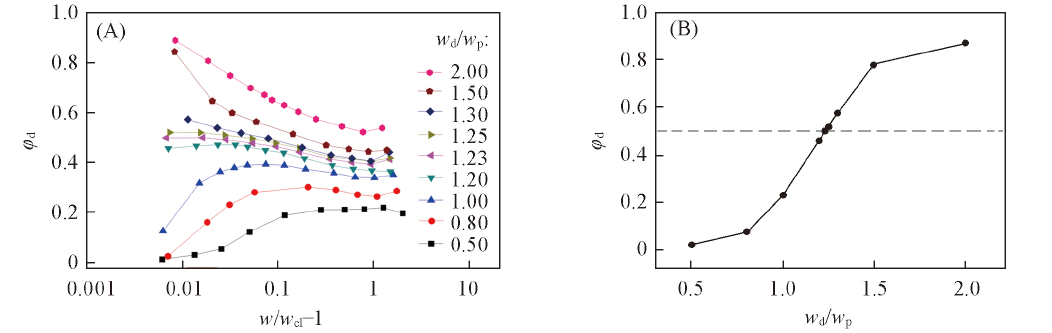
Fig.2 Volume fraction(φd) of the dextran-rich phase as a function of the normalized distance from the cloud point(w/wcl-1) for polymer solutions of different mass ratios(wd/wp) between dextran and PEG(A) and dependence of the volume fraction φd on the mass ratio wd/wp at w/wcl=1.01(B)
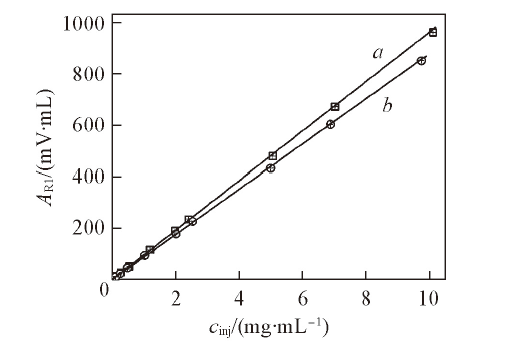
Fig.3 Dependence of the RI peak area(ARI) as a function of polymer concentration(cinj) of the solutions injected into the SEC columns for dextran(a) and PEG(b)
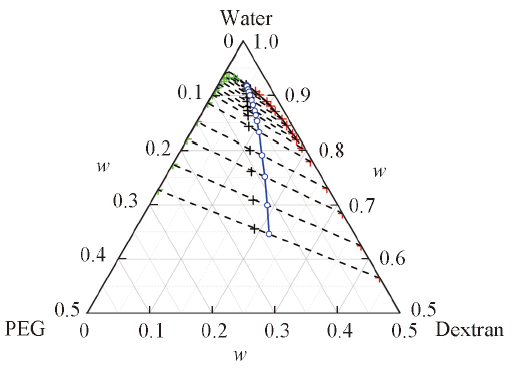
Fig.5 Phase diagram of the ternary dextran-PEG-water system^The cloud point curve(same data as in Fig.1) is shown as a solid curve. The compositions of the initial solutions(with mass ratio wd/wp=1.23) for which SEC measurements after phase separation are performed are indicated by black crosses. The end points of the respective tie lines(dashed lines) consist of red crosses indicating the compositions of the dextran-rich phases and green crosses indicating the compositions of the PEG-rich phases. The midpoints(blue circles) of the tie lines were extrapolated to determine the critical point.
| No. | ε | Dextran-rich phase | PEG-rich phase | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-3 Mw | 10-3 Mn | Mw/Mn | 10-3 Mw | 10-3 Mn | Mw/Mn | ||
| Native | ______ | 380.0 | 173.7 | 2.19 | 380.0 | 173.7 | 2.19 |
| 1 | 0.0098 | 453.9 | 192.9 | 2.35 | 249.3 | 152.6 | 1.63 |
| 2 | 0.030 | 426.9 | 182.0 | 2.35 | 208.9 | 138.3 | 1.51 |
| 3 | 0.092 | 394.1 | 172.1 | 2.29 | 167.6 | 120.8 | 1.39 |
| 4 | 0.134 | 397.9 | 177.8 | 2.24 | 152.3 | 112.5 | 1.35 |
| 5 | 0.200 | 380.6 | 170.3 | 2.23 | 136.0 | 103.1 | 1.32 |
| 6 | 0.302 | 369.8 | 164.2 | 2.25 | 116.9 | 90.0 | 1.30 |
| 7 | 0.389 | 373.3 | 167.1 | 2.23 | 109.4 | 84.8 | 1.29 |
| 8 | 0.508 | 371.3 | 164.6 | 2.26 | 97.1 | 76.9 | 1.26 |
| 9 | 0.599 | 370.6 | 163.1 | 2.27 | 95.9 | 69.4 | 1.38 |
| 10 | 0.729 | 375.2 | 166.0 | 2.26 | 82.2 | 66.9 | 1.23 |
| 11 | 0.982 | 372.4 | 163.7 | 2.28 | |||
| 12 | 1.552 | 368.7 | 161.8 | 2.28 | |||
| 13 | 2.087 | 368.6 | 155.8 | 2.37 | |||
| 14 | 2.825 | 374.7 | 160.5 | 2.34 | |||
| 15 | 3.605 | 368.7 | 161.8 | 2.28 | |||
Table 1 Molecular weight of dextran in dextran-rich and PEG-rich phases
| No. | ε | Dextran-rich phase | PEG-rich phase | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-3 Mw | 10-3 Mn | Mw/Mn | 10-3 Mw | 10-3 Mn | Mw/Mn | ||
| Native | ______ | 380.0 | 173.7 | 2.19 | 380.0 | 173.7 | 2.19 |
| 1 | 0.0098 | 453.9 | 192.9 | 2.35 | 249.3 | 152.6 | 1.63 |
| 2 | 0.030 | 426.9 | 182.0 | 2.35 | 208.9 | 138.3 | 1.51 |
| 3 | 0.092 | 394.1 | 172.1 | 2.29 | 167.6 | 120.8 | 1.39 |
| 4 | 0.134 | 397.9 | 177.8 | 2.24 | 152.3 | 112.5 | 1.35 |
| 5 | 0.200 | 380.6 | 170.3 | 2.23 | 136.0 | 103.1 | 1.32 |
| 6 | 0.302 | 369.8 | 164.2 | 2.25 | 116.9 | 90.0 | 1.30 |
| 7 | 0.389 | 373.3 | 167.1 | 2.23 | 109.4 | 84.8 | 1.29 |
| 8 | 0.508 | 371.3 | 164.6 | 2.26 | 97.1 | 76.9 | 1.26 |
| 9 | 0.599 | 370.6 | 163.1 | 2.27 | 95.9 | 69.4 | 1.38 |
| 10 | 0.729 | 375.2 | 166.0 | 2.26 | 82.2 | 66.9 | 1.23 |
| 11 | 0.982 | 372.4 | 163.7 | 2.28 | |||
| 12 | 1.552 | 368.7 | 161.8 | 2.28 | |||
| 13 | 2.087 | 368.6 | 155.8 | 2.37 | |||
| 14 | 2.825 | 374.7 | 160.5 | 2.34 | |||
| 15 | 3.605 | 368.7 | 161.8 | 2.28 | |||
| No. | ε | Dextran-rich phase | PEG-rich phase | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-3 Mw | 10-3 Mn | Mw/Mn | 10-3 Mw | 10-3 Mn | Mw/Mn | ||
| Native | _____ | 8.45 | 7.64 | 1.11 | 8.45 | 7.64 | 1.11 |
| 1 | 0.0098 | 8.38 | 7.57 | 1.11 | 8.35 | 7.58 | 1.10 |
| 2 | 0.030 | 8.12 | 7.33 | 1.11 | 8.35 | 7.61 | 1.10 |
| 3 | 0.092 | 8.08 | 7.25 | 1.11 | 8.30 | 7.52 | 1.10 |
| 4 | 0.134 | 8.18 | 7.31 | 1.12 | 8.41 | 7.65 | 1.10 |
| 5 | 0.200 | 8.02 | 7.06 | 1.14 | 8.39 | 7.63 | 1.10 |
| 6 | 0.302 | 8.02 | 7.00 | 1.15 | 8.28 | 7.53 | 1.10 |
| 7 | 0.389 | 7.98 | 6.89 | 1.16 | 8.40 | 7.63 | 1.10 |
| 8 | 0.508 | 7.93 | 6.69 | 1.19 | 8.38 | 7.60 | 1.10 |
| 9 | 0.599 | 7.88 | 6.55 | 1.20 | 8.50 | 7.70 | 1.10 |
| 10 | 0.729 | 7.78 | 6.22 | 1.25 | 8.29 | 7.49 | 1.11 |
| 11 | 0.982 | 8.44 | 7.65 | 1.10 | |||
| 12 | 1.552 | 8.63 | 7.82 | 1.10 | |||
| 13 | 2.087 | 8.43 | 7.64 | 1.10 | |||
| 14 | 2.825 | 8.40 | 7.57 | 1.11 | |||
| 15 | 3.605 | 8.56 | 7.76 | 1.10 | |||
Table 2 Molecular weight of PEG in dextran-rich and PEG-rich phases
| No. | ε | Dextran-rich phase | PEG-rich phase | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-3 Mw | 10-3 Mn | Mw/Mn | 10-3 Mw | 10-3 Mn | Mw/Mn | ||
| Native | _____ | 8.45 | 7.64 | 1.11 | 8.45 | 7.64 | 1.11 |
| 1 | 0.0098 | 8.38 | 7.57 | 1.11 | 8.35 | 7.58 | 1.10 |
| 2 | 0.030 | 8.12 | 7.33 | 1.11 | 8.35 | 7.61 | 1.10 |
| 3 | 0.092 | 8.08 | 7.25 | 1.11 | 8.30 | 7.52 | 1.10 |
| 4 | 0.134 | 8.18 | 7.31 | 1.12 | 8.41 | 7.65 | 1.10 |
| 5 | 0.200 | 8.02 | 7.06 | 1.14 | 8.39 | 7.63 | 1.10 |
| 6 | 0.302 | 8.02 | 7.00 | 1.15 | 8.28 | 7.53 | 1.10 |
| 7 | 0.389 | 7.98 | 6.89 | 1.16 | 8.40 | 7.63 | 1.10 |
| 8 | 0.508 | 7.93 | 6.69 | 1.19 | 8.38 | 7.60 | 1.10 |
| 9 | 0.599 | 7.88 | 6.55 | 1.20 | 8.50 | 7.70 | 1.10 |
| 10 | 0.729 | 7.78 | 6.22 | 1.25 | 8.29 | 7.49 | 1.11 |
| 11 | 0.982 | 8.44 | 7.65 | 1.10 | |||
| 12 | 1.552 | 8.63 | 7.82 | 1.10 | |||
| 13 | 2.087 | 8.43 | 7.64 | 1.10 | |||
| 14 | 2.825 | 8.40 | 7.57 | 1.11 | |||
| 15 | 3.605 | 8.56 | 7.76 | 1.10 | |||
| [1] | Albertsson P.Å., Partition of Cell Particles and Macromolecules: Separation and Purification of Biomolecules, Cell Organelles, Membranes, and Cells in Aqueous Polymer Two-phase Systems and Their Use in Biochemical Analysis and Biotechnology, 3rd Ed., Wiley, New York, 1986 |
| [2] | Walter H., Brooks D.E., Fisher D., Partitioning in Aqueous Two-phase Systems:Theory, Methods, Uses, and Applications to Biotechnology, Academic Press, Orlando, 1985 |
| [3] | Flory P.J., Principles of Polymer Chemistry, Cornell University Press, Ithaca, 1953 |
| [4] | Koningsveld R., Stockmayer W.H., Nies E., Polymer Phase Diagrams, Oxford University Press, New York, 2001 |
| [5] | Hatti-Kaul R., Methods in Biotechnology, Vol. 11, Aqueous Two-phase Systems: Methods and Protocols, Humana Press, Totowa, 2000 |
| [6] | Pudney P. D. A., Hancewicz T. M., Cunningham D. G., Gray C., Food Hydrocolloids, 2003, 17, 345—353 |
| [7] | Loret C., Schumm S., Pudney P. D. A., Frith W. J., Fryer P. J., Food Hydrocolloids, 2005, 19, 557—565 |
| [8] | Liu Y. G., Lipowsky R., Dimova R., Langmuir,2012, 28, 3831—3839 |
| [9] | Kang C. H., Sandler S. I., Macromolecules,1988, 21, 3088—3095 |
| [10] | Connemann M., Gaube J., Leffrang U., Muller S., Pfennig A., J. Chem. Eng. Data, 1991, 36, 446—448 |
| [11] | Bailey F. E., Kucera J. L., ImhofL. G., J. Polym. Sci., 1958, 32, 517—518 |
| [12] | Senti F. R., Hellman N. N., Ludwig N. H., Babcock G. E., Tobin R., Glass C. A., Lamberts B. L. J. Polym. Sci., 1955, 17, 527—546 |
| [13] | Ioan C. E., Aberle T., Burchard W., Macromolecules,2000, 33, 5730—5739 |
| [14] | Helfrich M. R., Mangeney-Slavin L. K., Long M. S., Djoko Y., Keating C. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124, 13374—13375 |
| [15] | Yan X.H., Cheng R. S.,Acta Polymerica Sinica, 1989, (6), 647—654 |
| (严晓虎, 程镕时. 高分子学报, 1989, (6), 647—654) | |
| [16] | Liu C.G., Xie H. F., Zheng Y., Cheng R. S.,Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2008, (11), 1031—1036 |
| (刘承果, 谢鸿峰, 郑云, 程镕时. 高分子学报, 2008, (11), 1031—1036) | |
| [17] | Michielsen S., In Polymer Handbook, Ed.: Brandrup J., Immergut E. H., Grulke E. A., Abe A., Bloch D. R., John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2003 |
| [18] | van Heukelum A., Barkema G. T., Edelman M. W., van der Linden E., Hoog E. H. A., Tromp R. H., Macromolecules,2003, 36, 6662—6667 |
| [19] | Edelman M. W., van der Linden E., Tromp R. H., Macromolecules,2003, 36, 7783—7790 |
| [20] | Edelman M. W., Tromp R. H., van der Linden E., Phys. Rev. E, 2003, 67, 021404 |
| [1] | WANG Mingfang, FU Hua, FU Zhibo, WANG Yuerong, ZHANG Hongyang, ZHANG Min, HU Ping. Separation and Characterization of Polymer Blends Using Online Ultra-high Performance Liquid Chromatography-Size Exclusion Chromatography [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210865. |
| [2] | TANG Yuanhui, LI Chunyu, LIN Yakai, ZHANG Chunhui, LIU Ze, YU Lixin, WANG Haihui, WANG Xiaolin. Dissipative Particle Dynamics Simulation of the Effect of Polymer Chain Rigidity on Membranes Formation by Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation Process [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220169. |
| [3] | LIN Ningqin, YAO Ke, CHEN Xiangjun. Research Progress of Molecular Recognition and Interaction of Crystallins Linking Cataract [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3379. |
| [4] | GAO Miaomiao,WANG Chenglong,DOU Hongjing,XU Guoxiong. One-step Self-assembly/polymerization Fabrication and Biomedical Application of Carboplatin@Dextran Nanocarrier† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1301. |
| [5] | ZHENG Qiuguang,LIU Hailiang,XIAO Changfa. Preparation and Performance of Poly(vinylidene chloride-co-vinyl chloride) Porous Membranes via Thermally Induced Phase Separation† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 841. |
| [6] | LU Zhiwei, CHEN Shun, JU Yanyun, ZHANG Yang, XIONG Chuanxi, DONG Lijie. Synthesis and Properties of PS-b-P(DMS-stat-VMS) Block Copolymer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8): 1484. |
| [7] | XU Hongmei, LI Jie, QIAO Yunfan, ZHANG Min, ZHANG Hongyang, WANG Yuerong, HU Ping. Dispersion of Single-wall Carbon Nanotubes in Bile Salt Surfactants and Separation of SWCNTs(6,5) by Aqueous Two-phase Extraction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1148. |
| [8] | ZHAO Qi, HE Wanying, DUAN Lijie, ZHANG Yu, YU Shuangjiang, GAO Guanghui. Fabrication and Characterization of Injectable Polysaccharide-polypeptide Hydrogel Based on Schiff’s Base† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(9): 1750. |
| [9] | XU Fanhua, HENG Xiao, REN Jianxue, ZHOU Hengwei. Simulation Study of the Phase Separation and Self-assembly of Nanoparticles Coated with Ligands† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6): 1115. |
| [10] | LI Xingjian, WU Ruiqing, LAI Jingjuan, PAN Yi, ZHENG Zhaohui, DING Xiaobin. Shape-memory Properties and Molecular Mechanism of Poly(methyl methacrylate)/Star-shaped Poly(ethylene glycol) Semi-interpenetrating Polymer Network† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(10): 1932. |
| [11] | XUE Li, NIE Taotao, MA Haiyun. Precise Structural Regulation of Poly(L-lactide) Acid Tissue Engineering Scaffolds† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(7): 1409. |
| [12] | LI Xianhua, ZHANG Leigang, WANG Xuexue, YU Qingbo. Fabrication and Multi-antitumor Effect of Novel Dextran-hemin Crosslinked Micelles Triggered by Photo Conditions† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(5): 1004. |
| [13] | MU Siyang, GUO Jing, QI Shanwei, ZHANG Bo, ZHANG Hong, YU Yue. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly(acrylonitrile-co-itaconate)-graft-Poly(ethylene glycol) Copolymers as Novel Solid-Solid Phase Change Materials for Thermal Energy Storage† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(12): 2557. |
| [14] | HU Qi, FANG Chao, ZHAO Wai’ou, LI Yapeng, CHEN Xia, WANG Jingyuan. Synthetic of PGMA-EDA-g-PEG-g-DS@IO as a Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agent for Atherosclerosis† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 2061. |
| [15] | HE Ning, SUN Hechun, XU Huanxi, SHAO Zhangzhang. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Comblike Non-virus Gene Delivery Vector with the Poly(L-glutamic acid) as Backbone† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(9): 2019. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||