

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 180.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150510
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
TIAN Min1,2, YANG Yingjuan1,2, HE Wentao1,*( ), LI Juan1, QIN Shuhao1, YU Jie1,2,*(
), LI Juan1, QIN Shuhao1, YU Jie1,2,*( )
)
Received:2015-06-30
Online:2016-01-10
Published:2015-11-17
Contact:
HE Wentao,YU Jie
E-mail:wentaohe@aliyun.com;yujiegz@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
TIAN Min, YANG Yingjuan, HE Wentao, LI Juan, QIN Shuhao, YU Jie. Preparation, Characterization and Application of Silica Nanoparticle Micro-aggregates with Circular Structure†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(1): 180.
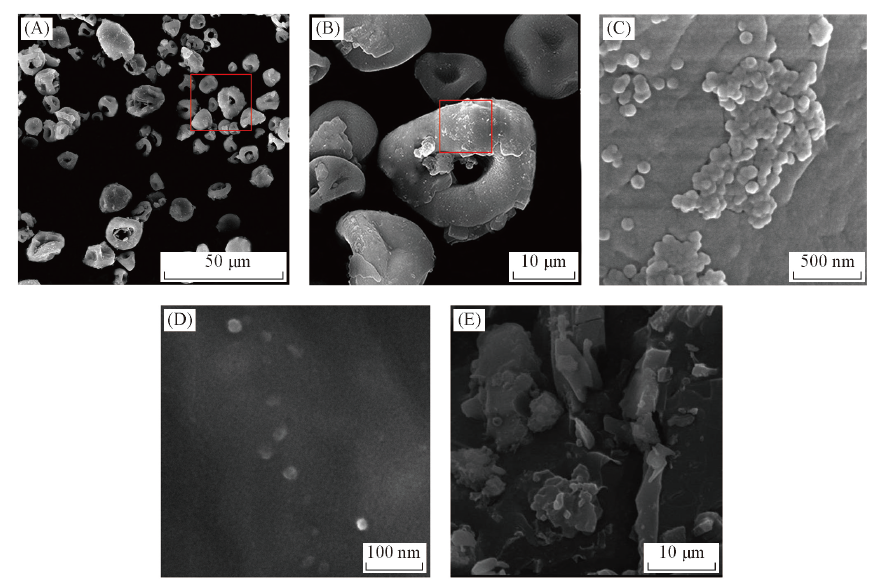
Fig.4 SEM images of PC16MS(A—D) and NC16MS(E)^(B) Partial view of (A); (C) partial view of (B); (D) re-dispersed in alcohol by ultrasonic and then dried on copper.
| Sample | Tc/℃ | Tm/℃ | Hm/(J·g-1) | Xc(%) | NE(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP | 111.39 | 164.85 | 90.94 | 43.51 | 0 |
| 0.2%PC16MS/PP | 112.08 | 165.02 | 91.49 | 43.78 | 2.6 |
| 2%PC16MS/PP | 121.79 | 164.43 | 94.18 | 45.06 | 39.1 |
| 2%NC16MS/PP | 114.65 | 164.48 | 94.46 | 45.20 | 12.3 |
Table 1 Crystalline parameters of PP and nucleated PP
| Sample | Tc/℃ | Tm/℃ | Hm/(J·g-1) | Xc(%) | NE(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP | 111.39 | 164.85 | 90.94 | 43.51 | 0 |
| 0.2%PC16MS/PP | 112.08 | 165.02 | 91.49 | 43.78 | 2.6 |
| 2%PC16MS/PP | 121.79 | 164.43 | 94.18 | 45.06 | 39.1 |
| 2%NC16MS/PP | 114.65 | 164.48 | 94.46 | 45.20 | 12.3 |
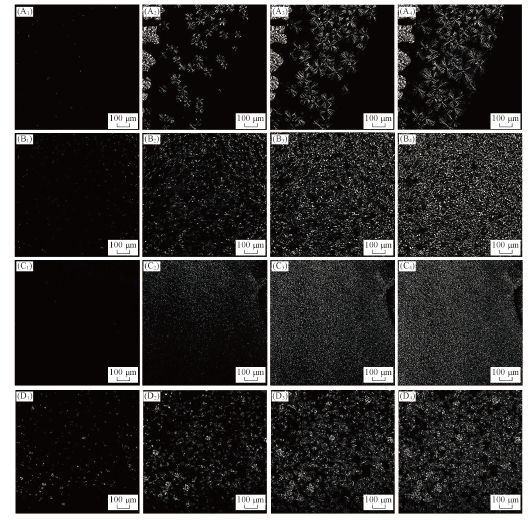
Fig.9 Polarized optical microscope images of PP(A1—A4), 0.2%PC16MS/PP(B1—B4), 2%PC16MS/PP(C1—C4) and 2%NC16MS/PP(D1—D4) composites^(A1—A4) are the POM photographs of PP on crystallizing at 15, 60, 105 and 150 min, respectively; (B1—4—D1—4) represent the crystallization time at 5, 7.5, 10 and 12.5 min, respectively.
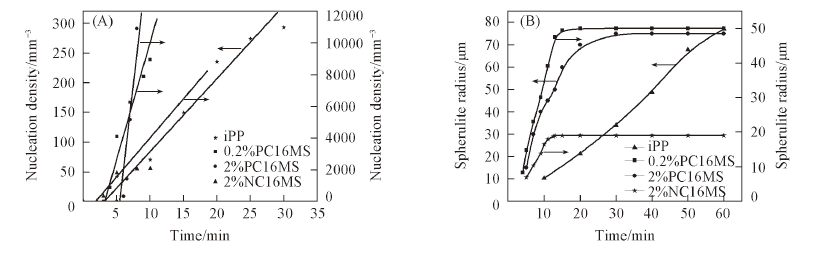
Fig.10 Nucleation density calibrated by the volume measured area in the POM(A) and the spherulite radius plotted(B) against the crystallization time for PP , NC16MS/PP and PC16MS/PP composites
| [1] | Jain S., Goossens H., van Duin M., Lemstra P., Polymer,2005, 46(20), 8805—8818 |
| [2] | Nitta K., Asuka K., Liu B., Terano M., Polymer,2006, 47(18), 6457—6463 |
| [3] | Asuka K., Liu B., Terano M., Nitta K. H., Macromol. Rapid Comm., 2006, 27(12), 910—913 |
| [4] | Sun D. H., Zhang R., Liu Z. M., Huang Y., Wang Y., He J., Han B. X., Yang G. Y., Macromolecules,2005, 38, 5617—5624 |
| [5] | García M., Van V. G., Jain S., Schrauwen B. A. G., Sarkissov A., Van Zyl W. E., Boukamp B., Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci., 2004, 6, 169—175 |
| [6] | Wu L. B., Cao D., Huang Y., Li B. G., Polymer,2008, 49, 742—748 |
| [7] | Li J., Qin S. H., He W. T., Xiang Y. S., Zhang Q., Zhang K., Zhang M. M., Zhou Y., Yu J., J. Polym. Eng., 2015, 35(6), 565—573 |
| [8] | Urata C., Aoyama Y., Tonegawa A., Yamauchi Y., Kuroda K.,Chem. Commun., 2009, (34), 5094—5096 |
| [9] | Nandiyanto A. B. D., Okuyama K., Adv. Powder Technol., 2011, 22(1), 1—19 |
| [10] | Iskandar F., Gradon L., Okuyama K., J.Colloid Interface Sci., 2003, 265, 296—303 |
| [11] | Sing K., Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp., 2001, 187/188, 3—9 |
| [12] | Hu J. S., Kong B., Chao C. Y., Sun J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(6), 1253—1255 |
| (胡建设, 孔波, 钞春英, 孙静. 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30(6), 1253—1255) | |
| [13] | Gahleitner M., Grein C., Kheirandish S., Wolfschwenger J., Int. Polym. Proc., 2011, 26(1), 2—20 |
| [14] | Lin Z., Huang Z., Zhang Y., Mai K., Zeng H., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2004, 91(4), 2443—2453 |
| [15] | Xu W., Ge M., He P., J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys., 2002, 40(5), 408—414 |
| [1] | JIANG Shenghan, CAO Changlin, XIAO Liren, YANG Tang, QIAN Qingrong, CHEN Qinghua. Preparation of Composite Semiconductor Micro-sheets with UV Shielding Performance and Its Application in Polypropylene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220071. |
| [2] | ZHOU Chengsi, ZHAO Yuanjin, HAN Meichen, YANG Xia, LIU Chenguang, HE Aihua. Regulation of Silanes as External Electron Donors on Propylene/butene Sequential Polymerization [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220290. |
| [3] | LI Yichuan, ZHU Guofu, WANG Yu, CHAI Yongming, LIU Chenguang, HE Shengbao. Effects of Substrate Surface Properties and Precursor Chemical Environment on In⁃situ Oriented Construction of Titanium Silicalite Zeolite Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2934. |
| [4] | LI Yanyan, DUAN Linrui, LUO Jingshan. Moisture-assisted Crystallization of Inorganic Perovskite CsPbI3 Film [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1785. |
| [5] | DU Bin, CHEN Shangtao, ZHANG Fengbo, SHI Xingbo, LI Rongbo. Nonlinear Rheological Behavior of Long Chain Branching Polypropylene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2034. |
| [6] | MIAO Weijun, WU Feng, WANG Yong, WANG Zongbao. In⁃situ Study of the Epitaxial Crystallization of PCL/RGO at High Shear Rate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 910. |
| [7] | WANG Bodong, PAN Meichen, ZHUO Ying. Construction of Electrochemiluminescence Sensing Interface Based on Silver Nanoclusters-Silica Nanoparticles and Biomolecular Recognition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3519. |
| [8] | HUANG Huilong, HUANG Hanxiong. Low-temperature Impact Behavior of Droplet on Injection-compression Molded Nanostructured PP/POE Blend Surfaces [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3195. |
| [9] | WANG Juan, WANG Linying, ZHU Dali, CUI Wenhao, WANG Yifeng, TIAN Peng, LIU Zhongmin. Progress in Direct Synthesis of High Silica Zeolite Y [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 1. |
| [10] | WU Qinming, WANG Yeqing, MENG Xiangju, XIAO Fengshou. Reconsideration of Crystallization Process for Aluminosilicate Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 21. |
| [11] | WANG Huan, SUO Jinquan, WANG Chunyan, WANG Runwei. Glucose Oxidase Immobilization with Amino Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and Its Application in Glucose Detection [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1731. |
| [12] | AN Yue, HUANG Hanxiong. Condensate Microdrop Dynamic Behavior on Injection-compression Molded Bionic Polypropylene Nanosurfaces [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1888. |
| [13] | WANG Yang, WANG Sidi, TANG Shaokun. Synthesis and Characterization of Imine-based Covalent Organic Framework(COF-LZU1) in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1792. |
| [14] | ZHANG Chenyang,WEN Yuehua,ZHAO Pengcheng,CHENG Jie,QIU Jingyi,SUN Yanzhi. Effect of Organic Carbon Source on Performance of LiTi2(PO4)3/C Composite Electrodes in Aqueous Solutions † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1352. |
| [15] | HE Zhechao, XIA Kun, WANG Jing, ZHOU Dan, LU Xinhuan, XIA Qinghua. Controllable Synthesis of SAPO-5 Molecular Sieves and Exploration of the Crystallization Process † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1224. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||