

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (8): 1606.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150069
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIANG Longqi, HUANG Weimin*( ), LIN Haibo
), LIN Haibo
Received:2015-01-20
Online:2015-08-10
Published:2015-07-17
Contact:
HUANG Weimin
E-mail:huangwm@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIANG Longqi, HUANG Weimin, LIN Haibo. Electrochemical Oxidation of Dimethyl Phthalate on Porous Titanium Based Boron-dopped Diamond Electrode†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(8): 1606.
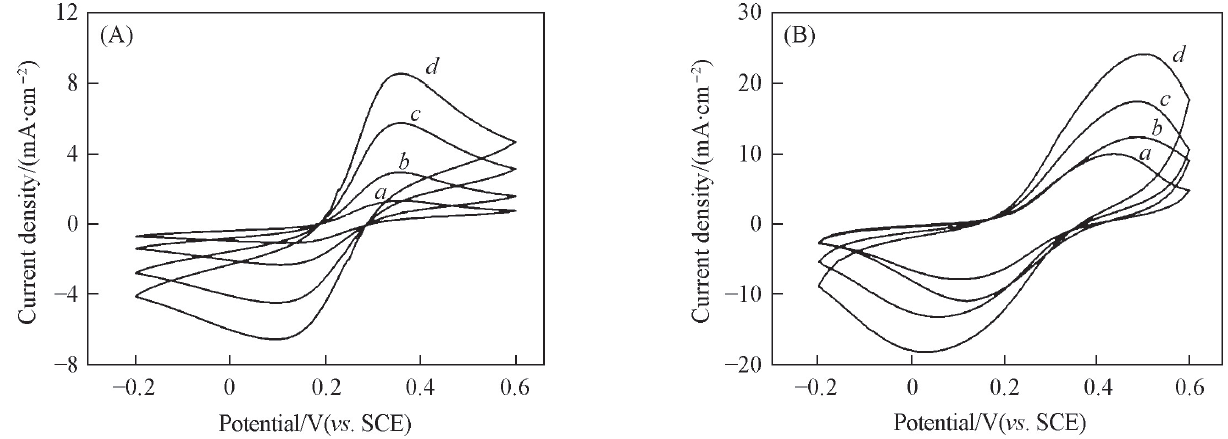
Fig.1 Cyclic voltammograms of planar Ti/BPP electrode(A) and porous Ti/BDD electrode(B) in 1 mol/L KCl solution with different concentrations of [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-Concentration of [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-/(mol·L-1): a. 5; b. 10; c. 20; d. 30.
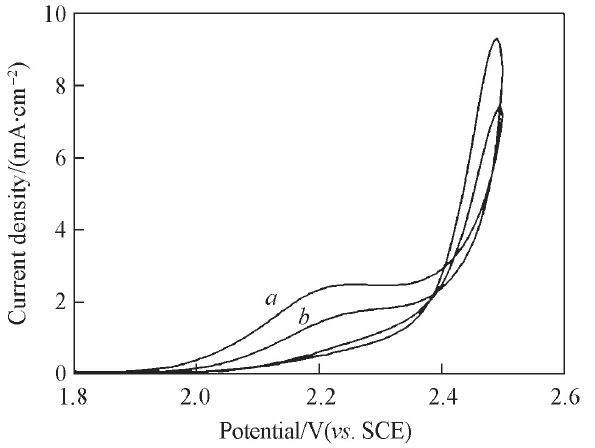
Fig.2 Cyclic voltammograms of planar Ti/BDD electrodes at scan rate of 100 mV/s in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 containing 100 mg/L DMPa. The 1st cycle; b. the 5th cycle.
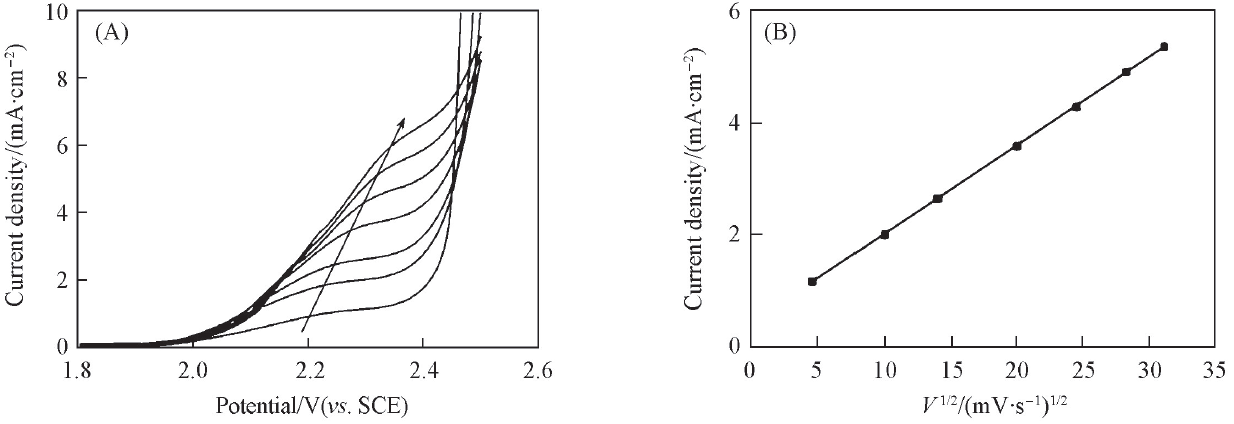
Fig.3 Linear sweep voltammograms of a planar Ti/BDD electrode in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solution containing 100 mg/L DMP at different scan rates(A) and the relationship between response current density and square root of scan rate(B)The scan rates are 20, 100, 200, 400, 600, 800 and 1000 mV/s with the direction of the arrow.
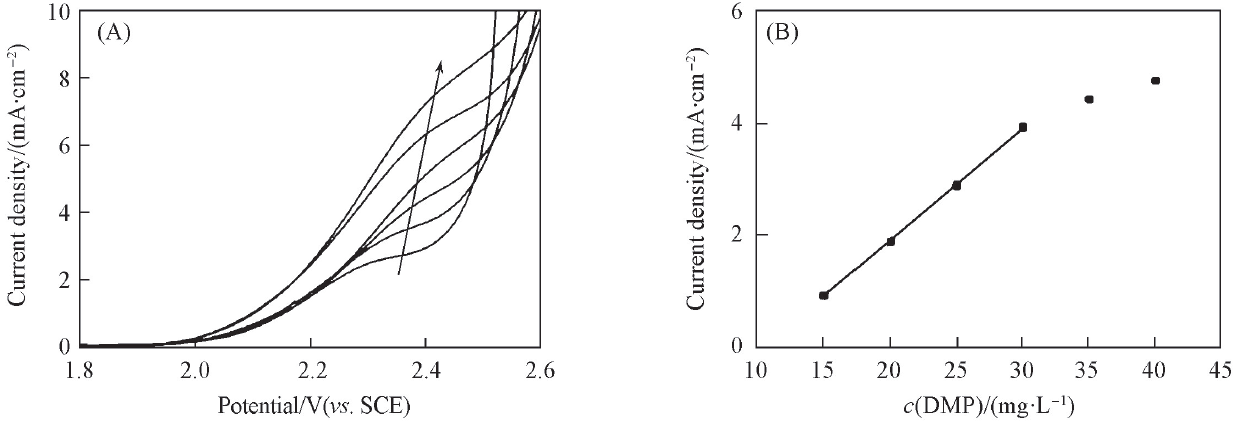
Fig.4 Linear sweep voltammograms of planar Ti/BDD electrode in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solution containing different concentrations of DMP(A) and relationship between response current density and DMP concentration(B)The concentration of DMP is 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 and 40 mmol/L with the direction of the arrow.
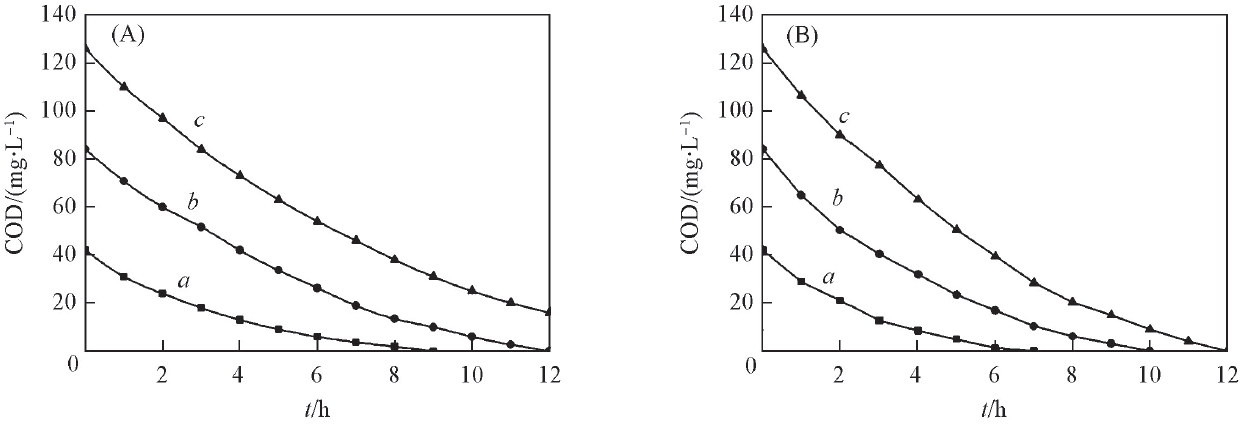
Fig.5 Change of COD value during the degradation of DMP at planar Ti/BDD(A) and porous Ti/BDD anodes(B)Concentration of DMP/(mg·L-1): a. 20; b. 40; c.60.
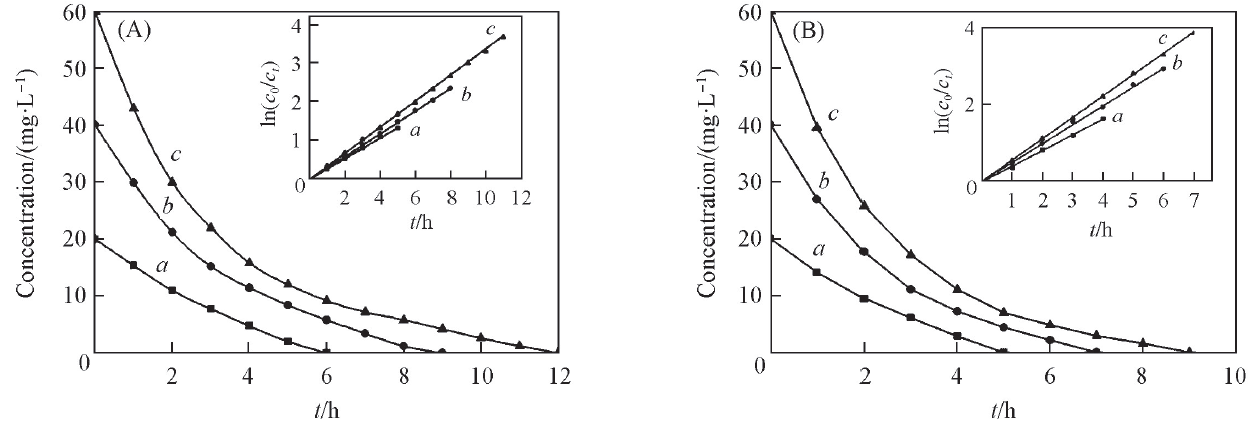
Fig.6 Change of concentration of DMP during degradation using planar Ti/BDD(A) and porous Ti/BDD anodes(B)Concentration of DMP/(mg·L-1): a. 20; b. 40; c.60.The insets show the relationship between value of ln(c0/ct) and time.
| [1] | Giam C. S., Chan H. S., Neff. G. S., Atlas E. L., Science, 1978, 199(4327), 419—421 |
| [2] | Baikova S. V., Samsonova A. S., Aleshchenkova Z. M., Shcherbina A. N., Eurasian Soil Sci., 1999, 32, 701—704 |
| [3] | Hou Y. N., Qu J. H., Zhan X., Liu H. J., J. Environ. Sci., 2009, 21, 1321—1328 |
| [4] | Yin X. T., Xu Q., Wu S. Y., Wang M., Gu Z. Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(4), 690—695 |
| (殷雪琰, 许茜, 吴淑燕, 王敏, 顾忠泽. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(4), 690—695) | |
| [5] | Wolf C., Lanbright C., Mann P., Price M., Cooper R. L., Ostby J., Gray L. E., Toxicol. Ind. Health, 1999, 15(1/2), 94—118 |
| [6] | Zacharewski T. R., Meek M. D., Clemons J. H., Wu Z. F., Fielden M. R., Matthews J. B., Toxicolo. Sci., 1998, 46(2), 282—293 |
| [7] | Jobling S., Reynolds T., White R., Parker M. G., Sumper J. P., Environ.Health Persp., 1995, 103(6), 582—587 |
| [8] | Stales C. A., Peterson D. R., Parkerton T. F., Adams W. J., Chemosphere, 1997, 35(4), 667—749 |
| [9] | Rodgers J. D., Jedral W., Bunce N. J., Enviro. Sci. Tech., 1999, 33(9), 1453—1457 |
| [10] | Wu M. H., Liu N., Xu G., Ma J., Tang L., Wang L., Fu H. Y., Radiat. Phys. Chem., 2011, 80(3), 420—425 |
| [11] | Torres R. A., Torres W., Periger P., Pulgarin C., Chemosphere, 2003, 50(1), 97—104 |
| [12] | Brillas E., Boye B., Sires J., Garrido J. A., Rodriguez R. M., Arias C., Cabot P., Chemosphere, 2004, 49(25), 4487—4496 |
| [13] | Chen X., Chen G., Gao F., Yue L. P., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2003, 37, 5021—5026 |
| [14] | Iniesta J., Michaud P. A., Panizza M., Cerisola G., Aldaz A., Comninellis C., Electrochim. Acta, 2001, 46(23), 3573—3578 |
| [15] | Rodrigo M. A., Michaud P. A., Duo I., Panizza M., Cerisola G., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2001, 148(5), D60—D64 |
| [16] | Panizza M., Michaud P. A., Cerosola G., Comninellis C., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2001, 507(1/2), 206—214 |
| [17] | Canizares P., Saez C., Lobato J., Rodrigo M. A., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2004, 43(9), 1944—1951 |
| [18] | Montilla F., Michaud P. A., Morallon E., Vazquez J. L., Comninellis C., Electrochim. Acta, 2002, 47(21), 3509—3513 |
| [19] | Canizares P., Garcia-Gomez J., Lobato J., Rodrigo M. A., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2003, 42(5), 956—962 |
| [20] | Braga N. A., Baldan M. R., Ferreira N. G. J. Mater. Sci., 2012, 47, 23—40 |
| [21] | Canizares P., Saez C., Lobato J., Paz R., Rodrigo M. A., J. Electroche. Soc., 2007, 154, E37—E44 |
| [22] | Panizza M., Cerisola G., Electrochim. Acta, 2005, 51, 191—199 |
| [23] | Li H., Zhu X., Jiang Y., Ni J., Chemosphere, 2010, 80, 845—851 |
| [24] | Souzad F., Saez C., Canizares P., Motheo D. A., Rodrigo M., J. Chem. Tech. Biotech., 2014, 89, 282—289 |
| [25] | Vazquez-Gomez L., Battisti D. A., Ferro S., Cerro M., Reyna S., Clean-Soil, Air Water, 2012, 40, 408—415 |
| [1] | GONG Yanxi, WANG Jianbing, CHAI Buyu, HAN Yuanchun, MA Yunfei, JIA Chaomin. Preparation of Potassium Doped g-C3N4 Thin Film Photoanode and Its Application in Photoelectrocatalytic Oxidation of Diclofenac Sodium in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220005. |
| [2] | HUANG Weimin, LIN Haibo. Effect of Structure of Ti/Boron-doped Diamond Electrode on the Electrochemical Degradation Performance for Aspirin† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1765. |
| [3] | LI Haili, ZHU Hongqiao, CAO Fahe, LENG Wenhua. Enhanced the Performance of Photoelectrochemical Oxidation of Water over BiVO4 Film Electrodes by Electrochemical Reduction Pretreatment† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(2): 377. |
| [4] | MA Chun-An, WANG Fen, LU Jin-Jin, LI Mei-Chao, ZHENG Wan-Fang. Studies on Electrochemical Oxidation Reaction of 2,4-Dichlorophenol on Pt Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(12): 2850. |
| [5] | HUANG Yao, ZHU Zhao-Jin, XU Jing-Kun, LU Bao-Yang, YUE Rui-Rui. Novel Copolymers Synthesis by Second Polymerization of Acrylate Acid Grafted 1,2-Dihydroxylbenzene Derivatives [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(03): 608. |
| [6] | WANG Xuan, HUANG Wei-Min, LIU Xiao-Bo, LU Hai-Yan, LIN Hai-Bo*. Influence of Chloride Ion on Electrochemical Oxidation Degradation of Phenol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(2): 361. |
| [7] | WANG Gui-Ling1, WANG Jing1, CAO Dian-Xue1*, TANG Yong-Fu1, L Yan-Zhuo1, LU Tian-Hong2, XING Wei2. Performance of Electrochemical Oxidation of Carbon in Molten Carbonates [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(9): 1829. |
| [8] | LIU Xiao-Bo, HUANG Wei-Min , REN Xiu-Bin, DONG Yan-Jie, XU Hong, LIN Hai-Bo*. Effect of Structure-Activity Relationship on Electrochemical Degradation of Substituted Aniline [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(6): 1131. |
| [9] |
WANG Hai-Tao1,2, ZHAO Mei-Ling2, XU Wei-Lin1, XING Wei1, LU Tian-Hong1.
Effect of Rare Earth Ions on Electro-oxidation of Methanol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(2): 352. |
| [10] | XU Wei, ZHU Rong-Jiao, LIU Zhi-Hua, TIAN Yi-Ling, LI Dan. Isobaric Vapor-liquid Equilibria of Binary System of Maleic Anhydride and Dimethyl Phthalate at 4.00, 8.00 and 12.00 kPa [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(12): 2349. |
| [11] | LIN Hai-Bo, LIU Xiao-Bo, SUN Zhi-Quan, ZHANG Heng-Bin. Electrochemical Oxidation-degradation of Phenol on Ti/PbO2 and Ti/Ru-Ti-Sn Oxide Coating Electrodes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2005, 26(9): 1704. |
| [12] | DU Bing-Chen, LIU Jing-Hua, XUE Xin-Zhong, XU Wei-Lin, XING Wei, LU Tian-Hong, SANG Ge . Studies on Promoting Catalysis of Sm3+ Towards Oxidation of Methanol on the Pt Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(5): 917. |
| [13] | LÜ Yan-Zhuo, HAN Fei, LIU Chang-Peng, LI Chang-Zhi, XING Wei, LU Tian-Hong, SANG Ge . Promotion Effect of Heteropoly Acids Modified Electrode to Methanol Electrochemical Oxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(10): 1909. |
| [14] | HE Jian-Bo, LIN Jian-Xin. A Study of Anodic Process of Copper in NaOH Solution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1996, 17(2): 290. |
| [15] | Guo Chun-xiao, Huang Chu-bao, Guo Fu-chun, Hou Dong-yan. The Quantum Chemistry Studies on Electrochemical Oxidation-Reduction of FeTPP and CoTPP [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1991, 12(9): 1242. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||