

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (6): 1067.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150008
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Jiang, LI Qian, GU Haiwei, GUO Xiaotun, YANG Shuiping*( ), WANG Zhihao
), WANG Zhihao
Received:2015-01-04
Online:2015-06-10
Published:2015-05-08
Contact:
YANG Shuiping
E-mail:wxipysp@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Jiang, LI Qian, GU Haiwei, GUO Xiaotun, YANG Shuiping, WANG Zhihao. Direct Analysis of Micro Area on Tooth Surface by Surface Desorption Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(6): 1067.
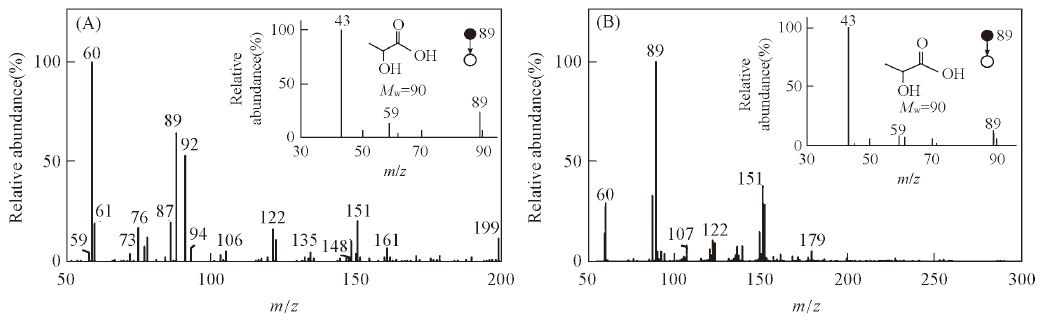
Fig.2 SDAPCI-MS spectra of a cavity sample(A) and standard lactic acid(B) in negative ion detection mode Insets are MS/MS spectra of the peak at m/z 89(lactic acid).
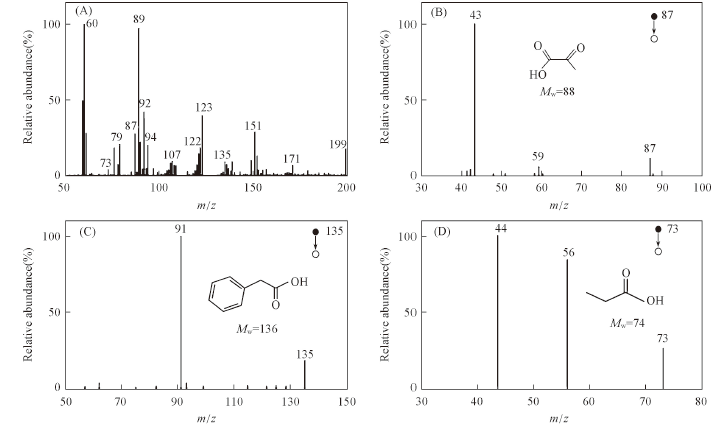
Fig.4 nano-SDAPCI-MS(A) and MS/MS(B—D) spectra for cavity samples in negative ion detection mode(B)—(D): MS/MS spectra of m/z 87, 135 and 73, respectively.
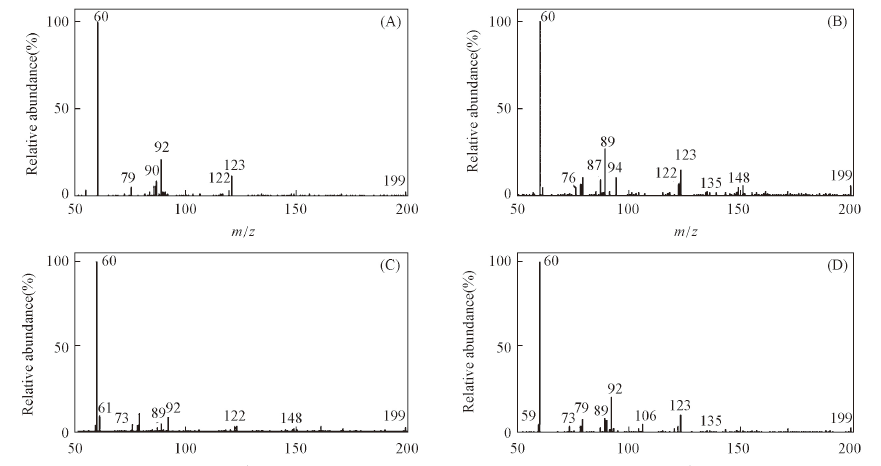
Fig.5 SDAPCI-MS spectra of an acupuncture needle for a blank sample(A), edge of cavity(B), tooth cusp(C) and tooth sulcus(D) from one tooth in negative ion detection mode
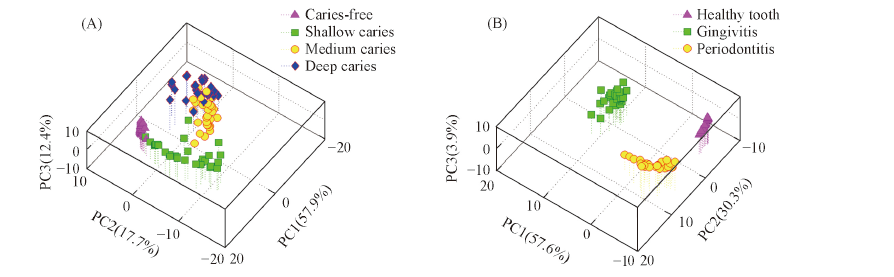
Fig.7 PCA results of dental disease in different degrees using SDAPCI-MS data in negative ion detection mode (A) 3D plots of PCA of caries-free, shallow caries, medium caries and deep caries; (B) 3D plots of PCA of healthy tooth, gingivitis, and periodontitis.
| [1] | Hertz-Schünemann R., Streibel T., Ehlert S., Zimmermann R., Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2013, 405(22), 7083—7096 |
| [2] | Xu Q., Wang M., Yu S. Q., Tao Q., Tang M., Analyst, 2011, 136(23), 5030—5037 |
| [3] | Wurz P., Abplanalp D., Tulej M., Iakovleva M., Fernandes V., Chumikov A., Managadze G., Solar Syst. Res., 2012, 46(6), 408—422 |
| [4] | Wang Q. G., Li D., Lu N., Tong D. Y., Zhuang H. J., Li F. Q., Wang L., Duan H. F., Lin Y. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(10), 2114—2118 |
| (王庆国, 李丹, 鹿宁, 童丁毅, 庄何靖, 李福秋, 王岚, 段海峰, 林英杰.高等学校化学学报, 2014,35(10), 2114—2118) | |
| [5] | Xiu Y., Zhou Y., Gao Q., Chen J. S., Li G. D., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2013, 29(1), 189—192 |
| [6] | Arrowsmith P., Anal. Chem., 1987, 59(10), 1437—1444 |
| [7] | Abdullah M. M., Ly A. R., Goldberg W. A., Clarke-Stewart K. A., Dudgeon J. V., Mull C. G., Chan T. J., Kent E. E., Mason A. Z., Ericson J. E., J. Autism Dev. Disord., 2012, 42(6), 929—936 |
| [8] | Huth K.C., Lussi A., Gygax M., Thum M., Crispin A., Paschos E., Hickel R., Neuhaus K. W., J. Dent., 2010, 38(12), 1019—1026 |
| [9] | Liu M. W., He Y., Adv. Earth. Sci., 2003, 18(1), 116—121 |
| (刘民武, 赫英.地球科学进展, 2003,18(1), 116—121) | |
| [10] | Zhang D., Feng L. X., Wang J., Shen D. R., Xiong J. P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(9), 1889—1895 |
| (张丹, 冯流星, 王军, 申黛瑞, 熊金平.高等学校化学学报, 2014,35(9), 1889—1895) | |
| [11] | Liu Y., Yang Z. W., Desyaterik Y., Gassman P. L., Wang H., Laskin A., Anal. Chem., 2008, 80(3), 633—642 |
| [12] | Dierolf M., Menzel A., Thibault P., Schneider P., Kewish C. M., Wepf R., Bunk O., Pfeiffer F., Nature, 2010, 467(7314), 436—439 |
| [13] | Wang J. Z., Lu L., Choucair M., Stride J. A., Xu X., Liu H. K., J. Power Sources, 2011, 196(16), 7030—7034 |
| [14] | Ma G. B., Yang P., Chemistry, 1993, 3(3), 29—29 |
| (马贵斌, 杨频.化学通报, 1993,3(3), 29—29) | |
| [15] | Chen H. W., Lai J. H., Zhou Y. F., Xun Y. F., Li J. Q., Zhang X., Wang Z. C., Luo M. B., Chinese J. Anal. Chem., 2007, 35(8), 1233—1240 |
| (陈焕文, 赖劲虎, 周瑜芬, 郇延富, 李建强, 张燮, 王志畅, 罗明标.分析化学, 2007,35(8), 1233—1240) | |
| [16] | Weston D. J., Analyst, 2010, 135(4), 661—668 |
| [17] | Kavvalakis M. P., Tzatzarakis M. N., Theodoropoulou E. P., Barbounis E. G., Tsakalof A. K., Tsatsakis A. M., Chemosphere, 2013, 93(10), 2612—2620 |
| [18] | Takats Z., Wiseman J. M., Gologan B., Cooks R. G., Science, 2004, 306(5695), 471—473 |
| [19] | Zhang X. L., Jia B., Huang K. K., Hu B., Chen R., Chen H. W., Anal. Chem., 2010, 82(19), 8060—8070 |
| [20] | Yang S. P., Ding J. H., Zheng J., Hu B., Li J. Q., Chen H. W., Zhou Z. Q., Qiao X. L., Anal. Chem., 2009, 81(7), 2426—2436 |
| [21] | Li J. Q., Jia B., Hu B., Chen H. W., Zeng X. T., Xiao R. H., Chinese. J. Anal. Chem., 2010, 38(9), 1325—1328 |
| (李建强, 贾滨, 胡斌, 陈焕文, 曾祥泰, 肖日海.分析化学, 2010,38(9), 1325—1328) | |
| [22] | Zhu L., Yan J. P., Zhu Z. Q., Ouyang Y. Z., Zhang X. L., Zhang W. J., Dai X. M., Luo L. P., Chen H. W., J. Agric. Food Chem., 2013, 61(3), 547—552 |
| [23] | Luo L. P., Wang J., Zhang W. J., Dai X. M., Fang X. W., Zhang X., Liu Y. L., Chen H. W., Chinese J. Anal. Chem., 2013, 41(7), 1050—1056 |
| (罗丽萍, 王姜, 章文军, 戴喜末, 方小伟, 张茜, 刘亚丽, 陈焕文.分析化学, 2013,41(7), 1050—1056) | |
| [24] | Wang J., Yang S. P., Yan F. Y., Liu Y., Li M., Song Y. H., Zhan Y. B., Chen H. W., Chinese J. Anal. Chem., 2010, 38(4), 453—457 |
| (王姜, 杨水平, 鄢飞燕, 刘艳, 李明, 宋宇航, 占叶兵, 陈焕文.分析化学, 2010,38(4), 453—457) | |
| [25] | Wold S., Esbensen K., Geladi P., Chemometr. Intell. Lab, 1987, 2(1), 37—52 |
| [26] | Margolis H. C., Moreno E. C., Crit. Rev. Oral. Biol. Med., 1994, 5(1), 1—25 |
| [27] | Ross K. L., Tu T. T., Smith S., Dalluge J. J., Anal. Chem., 2007, 79(13), 4840—4844 |
| [28] | Selwitz R. H., Ismail A. I., Pitts N. B., The Lancet, 2007, 369(9555), 51—59 |
| [29] | Bandu M. L., Watkins K. R., Bretthauer M. L., Moore C. A., Desaire H., Anal. Chem., 2004, 76(6), 1746—1753 |
| [30] | Marahatta A., Bhandary B., Lee M., Kim D. S., Lee Y. C., Kim S. R., Kim H. R., Chae H. J., J. Chrom. B, 2012, 903, 118—125 |
| [31] | Donald L.P., Garry M. L., George S. K., WB Saunder’s College Publishers, 1996, 300—310 |
| [32] | Li M., Jia B., Ding L.Y., Hong F., Ouyang Y. Z., Chen R., Zhou S. M., Chen H. W., Fang X., J. Mass Spectrom., 2013, 48(9), 1042—1049 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||