

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 589.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20130971
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Jiandong1, HUANG Zhanggen2,*( ), LI Zhe1,*(
), LI Zhe1,*( ), GUO Qianqian2, LI Qiaoyan2
), GUO Qianqian2, LI Qiaoyan2
Received:2013-10-08
Online:2014-03-10
Published:2019-08-01
Contact:
HUANG Zhanggen,LI Zhe
E-mail:zghuang@sxicc.ac.cn;lizhe@tyut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Jiandong, HUANG Zhanggen, LI Zhe, GUO Qianqian, LI Qiaoyan. Ce Modification on Mn/TiO2/cordierite Monolithic Catalyst for Low-temperature NOx Reduction†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(3): 589.
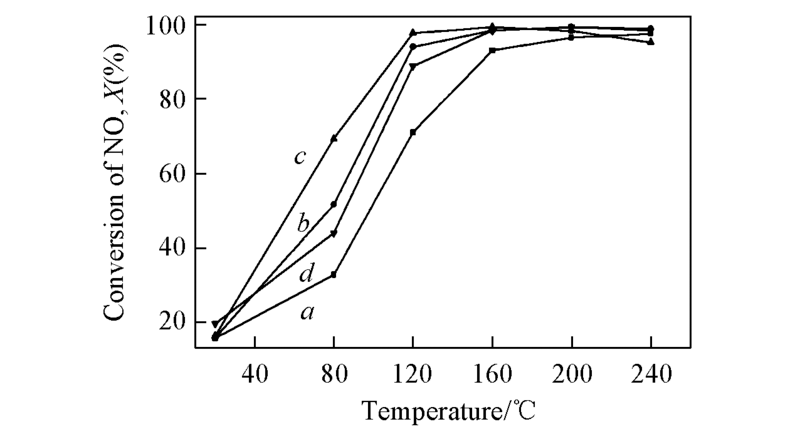
Fig.1 Influence of Ce on the catalytic activity of Mn-Ce(x)/TiO2/CC catalysts a. Mn/TiO2/CC; b. Mn-Ce(0.10)/TiO2/CC; c. Mn-Ce(0.15)/TiO2/CC; d. Mn-Ce(0.40)/TiO2/CC.
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Vt/(cm3·g-1) | Vmicro/(cm3·g-1) | Dp/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated cordierite | 0.0003 | 6.80 | ||
| Pretreated cordierite with ammonia | 42 | 0.0236 | 0.0079 | 2.27 |
| TiO2/CC | 43 | 0.0390 | 0.0071 | 3.64 |
| Mn/TiO2/CC | 42 | 0.0379 | 0.0055 | 3.62 |
| Mn-Ce(0.10)/TiO2/CC | 43 | 0.0385 | 0.0061 | 3.68 |
| Mn-Ce(0.15)/TiO2/CC | 45 | 0.0401 | 0.0065 | 3.57 |
| Mn-Ce(0.40)/TiO2/CC | 39 | 0.0354 | 0.0054 | 3.66 |
| TiO2 | 59 | 0.0894 | 6.08 |
Table 1 Physical characteristic of the samples
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Vt/(cm3·g-1) | Vmicro/(cm3·g-1) | Dp/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated cordierite | 0.0003 | 6.80 | ||
| Pretreated cordierite with ammonia | 42 | 0.0236 | 0.0079 | 2.27 |
| TiO2/CC | 43 | 0.0390 | 0.0071 | 3.64 |
| Mn/TiO2/CC | 42 | 0.0379 | 0.0055 | 3.62 |
| Mn-Ce(0.10)/TiO2/CC | 43 | 0.0385 | 0.0061 | 3.68 |
| Mn-Ce(0.15)/TiO2/CC | 45 | 0.0401 | 0.0065 | 3.57 |
| Mn-Ce(0.40)/TiO2/CC | 39 | 0.0354 | 0.0054 | 3.66 |
| TiO2 | 59 | 0.0894 | 6.08 |
| Catalyst | Surface atomic content(%) | Molar ratio of Mn4+/(Mn3++Mn4+) | Molar ratio of Oα/(Oα+Oβ) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ce | Mn | Ti | O | |||
| Mn/TiO2/CC | 13.76 | 15.96 | 70.28 | 0.60 | 0.16 | |
| Mn-Ce(0.15)/TiO2/CC | 5.89 | 8.60 | 14.78 | 70.73 | 0.76 | 0.31 |
Table 2 XPS results of monolithic catalysts
| Catalyst | Surface atomic content(%) | Molar ratio of Mn4+/(Mn3++Mn4+) | Molar ratio of Oα/(Oα+Oβ) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ce | Mn | Ti | O | |||
| Mn/TiO2/CC | 13.76 | 15.96 | 70.28 | 0.60 | 0.16 | |
| Mn-Ce(0.15)/TiO2/CC | 5.89 | 8.60 | 14.78 | 70.73 | 0.76 | 0.31 |
| Catalyst | Mass fraction by ICP(%) | Surface atomic content by XPS(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | Ce | Mn | Ce | |
| Mn/TiO2/CC | 1.18 | 13.76 | ||
| Mn-Ce(0.15)/TiO2/CC | 1.12 | 0.52 | 8.60 | 5.89 |
Table 3 Total loading and surface chemical composition of different catalysts
| Catalyst | Mass fraction by ICP(%) | Surface atomic content by XPS(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | Ce | Mn | Ce | |
| Mn/TiO2/CC | 1.18 | 13.76 | ||
| Mn-Ce(0.15)/TiO2/CC | 1.12 | 0.52 | 8.60 | 5.89 |
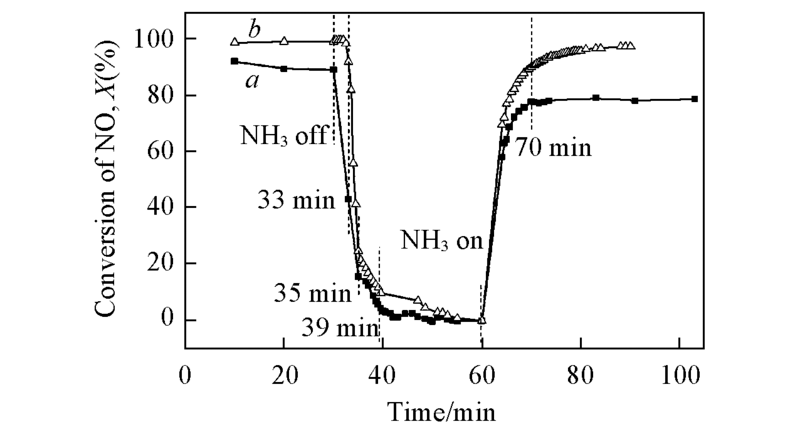
Fig.4 NH3 transient response of the SCR reaction over monolithic catalysts at 120 ℃a. Mn/TiO2/CC; b. Mn-Ce(0.15)/TiO2/CC. Reaction conditions: 0.05% NO, 0.05% NH3, 5% O2, balanced by N2, 400 mL/min of total flow rate; GHSV=6000 h-1.
| [1] | Qi G., Yang R. T., J. Phys. Chem. B,2004, 108(40), 15738—15747 |
| [2] | Twigg M. V., Appl. Catal. B, 2007, 70(1), 2—15 |
| [3] | Lietti L., Ramis G., Berti F., Appl. Catal. B,1998, 18(1), 1—36 |
| [4] | Zheng Z. H., Tong H., Tong Z. Q., Huang Y., Luo Y., Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology,2010, 38(3), 343—351 |
| (郑足红, 童华, 童志权, 黄妍, 罗英. 燃料化学学报, 2010, 38(3), 343—351) | |
| [5] | Huang Z., Zhu Z., Liu Z., Appl. Catal. B,2002, 39(4), 361—368 |
| [6] | Peña D. A., Uphade B. S., Reddy E. P., Smirniotis P. G., J. Phys. Chem. B,2004, 108(28), 9927—9936 |
| [7] | Pena D. A., Uphade B. S., Smirniotis P. G., J. Catal., 2004, 221(2), 421—431 |
| [8] | Smirniotis P. G., Pena D. A., Uphade B. S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2001, 40(13), 2479—2482 |
| [9] | Qi G., Yang R. T., J. Catal., 2003, 217(2), 434—441 |
| [10] | Long R. Q., Yang R. T., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1999, 121(23), 5595—5596 |
| [11] | Long R., Yang R., Appl. Catal. B,2000, 27(2), 87—95 |
| [12] | Wu Z., Jiang B., Liu Y., Zhao W., Guan B., J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 145(3), 488—494 |
| [13] | Wu Z., Jin R., Liu Y., Wang H., Catal. Commun., 2008, 9(13), 2217—2220 |
| [14] | Zhang X., Ji L., Zhang S., Yang W., J. Power Sources,2007, 173(2), 1017—1023 |
| [15] | Romeo M., Bak K., El Fallah J., Le Normand F., Hilaire L., Surf. Interface Anal., 1993, 20(6), 508—512 |
| [16] | Kang M., Park E. D., Kim J. M., Yie J. E., Appl. Catal. B,2007, 327(2), 261—269 |
| [17] | Yang S., Zhu W., Jiang Z., Chen Z., Wang J., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2006, 252(24), 8499—8505 |
| [18] | Jing L., Xu Z., Sun X., Shang J., Cai W., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2001, 180(3), 308—314 |
| [19] | He L. F., Liu J. D., Huang W., Li Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2012, 33(11), 2532—2536 |
| (贺丽芳, 刘建东, 黄伟, 李哲. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(11), 2532—2536) | |
| [20] | Busca G., Lietti L., Ramis G., Berty F., Appl. Catal. B,1998, 18(1/2), 1—36 |
| [21] | Yao S. M., Zhang J. W., Guo X., Qiu X. P., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2013, 29(2), 307—310 |
| [22] | Long R., Yang R., J. Catal., 2001, 198(1), 20—28 |
| [23] | Koebel M., Madia G., Elsener M., Catal. Today,2002, 73(3), 239—247 |
| [1] | YANG Lijun, YU Yang, ZHANG Lei. Construction of Dual-functional 2D/3D Hydrid Co2P-CeO x Heterostructure Integrated Electrode for Electrocatalytic Urea Oxidation Assisted Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220082. |
| [2] | WANG Qishun, ZHANG Zeshu, WANG Huan, LIU Yu, SONG Shuyan, ZHANG Hongjie. Synthesis and Enzymatic Activity of Ni, Ru Co-doped CePO4 Nanomaterials † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 947. |
| [3] | ZHANG Ling,DUAN Hongchang,TAN Zhengguo,WU Qinming,MENG Xiangju,XIAO Fengshou. Recent Advances in the Preparation of 8MR Zeolites for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx(NH3-SCR) in Diesel Engines † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 19. |
| [4] | DU Yifan, AI Chaoqian, ZHANG Yaoyao, WANG Wei. Preparation and Quasi-superhydrophobic Properties of the Surface of Mullite Whiskers/Cordierite † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1955. |
| [5] |
ZHANG Yan, ZHANG Shengming, FANG Guizhen.
Antioxidant Property of Catalyzed Lignosulfonate Using S2 |
| [6] | LI Xiaoci, XI Zhiwen, LIU Xing, LI Ming, HAO Zhixian, ZHU Zhirong. Effect of Additives TiO2 on Catalyst Performance for Dehydrogenation of Ethylbenzene to Styrene† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1229. |
| [7] | SUN Xiangli, HE Hong, SU Yaochao, YAN Jingfang, SONG Liyun, QIU Wenge. CeO2-TiO2 Mixed Oxides Catalysts for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3: Structure-properties Relationships† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 814. |
| [8] | YANG Caihong, MAN Chunli, XUE Wanlei, WANG Ting, CHEN Di, CHEN Qian, WU Liguang. Fabrication of TiO2-GO/PI Mixed Matrix Membranes by In-situ Polymerization and Their Gas Permeation Property† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(4): 686. |
| [9] | BAO Yan, GAO Min, DONG Yufei, KANG Qiaoling, GAO Zhipeng, WU Guodong, LI Yan. Fabrication of Hollow TiO2 Spheres and Effect on Properties of Polyacrylate Film† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12): 2328. |
| [10] | ZHENG Jiawei, JIANG Ling, DING Yong, MO Lie, DING Youcai, HU Linhua, DAI Songyuan. Influence of Au Doping on the Surface States and Charge Transport in TiO2 Films† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 2038. |
| [11] | YANG Ziwei, ZHOU Shunli, WANG Rui, WANG Feng, JIANG Yan, ZHANG Xiuqin. Preparation and Characterization of Self-cleaning Cotton Fabric† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1880. |
| [12] | ZHANG Jin, LIU Jia, MA Yangmin, YANG Xiufang, CHENG Pei, FAN Chao, LU Ping. TiO2 Nanoparticles-catalyzed One-pot Synthesis of Quinazolino[2,1-b]phthalazin-8-one and 3-Acylamino Isoindolo[2,1-a]quinazoline Derivatives† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(9): 1629. |
| [13] | AN Huiqin, YU Yucai, YAN Lin, WU Tingting, LI Xiaofeng, HE Xiaoling, ZHAO Lizhi, HUANG Weiping. Synthesis of Highly Dispersed Au Nanoparticles Modified N-Doped TiO2 Nanotubes by the Assist of Lysine and Their Photocatalytic Activity† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(11): 2034. |
| [14] | ZHU Jielian, XIA Xiaofeng, ZHU Shanshan, LIU Xiang, LI Hexing. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity of Cr Doped TiO2 Nanowires/Reduced Graphene Oxide Composites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(10): 1833. |
| [15] | MENG Zhiyu, ZHANG Yin, ZHAO Lili, ZHANG Hongxi, ZHAO Yongxiang. Liquid Phase Hydrogenation of Maleic Anhydride over Ni/TiO2 Catalysts with Different TiO2 Polymorphs† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1779. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||