

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 433.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20130605
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
GONG Feixiang*( ), QI Yonghong, XUE Qunxiang
), QI Yonghong, XUE Qunxiang
Received:2013-07-01
Online:2014-02-10
Published:2013-09-02
Contact:
GONG Feixiang
E-mail:gong_fx@163.com
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
GONG Feixiang, QI Yonghong, XUE Qunxiang. Synthesis and Properties of Fluorinated Poly(arylene ether sulfone)s with Sulfonated Pentiptycene Pendants as Proton Exchange Membranes†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(2): 433.
| Polymer | n(PPD)/ mmol | n(6F-BPA)/ mmol | n(TFDPS) or n(DFBP)/ mmol | 10-4 Mn | PDI | (dL·g-1) | (dL·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PES-30-PPD(4F) | 1.5 | 3.5 | 5 | 6.5 | 2.1 | 0.42 | 0.59 |
| PES-35-PPD(4F) | 1.75 | 3.25 | 5 | 6.8 | 2.2 | 0.45 | 0.65 |
| PES-32-PPD(10F) | 1.6 | 3.4 | 5 | 7.3 | 2.5 | 0.51 | 0.73 |
| PES-36-PPD(10F) | 1.8 | 3.2 | 5 | 7.5 | 2.3 | 0.52 | 0.75 |
Table 1 Physical properties of PES-x-PPD copolymers
| Polymer | n(PPD)/ mmol | n(6F-BPA)/ mmol | n(TFDPS) or n(DFBP)/ mmol | 10-4 Mn | PDI | (dL·g-1) | (dL·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PES-30-PPD(4F) | 1.5 | 3.5 | 5 | 6.5 | 2.1 | 0.42 | 0.59 |
| PES-35-PPD(4F) | 1.75 | 3.25 | 5 | 6.8 | 2.2 | 0.45 | 0.65 |
| PES-32-PPD(10F) | 1.6 | 3.4 | 5 | 7.3 | 2.5 | 0.51 | 0.73 |
| PES-36-PPD(10F) | 1.8 | 3.2 | 5 | 7.5 | 2.3 | 0.52 | 0.75 |
| Polymer | IEC/(mmol·g-1) | σmax/MPa(r.t., 60%RH) | ε(%) | E/GPa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcd. | 1H NMR | Titration | ||||
| SPES-30-PPD(4F) | 1.66 | 1.65 | 1.66 | 46.2 | 7.8 | 1.145 |
| SPES-35-PPD(4F) | 1.88 | 1.85 | 1.87 | 42.5 | 14 | 0.916 |
| SPES-32-PPD(10F) | 1.65 | 1.65 | 1.65 | 44.7 | 13 | 0.989 |
| SPES-36-PPD(10F) | 1.82 | 1.79 | 1.81 | 37.7 | 28 | 0.710 |
Table 2 IEC and mechanical properties of SPES-x-PPD(10F) and SPES-x-PPD(4F) membranes
| Polymer | IEC/(mmol·g-1) | σmax/MPa(r.t., 60%RH) | ε(%) | E/GPa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcd. | 1H NMR | Titration | ||||
| SPES-30-PPD(4F) | 1.66 | 1.65 | 1.66 | 46.2 | 7.8 | 1.145 |
| SPES-35-PPD(4F) | 1.88 | 1.85 | 1.87 | 42.5 | 14 | 0.916 |
| SPES-32-PPD(10F) | 1.65 | 1.65 | 1.65 | 44.7 | 13 | 0.989 |
| SPES-36-PPD(10F) | 1.82 | 1.79 | 1.81 | 37.7 | 28 | 0.710 |
| Polymer | IEC/(mmol·g-1) | WU(%)(80 ℃) | Swelling ratio(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34%RH | 94%RH | Δl(20 ℃) | Δt(80 ℃) | ||
| SPES-30-PPD(4F) | 1.66 | 7.9 | 17.6 | 3.5 | 7.3 |
| SPES-35-PPD(4F) | 1.88 | 9.8 | 29.9 | 6.3 | 11.6 |
| SPES-32-PPD(10F) | 1.65 | 6.7 | 13.9 | 3.1 | 6.5 |
| SPES-36-PPD(10F) | 1.82 | 8.5 | 25.2 | 5.6 | 10.4 |
| SPES-25-PPD[ | 1.67 | 9.3 | 31.8 | 11.8 | 15.6 |
| SPES-30-PPD[ | 1.92 | 10.9 | 39.3 | 13.7 | 18.8 |
| Nafion 117 | 0.91 | 6.6 | 11.6 | ||
Table 3 Water uptake(WU) and swelling ratio of SPES-x-PPD(10F) and SPES-x-PPD(4F) copolymers
| Polymer | IEC/(mmol·g-1) | WU(%)(80 ℃) | Swelling ratio(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34%RH | 94%RH | Δl(20 ℃) | Δt(80 ℃) | ||
| SPES-30-PPD(4F) | 1.66 | 7.9 | 17.6 | 3.5 | 7.3 |
| SPES-35-PPD(4F) | 1.88 | 9.8 | 29.9 | 6.3 | 11.6 |
| SPES-32-PPD(10F) | 1.65 | 6.7 | 13.9 | 3.1 | 6.5 |
| SPES-36-PPD(10F) | 1.82 | 8.5 | 25.2 | 5.6 | 10.4 |
| SPES-25-PPD[ | 1.67 | 9.3 | 31.8 | 11.8 | 15.6 |
| SPES-30-PPD[ | 1.92 | 10.9 | 39.3 | 13.7 | 18.8 |
| Nafion 117 | 0.91 | 6.6 | 11.6 | ||
| Polymer | IEC/(mmol·g-1) | WU(%)(80 ℃) | σ/(S·cm-1)(80 ℃) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34%RH | 94%RH | 34%RH | 94%RH | ||
| SPES-30-PPD(4F) | 1.66 | 7.9 | 17.6 | 8.56×104 | 0.173 |
| SPES-35-PPD(4F) | 1.88 | 9.8 | 29.9 | 1.46×103 | 0.191 |
| SPES-32-PPD(10F) | 1.65 | 6.7 | 13.9 | 1.21×103 | 0.181 |
| SPES-36-PPD(10F) | 1.82 | 8.5 | 25.2 | 2.25×103 | 0.213 |
| Nafion 117 | 6.6 | 11.6 | 3.0×103 | 0.110 | |
Table 4 Water uptake(WU) and conductivity of SPES-x-PPD(10F), SPES-x-PPD(4F) and Nafion 117 membranes
| Polymer | IEC/(mmol·g-1) | WU(%)(80 ℃) | σ/(S·cm-1)(80 ℃) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34%RH | 94%RH | 34%RH | 94%RH | ||
| SPES-30-PPD(4F) | 1.66 | 7.9 | 17.6 | 8.56×104 | 0.173 |
| SPES-35-PPD(4F) | 1.88 | 9.8 | 29.9 | 1.46×103 | 0.191 |
| SPES-32-PPD(10F) | 1.65 | 6.7 | 13.9 | 1.21×103 | 0.181 |
| SPES-36-PPD(10F) | 1.82 | 8.5 | 25.2 | 2.25×103 | 0.213 |
| Nafion 117 | 6.6 | 11.6 | 3.0×103 | 0.110 | |
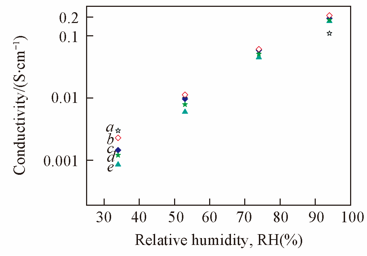
Fig.3 Humidity dependence of the proton conductivity of Nafion 117(a), SPES-36-PPD(10F)(b), SPES-35-PPD(4F)(c), SPES-32-PPD(10F)(d), and SPES-30-PPD(4F)(e) membranes at 80 ℃
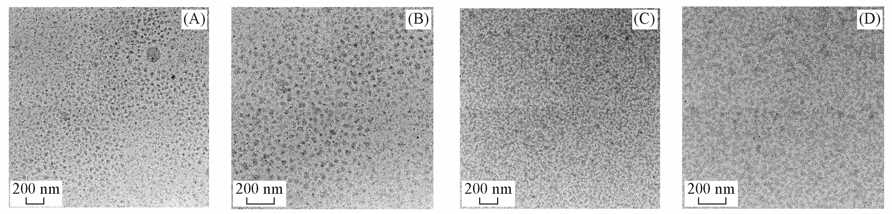
Fig.4 TEM images of SPES-30-PPD(4F)(IEC=1.66 mmol/g)(A), SPES-32-PPD(10F)(IEC=1.65 mmol/g)(B), SPES-35-PPD(4F)(IEC=1.88 mmol/g)(C) and SPES-36-PPD(10F)(IEC=1.82 mmol/g)(D)
| Polymer | IEC/(mmol·g-1) | Oxidative stabilitya | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decrease in mass(%) | Decrease in ηinh(%) | ||
| SPES-30-PPD(4F) | 1.66 | 0a; 7b | 2 |
| SPES-35-PPD(4F) | 1.88 | 2a; 18b | 7 |
| SPES-32-PPD(10F) | 1.65 | 0a; 0b | 1 |
| SPES-36-PPD(10F) | 1.82 | 1a; 10c | 5 |
| Nafion 117 | 0.91 | 0a; 0b | |
Table 5 Oxidative stability results of SPES-x-PPD(10F) and SPES-x-PPD(4F) membranes
| Polymer | IEC/(mmol·g-1) | Oxidative stabilitya | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decrease in mass(%) | Decrease in ηinh(%) | ||
| SPES-30-PPD(4F) | 1.66 | 0a; 7b | 2 |
| SPES-35-PPD(4F) | 1.88 | 2a; 18b | 7 |
| SPES-32-PPD(10F) | 1.65 | 0a; 0b | 1 |
| SPES-36-PPD(10F) | 1.82 | 1a; 10c | 5 |
| Nafion 117 | 0.91 | 0a; 0b | |
| [1] | Kreuer K., Chem. Mater., 1996, 8(3), 610—641 |
| [2] | Mauritz A., Moore R. B., Chem. Rev., 2004, 104, 4535—4585 |
| [3] | Yossef A. E., Hickner M. A., Macromolecules, 2011, 44, 1—11 |
| [4] | Hickner M., Ghassemi H., Kim Y., Einsla B., McGrath J., Chem. Rev., 2004, 104(10), 4587—4612 |
| [5] | Eisenberg A., Yeager H.L., Perfluorinated Ionomer Membranes, ACS Symp. Ser., Washington D. C., 1982, 180 |
| [6] | Zhang H. W., Shen P. K., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 2382—2394 |
| [7] | Parka C. H., Lee C. H., Guiver M. D., Lee Y. M., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2011, 36, 1443—1498 |
| [8] | Mohanty A. K., Mistri E. A., Banerjee S., Komber H., Voit B., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2013, 52(8), 2772—2783 |
| [9] | Weiber E. A., Takamuku S., Jannasch P., Macromolecules, 2013, 46(9), 3476—3485 |
| [10] | Miyake J., Watanabe M., Miyatake K., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5(13), 5903—5907 |
| [11] | Lafitte B., Jannasch P., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2007, 17, 2823—2834 |
| [12] | Nanwen L., Dong W. S., Doo S. H., Young M. L., Guiver M. D., Macromolecules, 2010, 43, 9810—9820 |
| [13] | Zhao C., Li X., Wang Z., Dou Z., Zhong S., Hui N., J. Membr. Sci., 2006, 280, 643—650 |
| [14] | Xu D., Wang Y., Zhang Y., Zhang G., Shao K., Li S., Na H., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2010, 26(6), 1031—1034 |
| [15] | Wang Y. P., Yue X. G., Pang J. H., Li X. F., Li Y. N., Zhang H. B., Jiang Z. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(5), 1100—1105 |
| (王永鹏, 岳喜贵, 庞金辉, 李雪峰, 李摇娜, 张海博, 姜振华.高等学校化学学报,2012, 33(5), 1100—1105) | |
| [16] | Li X. F., Guo M. M., Liu B. J., Jiang Z. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(5), 1022—1024 |
| (李雪峰, 郭梅梅, 刘佰军, 姜振华.高等学校化学学报,2011, 32(5), 1022—1024) | |
| [17] | Pang J. H., Zhang H. B., Li X. F., Jiang Z. H., Macromolecules, 2007, 40, 9435—9442 |
| [18] | Gao N., Zhang S., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2013, 128, 1—12 |
| [19] | Peckham T., Holdcroft S., Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 4667—4690 |
| [20] | Miyatake K., Chikashige Y., Higuchi E., Watanabe M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129(13), 3879—3887 |
| [21] | Matsumoto K., Nakagawa T., Higashihara T., Ueda M., J. Polym. Sci. Part. A: Polym. Chem., 2009, 47, 5827—5834 |
| [22] | Nakabayashi K., Higashihara T., Ueda M., J. Polym. Sci. Part. A: Polym. Chem., 2010, 48, 2757—2764 |
| [23] | Matsumoto K., Higashihara T., Ueda M., Macromolecules, 2009, 42(4), 1161—1166 |
| [24] | Matsumura S., Hlil A., Lepiller C., Gaudet J., Guay D., Shi Z., Holdcroft S., Hay A., Macromolecules, 2008, 41(2), 281—284 |
| [25] | Miyatake K., Shimura T., Mikami T., Watanabe M., Chem. Commun., 2009, 42, 6403—6405 |
| [26] | Gong F., Mao H., Zhang Y., Zhang S., Xing W., Polymer, 2011, 52, 1738—1747 |
| [27] | Gong F., Zhang S., J. Power Sources, 2011, 196, 9876—9883 |
| [28] | Wang J. H., Zhao Z., Gong F. X., Li S. H., Zhang S. B., Macromolecules, 2009, 42, 8711—8717 |
| [29] | Rubatat L., Shi Z. Q., Diat O., Holdcroft S., Frisken B. J., Macromolecules, 2006, 39, 720—730 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||