

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (12): 20220440.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220440
收稿日期:2022-06-21
出版日期:2022-12-10
发布日期:2022-09-29
通讯作者:
王睿,梁高林
E-mail:ruiwang938@seu.edu.cn;gliang@seu.edu.cn
基金资助:
XU Haidong, WANG Rui( ), LIANG Gaolin(
), LIANG Gaolin( )
)
Received:2022-06-21
Online:2022-12-10
Published:2022-09-29
Contact:
WANG Rui, LIANG Gaolin
E-mail:ruiwang938@seu.edu.cn;gliang@seu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
磁共振成像(MRI)是一种强大的非侵入式生物医学诊断技术. 临床上, MRI需要借助造影剂来提高成像质量, 从而提高诊断的准确性. 由于具有优越的信号放大能力和生物相容性, 自组装多肽探针可负载特定的MRI分子, 通过酶促自组装过程实现肿瘤靶向和特异性富集, 增强肿瘤病灶区MRI信号, 从而进一步提高MRI的准确性和灵敏度. 本综述总结了近年来多肽自组装探针在不同MRI模式( 1H MRI, 19F MRI和双自旋核MRI)下的最新进展, 并展望了这类新型探针在MRI领域的应用前景.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
徐海东, 王睿, 梁高林. 自组装多肽探针在磁共振成像中的应用. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220440.
XU Haidong, WANG Rui, LIANG Gaolin. Applications of Self-assembled Peptide Probes in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(12): 20220440.
| Advantage | Disadvantage | |
|---|---|---|
| 1H MRI | High sensitivity, high imaging signal | High background, low contrast |
| 19F MRI | Low background noise, high selectivity | Low sensitivity |
Table 1 Comparisons between the 1H MRI and the 19F MRI [ 9, 10]
| Advantage | Disadvantage | |
|---|---|---|
| 1H MRI | High sensitivity, high imaging signal | High background, low contrast |
| 19F MRI | Low background noise, high selectivity | Low sensitivity |
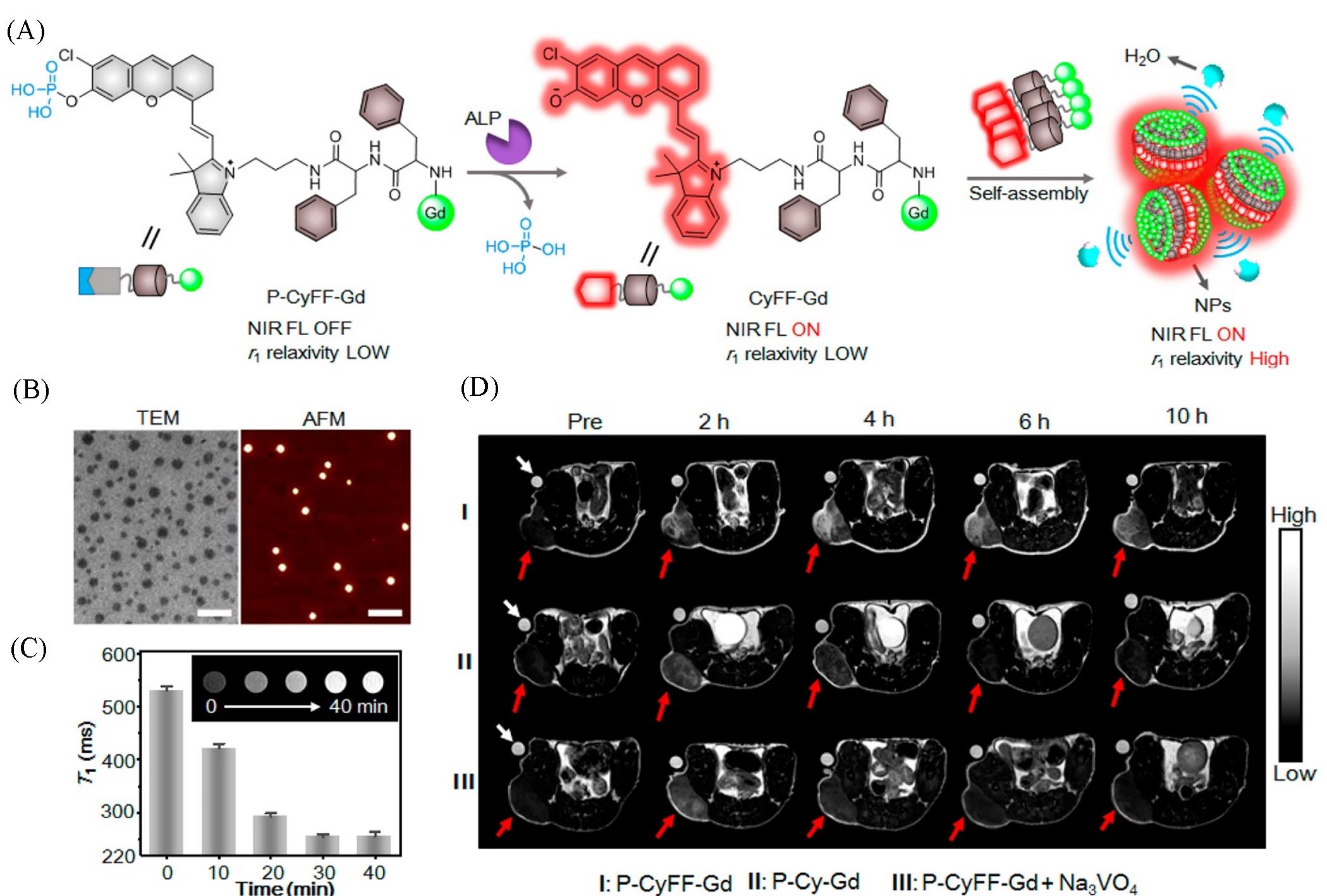
Fig.1 Schematic illustration of P⁃CyFF⁃Gd and fluorogenic reaction and in situ self⁃assembly of P⁃CyFF⁃Gd into NPs mediated by ALP that show increased NIR FL and r1 relaxivity(A), TEM and AFM images of NPs after incubating P⁃CyFF⁃Gd(200 μmol/L) with ALP(2 U/mL, 37 ℃) for 30 min(Scale bars: 200 nm)(B), T1⁃weighted MR images and T1 values(0.5 T) of P⁃CyFF⁃Gd(200 μmol/L) in Tris buffer by incubating with ALP(2 U/mL) for 0—40 min(C), T1⁃weighted MR images of HeLa tumor⁃bearing mice receiving i.p. injection of P⁃CyFF⁃Gd(I), P⁃Cy⁃Gd(II), P⁃CyFF⁃Gd(III) together with Na3VO4. Images were acquired before(Pre) or 2, 4, 6, 10 h after injection using TE/TR=15/446 ms at 1.0 T. White arrows indicate the Dotarem solution(1 mmol/L) as the internal standard. Red arrows point the tumor locations in mice(D) [ 31]Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
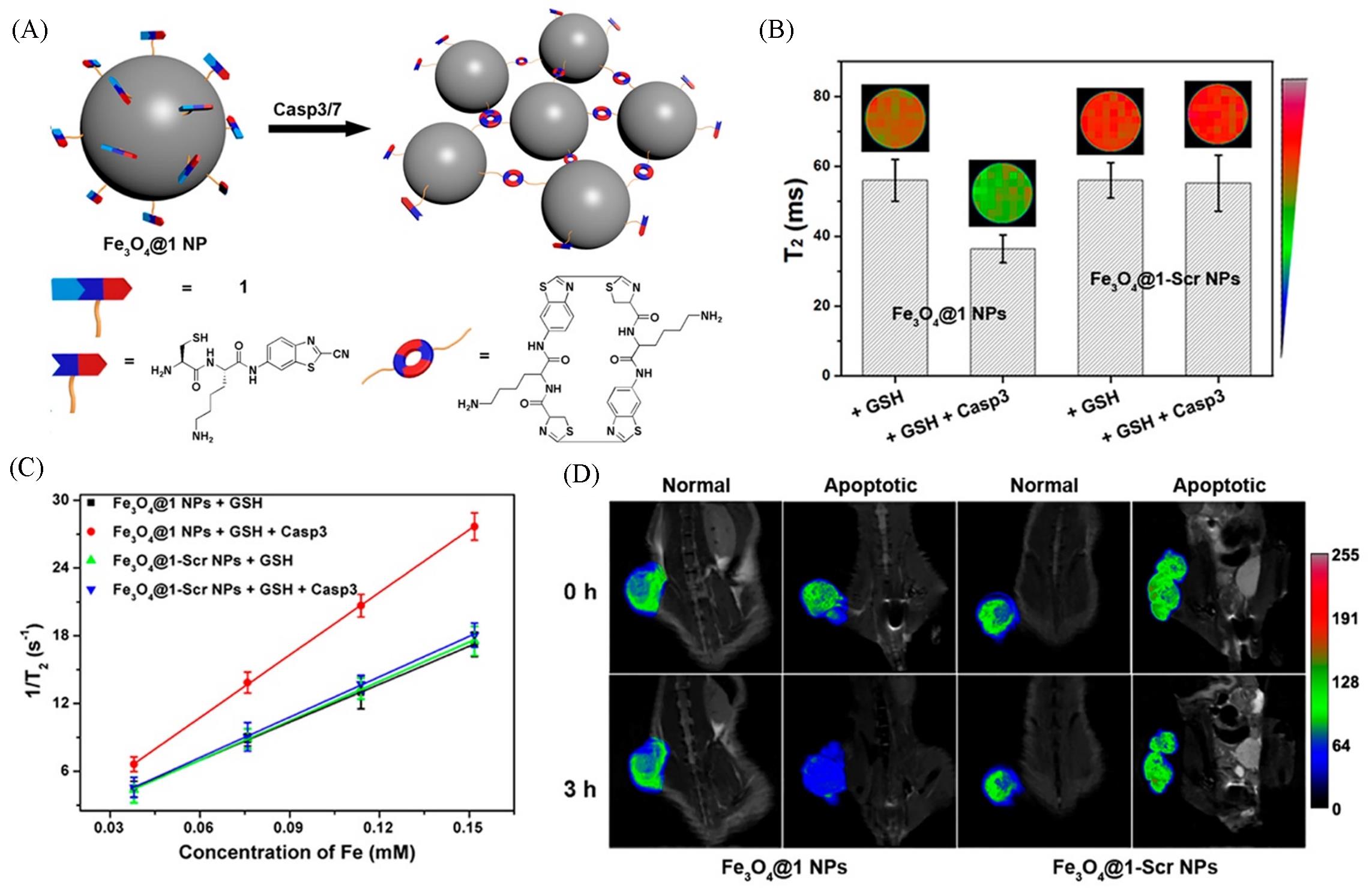
Fig.2 Schematic illustration of intracellular Casp3/7⁃instructed aggregation of Fe3O4@1 NPs(A), T2⁃weighted MR phantom images(echo time: 75 ms) and T2 relaxation times of Fe3O4@1 NPs treated with 1 mmol/L GSH for 2 h at 37 ℃ or 1 mmol/L GSH and 5 unit Casp3 for 8 h at 37 ℃, Fe3O4@1⁃Scr NPs treated with 1 mmol/L GSH for 2 h at 37 ℃ or 1 mmol/L GSH and 5 unit Casp3 for 8 h at 37 ℃ on a 9.4 T MR scanner(TR 5, 500 ms, TE 15—180 ms)(B), transverse relaxation rates(1/ T2) of Fe3O4@1 NPs or Fe3O4@1⁃Scr NPs at different concentrations in the presence/absence of Casp3(C), T2⁃weighted coronal MR images of Fe3O4@1 NPs⁃injected saline⁃treated mice, Fe3O4@1 NPs⁃injected DOX⁃treated mice, Fe3O4@1⁃Scr NPs⁃injected saline⁃treated mice, and Fe3O4@1⁃Scr NPs⁃injected DOX⁃treated mice after 0 h or 3 h injection(D) [ 42]Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society.
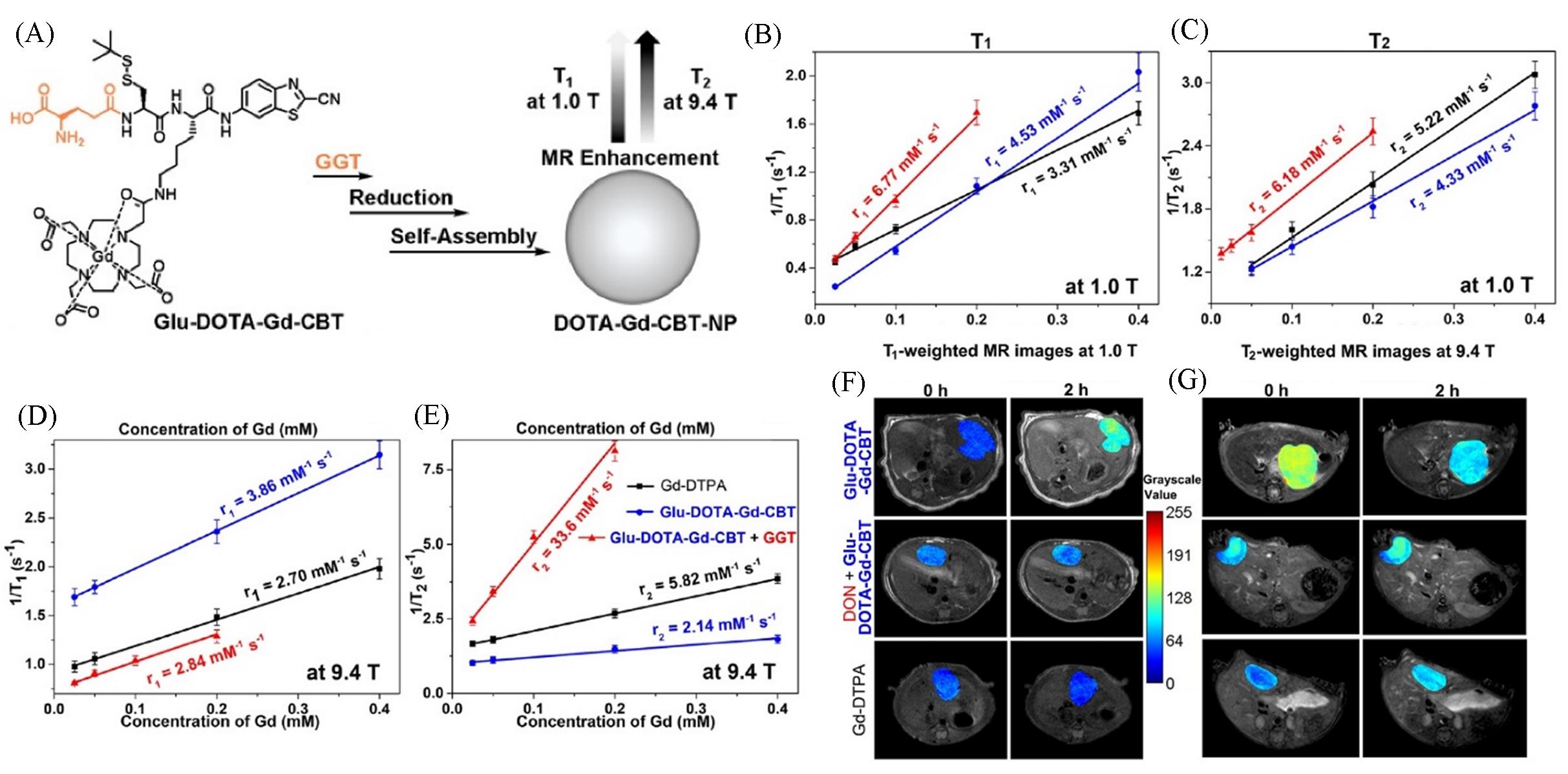
Fig.3 Schematic illustration of the formation of DOTA⁃Gd⁃CBT⁃NP guided by GGT to enhance T1 and T2 MR contrasts at low(1.0 T) and high(9.4 T) magnetic fields(A), longitudinal relaxation rates(1/ T1) and transverse relaxation rates(1/ T2) of Group Glu⁃DOTA⁃Gd⁃CBT+GGT, Group Glu⁃DOTA⁃Gd⁃CBT, and Group Gd⁃DTPA at low(1.0 T) or high(9.4 T) magnetic field(B—E), T1⁃weighted transverse MR images at 1.0 T and T2⁃weighted transverse MR images at 9.4 T of liver tumors in groups in (C) at 0 h and 2 h(F, G) [ 47]Copyright 2022, Ivyspring International Publisher.
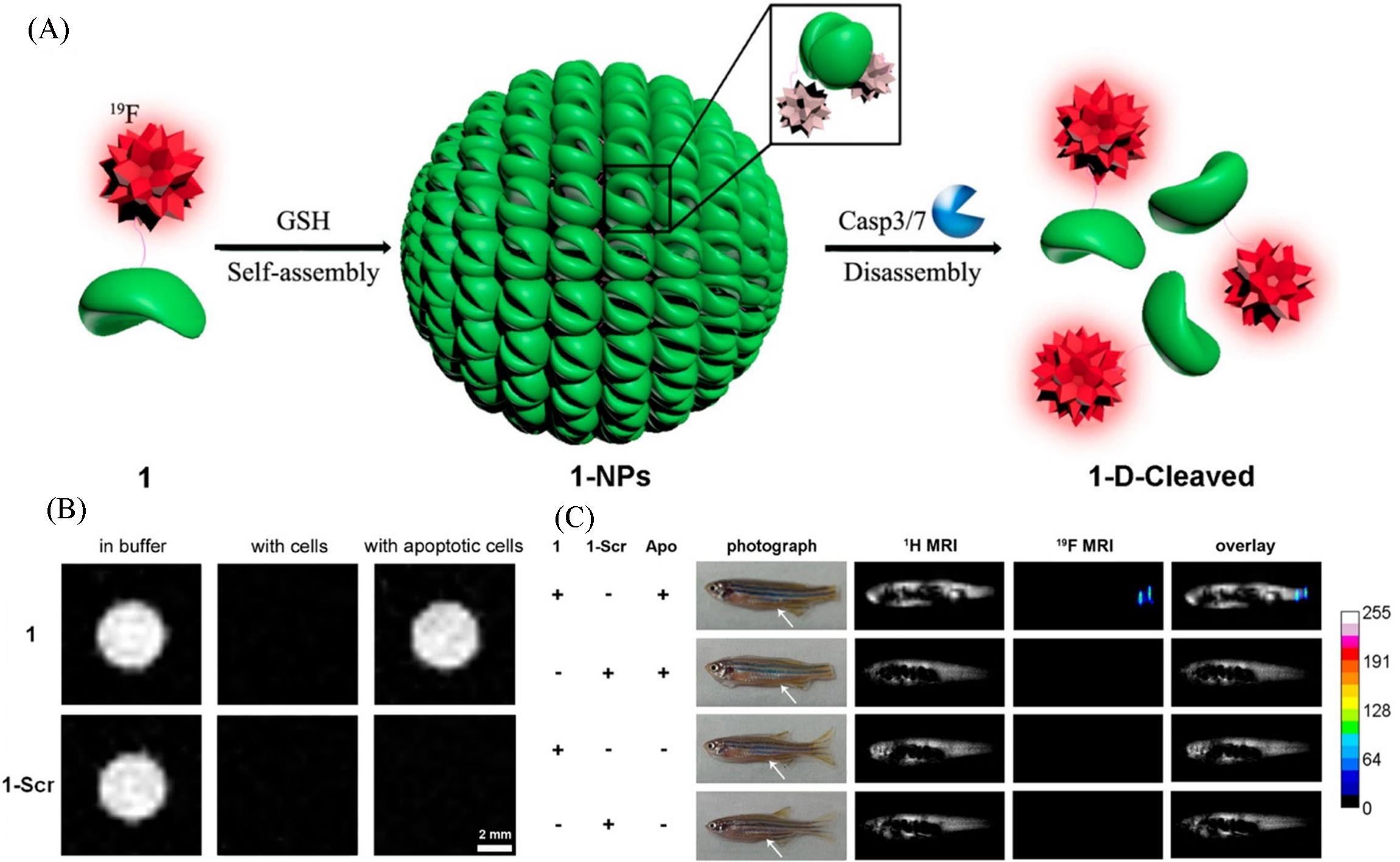
Fig.4 Schematic illustration of GSH⁃controlled self⁃assembly of 19F probe to turn 19F NMR signals “off” and Caspase 3/7⁃controlled disassembly of 19F NPs to turn 19F NMR signals “on”(A), 19F MR imaging of 1 or 1⁃Scr in RIPA lysis buffer, in cell lysate after being incubated with HepG2 cells at 37 ℃ for 30 min, and in cell lysate after being incubated with apoptotic HepG2 cells at 37 ℃ for 30 min(B), 2.1 g/kg of 1 and 1⁃Scr(10 μL, dissolved in DMSO) injected into the enterocoelia of zebrafish 3 h after tail amputation and a healthy zebrafish(White arrows indicate the injection sites)(C) [ 50]Copyright 2015, American Chemical Society.
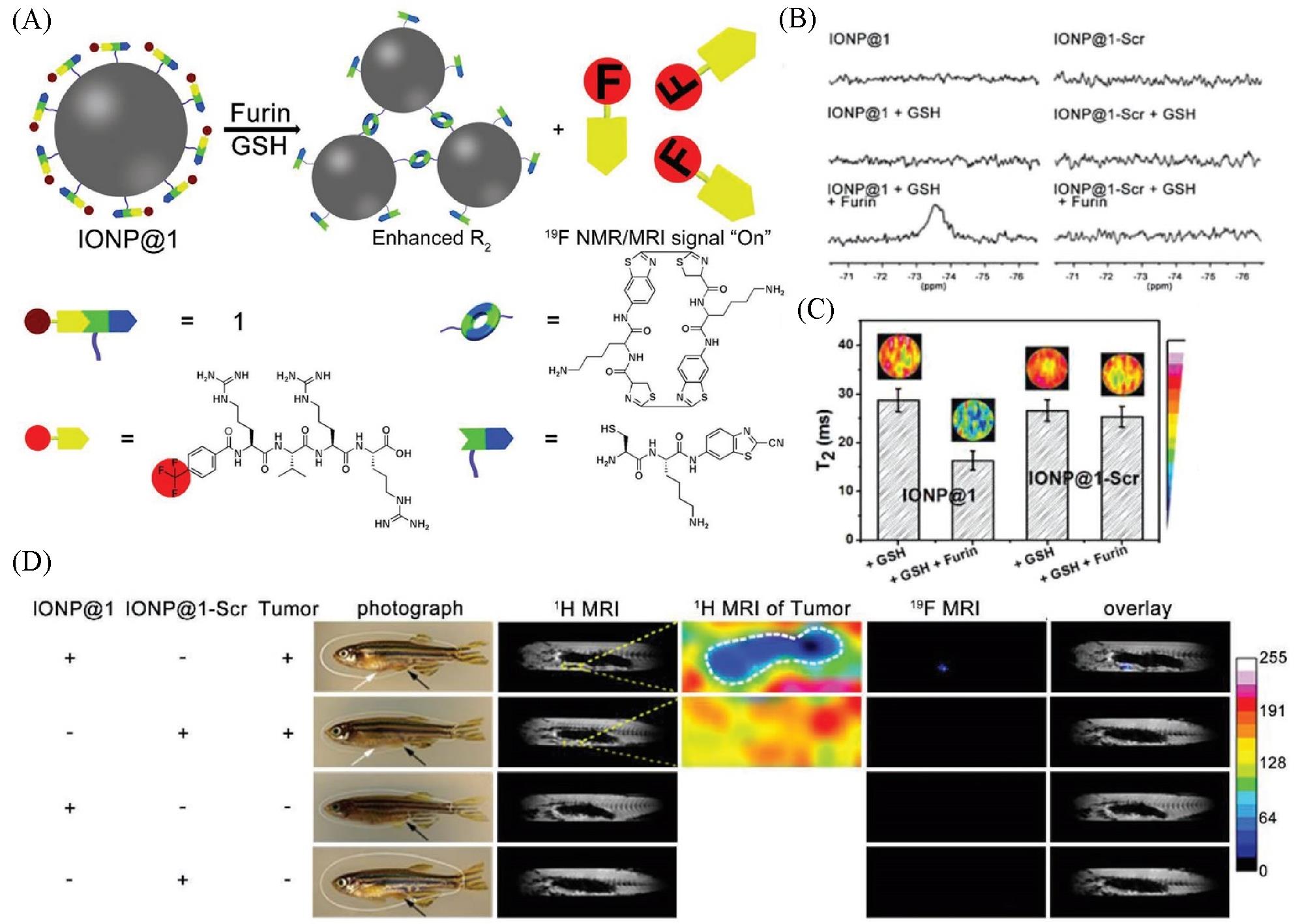
Fig.5 Schematic illustration showing furin⁃mediated formation of IONP aggregates for enhanced r2 and release of TFMB⁃Arg⁃Val⁃Arg⁃Arg⁃OH to “turn on” 19F NMR/MRI signal(A), 19F NMR spectra recorded for IONP@1 or IONP@1⁃Scr before or after incubation with GSH, and after co⁃incubation with GSH followed with furin(B), T2 images of phantoms, and corresponding T2 value of samples in IONP@1 and IONP@1⁃Scr after treating with GSH, or GSH and furin(C), 1H MRI and 19F MRI of the enterocoelia of a healthy zebrafish or tumor⁃bearing zebrafish using IONP@1 or IONP@1⁃Scr(D) [ 54](D) DMSO dispersion of IONP@1 or IONP@1 ⁃Scr was administered into the enterocoelia of a healthy zebrafish or tumor ⁃bearing zebrafish for 3 h before imaging. White arrows indicate the tumor sites. Black arrows indicate the injection sites of IONP@1/IONP@1 ⁃Scr. Yellow arrows indicate the tumor sites. Copyright 2019, Wiley‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
| 1 | Lyu P. J., Liu X., Zhang R., Shi L., Gao J. B., Invest. Radiol., 2020, 55(7), 412—421 |
| 2 | Ruiz⁃Cabello J., Barnett B. P., Bottomley P. A., Bulte J. W. M., NMR Biomed., 2011, 24(2), 114—129 |
| 3 | Wu Y., Ali M. R. K., Chen K., Fang N., El⁃Sayed M. A., Nano Today, 2019, 24, 120—140 |
| 4 | Deri M. A., Zeglis B. M., Francesconi L. C., Lewis J. S., Nucl. Med. Biol., 2013, 40(1), 3—14 |
| 5 | Wells P. N. T., Ultrasonics, 1993, 31(5), 345—352 |
| 6 | Key J., Cooper C., Kim A. Y., Dhawan D., Knapp D. W., Kim K., Park J. H., Choi K., Kwon I. C., Park K., Leary J. F., J. Controlled Release, 2012, 163(2), 249—255 |
| 7 | Pirogov Y. A., Phys. Procedia, 2016, 82, 3—7 |
| 8 | Gutberlet M., Kaireit T. F., Voskrebenzev A., Lasch F., Freise J., Welte T., Wacker F., Hohlfeld J. M., Vogel⁃Claussen J., Radiology, 2018, 286(3), 1040—1051 |
| 9 | Mohamed R. E., Zytoon H. A., Amin M. A., Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med., 2018, 49(2), 536—552 |
| 10 | Takaoka Y., Kiminami K., Mizusawa K., Matsuo K., Narazaki M., Matsuda T., Hamachi I., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(30), 11725—11731 |
| 11 | Cho M. H., Shin S. H., Park S. H., Kadayakkara D. K., Kim D., Choi Y., Bioconjugate Chem., 2019, 30(10), 2502—2518 |
| 12 | Kirschenlohr H. L., Metcalfe J. C., Morris P. G., Rodrigo G. C., Smith G. A., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1988, 85(23), 9017—9021 |
| 13 | Chen S. Z., Yang Y. Q., Li H. D., Zhou X., Liu M. L., Chem. Commun., 2014, 50(3), 283—285 |
| 14 | Huang J., Li Y. C., Orza A., Lu Q., Guo P., Wang L. Y., Yang L., Mao H., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26(22), 3818—3836 |
| 15 | Huang X. L., Song J. B., Yung B. C., Huang X. H., Xiong Y. H., Chen X. Y., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47(8), 2873—2920 |
| 16 | Cui H. G., Webber M. J., Stupp S. I., Biopolymers, 2010, 94(1), 1—18 |
| 17 | Gao G., Sun X. B., Liu X. Y., Jiang Y. W., Tang R. Q., Guo Y. X., Wu F. G., Liang G. L., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31(34), 2102832 |
| 18 | Wu C. F., Wang C. C., Zhang T., Gao G., Wei M. X., Chen Y. L., Li X. Y., Wang F. Q., Liang G. L., Adv. Healthcare Mater., 2022, 11(1), 2101346 |
| 19 | Shi H. B., Kwok R. T. K., Liu J. Z., Xing B. G., Tang B. Z., Liu B., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(43), 17972—17981 |
| 20 | Wang J., Liu K., Xing R. R., Yan X. H., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45(20), 5589—5604 |
| 21 | Paramonov S. E., Jun H. W., Hartgerink J. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128(22), 7291—7298 |
| 22 | Rybtchinski B., ACS Nano, 2011, 5(9), 6791—6818 |
| 23 | Wang C., Wang Z. Q., Zhang X., Acc. Chem. Res., 2012, 45(4), 608—618 |
| 24 | Zhang S., Shao Y. Y., Yin G. P., Lin Y. H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2010, 49(12), 2211—2214 |
| 25 | Castelletto V., Seitsonen J., Tewari K. M., Hasan A., Edkins R. M., Ruokolainen J., Pandey L. M., Hamley I. W., Lau K. H. A., ACS Macro Lett., 2020, 9(4), 494—499 |
| 26 | Wang C., Du W., Wu C., Dan S., Sun M., Zhang T., Wang B., Yuan Y., Liang G., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2022, 61(5), e202114766 |
| 27 | Yang Z. M., Gu H. W., Fu D. G., Gao P., Lam J. K., Xu B., Adv. Mater., 2004, 16(16), 1440—1444 |
| 28 | Yang Z. M., Liang G. L., Xu B., Acc. Chem. Res., 2008, 41(2), 315—326 |
| 29 | Liu S., Zhang Q. X., Shy A. N., Yi M. H., He H. J., Lu S. J., Xu B., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143(38), 15852—15862 |
| 30 | Hai Z., Ni Y., Saimi D., Yang H., Tong H., Zhong K., Liang G., Nano Lett., 2019, 19(4), 2428—2433 |
| 31 | Yan R. Q., Hu Y. X., Liu F., Wei S. X., Fang D. Q., Shuhendler A. J., Liu H., Chen H. Y., Ye D. J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(26), 10331—10341 |
| 32 | Khairnar S., More N., Mounika C., Kapusetti G., J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Sci., 2019, 50(4), 575—589 |
| 33 | Bull S. R., Guler M. O., Bras R. E., Meade T. J., Stupp S. I., Nano Lett., 2005, 5(1), 1—4 |
| 34 | Li W. S., Luo J., Jiang F., Chen Z. N., Dalton Trans., 2012, 41(31), 9405—9410 |
| 35 | Ha B. C., Jung J., Kwak B. K., Acta Radiol., 2015, 56(2), 219—227 |
| 36 | Zhang H., Liu K., Li S. K., Xin X., Yuan S. L., Ma G. H., Yan X. H., ACS Nano, 2018, 12(8), 8266—8276 |
| 37 | Lee N., Hyeon T., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41(7), 2575—2589 |
| 38 | Fan C. H., Ting C. Y., Lin H. J., Wang C. H., Liu H. L., Yen T. C., Yeh C. K., Biomaterials, 2013, 34(14), 3706—3715 |
| 39 | Melancon M. P., Elliott A., Ji X. J., Shetty A., Yang Z., Tian M., Taylor B., Stafford R. J., Li C., Invest. Radiol., 2011, 46(2), 132—140 |
| 40 | Zheng S. W., Huang M., Hong R. Y., Deng S. M., Cheng L. F., Gao B., Badami D., J. Biomater. Appl., 2014, 28(7), 1051—1059 |
| 41 | Wang Y. L., Xu C., Chang Y. N., Zhao L. N., Zhang K., Zhao Y. L., Gao F. P., Gao X. Y., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(34), 28959—28966 |
| 42 | Yuan Y., Ding Z. L., Qian J. C., Zhang J., Xu J. Y., Dong X. J., Han T., Ge S. C., Luo Y. F., Wang Y. W., Zhong K., Liang G. L., Nano Lett., 2016, 16(4), 2686—2691 |
| 43 | Wang Y. G., Li X. H., Chen P. Y., Dong Y., Liang G. L., Yu Y. Q., Nanoscale, 2020, 12(3), 1886—1893 |
| 44 | Li F. F., Zhi D. B., Luo Y. F., Zhang J. Q., Nan X., Zhang Y. J., Zhou W., Qiu B. S., Wen L. P., Liang G. L., Nanoscale, 2016, 8(25), 12826—12833 |
| 45 | Wang L. Y., Huang J., Chen H. B., Wu H., Xu Y. L., Li Y. C., Yi H., Wang Y. A., Yang L. L., Mao H., ACS Nano, 2017, 11(5), 4582—4592 |
| 46 | Dong L., Qian J. C., Hai Z. J., Xu J. Y., Du W., Zhong K., Liang G. L., Anal. Chem., 2017, 89(13), 6922—6925 |
| 47 | Li H., Hai Z. J., Zou L. W., Zhang L. L., Wang L. L., Wang L. S., Liang G. L., Theranostics, 2022, 12(1), 410—417 |
| 48 | Rolfe B. E., Blakey I., Squires O., Peng H., Boase N. R. B., Alexander C., Parsons P. G., Boyle G. M., Whittaker A. K., Thurecht K. J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(6), 2413—2419 |
| 49 | Zhang C., Peng H., Puttick S., Searles D., Whittaker A., Moonshi S. S., Han Y. X., Puttick S., Peng H., Abel M. B. J., Reid J. C., Bernardi S., Searles D. J., Král P., Whittaker A. K., Macromolecules, 2017, 50, 5953—5963 |
| 50 | Yuan Y., Sun H. B., Ge S. C., Wang M. J., Zhao H. X., Wang L., An L., Zhang J., Zhang H. F., Hu B., Wang J. F., Liang G. L., ACS Nano, 2015, 9(1), 761—768 |
| 51 | Zheng Z., Sun H. B., Hu C., Li G. Y., Liu X. M., Chen P. Y., Cui Y. S., Liu J., Wang J. F., Liang G. L., Anal. Chem., 2016, 88(6), 3363—3368 |
| 52 | Bouchoucha M., van Heeswijk R. B., Gossuin Y., Kleitz F., Fortin M. A., Langmuir, 2017, 33(40), 10531—10542 |
| 53 | Hu Y. X., Wang Y. Q., Wen X. D., Pan Y. F., Cheng X., An R. B., Gao G. D., Chen H. Y., Ye D. J., Research, 2020, 2020, 4087069 |
| 54 | Ding Z. L., Sun H. B., Ge S. C., Cai Y., Yuan Y., Hai Z. J., Tao T. X., Hu J. M., Hu B., Wang J. F., Liang G. L., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29(43), 1903860 |
| [1] | 李奥, 李凌轩, 左翠翠, 陈传凯, 樊一凡, 步逸凡, 林泓域, 高锦豪. 基于硼酸酯的19F磁共振分子探针的设计合成及活体深组织活性氧物种的激活响应成像[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220545. |
| [2] | 吕丰, 李艳周, 武莉, 刘天军. 用于肿瘤成像的半乳糖/酞菁近红外荧光探针[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(5): 1010. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||