

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (9): 1893.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180262
收稿日期:2018-04-04
出版日期:2018-09-07
发布日期:2018-06-26
作者简介:联系人简介: 练鸿振, 男, 博士, 教授, 博士生导师, 主要从事色谱分离和分析方面的研究. E-mail:
基金资助:
QIAO Junqin, LIANG Chao, CAO Zhaoming, LIAN Hongzhen*( )
)
Received:2018-04-04
Online:2018-09-07
Published:2018-06-26
Contact:
LIAN Hongzhen
E-mail:hzlian@nju.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
利用离子对反相液相色谱(IP-RPLC)对寡核苷酸在混合离子对试剂三乙胺/丙胺-乙酸盐(TEA/PA-AA)体系下的保留行为进行了研究, 并与经典离子对试剂三乙胺乙酸盐(TEAA)体系下的保留行为进行了对比. 实验结果表明, 相同离子对试剂浓度下, 寡核苷酸在TEA/PA-AA体系下的保留均弱于TEAA体系下的保留, 且寡核苷酸的保留均随着离子对试剂浓度(20~120 mmol/L)的增加而增强. 同型寡核苷酸(dC)n作为特例, 当n>10时, 保留基本趋于稳定, 这是由于(dC)n随着离子对试剂浓度的增加保留增长较快, 在较低的离子对试剂浓度下即可达到最大保留. 同时发现, 短链同型寡核苷酸(dT)n和异型寡核苷酸在TEA/PA-AA体系下的分离均优于TEAA体系, 而同型寡核苷酸(dA)n和(dC)n的分离则在TEAA体系下更优. 通过研究流动相中离子对试剂总浓度cp与寡核苷酸保留因子k之间的关系, 推断出2种体系下寡核苷酸的保留机理均以离子对模型占主导地位. 总体而言, 分离相同长度的异型寡核苷酸时, TEA/PA-AA混合离子对体系尤其在中等离子对浓度下比TEAA体系具有明显优势, 低的离子对试剂浓度可增加与后续电喷雾质谱(ESI-MS)的兼容性, 有利于寡核苷酸的定性分析.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
乔俊琴, 梁超, 曹兆明, 练鸿振. 混合离子对试剂体系下寡核苷酸的IP-RPLC保留行为. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(9): 1893.
QIAO Junqin,LIANG Chao,CAO Zhaoming,LIAN Hongzhen. Retention Behavior of Oligonucleotides under System Containing Mixed Ion-pair Reagents by IP-RPLC†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1893.
| Oligonucleotide | Sequence(5'-3') | Percentage(%) | ΔG*/(J·mol-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G | C | A | T | |||
| Oligo20-1 | CTTAGTGAAGAGCTCAGTTA | 25 | 15 | 30 | 30 | -3.97×104 |
| Oligo20-2 | CTTAGTGAAGAGTCTCTAAG | 25 | 15 | 30 | 30 | -2.55×104 |
| Oligo20-3 | GACAGGAAAGACATTCTGGC | 30 | 20 | 35 | 15 | -1.48×104 |
| Oligo20-4 | GACAGGAAAGACATTCCGGT | 30 | 20 | 35 | 15 | -4.08×104 |
| Oligo32-1 | GTCGTTATCATCAGAGTAGCCCAGGAAGCTTC | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | -5.60×104 |
| Oligo32-2 | GCGTACAGTATAGCCCAGTCTTGAGTGCCATA | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | -1.53×104 |
| Oligo32-3 | GGTATGGTTTACGAGTATTGCCTGAAGCGAGG | 37.5 | 12.5 | 21.9 | 28.1 | -1.95×104 |
| Oligo32-4 | CCTCGCTTCAGGCAATACTCGTAAACCATACC | 12.5 | 37.5 | 28.1 | 21.9 | -1.95×104 |
Table 1 Hetero-oligonucleotides used in the experiment
| Oligonucleotide | Sequence(5'-3') | Percentage(%) | ΔG*/(J·mol-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G | C | A | T | |||
| Oligo20-1 | CTTAGTGAAGAGCTCAGTTA | 25 | 15 | 30 | 30 | -3.97×104 |
| Oligo20-2 | CTTAGTGAAGAGTCTCTAAG | 25 | 15 | 30 | 30 | -2.55×104 |
| Oligo20-3 | GACAGGAAAGACATTCTGGC | 30 | 20 | 35 | 15 | -1.48×104 |
| Oligo20-4 | GACAGGAAAGACATTCCGGT | 30 | 20 | 35 | 15 | -4.08×104 |
| Oligo32-1 | GTCGTTATCATCAGAGTAGCCCAGGAAGCTTC | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | -5.60×104 |
| Oligo32-2 | GCGTACAGTATAGCCCAGTCTTGAGTGCCATA | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | -1.53×104 |
| Oligo32-3 | GGTATGGTTTACGAGTATTGCCTGAAGCGAGG | 37.5 | 12.5 | 21.9 | 28.1 | -1.95×104 |
| Oligo32-4 | CCTCGCTTCAGGCAATACTCGTAAACCATACC | 12.5 | 37.5 | 28.1 | 21.9 | -1.95×104 |
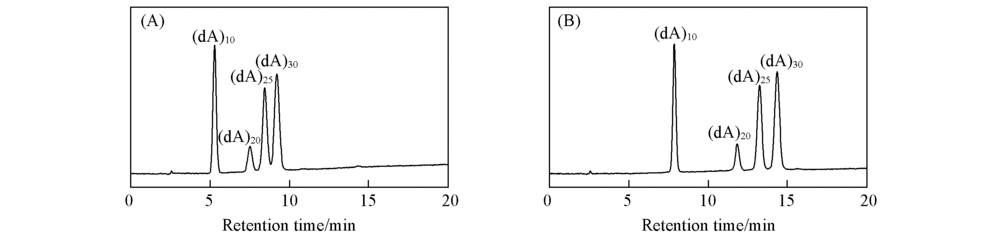
Fig.1 Chromatograms of (dA)n under mobile phases containing either 10 mmol/L TEA/10 mmol/L PA(A)or 20 mmol/L TEA(B)Purospher© STAR RP-18 endcapped column(50 mm×4.6 mm i.d., 5 μm); column temperature: 30 ℃; mobile phase A(10 mmol/L TEA/10 mmol/L PA-20 mmol/LAA-5%CH3CN, pH=7.0) or (20 mmol/L TEAA-5%CH3CN, pH=7.0), mobile phase B(10 mmol/L TEA/10 mmol/L PA-20 mmol/L AA-25%CH3CN, pH=7.0) or (20 mmol/L TEAA-25%CH3CN, pH=7.0); gradient elution: 0—40 min, 15%B—45%B; 40—43 min, 45%B—15%B; 43—58 min, 15%B—15%B; flow rate: 1.0 mL/min; detection wavelength: 260 nm.
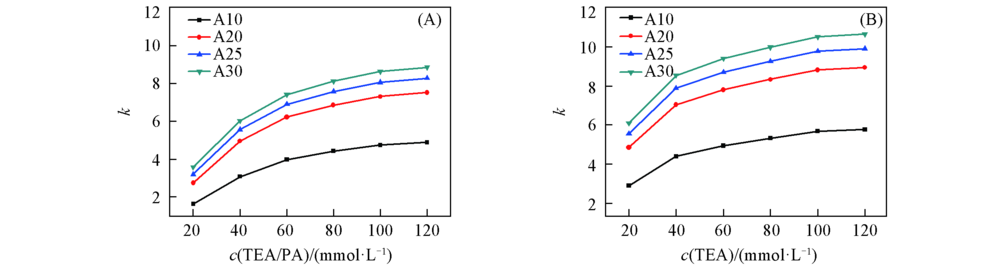
Fig.2 Retention factor k of (dA)n under mobile phases containing different concentrations of ion-pair reagent(A) TEA/PA; (B) TEA. The concentrations of ion-pair reagent in mobile phase were 20, 40, 60, 80, 100 and 120 mmol/L, respectively. Other chromatographic conditions were the same as in Fig.1.
| TEA/PA | TEA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A10/A20 | A20/A25 | A25/A30 | A10/A20 | A20/A25 | A25/A30 | |
| 20 | 5.02 | 1.76 | 1.34 | 9.06 | 2.73 | 1.97 |
| 40 | 9.20 | 2.66 | 1.89 | 12.47 | 3.47 | 2.55 |
| 60 | 10.90 | 2.96 | 2.12 | 13.36 | 3.74 | 2.77 |
| 80 | 11.58 | 3.17 | 2.29 | 13.98 | 3.92 | 2.89 |
| 100 | 12.37 | 3.33 | 2.37 | 14.76 | 4.03 | 2.96 |
| 120 | 12.55 | 3.34 | 2.39 | 14.42 | 3.99 | 2.94 |
Table 2 Resolution(Rs) of adjacent peaks in (dA)n under different concentrations of ion-pair reagent
| TEA/PA | TEA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A10/A20 | A20/A25 | A25/A30 | A10/A20 | A20/A25 | A25/A30 | |
| 20 | 5.02 | 1.76 | 1.34 | 9.06 | 2.73 | 1.97 |
| 40 | 9.20 | 2.66 | 1.89 | 12.47 | 3.47 | 2.55 |
| 60 | 10.90 | 2.96 | 2.12 | 13.36 | 3.74 | 2.77 |
| 80 | 11.58 | 3.17 | 2.29 | 13.98 | 3.92 | 2.89 |
| 100 | 12.37 | 3.33 | 2.37 | 14.76 | 4.03 | 2.96 |
| 120 | 12.55 | 3.34 | 2.39 | 14.42 | 3.99 | 2.94 |
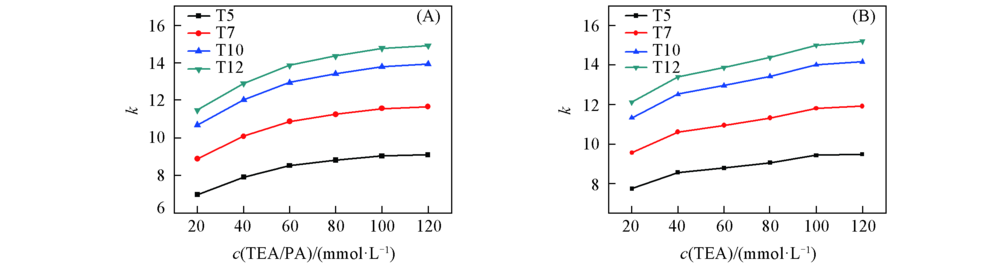
Fig.3 Retention factor k of (dT)n under mobile phases containing different concentrations of ion-pair reagent (A) TEA/PA; (B) TEA. The chromatographic conditions are the same as those in Fig.2.
| cp/(mmol·L-1) | TEA/PA | TEA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T5/T7 | T7/T10 | T10/T12 | T5/T7 | T7/T10 | T10/T12 | |
| 20 | 10.28 | 9.24 | 3.78 | 9.79 | 9.26 | 4.08 |
| 40 | 11.79 | 10.42 | 4.44 | 10.96 | 10.20 | 4.53 |
| 60 | 12.50 | 10.96 | 4.76 | 11.58 | 10.48 | 4.85 |
| 80 | 12.92 | 11.32 | 4.85 | 11.83 | 10.98 | 5.06 |
| 100 | 13.32 | 11.63 | 5.06 | 12.24 | 11.40 | 5.07 |
| 120 | 13.49 | 11.78 | 5.31 | 12.54 | 11.60 | 5.26 |
Table 3 Resolution(Rs) of adjacent peaks in (dT)n under different concentrations of ion-pair reagent
| cp/(mmol·L-1) | TEA/PA | TEA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T5/T7 | T7/T10 | T10/T12 | T5/T7 | T7/T10 | T10/T12 | |
| 20 | 10.28 | 9.24 | 3.78 | 9.79 | 9.26 | 4.08 |
| 40 | 11.79 | 10.42 | 4.44 | 10.96 | 10.20 | 4.53 |
| 60 | 12.50 | 10.96 | 4.76 | 11.58 | 10.48 | 4.85 |
| 80 | 12.92 | 11.32 | 4.85 | 11.83 | 10.98 | 5.06 |
| 100 | 13.32 | 11.63 | 5.06 | 12.24 | 11.40 | 5.07 |
| 120 | 13.49 | 11.78 | 5.31 | 12.54 | 11.60 | 5.26 |
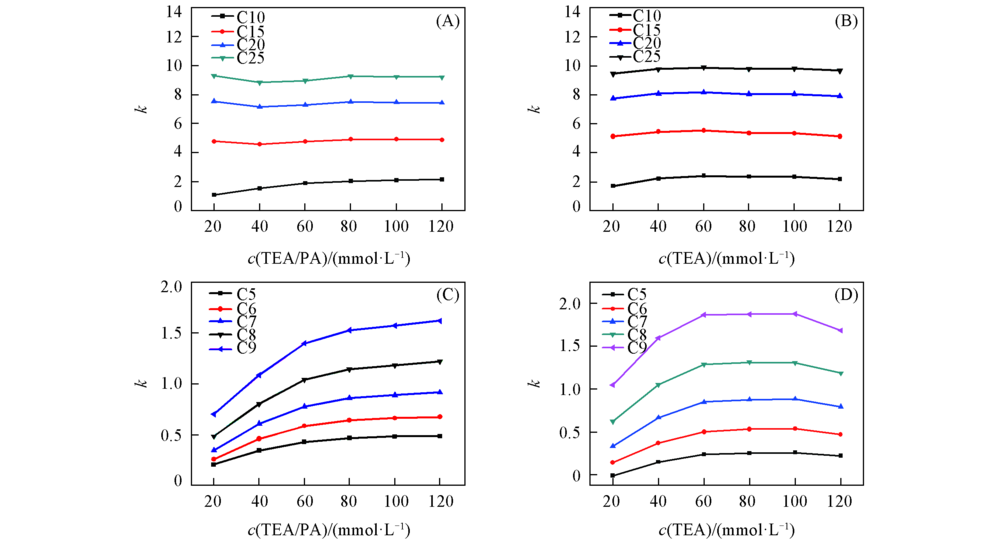
Fig.4 Retention factor(k) of (dC)n under mobile phases containing different concentrations of ion-pair reagent (A), (C) TEA/PA; (B), (D) TEA. The chromatographic conditions are the same as those in Fig.2.
| System | cp/(mmol·L-1) | C5/C6 | C6/C7 | C7/C8 | C8/C9 | C10/C15 | C15/C20 | C20/C25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEA/PA | 20 | 0.43 | 0.76 | 1.15 | 1.53 | 12.90 | 5.24 | 1.88 |
| 40 | 1.21 | 1.33 | 1.38 | 1.68 | 12.03 | 5.44 | 2.09 | |
| 60 | 1.54 | 1.58 | 1.80 | 2.02 | 11.46 | 5.37 | 2.01 | |
| 80 | 1.67 | 1.81 | 1.91 | 2.12 | 11.37 | 5.47 | 1.93 | |
| 100 | 1.72 | 1.86 | 1.94 | 2.10 | 11.43 | 5.09 | 2.06 | |
| 120 | 1.79 | 1.95 | 2.02 | 2.16 | 10.94 | 5.45 | 2.15 | |
| TEA | 20 | 1.16 | 1.25 | 1.67 | 2.00 | 13.01 | 5.57 | 2.00 |
| 40 | 1.69 | 1.86 | 1.98 | 2.35 | 13.46 | 5.53 | 1.94 | |
| 60 | 1.82 | 1.98 | 2.12 | 2.46 | 13.05 | 5.51 | 1.97 | |
| 80 | 1.91 | 1.98 | 2.16 | 2.41 | 12.48 | 5.62 | 1.99 | |
| 100 | 1.86 | 1.93 | 2.07 | 2.29 | 12.36 | 5.31 | 2.01 | |
| 120 | 1.73 | 1.90 | 1.96 | 2.15 | 12.04 | 5.71 | 2.04 |
Table 4 Resolution(Rs) of adjacent peaks in (dC)n under different concentrations of ion-pair reagent
| System | cp/(mmol·L-1) | C5/C6 | C6/C7 | C7/C8 | C8/C9 | C10/C15 | C15/C20 | C20/C25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEA/PA | 20 | 0.43 | 0.76 | 1.15 | 1.53 | 12.90 | 5.24 | 1.88 |
| 40 | 1.21 | 1.33 | 1.38 | 1.68 | 12.03 | 5.44 | 2.09 | |
| 60 | 1.54 | 1.58 | 1.80 | 2.02 | 11.46 | 5.37 | 2.01 | |
| 80 | 1.67 | 1.81 | 1.91 | 2.12 | 11.37 | 5.47 | 1.93 | |
| 100 | 1.72 | 1.86 | 1.94 | 2.10 | 11.43 | 5.09 | 2.06 | |
| 120 | 1.79 | 1.95 | 2.02 | 2.16 | 10.94 | 5.45 | 2.15 | |
| TEA | 20 | 1.16 | 1.25 | 1.67 | 2.00 | 13.01 | 5.57 | 2.00 |
| 40 | 1.69 | 1.86 | 1.98 | 2.35 | 13.46 | 5.53 | 1.94 | |
| 60 | 1.82 | 1.98 | 2.12 | 2.46 | 13.05 | 5.51 | 1.97 | |
| 80 | 1.91 | 1.98 | 2.16 | 2.41 | 12.48 | 5.62 | 1.99 | |
| 100 | 1.86 | 1.93 | 2.07 | 2.29 | 12.36 | 5.31 | 2.01 | |
| 120 | 1.73 | 1.90 | 1.96 | 2.15 | 12.04 | 5.71 | 2.04 |
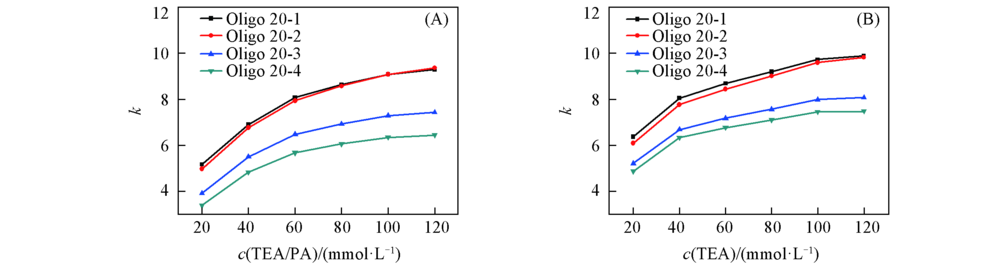
Fig.5 Retention factor(k) of 20mer hetero-oligonucleotides under mobile phases containing different concentrations of ion-pair reagent (A) TEA/PA; (B) TEA. The chromatographic conditions are the same as those in Fig.2.
| cp/(mmol·L-1) | TEA/PA | TEA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20-4/20-3 | 20-3/20-2 | 20-2/20-1 | 20-4/20-3 | 20-3/20-2 | 20-2/20-1 | |
| 20 | 2.18 | 4.41 | 0.87 | 1.50 | 3.90 | 1.29 |
| 40 | 3.34 | 6.29 | 0.61 | 1.61 | 5.00 | 1.32 |
| 60 | 3.73 | 6.88 | 0.61 | 1.88 | 5.88 | 1.15 |
| 80 | 4.01 | 7.59 | 0.28 | 2.12 | 6.65 | 0.84 |
| 100 | 4.39 | 8.52a | 0.02b | 2.42 | 7.29 | 0.60 |
| 120 | 4.53 | 8.74a | 0.34b | 2.65 | 7.84 | 0.28 |
Table 5 Resolution(Rs) of adjacent peaks in 20mer hetero-oligonucleotides under different concentrations of ion-pair reagent
| cp/(mmol·L-1) | TEA/PA | TEA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20-4/20-3 | 20-3/20-2 | 20-2/20-1 | 20-4/20-3 | 20-3/20-2 | 20-2/20-1 | |
| 20 | 2.18 | 4.41 | 0.87 | 1.50 | 3.90 | 1.29 |
| 40 | 3.34 | 6.29 | 0.61 | 1.61 | 5.00 | 1.32 |
| 60 | 3.73 | 6.88 | 0.61 | 1.88 | 5.88 | 1.15 |
| 80 | 4.01 | 7.59 | 0.28 | 2.12 | 6.65 | 0.84 |
| 100 | 4.39 | 8.52a | 0.02b | 2.42 | 7.29 | 0.60 |
| 120 | 4.53 | 8.74a | 0.34b | 2.65 | 7.84 | 0.28 |
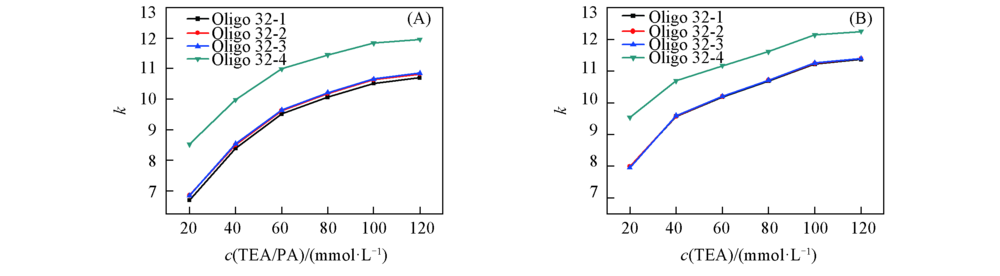
Fig.6 Retention factor(k) of 32mer hetero-oligonucleotides under mobile phases containing different concentrations of ion-pair reagent (A) TEA/PA; (B) TEA. The chromatographic conditions a the same as those in Fig.2.
| cp/(mmol·L-1) | TEA/PA | TEA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 32-1/32-2 | 32-2/32-3 | 32-3/32-4 | 32-1/32-2 | 32-2/32-3 | 32-3/32-4 | |
| 20 | 0.49 | 0.02 | 4.92 | 0.10a | 0.02b | 5.07c |
| 40 | 0.48 | 0.13 | 5.24 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 4.22 |
| 60 | 0.46 | 0.07 | 5.16 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 3.84 |
| 80 | 0.48 | 0.10 | 4.81 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 3.65 |
| 100 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 4.65 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 3.61 |
| 120 | 0.50 | 0.16 | 4.48 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 3.42 |
Table 6 Resolution of adjacent peaks in 32mer hetero-oligonucleotides under different concentrations of ion-pair reagent
| cp/(mmol·L-1) | TEA/PA | TEA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 32-1/32-2 | 32-2/32-3 | 32-3/32-4 | 32-1/32-2 | 32-2/32-3 | 32-3/32-4 | |
| 20 | 0.49 | 0.02 | 4.92 | 0.10a | 0.02b | 5.07c |
| 40 | 0.48 | 0.13 | 5.24 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 4.22 |
| 60 | 0.46 | 0.07 | 5.16 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 3.84 |
| 80 | 0.48 | 0.10 | 4.81 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 3.65 |
| 100 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 4.65 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 3.61 |
| 120 | 0.50 | 0.16 | 4.48 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 3.42 |
| Oligonucleotide | TEA/PA | TEA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | Slope | R2 | Intercept | Slope | R2 | |
| A10 | 1.6110 | 0.0310 | 0.841 | 2.9782 | 0.0266 | 0.816 |
| A20 | 2.7694 | 0.0452 | 0.830 | 5.0068 | 0.0376 | 0.806 |
| A25 | 3.2356 | 0.0480 | 0.830 | 5.7163 | 0.0399 | 0.804 |
| A30 | 3.6109 | 0.0498 | 0.831 | 6.2791 | 0.0417 | 0.802 |
| T5 | 6.9595 | 0.0204 | 0.834 | 7.6807 | 0.0165 | 0.894 |
| T7 | 8.8489 | 0.0268 | 0.849 | 9.4400 | 0.0225 | 0.911 |
| T10 | 10.6040 | 0.0314 | 0.866 | 11.1440 | 0.0274 | 0.923 |
| T12 | 11.3850 | 0.0333 | 0.868 | 11.9050 | 0.0297 | 0.929 |
| C5 | 0.2155 | 0.0027 | 0.772 | 0.4297 | 0.0017 | 0.496 |
| C6 | 0.2714 | 0.0039 | 0.783 | 0.5674 | 0.0025 | 0.488 |
| C7 | 0.3539 | 0.0054 | 0.808 | 0.7494 | 0.0034 | 0.459 |
| C8 | 0.4859 | 0.0071 | 0.815 | 1.0169 | 0.0041 | 0.397 |
| C9 | 0.6992 | 0.0088 | 0.816 | 1.4032 | 0.0046 | 0.316 |
| Oligo20-1 | 5.0833 | 0.0396 | 0.860 | 6.3444 | 0.0330 | 0.867 |
| Oligo20-2 | 4.8244 | 0.0422 | 0.880 | 5.9811 | 0.0353 | 0.893 |
| Oligo20-3 | 3.9152 | 0.0334 | 0.836 | 5.2573 | 0.0266 | 0.836 |
| Oligo20-4 | 3.4328 | 0.0289 | 0.814 | 4.9940 | 0.0239 | 0.788 |
| Oligo32-1 | 6.6123 | 0.0386 | 0.860 | 7.9326 | 0.0319 | 0.876 |
| Oligo32-2 | 6.7599 | 0.0383 | 0.864 | 7.9301 | 0.0322 | 0.879 |
| Oligo32-3 | 6.7601 | 0.0386 | 0.863 | 7.9182 | 0.0324 | 0.870 |
| Oligo32-4 | 8.4744 | 0.0331 | 0.852 | 9.3990 | 0.02617 | 0.915 |
Table 7 Linear correlation between k and cp
| Oligonucleotide | TEA/PA | TEA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | Slope | R2 | Intercept | Slope | R2 | |
| A10 | 1.6110 | 0.0310 | 0.841 | 2.9782 | 0.0266 | 0.816 |
| A20 | 2.7694 | 0.0452 | 0.830 | 5.0068 | 0.0376 | 0.806 |
| A25 | 3.2356 | 0.0480 | 0.830 | 5.7163 | 0.0399 | 0.804 |
| A30 | 3.6109 | 0.0498 | 0.831 | 6.2791 | 0.0417 | 0.802 |
| T5 | 6.9595 | 0.0204 | 0.834 | 7.6807 | 0.0165 | 0.894 |
| T7 | 8.8489 | 0.0268 | 0.849 | 9.4400 | 0.0225 | 0.911 |
| T10 | 10.6040 | 0.0314 | 0.866 | 11.1440 | 0.0274 | 0.923 |
| T12 | 11.3850 | 0.0333 | 0.868 | 11.9050 | 0.0297 | 0.929 |
| C5 | 0.2155 | 0.0027 | 0.772 | 0.4297 | 0.0017 | 0.496 |
| C6 | 0.2714 | 0.0039 | 0.783 | 0.5674 | 0.0025 | 0.488 |
| C7 | 0.3539 | 0.0054 | 0.808 | 0.7494 | 0.0034 | 0.459 |
| C8 | 0.4859 | 0.0071 | 0.815 | 1.0169 | 0.0041 | 0.397 |
| C9 | 0.6992 | 0.0088 | 0.816 | 1.4032 | 0.0046 | 0.316 |
| Oligo20-1 | 5.0833 | 0.0396 | 0.860 | 6.3444 | 0.0330 | 0.867 |
| Oligo20-2 | 4.8244 | 0.0422 | 0.880 | 5.9811 | 0.0353 | 0.893 |
| Oligo20-3 | 3.9152 | 0.0334 | 0.836 | 5.2573 | 0.0266 | 0.836 |
| Oligo20-4 | 3.4328 | 0.0289 | 0.814 | 4.9940 | 0.0239 | 0.788 |
| Oligo32-1 | 6.6123 | 0.0386 | 0.860 | 7.9326 | 0.0319 | 0.876 |
| Oligo32-2 | 6.7599 | 0.0383 | 0.864 | 7.9301 | 0.0322 | 0.879 |
| Oligo32-3 | 6.7601 | 0.0386 | 0.863 | 7.9182 | 0.0324 | 0.870 |
| Oligo32-4 | 8.4744 | 0.0331 | 0.852 | 9.3990 | 0.02617 | 0.915 |
| Oligonucleotide | TEA/PA | TEA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | B1 | R2 | A1 | B1 | R2 | |
| A10 | 0.1012 | 10.026 | 0.984 | 0.1339 | 4.1449 | 0.991 |
| A20 | 0.0750 | 5.6674 | 0.985 | 0.0907 | 2.2607 | 0.993 |
| A25 | 0.0737 | 4.6767 | 0.988 | 0.0834 | 1.9013 | 0.994 |
| A30 | 0.0726 | 4.0594 | 0.990 | 0.0784 | 1.6810 | 0.994 |
| T5 | 0.1035 | 0.8199 | 0.987 | 0.1024 | 0.5507 | 0.957 |
| T7 | 0.0791 | 0.7760 | 0.999 | 0.0815 | 0.4808 | 0.955 |
| T10 | 0.0677 | 0.5527 | 0.987 | 0.0686 | 0.4111 | 0.948 |
| T12 | 0.0636 | 0.4860 | 0.980 | 0.0640 | 0.3872 | 0.946 |
| C5 | 1.3103 | 69.715 | 0.984 | 1.4721 | 20.595 | 0.942 |
| C6 | 0.8572 | 58.660 | 0.981 | 1.0707 | 16.734 | 0.937 |
| C7 | 0.6338 | 44.098 | 0.986 | 0.7867 | 13.573 | 0.930 |
| C8 | 0.5083 | 30.667 | 0.990 | 0.6100 | 9.5254 | 0.915 |
| C9 | 0.4201 | 19.968 | 0.993 | 0.4803 | 6.1408 | 0.877 |
| C10 | 0.3614 | 11.452 | 0.994 | 0.3818 | 3.6390 | 0.762 |
| Oligo20-1 | 0.0901 | 2.0868 | 0.998 | 0.0825 | 1.3597 | 0.995 |
| Oligo20-2 | 0.0881 | 2.2844 | 0.998 | 0.0821 | 1.2991 | 0.993 |
| Oligo20-3 | 0.1079 | 2.9454 | 0.999 | 0.0881 | 2.2844 | 0.998 |
| Oligo20-4 | 0.1228 | 3.4268 | 0.997 | 0.1079 | 2.9454 | 0.999 |
| Oligo32-1 | 0.0825 | 1.3597 | 0.995 | 0.0818 | 0.8813 | 0.989 |
| Oligo32-2 | 0.0821 | 1.2991 | 0.993 | 0.0816 | 0.8847 | 0.989 |
| Oligo32-3 | 0.0817 | 1.3088 | 0.994 | 0.0813 | 0.8989 | 0.991 |
| Oligo32-4 | 0.0773 | 0.8182 | 0.988 | 0.0786 | 0.5428 | 0.960 |
Table 8 Correlations of k-1-cp fitted according to Eq.(9)
| Oligonucleotide | TEA/PA | TEA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | B1 | R2 | A1 | B1 | R2 | |
| A10 | 0.1012 | 10.026 | 0.984 | 0.1339 | 4.1449 | 0.991 |
| A20 | 0.0750 | 5.6674 | 0.985 | 0.0907 | 2.2607 | 0.993 |
| A25 | 0.0737 | 4.6767 | 0.988 | 0.0834 | 1.9013 | 0.994 |
| A30 | 0.0726 | 4.0594 | 0.990 | 0.0784 | 1.6810 | 0.994 |
| T5 | 0.1035 | 0.8199 | 0.987 | 0.1024 | 0.5507 | 0.957 |
| T7 | 0.0791 | 0.7760 | 0.999 | 0.0815 | 0.4808 | 0.955 |
| T10 | 0.0677 | 0.5527 | 0.987 | 0.0686 | 0.4111 | 0.948 |
| T12 | 0.0636 | 0.4860 | 0.980 | 0.0640 | 0.3872 | 0.946 |
| C5 | 1.3103 | 69.715 | 0.984 | 1.4721 | 20.595 | 0.942 |
| C6 | 0.8572 | 58.660 | 0.981 | 1.0707 | 16.734 | 0.937 |
| C7 | 0.6338 | 44.098 | 0.986 | 0.7867 | 13.573 | 0.930 |
| C8 | 0.5083 | 30.667 | 0.990 | 0.6100 | 9.5254 | 0.915 |
| C9 | 0.4201 | 19.968 | 0.993 | 0.4803 | 6.1408 | 0.877 |
| C10 | 0.3614 | 11.452 | 0.994 | 0.3818 | 3.6390 | 0.762 |
| Oligo20-1 | 0.0901 | 2.0868 | 0.998 | 0.0825 | 1.3597 | 0.995 |
| Oligo20-2 | 0.0881 | 2.2844 | 0.998 | 0.0821 | 1.2991 | 0.993 |
| Oligo20-3 | 0.1079 | 2.9454 | 0.999 | 0.0881 | 2.2844 | 0.998 |
| Oligo20-4 | 0.1228 | 3.4268 | 0.997 | 0.1079 | 2.9454 | 0.999 |
| Oligo32-1 | 0.0825 | 1.3597 | 0.995 | 0.0818 | 0.8813 | 0.989 |
| Oligo32-2 | 0.0821 | 1.2991 | 0.993 | 0.0816 | 0.8847 | 0.989 |
| Oligo32-3 | 0.0817 | 1.3088 | 0.994 | 0.0813 | 0.8989 | 0.991 |
| Oligo32-4 | 0.0773 | 0.8182 | 0.988 | 0.0786 | 0.5428 | 0.960 |
| Oligonucleotide | TEA/PA | TEA | Oligonucleotide | TEA/PA | TEA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K4 | K5 | K4 | K5 | K4 | K5 | K4 | K5 | ||
| A10 | 0.010 | 9.881β | 0.0323 | 7.468β | C8 | 0.017 | 1.967β | 0.0640 | 1.639β |
| A20 | 0.013 | 13.333β | 0.0401 | 11.025β | C9 | 0.021 | 2.380β | 0.0782 | 2.082β |
| A25 | 0.016 | 13.568β | 0.0439 | 11.990β | C10 | 0.032 | 2.767β | 0.1049 | 2.619β |
| A30 | 0.018 | 13.774β | 0.0466 | 12.755β | Oligo20-1 | 0.043 | 11.099β | 0.0607 | 12.121β |
| T5 | 0.126 | 9.662β | 0.1859 | 9.766β | Oligo20-2 | 0.039 | 11.351β | 0.0632 | 12.180β |
| T7 | 0.102 | 12.642β | 0.1695 | 12.270β | Oligo20-3 | 0.037 | 9.268β | 0.0386 | 11.351β |
| T10 | 0.122 | 14.771β | 0.1669 | 14.577β | Oligo20-4 | 0.036 | 8.143β | 0.0366 | 9.268β |
| T12 | 0.131 | 15.723β | 0.1653 | 15.625β | Oligo32-1 | 0.061 | 12.121β | 0.0928 | 12.225β |
| C5 | 0.019 | 0.763β | 0.0715 | 0.679β | Oligo32-2 | 0.063 | 12.180β | 0.0922 | 12.255β |
| C6 | 0.015 | 1.167β | 0.0640 | 0.934β | Oligo32-3 | 0.062 | 12.240β | 0.0904 | 12.300β |
| C7 | 0.014 | 1.578β | 0.0580 | 1.271β | Oligo32-4 | 0.094 | 12.937β | 0.1448 | 12.723β |
Table 9 Quilibrium constants of K4 and K5 for oligonucleotides
| Oligonucleotide | TEA/PA | TEA | Oligonucleotide | TEA/PA | TEA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K4 | K5 | K4 | K5 | K4 | K5 | K4 | K5 | ||
| A10 | 0.010 | 9.881β | 0.0323 | 7.468β | C8 | 0.017 | 1.967β | 0.0640 | 1.639β |
| A20 | 0.013 | 13.333β | 0.0401 | 11.025β | C9 | 0.021 | 2.380β | 0.0782 | 2.082β |
| A25 | 0.016 | 13.568β | 0.0439 | 11.990β | C10 | 0.032 | 2.767β | 0.1049 | 2.619β |
| A30 | 0.018 | 13.774β | 0.0466 | 12.755β | Oligo20-1 | 0.043 | 11.099β | 0.0607 | 12.121β |
| T5 | 0.126 | 9.662β | 0.1859 | 9.766β | Oligo20-2 | 0.039 | 11.351β | 0.0632 | 12.180β |
| T7 | 0.102 | 12.642β | 0.1695 | 12.270β | Oligo20-3 | 0.037 | 9.268β | 0.0386 | 11.351β |
| T10 | 0.122 | 14.771β | 0.1669 | 14.577β | Oligo20-4 | 0.036 | 8.143β | 0.0366 | 9.268β |
| T12 | 0.131 | 15.723β | 0.1653 | 15.625β | Oligo32-1 | 0.061 | 12.121β | 0.0928 | 12.225β |
| C5 | 0.019 | 0.763β | 0.0715 | 0.679β | Oligo32-2 | 0.063 | 12.180β | 0.0922 | 12.255β |
| C6 | 0.015 | 1.167β | 0.0640 | 0.934β | Oligo32-3 | 0.062 | 12.240β | 0.0904 | 12.300β |
| C7 | 0.014 | 1.578β | 0.0580 | 1.271β | Oligo32-4 | 0.094 | 12.937β | 0.1448 | 12.723β |
| [1] | Huber C. G., Oefner P. K., Bonn G. K., J. Chromatogr. A, 1992, 599(1/2), 113—118 |
| [2] | Apfell A., Chakel J. A., Fischer S., Lichtenwalter K., Hancock W. S., Anal. Chem., 1997, 69(7), 1320—1325 |
| [3] | Gilar M., Foutain K. J., Budman Y., Neue U. D., Yardley K. R., Rainville P. D., Russell R. J., Gebler J.C., J. Chromatogr. A, 2002, 958(1/2), 167—182 |
| [4] | Huber C. G., Krajete A., Anal. Chem., 1999, 71(17), 3730—3739 |
| [5] | Huber C. G., Krajete A., J. Chromatogr. A, 2000, 870(1/2), 413—424 |
| [6] | Buncek M., Backovska V., Holasova A., Radilova H., Safarova M., Kunc F., Haluza R., Anal. Biochem., 2006, 348(2), 300—306 |
| [7] | Bothner B., Chatman K., Sarkisian M., Siuzdak G., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 1995, 5(23), 2863—2868 |
| [8] | Apffel A., Chakel J., Fischer S., Lichtenwalter K., Hancock W., J. Chromatogr. A, 1997, 777(1), 3—21 |
| [9] | Kenski D. M., Cooper A. J., Li J. J., Willingham A. T., Haringsma H. J., Young T. A., Kuklin N. A., Jones J. J., Cancilla M. T., McMasters D. R., Nucleic Acids Res., 2010, 38(2), 660—671 |
| [10] | Dai G., Wei X., Liu Z., Liu S., Marcucci G., Chan K. K., J. Chromatogr. B, 2005, 825(2), 201—213 |
| [11] | Deng P., Chen X., Zhang G., Zhong D., J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2010, 52(4), 571—579 |
| [12] | Zhang G., Lin J., Srinivasan K., Kavetskaia O., Duncan J., Anal. Chem., 2007, 79(9), 3416—3424 |
| [13] | Lin Z., Li W., Dai G., J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2007, 44(2), 330—341 |
| [14] | Oberacher H., Parson W., Muhlmann R., Huber C., Anal. Chem., 2001, 73(21), 5109—5115 |
| [15] | Oberacher H., Oefner P., Parson W., Huber C., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2001, 40(20), 3828—3830 |
| [16] | Oberacher H., Niederstatter H., Pitterl F., Parson W., Anal. Chem., 2006, 78(22), 7816—7827 |
| [17] | Erb R., Leithner K., Bernkop-Schnürch A., Oberacher H., AAPS J., 2012, 14(4), 728—736 |
| [18] | McCarthy S. M., Gilar M., Gebler J., Anal. Biochem., 2009, 390(2), 181—188 |
| [19] | Gong L. Z., McCullagh J. S. O., Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 2014, 28(4), 339—350 |
| [20] | Miyaguchi H., JoVE-J. Vis. Exp., 2016, (115), e54402 |
| [21] | Beverly M., Hartsough K., Machemer L., Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom.,2005, 19(12), 1675—1682 |
| [22] | Beverly M., Hartsough K., Machemer L., Pavco P., Lockridge J., J. Chromatogr. B, 2006, 835(1/2), 62—70 |
| [23] | Levin D. S., Shepperd B. T., Gruenloh C. J., J. Chromatogr. B, 2011, 879(19), 1587—1595 |
| [24] | Yuan N., Han S. Y., Yang J., Qiao J. Q., Liu Y., Lian H. Z., Curr. Anal. Chem.,2012, 8(4), 550—556 |
| [25] | Qiao J. Q., Liang C., Wei L. C., Cao Z. M., Lian H. Z., J. Sep. Sci., 2016, 39(23), 4502—4511 |
| [26] | Tomlinson E., Riley C. M., Jefferies T. M., J. Chromatogr. A, 1979, 173(1), 89—100 |
| [27] | Wang Y. P., Shen G. Q., Zhu M. H., Acta Chim. Sinica, 1993, 51, 392—396 |
| (王延平, 沈国钦, 朱明华. 化学学报, 1993, 51, 392—396) | |
| [28] | Han S. Y., Qiao J. Q., Zhang Y. Y., Yang L. L., Lian H. Z., Ge X., Chen H. Y., Chemosphere, 2011, 83(2), 131—136 |
| [29] | Huber C. G., Oefner P. J., Bonn G. K., Anal. Biochem., 1993, 212(2), 351—358 |
| [30] | Lee D. P., Kindsvater J. H., Anal. Chem., 1980, 52(14), 2425—2428 |
| [31] | Huber C. G., Oefner P. J., Bonn G. K., J. Chromatogr. A, 1992, 599(1/2), 113—118 |
| [32] | Knox J. H., Hartwick R. A., J Chromatogr., 1981, 204(1), 3—21 |
| [33] | Horvath C., Melander W., Monlar I., Anal. Chem., 1977, 49(1), 142—154 |
| [1] | 余琼卫, 郑凤, 方凯敏, 冯钰锜. 纳米氧化锆沉积硅胶色谱固定相的制备及亲水作用色谱行为[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(9): 1857. |
| [2] | 陈琰, 刘桂锋, 刘霞, 张桂珍, 王振新. 应用微阵列芯片检测与2型糖尿病相关的单核苷酸多态性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(5): 1078. |
| [3] | 陈敏敏, 邹永存, 孟云君, 张琪, 张卓琦, 曹希传. AMS-8-NH2的合成及其对ODN的负载释放[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(4): 649. |
| [4] | 李富荣,乔飞燕,孔小丽,周汉新,齐晖,任莉莉 . 抗体和寡核苷酸双标记纳米金生物探针的制备及生物学特性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30(1): 60. |
| [5] | 潘沁, 许利剑, 王志飞, 陆祖宏, 何农跃. 纳米金标记电化学检测DNA特异性结合蛋白[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(12): 2290. |
| [6] | 雷荣, 邢毓杰, 杨俊佼, 左育民. 用线性溶剂化能相关(LSERs)方法评价聚合物包覆钛胶固定相并与相关固定相比较[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2001, 22(S1): 45. |
| [7] | 申贵隽, 彭增辉, 黄海英, 师宇华, 于爱民, 金钦汉. 静电离子色谱用于硼酸溶液中硼不同形态组分分离的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1999, 20(10): 1538. |
| [8] | 栾连军, 曾苏, 刘志强, 傅旭春. 羟基化合物及其葡醛酸苷化学结构与RP-HPLC保留行为相关性研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1997, 18(1): 42. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||