

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (9): 2046.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200291
收稿日期:2020-05-25
出版日期:2020-09-10
发布日期:2020-09-02
通讯作者:
王一波
E-mail:ybw@gzu.edu.cn
基金资助:Received:2020-05-25
Online:2020-09-10
Published:2020-09-02
Contact:
WANG Yibo
E-mail:ybw@gzu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
以CCSD(T)/CBS方法的结合能计算结果为标准, 选择CAM-B3LYP-D3BJ/def2-SVPD密度泛函理论方法计算了甲氧基柱[5]芳烃(MeP5)与CnH2n+2(n=1~10, 12, 14, 16) 复合物的结合能, 结果表明, 它们之间存在强烈的相互作用, 且随着烷烃分子碳链的增长而增大; 热力学函数计算结果表明, 在298.15 K, 101325 Pa下, MeP5与CnH2n+2(n=3~10, 12, 14, 16)形成复合物的过程中, ΔG和ΔH均小于零, 是焓驱动的自发过程. 烷烃与MeP5之间C―H…π和C―H…O的协同作用是主客体复合物稳定化的起因, 用二代绝对局域分子轨道能量分解(ALMO-EDA)方法分析此协同作用, 发现其中静电作用和色散作用的贡献相近, 二者加和约占总吸引的94%, 极化能和电荷转移能仅占6%.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
孙涛, 王一波. 柱芳烃与烷烃间C―H…π和C―H…O的作用本质及协同性. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(9): 2046.
SUN Tao, WANG Yibo. Theoretical Study on the Nature and Cooperation of C―H•••O and C―H•••π Interactions in the Pillar[5]arene and n⁃Alkanes Complexes. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2046.
| Method | ΔEb/(kJ·mol-1) | Method | ΔEb/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| def2?SVPD | def2?TZVPP | def2?SVPD | def2?TZVPP | ||
| CCSD(T)/CBS | -23.77 | -23.77 | PBE0?D3BJ | -24.69 | -24.89 |
| ωB97X?V | -24.31 | -24.81 | B3LYP?D3BJ | -25.10 | -25.31 |
| ωB97M?V | -24.48 | -25.19 | B3PW91?D3BJ | -24.85 | -25.15 |
| ωB97X?D | -28.03 | -28.58 | CAM?B3LYP?D3BJ | -23.97 | -24.14 |
| M06?2X?D3 | -23.26 | -23.10 | LC?ωPBE?D3BJ | -24.56 | -24.77 |
| PBE?D3BJ | -24.94 | -25.15 | B2PLYP?D3BJ | -21.55 | -21.92 |
Table 1 Binding energies(ΔEb) of C10H14O2…C8H18 complex using density functional theory methods with different basis sets
| Method | ΔEb/(kJ·mol-1) | Method | ΔEb/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| def2?SVPD | def2?TZVPP | def2?SVPD | def2?TZVPP | ||
| CCSD(T)/CBS | -23.77 | -23.77 | PBE0?D3BJ | -24.69 | -24.89 |
| ωB97X?V | -24.31 | -24.81 | B3LYP?D3BJ | -25.10 | -25.31 |
| ωB97M?V | -24.48 | -25.19 | B3PW91?D3BJ | -24.85 | -25.15 |
| ωB97X?D | -28.03 | -28.58 | CAM?B3LYP?D3BJ | -23.97 | -24.14 |
| M06?2X?D3 | -23.26 | -23.10 | LC?ωPBE?D3BJ | -24.56 | -24.77 |
| PBE?D3BJ | -24.94 | -25.15 | B2PLYP?D3BJ | -21.55 | -21.92 |
| Complex | (kJ·mol-1) | (kJ·mol-1) | Complex | (kJ·mol-1) | (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MeP5…CH4 | -32.68 | -30.33 | MeP5…C8H18 | -129.37 | -113.80 |
| MeP5…C2H6 | -55.69 | -49.62 | MeP5 …C9H20 | -133.43 | -117.53 |
| MeP5 …C3H8 | -74.35 | -65.73 | MeP5…C10H22 | -137.74 | -121.38 |
| MeP5…C4H10 | -91.42 | -81.34 | MeP5…C12H26 | -141.92 | -124.77 |
| MeP5…C5H12 | -103.85 | -91.17 | MeP5…C14H30 | -144.10 | -126.52 |
| MeP5…C6H14 | -112.97 | -100.29 | MeP5…C16H34 | -144.64 | -126.98 |
| MeP5…C7H16 | -121.63 | -106.82 |
Table 2 Binding energies of MeP5…CnH2n+2(n=1―10, 12, 14, 16)
| Complex | (kJ·mol-1) | (kJ·mol-1) | Complex | (kJ·mol-1) | (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MeP5…CH4 | -32.68 | -30.33 | MeP5…C8H18 | -129.37 | -113.80 |
| MeP5…C2H6 | -55.69 | -49.62 | MeP5 …C9H20 | -133.43 | -117.53 |
| MeP5 …C3H8 | -74.35 | -65.73 | MeP5…C10H22 | -137.74 | -121.38 |
| MeP5…C4H10 | -91.42 | -81.34 | MeP5…C12H26 | -141.92 | -124.77 |
| MeP5…C5H12 | -103.85 | -91.17 | MeP5…C14H30 | -144.10 | -126.52 |
| MeP5…C6H14 | -112.97 | -100.29 | MeP5…C16H34 | -144.64 | -126.98 |
| MeP5…C7H16 | -121.63 | -106.82 |
| Complex | EALMO-EDA/(kJ·mol-1) | EElec/(kJ·mol-1) | EPauli/(kJ·mol-1) | EDisp/(kJ·mol-1) | EPol/(kJ·mol-1) | ECT/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MeP5…C12H26 | -124.75 | -210.48(46.06%) | 332.23 | -219.45(48.02%) | -15.28(3.34%) | -11.76(2.57%) |
| Model A | -21.18 | -72.98(47.92%) | 131.10 | -66.15(43.44%) | -5.13(3.37%) | -8.03(5.27%) |
| Model B | -72.25 | -136.60(47.98%) | 212.49 | -131.44(46.16%) | -8.26(2.90%) | -8.43(2.96%) |
Table 3 Binding energies and energy components of MeP5…C12H26 in models A and B*
| Complex | EALMO-EDA/(kJ·mol-1) | EElec/(kJ·mol-1) | EPauli/(kJ·mol-1) | EDisp/(kJ·mol-1) | EPol/(kJ·mol-1) | ECT/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MeP5…C12H26 | -124.75 | -210.48(46.06%) | 332.23 | -219.45(48.02%) | -15.28(3.34%) | -11.76(2.57%) |
| Model A | -21.18 | -72.98(47.92%) | 131.10 | -66.15(43.44%) | -5.13(3.37%) | -8.03(5.27%) |
| Model B | -72.25 | -136.60(47.98%) | 212.49 | -131.44(46.16%) | -8.26(2.90%) | -8.43(2.96%) |
| Complex | EALMO-EDA/ (kJ·mol-1) | EElec/(kJ·mol-1) | EPauli/ (kJ·mol-1) | EDisp/(kJ·mol-1) | EPol/(kJ·mol-1) | ECT/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MeP5…CH4 | -30.34 | -41.40(43.88%) | 64.01 | -47.75(50.61%) | -2.85(3.02%) | -2.35(2.49%) |
| MeP5…C2H6 | -49.62 | -80.48(46.13%) | 124.83 | -83.77(48.02%) | -5.79(3.32%) | -4.41(2.53%) |
| MeP5…C3H8 | -65.72 | -84.80(43.68%) | 128.43 | -99.12(51.06%) | -6.19(3.19%) | -4.04(2.08%) |
| MeP5…C4H10 | -81.34 | -107.92(43.70%) | 165.62 | -124.55(50.43%) | -8.51(3.44%) | -5.99(2.42%) |
| MeP5…C5H12 | -91.17 | -140.68(45.25%) | 219.71 | -150.93(48.55%) | -10.99(3.53%) | -8.28(2.66%) |
| MeP5 …C6H14 | -100.28 | -159.50(45.52%) | 250.15 | -168.81(48.17%) | -12.33(3.52%) | -9.79(2.79%) |
| MeP5…C7H16 | -106.80 | -181.70(46.40%) | 284.80 | -185.67(47.41%) | -13.49(3.45%) | -10.74(2.74%) |
| MeP5…C8H18 | -113.79 | -191.62(46.22%) | 300.76 | -197.79(47.71%) | -14.19(3.42%) | -10.95(2.64%) |
| MeP5…C9H20 | -117.48 | -199.39(46.23%) | 313.78 | -206.06(47.78%) | -14.59(3.38%) | -11.22(2.60%) |
| MeP5…C10H22 | -121.39 | -204.88(46.09%) | 323.10 | -213.30(47.99%) | -14.85(3.34%) | -11.46(2.58%) |
| MeP5…C12H26 | -124.75 | -210.48(46.06%) | 332.23 | -219.45(48.02%) | -15.28(3.34%) | -11.76(2.57%) |
| MeP5…C14H30 | -126.53 | -212.03(45.92%) | 335.19 | -222.26(48.14%) | -15.45(3.35%) | -11.98(2.60%) |
| MeP5…C16H34 | -126.96 | -212.72(45.92%) | 336.25 | -223.09(48.16%) | -15.50(3.35%) | -11.89(2.57%) |
Table 4 ALMO-EDA energy components calculated with CAM-B3LYP-D3BJ/def2-SVPD*
| Complex | EALMO-EDA/ (kJ·mol-1) | EElec/(kJ·mol-1) | EPauli/ (kJ·mol-1) | EDisp/(kJ·mol-1) | EPol/(kJ·mol-1) | ECT/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MeP5…CH4 | -30.34 | -41.40(43.88%) | 64.01 | -47.75(50.61%) | -2.85(3.02%) | -2.35(2.49%) |
| MeP5…C2H6 | -49.62 | -80.48(46.13%) | 124.83 | -83.77(48.02%) | -5.79(3.32%) | -4.41(2.53%) |
| MeP5…C3H8 | -65.72 | -84.80(43.68%) | 128.43 | -99.12(51.06%) | -6.19(3.19%) | -4.04(2.08%) |
| MeP5…C4H10 | -81.34 | -107.92(43.70%) | 165.62 | -124.55(50.43%) | -8.51(3.44%) | -5.99(2.42%) |
| MeP5…C5H12 | -91.17 | -140.68(45.25%) | 219.71 | -150.93(48.55%) | -10.99(3.53%) | -8.28(2.66%) |
| MeP5 …C6H14 | -100.28 | -159.50(45.52%) | 250.15 | -168.81(48.17%) | -12.33(3.52%) | -9.79(2.79%) |
| MeP5…C7H16 | -106.80 | -181.70(46.40%) | 284.80 | -185.67(47.41%) | -13.49(3.45%) | -10.74(2.74%) |
| MeP5…C8H18 | -113.79 | -191.62(46.22%) | 300.76 | -197.79(47.71%) | -14.19(3.42%) | -10.95(2.64%) |
| MeP5…C9H20 | -117.48 | -199.39(46.23%) | 313.78 | -206.06(47.78%) | -14.59(3.38%) | -11.22(2.60%) |
| MeP5…C10H22 | -121.39 | -204.88(46.09%) | 323.10 | -213.30(47.99%) | -14.85(3.34%) | -11.46(2.58%) |
| MeP5…C12H26 | -124.75 | -210.48(46.06%) | 332.23 | -219.45(48.02%) | -15.28(3.34%) | -11.76(2.57%) |
| MeP5…C14H30 | -126.53 | -212.03(45.92%) | 335.19 | -222.26(48.14%) | -15.45(3.35%) | -11.98(2.60%) |
| MeP5…C16H34 | -126.96 | -212.72(45.92%) | 336.25 | -223.09(48.16%) | -15.50(3.35%) | -11.89(2.57%) |
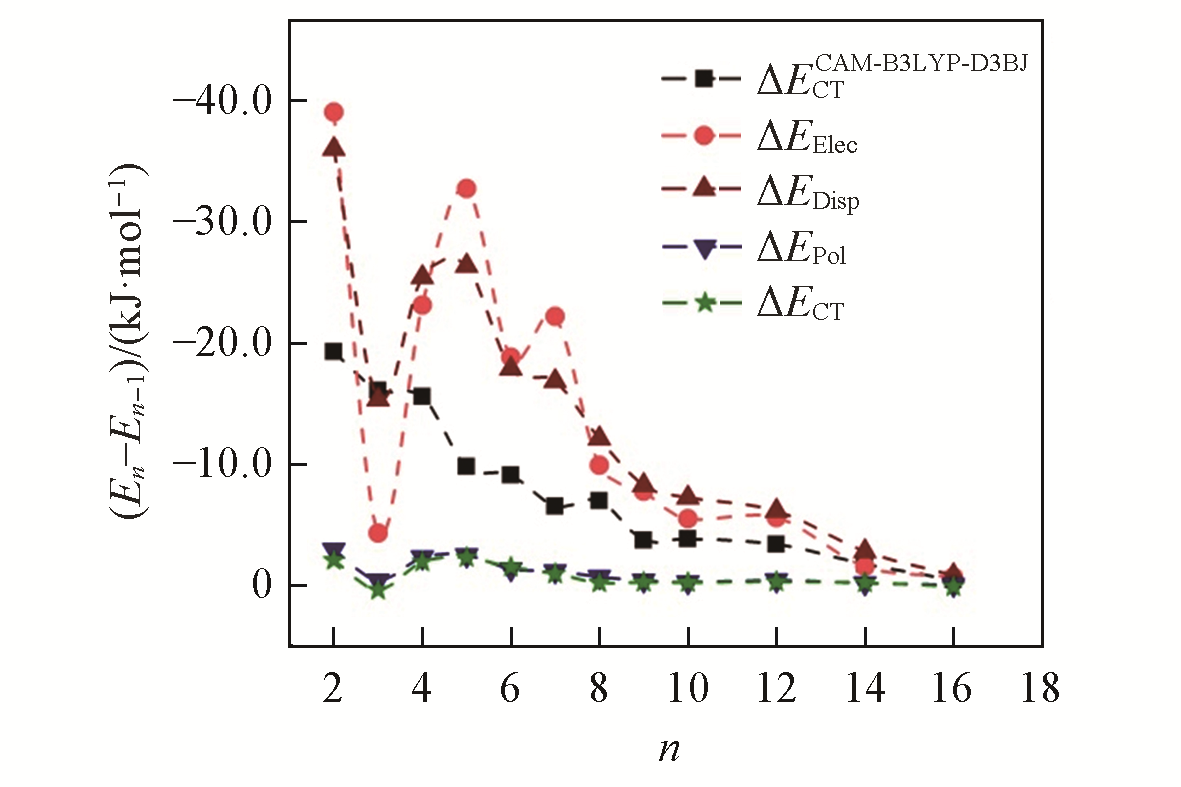
Fig.8 Subtracted value between the binding energy, electrostatics, dispersion, polarization and charge transfer of MeP5…CnH2n+2 and MeP5…Cn-1H2n(n=2―10, 12, 14, 16)
| 1 | Ogoshi T., Kanai S., Fujinami S., Yamagishi T. A., Nakamoto Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130(15), 5022―5023 |
| 2 | Yu G., HanC., Zhang Z., Chen J., Yan X., Zheng B., Liu S., Huang F. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(20), 8711―8717 |
| 3 | Han C. Y., Zhang Z. B., Chi X. D., Zhang M. M., Yu G. C., Huang F. H., Acta Chim. Sinica, 2012, 70(17), 1775―1778(韩成友, 张子彬, 池小东, 张明明, 喻国灿, 黄飞鹤. 化学学报, 2012, 70(17), 1775―1778) |
| 4 | Dai D. H., Li Z., Wang C. Y., Wu J. R., Wang Y., Zhang D. M., Yang Y. W., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2019, 141(11), 4756―4763 |
| 5 | Wang X. H., Song N., Hou W., Wang C. Y., Wang Y., Tang J., Yang Y. W., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(37), 1903962 |
| 6 | Song N., Kakuta T., Yamagishi T., Yang Y. W., Ogoshi T., Chem.,2018,4(9), 2029―2053 |
| 7 | Wang K., Yang Y. W., Zhang X. A., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(1), 1―13(王凯, 杨英威, 张晓安. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(1), 1―13) |
| 8 | Tan L. L., Li H., Tao Y., Zhang S. X., Wang B., Yang Y. W., Adv. Mater.,2014, 26(41), 7027―7031 |
| 9 | Tan L. L., Zhu Y., Long H., Jin Y., Zhang W., Yang Y. W., Chem. Commun., 2017, 53(48), 6409―6412 |
| 10 | Zhang Z. B., Xia B. Y., Han C. Y., Yu Y. H., Huang F. H., Org. Lett., 2010,12(15), 3285―3287 |
| 11 | Zhang Z. B., Luo Y., Chen J. Z., Dong S. Y., Yu Y. H., Ma Z., Huang F. H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011, 50(6), 1397―1401 |
| 12 | Zhang Z. B., Han C. Y., Yu G. C., Huang F. H., Chem. Sci., 2012, 3(10), 3026―3031 |
| 13 | Li C. J., Chen S. H., Li J., Han K., Xu M., Hu B. J., Yu Y. H., Jia X. S., Chem. Commun., 2011, 47(40), 11294―11296 |
| 14 | Shu X. Y., Chen S. H., Li J., Chen Z. X., Weng L. H., Jia X. S., Li C. Y., Chem. Commun., 2012, 48(24), 2967―2969 |
| 15 | Han K., Zhang Y. Y., Li J., Yu Y. H., Jia X. S., Li C. J., Eur. J. Org. Chem.,2013,2013(11), 2057―2060 |
| 16 | Ogoshi T., Sueto R., Yoshikoshi K., Yamaqishi T., Chem. Commun., 2014, 50(96), 15209―15211 |
| 17 | Ogoshi T., Demachi K., Kitajima K., Yamaqishi T., Chem. Commun., 2011,47(37), 10290―10292 |
| 18 | Ogoshi T., Sueto R., Yoshikoshi K., Sakata Y., Akine S., Yamagishi T., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(34), 9849―9852 |
| 19 | Ogoshi T., Sueto R., Hamada Y., Doitomi K., Hirao H., Sakata Y., Akine S., Kakuta T., Yamagishi T., Chem. Commun., 2017, 53(61),8577―8580 |
| 20 | Suvitha A., Venkataramanan N. S., J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem., 2017,87(1/2), 207―218 |
| 21 | Venkataramanan N. S., Suvitha A., Vijayaraghavan A., Thamotharan S., J. Mol. Liq., 2017, 241, 782―791 |
| 22 | Bhadane S. A., Lande D. N., Gejji S. P., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2016, 120(43), 8738―8749 |
| 23 | Grimme S., Antony J., Ehrlich S., Krieg H., J. Chem. Phys., 2010, 132(15), 154104 |
| 24 | Grimme S., Ehrlich S., Goerigk L., J. Comput. Chem., 2011, 32(7), 1456―1465 |
| 25 | Mardirossian N., Head⁃Gordon M., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16(21), 9904―9924 |
| 26 | Weigend F., Ahlrichs R., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2005, 7(18), 3297―3305 |
| 27 | Riley K. E., Pitoňák M., Jurečka P., Hobza P., Chem. Rev., 2010, 110(9), 5023―5063 |
| 28 | Chai J. D., Head⁃Gordon M., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2008, 10(44), 6615―6620 |
| 29 | Goerigk L., Grimme S., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011, 13(14), 6670―6688 |
| 30 | Wang Y. P., Study on Quantum Chemistry Method to Solve the Thermodynamic Functions in the Intermolecular Interaction, Guizhou University, Guiyang, 2018(王裕平. 分子间相互作用热力学函数的量子化学精确计算方法研究, 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2018) |
| 31 | Boys S. F., Bernardi F., Mol. Phys., 1970,19(4), 553―566 |
| 32 | Horn P. R., Mao Y., Head⁃Gordon M., J. Chem. Phys., 2016, 144(11), 114107 |
| 33 | Horn P. R., MaoY., Head⁃Gordon M., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18(33), 23067—23079 |
| 34 | Frisch M. J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Li X., Caricato M., Marenich A. V., Bloino J., Janesko B. G., Gomperts R., Mennucci B., Hratchian H. P., Ortiz J. V., Izmaylov A. F., Sonnenberg J. L., Williams⁃Young D., Ding F., Lipparini F., Egidi F., Goings J., Peng B., Petrone A., Henderson T., Ranasinghe D., Zakrzewski V. G., Gao J., Rega N., Zheng G., Liang W., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Vreven T., Throssell K., Montgomery J. A. Jr., Peralta J. E., Ogliaro F., Bearpark M. J., Heyd J. J., Brothers E. N., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N., Keith T. A., Kobayashi R., Normand J., Raghavachari K., Rendell A. P., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Millam J. M., Klene M., Adamo C., Cammi R., Ochterski J. W., Martin R. L., Morokuma K., Farkas O., Foresman J. B., Fox D. J., Gaussian 16, Revision A. 03, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT., 2016 |
| 35 | Shao Y. H., Gan Z. T., Epifanovsky E., Gilbert A. T. B., Wormit M., Kussmann J., Lange A. W., Behn A., Deng J., Feng X. T., Ghosh D., Goldey M., Horn P. R., Jacobson L. D., Kaliman I., Khaliullin R. Z., Kus T., Landau A., Liu J., Proynov E. I., Rhee Y. M., Richard R. M., Rohrdanz M. A., Steele R. P., Sundstrom E. J., Woodcock H. L., Zimmerman P. M., Zuev D., Albrecht B., Alguire E., Austin B., Beran G. J. O., Bernard Y. A., Berquist E., Brandhorst K., Bravaya K. B., Brown S. T., Casanova D., Chang C. M., Chen Y. Q., Chien S. H., Closser K. D., Crittenden D. L., Diedenhofen M., DiStasio R. A., Do H., Dutoi A. D., Edgar R. G., Fatehi S., FustiMolnar L., Ghysels A., Golubeva⁃Zadorozhnaya A., Gomes J., Hanson⁃Heine M. W. D., Harbach P. H. P., Hauser A. W., Hohenstein E. G., Holden Z. C., Jagau T. C., Ji H. J., Kaduk B., Khistyaev K., Kim J., King R. A., Klunzinger P., Kosenkov D., Kowalczyk T., Krauter C. M., Lao K. U., Laurent A. D., Lawler K. V., Levchenko S. V., Lin C. Y., Liu F., Livshits E., Lochan R. C., Luenser A., Manohar P., Manzer S. F., Mao S. P., Mardirossian N., Marenich A. V., Maurer S. A., Mayhall N. J., Neuscamman E., Oana C. M., Olivares⁃Amaya R., O’Neill D. P., Parkhill J. A., Perrine T. M., Peverati R., Prociuk A., Rehn D. R., Rosta E., Russ N. J., Sharada S. M., Sharma S., Small D. W., Sodt A., Stein T., Mol. Phys., 2015, 113(2), 184—215 |
| 36 | Elm J., Passananti M., Kurtén T., Vehkamäki H., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2017,121(32), 6155—6164 |
| 37 | Witte J., Neaton J. B., Head-Gordon M., J. Chem. Phys., 2017, 146(23), 234105 |
| [1] | 刘天伟, 张苏韬, 何江华, 张越涛. B(C6F5)3催化吲哚与苯乙炔的区域选择性加成[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(4): 719. |
| [2] | 刘艳芳, 杨华, 张辉. 分子动力学模拟烷烃混合物在石墨烯表面取向[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(8): 1729. |
| [3] | 阎小青, 刘秋双, 刘云凤, 牛侨. 季铵盐对碘代全氟烷烃的卤键吸附作用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(4): 743. |
| [4] | 方应国, 朱敏. 催化量碘代烷烃促进下合成3,5-二取代异噁唑啉[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(4): 660. |
| [5] | 董洁, 王丽, 赵越, 张家良, 郭洪臣. 添加气对非平衡等离子体转化低碳烷烃的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(1): 192. |
| [6] | 龚先杰, 郭永胜, 杨玉忠, 张玲玲, 方文军, 林瑞森. 直链烷烃与JP-10混配二元体系的体积性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(11): 2509. |
| [7] | 杨凤军, 郭永胜, 魏会, 邢燕, 方文军, 林瑞森. 正构烷烃/JP-10二元体系的体积性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(6): 1222. |
| [8] | 林永辉 宋凌春 莫亦荣 吴玮. 直链烷烃体系电子转移的价键方法研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2006, 27(1): 92. |
| [9] | 朱荣淑, 唐碧峰, 姬磊, 唐颖, 张嵩, 王艳梅, 张冰. 正一溴代烷烃的紫外光解动力学研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2004, 25(10): 1885. |
| [10] | 杜一平, 梁逸曾, 王文明. 用投影寻踪方法研究环烷烃保留指数与拓扑指数的定量构性关系[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2003, 24(10): 1795. |
| [11] | 张冬菊, 张长桥, 刘成卜. 过渡金属离子与烷烃反应机理的理论研究──镍离子(2D)与丙烷反应中氢分子的还原消除机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2002, 23(5): 876. |
| [12] | 田鹏, 许磊, 黄韬, 谢鹏, 刘中民. 含钴、锰杂原子分子筛上烷烃低温分子氧氧化[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2002, 23(4): 656. |
| [13] | 蒋亚琪, 周朝晖, 魏赞斌, 万惠霖. VPO催化剂前驱体的溶液法合成和结构研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2000, 21(8): 1177. |
| [14] | 魏俊发, 卓仁禧, 鄢国平, 杜波. 1,4,7,10-四氮杂环十二院的合成研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1997, 18(4): 658. |
| [15] | 冉琴, 陈从香, 张群, 俞书勤, 李月寒, 马兴孝. 电子激发态CH(C2Σ+)自由基的猝灭速率常数的测定[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1996, 17(3): 456. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
