

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (8): 1499.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160156
收稿日期:2016-03-18
出版日期:2016-07-19
发布日期:2016-07-19
作者简介:联系人简介: 张超杰, 女, 博士, 副教授, 主要从事工业污水处理理论与技术及难降解有机污染物的降解技术研究. E-mail:
基金资助:
GUO Rui, ZHANG Chaojie*( ), ZHANG Geng, ZHOU Qi
), ZHANG Geng, ZHOU Qi
Received:2016-03-18
Online:2016-07-19
Published:2016-07-19
Contact:
ZHANG Chaojie
E-mail:myrazh@tongji.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
研究了185 nm紫外光激发氯离子生成的水合电子还原降解全氟辛酸(PFOA)的效果. 结果表明, 该体系中氯离子、 紫外光和绝氧环境是保证PFOA高效降解的必要条件; 当PFOA的浓度为0.03 mmol/L时, 最佳反应条件为氯离子与PFOA摩尔浓度比(
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
郭睿, 张超杰, 张庚, 周琪. 紫外光致氯生水合电子对全氟辛酸的降解. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(8): 1499.
GUO Rui,ZHANG Chaojie,ZHANG Geng,ZHOU Qi. Degradation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid by UV/Chloride Process†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(8): 1499.
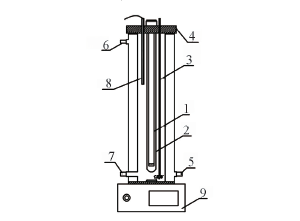
Fig.1 Equipment diagram 1. UV light; 2. quartz tube; 3. aerator pipe; 4. seal cover; 5. circulating water inlet valve; 6. circulating water outlet valve; 7. sampling place; 8. temperature probe; 9. magnetic stirring apparatus.
| System | cNaCl/(mmol·L-1) | Time(He)/min | pH | UV185 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFOA+He+NaCl+UV185 | 0.3 | 30 | 10.0 | Irradiate |
| PFOA+He+UV185 | 0 | 30 | 10.0 | Irradiate |
| PFOA+He+NaCl | 0.3 | 30 | 10.0 | None |
Table 1 Reaction conditions of three systems*
| System | cNaCl/(mmol·L-1) | Time(He)/min | pH | UV185 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFOA+He+NaCl+UV185 | 0.3 | 30 | 10.0 | Irradiate |
| PFOA+He+UV185 | 0 | 30 | 10.0 | Irradiate |
| PFOA+He+NaCl | 0.3 | 30 | 10.0 | None |
| System | Reaction kinetic | 103kobs/min-1 | Half-life/h | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFOA+NaCl+He+UV185 | First-order | 6.3 | 1.77 | This study |
| PFOA+KI+N2+UV254 | First-order | 7.0 | 1.58 | [ |
| PFOA+K2S2O8+O2+UV185 | First-order | 1.4 | 8.19 | [ |
| PFOA+N2+UV185 | First-order | 1.9 | [ |
Table 2 Degradations of PFOA in different reaction systems
| System | Reaction kinetic | 103kobs/min-1 | Half-life/h | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFOA+NaCl+He+UV185 | First-order | 6.3 | 1.77 | This study |
| PFOA+KI+N2+UV254 | First-order | 7.0 | 1.58 | [ |
| PFOA+K2S2O8+O2+UV185 | First-order | 1.4 | 8.19 | [ |
| PFOA+N2+UV185 | First-order | 1.9 | [ |
| [1] | Sagiv S., K. , Rifas-Shiman S., L. , Webster T., F. , Mora A., M. , Harris M., H. , Calafat A., M. , Ye X., Y. , Gillman M., W. , Oken, E. , Environl. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49( 19), 11849- 11858 |
| [2] |
Miller, A. , Elliott J., E. , Elliott K., H. , Lee, S. , Cyr, F. , Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2015, 34( 8), 1799- 1808
doi: 10.1002/etc.2992 URL pmid: 25989421 |
| [3] |
朱鹏, 段雪梅, 刘靖尧. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37( 1), 79- 87
doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150568 |
|
Zhu, P. , Duan X., M. , Liu J., Y. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37( 1), 79- 87
doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150568 |
|
| [4] |
Arvaniti O., S. , Stasinakis A., S. , Sci. Total. Environ., 2015, 524, 81- 92
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.023 URL pmid: 25889547 |
| [5] |
Wang T., Y. , Wang, P. , Meng, J. , Liu S., J. , Lu Y., L. , Khim J., S. , Giesy J., P. , Chemosphere, 2015, 129, 87- 99
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.09.021 URL pmid: 25262946 |
| [6] |
Armitage J., M. , Macleod, M. , Cousins I., T. , Environl. Sci. Technol., 2009, 43( 4), 1134- 1140
doi: 10.1021/es901832b URL pmid: 19320170 |
| [7] |
Prevedouros, K. , Cousins I., T. , Buck R., C. , Korzeniowski S., H. , Environl. Sci. Technol., 2006, 40( 1), 32- 44
doi: 10.1021/es0614870 URL pmid: 17154003 |
| [8] |
Domingo J., L. , Environ. Int., 2012, 40, 187- 195
doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2011.08.001 URL pmid: 21864910 |
| [9] |
李飞, 曾庆玲, 沈春花, 赵志领, 刘淑坡. 中国环境科学, 2012, (9), 1602- 1612
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.09.010 URL |
|
Li, F. , Zeng Q. L., Shen C. H., Zhao Z. L., Liu S. P., China Environ. Sci. , 2012, (9), 1602- 1612
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.09.010 URL |
|
| [10] |
Wang, P. , Lu Y., L. , Wang T., Y. , Fu Y., N. , Zhu Z., Y. , Liu S., J. , Xie S., W. , Xiao, Y. , Giesy J., P. , Environ. Pollut., 2014, 190, 115- 122
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2014.03.030 URL pmid: 24747105 |
| [11] |
崔瑞娜, 张亚婷, 王建设, 戴家银. 环境化学, 2013, (7), 1318- 1327
doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.07.027 URL |
|
Cui R., N. , Zhang Y. T., Wang J. S., Dai J. Y., Environ. Chem. , 2013, (7), 1318- 1327
doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.07.027 URL |
|
| [12] |
Xiao, F. , Simcik M., F. , Halbach T., R. , Gulliver J., S. , Water Res., 2015, 72, 64- 74
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.09.052 URL pmid: 25455741 |
| [13] |
Yao Y., M. , Zhu H., H. , Li, B. , Hu H., W. , Zhang, T. , Yamazaki, E. , Taniyasu, S. , Yamashita, N. , Sun H., W. , Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2014, 108, 318- 328
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.07.021 URL pmid: 25108512 |
| [14] | Guo C., S. , Zhang, Y. , Zhao, X. , Du, P. , Liu S., S. , Lv J., P. , Xu F., X. , Meng, W. , Xu, J. , Chemosphere, 2015, 127, 201- 207 |
| [15] |
Liu W., X. , He, W. , Qin, N. , Kong X., Z. , He Q., S. , Yang, B. , Yang, C. , Jorgensen S., E. , Xu F., L. , Environ. Pollut., 2015, 200, 24- 34
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.01.028 URL pmid: 25686885 |
| [16] | 陈舒, 焦杏春, 盖楠, 殷效彩, 朴海涛, 路国慧, 李小洁, 饶竹, 杨永亮. 岩矿测试, 2015, 34, 579- 585 |
| Chen, S. , Jiao X., C. , Gai, N. , Yin X., C. , Piao H., T. , Lu G., H. , Li X., J. , Rao, Z. , Yang Y., L. , Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34, 579- 585 | |
| [17] |
Vaalgamaa, S. , Vahatalo A., V. , Perkola, N. , Huhtala, S. , Sci. Total. Environ., 2011, 409( 16), 3043- 3048
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.04.036 URL pmid: 21592543 |
| [18] |
Senevirathna, S. , Tanaka, S. , Fujii, S. , Kunacheva, C. , Harada, H. , Shivakoti B., R. , Okamoto, R. , Chemosphere, 2010, 80( 6), 647- 651
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.04.053 |
| [19] |
Steinle D., E. , Reinhard, M. , Environ. Sci. Technol., 2008, 42( 14), 5292- 5297
doi: 10.1021/es703207s URL pmid: 18754383 |
| [20] | 宋洲. 紫外光化学氧化/还原处理全氟辛酸的研究, 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2014) |
| Song, Z. , Photochemical Oxidation or Reduction Degradation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid Using UV Irradiation, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 2014( | |
| [21] |
李星星, 黄在银, 范高超, 吴烨楠, 谭学才. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35( 7), 1480- 1483
doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140176 |
|
Li X., X. , Huang Z., Y. , Fan G., C. , Wu Y., N. , Tan X., C. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35( 7), 1480- 1483
doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140176 |
|
| [22] |
Vecitis C., D. , Park, H. , Cheng, J. , Mader B., T. , Hoffmann M., R. , Front Environ. Sci. Eng., 2009, 3( 2), 129- 151
doi: 10.1007/s11783-009-0022-7 URL |
| [23] |
Hori, H. , Nagaoka, Y. , Yamamoto, A. , Sano, T. , Yamashita, N. , Taniyasu, S. , Kutsuna, S. , Osaka, I. , Arakawa, R. , Environ Sci. Tech-nol., 2006, 40( 3), 1049- 1054
doi: 10.1021/es0517419 URL pmid: 16509356 |
| [24] |
Arvaniti O., S. , Hwang, Y. , Andersen H., R. , Stasinakis A., S. , Thomaidis N., S. , Aloupi, M. , Chem. Eng. J., 2015, 262, 133- 139
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.09.079 URL |
| [25] |
Zhang L., H. , Zhu, D. , Nathanson G., M. , Hamers R., J. , Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53( 37), 9746- 9751
doi: 10.1002/ange.201404328 URL pmid: 25044766 |
| [26] | Sauer M., C. , Crowell R., A. , Shkrob I., A. , J. Phy. Chem., 2004, 108( 25), 5490- 5502 |
| [27] |
Chen, J. , Zhang P., Y. , Liu, J. , J. Environ. Sci., 2007, 19( 4), 387- 390
doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(07)60064-3 URL pmid: 17915698 |
| [28] |
Thomsen C., L. , Madsen, D. , Keiding S., R. , J. Phy. Chem., 1999, 110( 7), 3453- 3462
doi: 10.1063/1.478212 URL |
| [29] |
Lehr, L. , Zanni M., T. , Frischkorn, C. , Science, 1999, 284( 5414), 635- 638
doi: 10.1126/science.284.5414.635 URL pmid: 10213684 |
| [30] |
Qu, Y. , Zhang C., J. , Li, F. , Chen, J. , Zhou, Q. , Water Res., 2010, 44( 9), 2939- 2947
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.02.019 URL pmid: 20227745 |
| [31] |
Chen, J. , Zhang P., Y. , Water Sci. Technol., 2006, 54( 11/12), 317- 325
doi: 10.2166/wst.2006.731 URL pmid: 17302335 |
| [32] |
Feng Y., G. , Smith D., W. , Bolton J., R. , Water Environ. Res., 2010, 82( 4), 328- 334
doi: 10.2175/106143009X447920 URL pmid: 20432650 |
| [33] |
马福军. 青海师范大学民族师范学院学报, 2007, 18, 65- 66
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7473.2007.01.021 URL |
|
Ma F., J. , Journal of Minorities Teachers College of Qinghai Teachers University, 2007, 18, 65- 66
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7473.2007.01.021 URL |
|
| [34] |
Ding G., H. , Fromel, T. , Brandhof E., J. , Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2012, 31( 3), 605- 610
doi: 10.1002/etc.1713 URL pmid: 22170568 |
| [35] | 杨佘维. 真空紫外耦合高频超声对水中全氟辛基磺酸钾(PFOS)的脱氟研究, 广州: 华南理工大学, 2013 ) |
| Yang S., W. , Defluorination of Aqueous Perfluorooctanesulfonate(PFOS ) by Combined Process of Vacuum Ultraviolet and High-frequency Ultrasound, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, 2013( | |
| [36] |
Thogersen, J. , Jensen S., K. , Christiansen, O. , Keiding S., R. , J. Phy. Chem., 2004, 108( 37), 7483- 7489
doi: 10.1136/jmg.2003.010447 URL |
| [37] |
陈静, 张彭义, 刘剑. 环境科学, 2007, 28, 772- 776
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.04.014 URL |
|
Chen, J. , Zhang P., Y. , Liu, J. , Environ. Sci., 2007, 28, 772- 776
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.04.014 URL |
| [1] | 林海, 李亚巍, 林华宽. 吲哚-3-醛-邻硝基苯基半卡巴腙的阴离子识别[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(3): 480. |
| [2] | 马永钧, 丁静, 金芝梅, 铁珍珍, 周敏. 修饰铂阳极上氯离子对4种有机醇电氧化反应的阻化作用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(5): 864. |
| [3] | 王璇 黄卫民 刘小波 陆海彦 林海波. 氯离子对苯酚电化学氧化降解过程的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(2): 361. |
| [4] | 刘军,那万里,辛伟红,刘丽丹,于波,麻彤辉,杨红 . 20(S)-原人参二醇促进CFTR氯离子通道开放[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2008, 29(4): 731. |
| [5] | 史生华, 郭艳丽, 索志荣. 氯离子选择电极瞬时电位分析法研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2001, 22(4): 556. |
| [6] | 郑文君, 杨萍华, 孟广耀. [(PbCl2)0.55(PbO)0.45]1-x(KCl)x系离子导电性研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1993, 14(3): 378. |
| [7] | 朱(王步)瑶, 余青. 全氟辛酸铵与全氟壬酸铵混合物的表面活性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1990, 11(10): 1091. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||