

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (4): 713.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150001
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
GUO Xiao, LIN Shaoying, QIN Kai, ZHANG Yahong*( ), TANG Yi
), TANG Yi
Received:2015-01-04
Online:2015-04-10
Published:2015-03-27
Contact:
ZHANG Yahong
E-mail:zhangyh@fudan.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
GUO Xiao, LIN Shaoying, QIN Kai, ZHANG Yahong, TANG Yi. Controllable Detemplation of Nanozeolites and Research of Molecular Diffusing Limitation†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(4): 713.
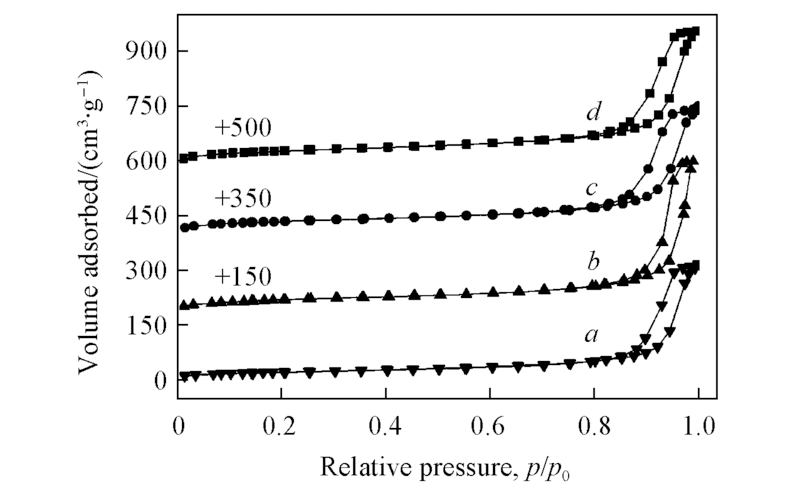
Fig.5 N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms of β nanozeolites with different micropore depths before/after Fenton-like oxidation a. β-unoxidized; b. β-6, +150; c. β-12, +350; d. β-24, +500.
| Sample | Micropore area/(m2·g-1) | Micropore volume/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|
| β-24 | 358.2 | 0.134 |
| β-12 | 263.8 | 0.077 |
| β-6 | 136.6 | 0.053 |
| β-unoxidized | 2.0 | 0 |
Table 1 Micropore information for β nanozeolites with different micropore depths
| Sample | Micropore area/(m2·g-1) | Micropore volume/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|
| β-24 | 358.2 | 0.134 |
| β-12 | 263.8 | 0.077 |
| β-6 | 136.6 | 0.053 |
| β-unoxidized | 2.0 | 0 |
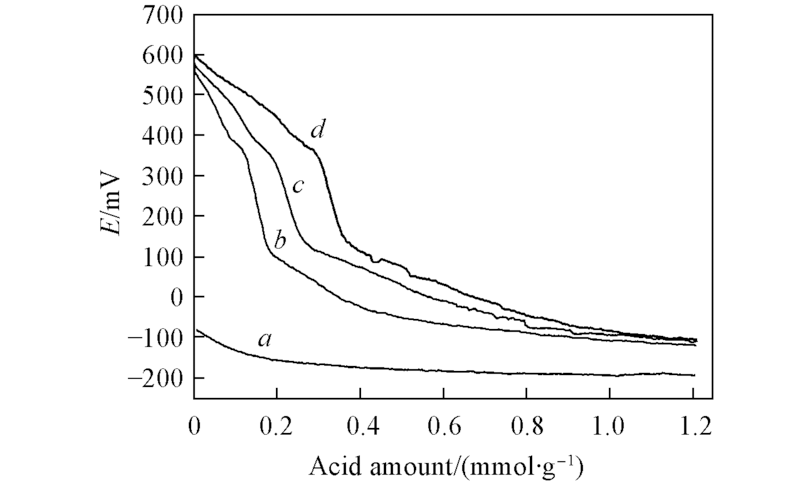
Fig.6 Total acidity measurements of β nanozeolites with different micropore depths by potentiometric titration in acetonitrile using n-butylamine a. β-unoxidized; b. β-6; c. β-12; d. β-24.
| Sample | Ei/mV | E(≥100 mV)/(mmol·g-1) | Acid number*/(μmol·m-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-24 | 603.8 | 0.425 | 1.187 |
| β-12 | 579.3 | 0.335 | 1.269 |
| β-6 | 563.0 | 0.194 | 1.420 |
| β-unoxidized | -79.4 |
Table 2 Acid strengths and numbers of β nanozeolites with different micropore depths
| Sample | Ei/mV | E(≥100 mV)/(mmol·g-1) | Acid number*/(μmol·m-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-24 | 603.8 | 0.425 | 1.187 |
| β-12 | 579.3 | 0.335 | 1.269 |
| β-6 | 563.0 | 0.194 | 1.420 |
| β-unoxidized | -79.4 |
| Catalyst | Micropore area/(m2·g-1) | Mass of used β nanozeolites/mg | Total micropore area of used β nanozeolites/m2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-24 | 358.2(358.2) | 6.29(12.5) | 2.25(4.48) |
| β-12 | 263.8(263.8) | 8.54(12.5) | 2.25(3.30) |
| β-6 | 136.6(136.6) | 16.49(12.5) | 2.25(1.71) |
| β-unoxidized | 2.0(2.0) | - (12.5) | - (0.025) |
Table 3 Used amount and micropore properties of β nanozeolites with different micropore depths in the two experiments designs*
| Catalyst | Micropore area/(m2·g-1) | Mass of used β nanozeolites/mg | Total micropore area of used β nanozeolites/m2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-24 | 358.2(358.2) | 6.29(12.5) | 2.25(4.48) |
| β-12 | 263.8(263.8) | 8.54(12.5) | 2.25(3.30) |
| β-6 | 136.6(136.6) | 16.49(12.5) | 2.25(1.71) |
| β-unoxidized | 2.0(2.0) | - (12.5) | - (0.025) |
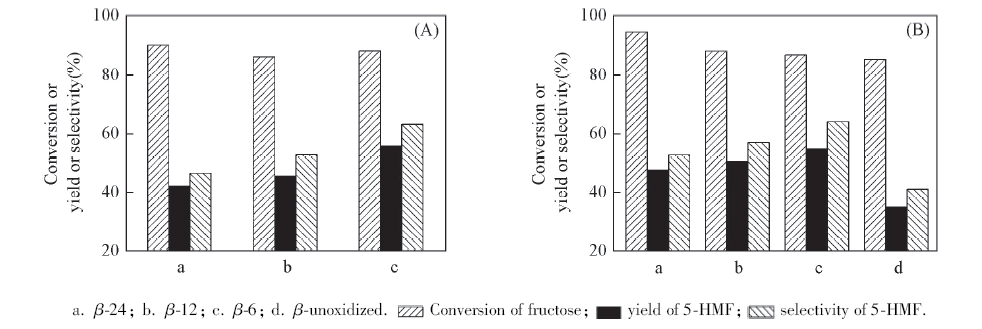
Fig.7 Conversions of 5%(mass fraction) fructose catalyzed by β nanozeolites with different micropore depths but the same acid sites numbers(A) or the same catalyst amounts(B) in water under microwave irradiation at 195 ℃ for 24 min
| [1] | Cundy C. S., Cox P. A., Chem. Rev., 2003, 103, 663—701 |
| [2] | Tanabe K., Hölderich W. F., Appl. Catal. A,1999, 181, 399—434 |
| [3] | Möller K., Bein T., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42, 3689—3707 |
| [4] | Valtchev V., Tosheva L., Chem. Mater., 2005, 17, 2494—2513 |
| [5] | Schoeman B. J., Sterte J., Otterstedt J. E., Zeolites,1994, 14, 110—116 |
| [6] | Muller M., Harvey G., Prins R., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2000, 34, 135—140 |
| [7] | Masuda T., Otani S., Tsuji T., Kitamura M., Mukai S., Sep. Purif. Technol., 2003, 32, 181—187 |
| [8] | Heng S., Lau P., Yeung K., Djafer M., Schrotter J., J. Membrane Sci., 2004, 243, 69—78 |
| [9] | Kuhn J., Motegh M., Gross J., Kapteijn F., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2009, 120, 35—38 |
| [10] | Parikh A., Navrotsky A., Li Q., Yee C., Amweg M., Corma A., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2004, 76, 17—22 |
| [11] | Hu Y. Y., Zhang Y. H., Tang Y., RSC Adv., 2012, 2, 6036—6041 |
| [12] | Maesen T., Kouwenhoven H., Bekkum H., Sulikowski B., Klinowski J., J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans., 1990, 86, 3967—3970 |
| [13] | Hu Y. Y., Liu C., Zhang Y. H., Ren N., Tang Y., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2009, 119, 306—314 |
| [14] | Xia Y. D., Mokaya R., J. Phys. Chem. B,2006, 110, 9122—9131 |
| [15] | Melian-Cabrera I., Kapteijn F., Moulijn J. A., Chem. Commun., 2005, 21, 2744—2746 |
| [16] | Maurya M. R., Titinchi S. J. J., Chand S., Mishra I. M., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2002, 18, 201—212 |
| [17] | Rivas F. J., Beltran F. J., Gimeno O., Frades J., J. Agric. Food Chem., 2001, 49, 1873—1880 |
| [18] | Cabrera I.M., Kapteijn F., Moulijn J. A.,Chem. Commun., 2005, 2178—2180 |
| [19] | RaoK. N., Reddy K. M., Lingaiah N., Suryanarayana I., Prasad P. S., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 2006, 300, 139—146 |
| [20] | KhderA. S., Ahmed A. I., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 2009, 354, 153—160 |
| [21] | CidR., Pecci G., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 1985, 14, 15—21 |
| [1] | WANG Zumin, MENG Cheng, YU Ranbo. Doping Regulation in Transition Metal Phosphides for Hydrogen Evolution Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220544. |
| [2] | ZHAO Wanjun, LI Xiao, Dang Hui, WANG Yongzhao, ZHAO Yongxiang. Preparation of Supported Pd-Cu Catalyst and Its Preferential Oxidation of CO Under Hydrogen-rich Atmosphere [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210754. |
| [3] | ZHANG Xiang, XIE Xulan, XIONG Likun, PENG Yang. Urchin-like Gold Nanoneedle for Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2824. |
| [4] | JI Xiaohao, WANG Zumin, CHEN Xiaoyu, YU Ranbo. Overview of Transition Metal Phosphide Catalysts and Hydrogen Production by Electrolyzed Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1377. |
| [5] | SU Gaoming, SHEN Ruichen, TAN Jie, YUAN Quan. Progress on the Application of Long Persistent Phosphors in Photocatalytic System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2404. |
| [6] | WU Hao, WANG Changzhen, QIU Yuan, TIAN Yani, ZHAO Yongxiang. Effect of Steric Confinement Dimension on Metal Site Anti-carbon Deposition Ability of Ni-SiO2 Catalysts in CH4-CO2 Reforming [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2488. |
| [7] | LI Xiao,XING Lisha,ZHAO Wanjun,WANG Yongzhao,ZHAO Yongxiang. Preparation and Characterization of Pd-Cu/hydroxyapatite Catalyst and Its Catalytic Performance for Room-temperature CO Oxidation in Humid Circumstances† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1600. |
| [8] | HAO Yan, YANG Hua, WANG Xiang, LI Qingyang, ZHAO Pan, TANG Qinghu, SONG Shili, XI Guoxi. Palladium-based Nanocatalysts Supported on Polybenzoxazine for Aromatic Alcohol Oxidation † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 757. |
| [9] | MENG Qingnan, WANG Kai, TANG Yufei, ZHAO Kang, XIANG Siyuan, ZHANG Kai, ZHAO Lang. Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles Loaded Hollow Silica Spheres and Their Catalytic Performance† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(3): 503. |
| [10] | WANG Huichun, WANG Fachun, LI Baolin. Preparation of Cyclodextrin-based Mesoporous Carbon and Its Catalytic Performance† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(11): 2076. |
| [11] | SONG Hua,YU Qi,XU Xiaowei,SONG Hualin,JIANG Nan,LI Feng,CHEN Yanguang. Effect of Yttrium and Citric Acid on the Hydrodesulfurization Performance of Unsupported Nickel Phosphide† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(8): 1528. |
| [12] | XIAO Ye, WANG Yang, ZHOU Wei, PENG Xiaohong. Preparation of Ru/Rh Bimetallic Nanoparticles Stabilized by Heterocyclic Poly(propylene imine) Dendrimer and Their Application for Catalytic Hydrogenation of Nitrile-Butadiene Rubber† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(4): 786. |
| [13] | MENG Zhiyu, ZHANG Yin, ZHAO Lili, ZHANG Hongxi, ZHAO Yongxiang. Liquid Phase Hydrogenation of Maleic Anhydride over Ni/TiO2 Catalysts with Different TiO2 Polymorphs† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1779. |
| [14] | KONG Lingzhi, WANG Qian, XU Li, YAN Yongsheng, LI Huaming, YANG Xiangguang. Influence of CuO on Ce-Zr-O2 Dispersion on Catalytic Properties in CO Oxidation† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(7): 1372. |
| [15] | LI Lingcong, HU Ruisheng, BAI Yaqin, LI Jingjia, TANG Hailian, WANG Junhu, JI Shengfu. Inverse CeO2/La2Sn1.7Co0.3O7-δ Catalyst for Methane Catalytic Combustion† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(7): 1328. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||