

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (12): 20220375.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220375
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Qingpeng, GUAN Guoqiang, LIU Huiyi, LU Chang, ZHOU Ying( ), SONG Guosheng(
), SONG Guosheng( )
)
Received:2022-05-25
Online:2022-12-10
Published:2022-07-21
Contact:
ZHOU Ying, SONG Guosheng
E-mail:zhouying2021@hnu.edu.cn;songgs@hnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHANG Qingpeng, GUAN Guoqiang, LIU Huiyi, LU Chang, ZHOU Ying, SONG Guosheng. Recent Development of Magnetic Particle Imaging Tracers[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(12): 20220375.
| Imaging modality | Input | Penetration depth | Spatial resolution | Temporal resolution | Sensitivity/(mol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPI | Radio frequency | Unlimited | ~500 mm | ms | 10-6 |
| MRI | Radio frequency | Unlimited | 25—100 mm | min—h | 10-3—10-5 |
| Optical | Light | <2 cm | 2—3 mm | s—min | 10-9—10-12 |
| Photoacoustics | Light | <6 cm | 5 μm—1 mm | s—min | 10-9—10-11 |
| CT | X⁃Rays | Unlimited | 25—200 μm | s—min | 10-3 |
| PET | Radionuclide | Unlimited | <1 mm | s—min | 10-11—10-12 |
| SPECT | Radionuclide | Unlimited | 0.5—2 mm | min | 10-10—10-11 |
| Ultrasound | Sound waves | Meter | 10—100 mm | s—min | 10-6—10-9 |
Table 1 Comparison of different imaging modalities
| Imaging modality | Input | Penetration depth | Spatial resolution | Temporal resolution | Sensitivity/(mol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPI | Radio frequency | Unlimited | ~500 mm | ms | 10-6 |
| MRI | Radio frequency | Unlimited | 25—100 mm | min—h | 10-3—10-5 |
| Optical | Light | <2 cm | 2—3 mm | s—min | 10-9—10-12 |
| Photoacoustics | Light | <6 cm | 5 μm—1 mm | s—min | 10-9—10-11 |
| CT | X⁃Rays | Unlimited | 25—200 μm | s—min | 10-3 |
| PET | Radionuclide | Unlimited | <1 mm | s—min | 10-11—10-12 |
| SPECT | Radionuclide | Unlimited | 0.5—2 mm | min | 10-10—10-11 |
| Ultrasound | Sound waves | Meter | 10—100 mm | s—min | 10-6—10-9 |
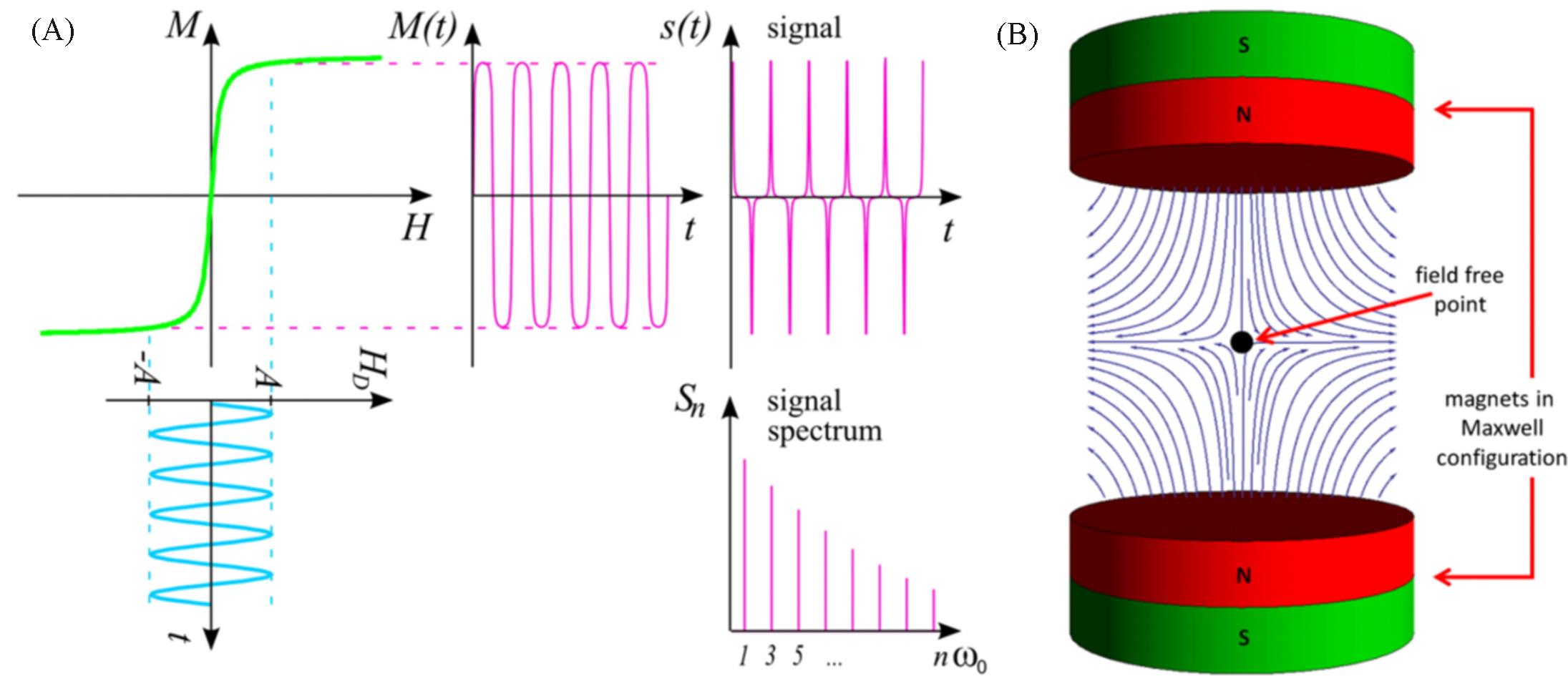
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of MPI signal generation[13](A) The upper left curve exemplifies the relation between the external magnetic drive field HD(usually measured in A/m or mT/μ0) and the magnetization of the particle M. The spectrum Sn of the signal s(t) generated by the changing magnetization then contains higher harmonics of the excitation frequency; (B) a selection field generated by 2 magnets in Maxwell configuration, that is, with opposing poles. Copyright 2012, Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography.
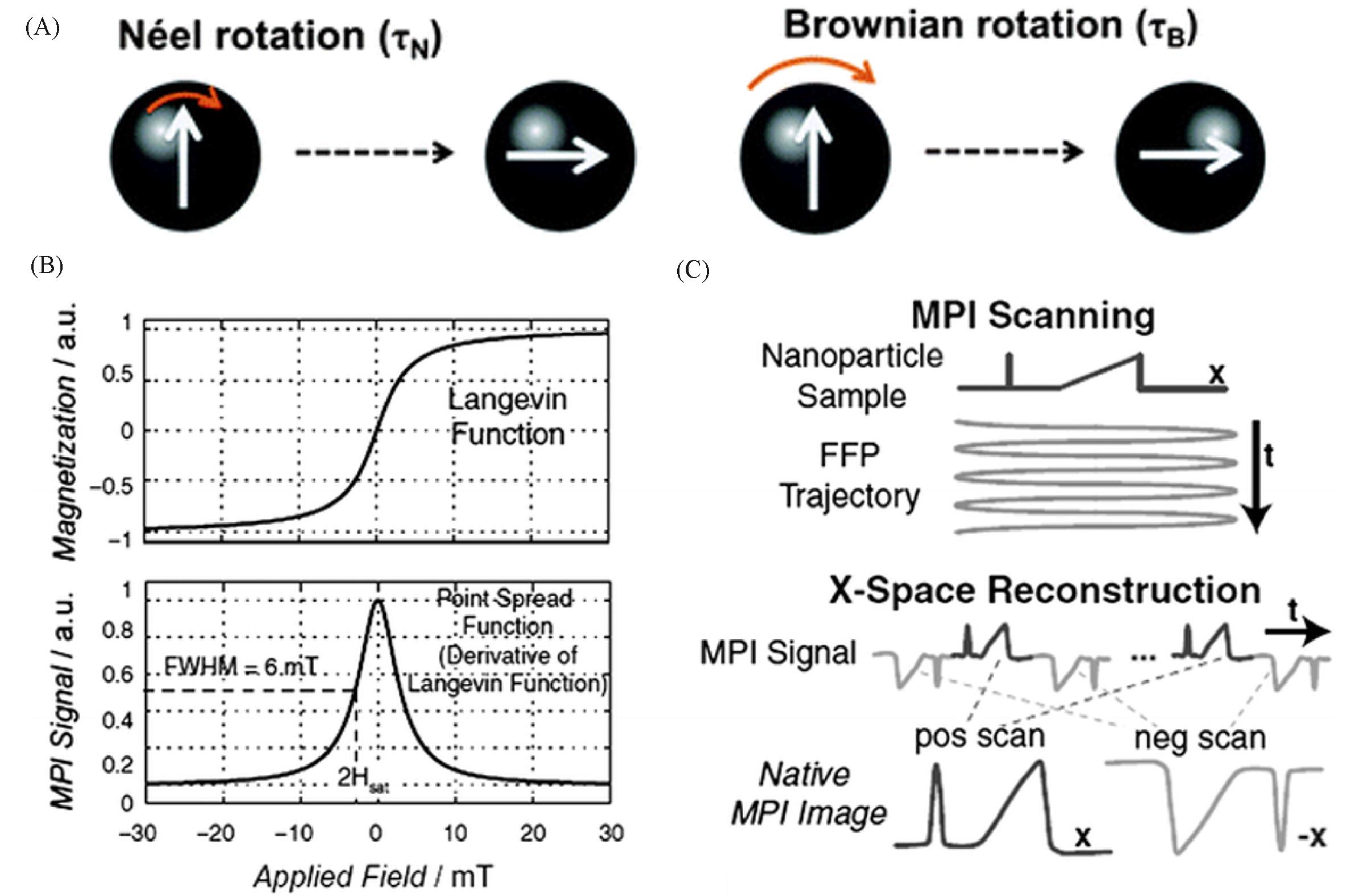
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of magnetic relaxation mechanism and X⁃space image reconstruction technique[16](A) Schematic representation of the magnetic relaxation mechanisms; (B) top figure shows magnetization of SPIONs modelled using a Langevin function; bottom figure shows the point spread function(PSF) as the derivative of the Langevin function; (C) X-space reconstruction involving a two-step process of velocity compensation and gridding of the instantaneous signal to the position of the FFP to form a native MPI image. Copyright 2012, John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
| MNPs | Composition | Size/nm | Sharp | Ms/(emu·g-1)* | MPI Signal(MNPs/Vivotrax) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vivotrax | Fe | ca. 10 | Amorphous | 54 | 1.0 | [ |
| SIONs⁃17 | Fe | 17 | Sphere | 32 | 0.5 | [ |
| CIONs⁃22 | Fe | 22 | Cube | 54 | 4.2 | [ |
| CIONs⁃26 | Fe | 26 | Cube | 72 | 3.5 | [ |
| CIONs⁃46 | Fe | 46 | Cube | 61 | 0.5 | [ |
| ZnFe2O4/C | Zn, Fe, C | 7—9 | Spindle | 32 | 4.7 | [ |
| CoFe2O4/C | Ni, Fe, C | 7—9 | Spindle | 36 | 1.8 | [ |
| MnFe2O4/C | Mn, Fe, C | 7—9 | Spindle | 50 | 2.1 | [ |
| ZnFe2O4 | Zn, Fe | 7—9 | Sphere | 48 | 0.6 | [ |
| γ⁃Fe2O3/C | Fe, C | 7—9 | Spindle | 48 | 1.9 | [ |
| FeCo@C | Fe, Co, C | 10 | Core⁃shell | 192 | 6.8 | [ |
| Fe@Fe3O4 | Fe | 14 | Core⁃shell | 176 | 0.8 | [ |
Table 2 Comparison of MPI performance of different MNPs
| MNPs | Composition | Size/nm | Sharp | Ms/(emu·g-1)* | MPI Signal(MNPs/Vivotrax) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vivotrax | Fe | ca. 10 | Amorphous | 54 | 1.0 | [ |
| SIONs⁃17 | Fe | 17 | Sphere | 32 | 0.5 | [ |
| CIONs⁃22 | Fe | 22 | Cube | 54 | 4.2 | [ |
| CIONs⁃26 | Fe | 26 | Cube | 72 | 3.5 | [ |
| CIONs⁃46 | Fe | 46 | Cube | 61 | 0.5 | [ |
| ZnFe2O4/C | Zn, Fe, C | 7—9 | Spindle | 32 | 4.7 | [ |
| CoFe2O4/C | Ni, Fe, C | 7—9 | Spindle | 36 | 1.8 | [ |
| MnFe2O4/C | Mn, Fe, C | 7—9 | Spindle | 50 | 2.1 | [ |
| ZnFe2O4 | Zn, Fe | 7—9 | Sphere | 48 | 0.6 | [ |
| γ⁃Fe2O3/C | Fe, C | 7—9 | Spindle | 48 | 1.9 | [ |
| FeCo@C | Fe, Co, C | 10 | Core⁃shell | 192 | 6.8 | [ |
| Fe@Fe3O4 | Fe | 14 | Core⁃shell | 176 | 0.8 | [ |
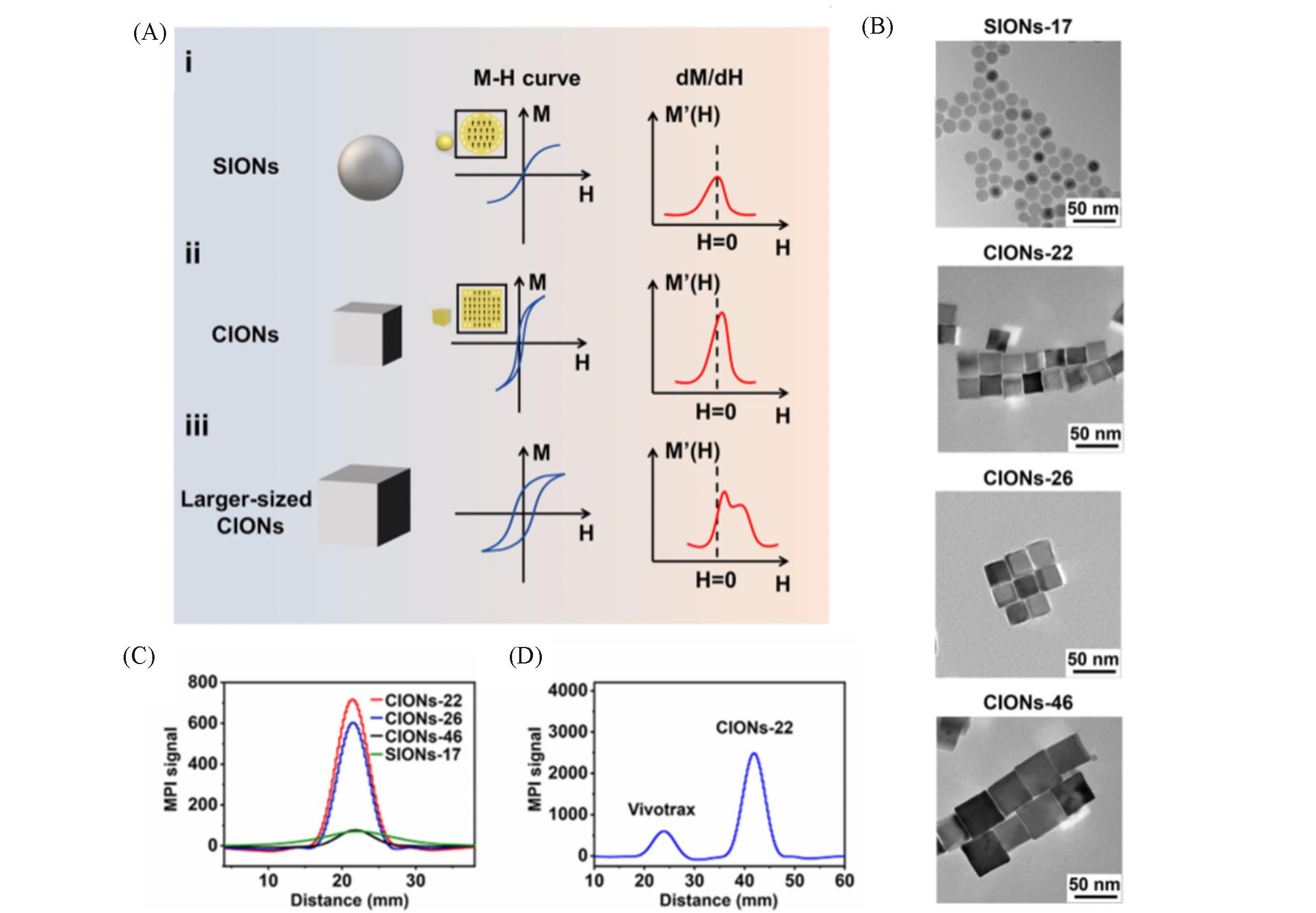
Fig.3 IONPs of different sizes and shapes act as MPI tracers[18](A) Schematic diagram of IONPs shape and size effects on MPI performance; (B) TEM images of SIONs-17 and CIONs of different sizes; (C) MPI performance of SIONs-17 and CIONs of different sizes at 1.7 mmol/L Fe concentration; (D) CIONs-22 versus commercial Vivotrax MPI performance. Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
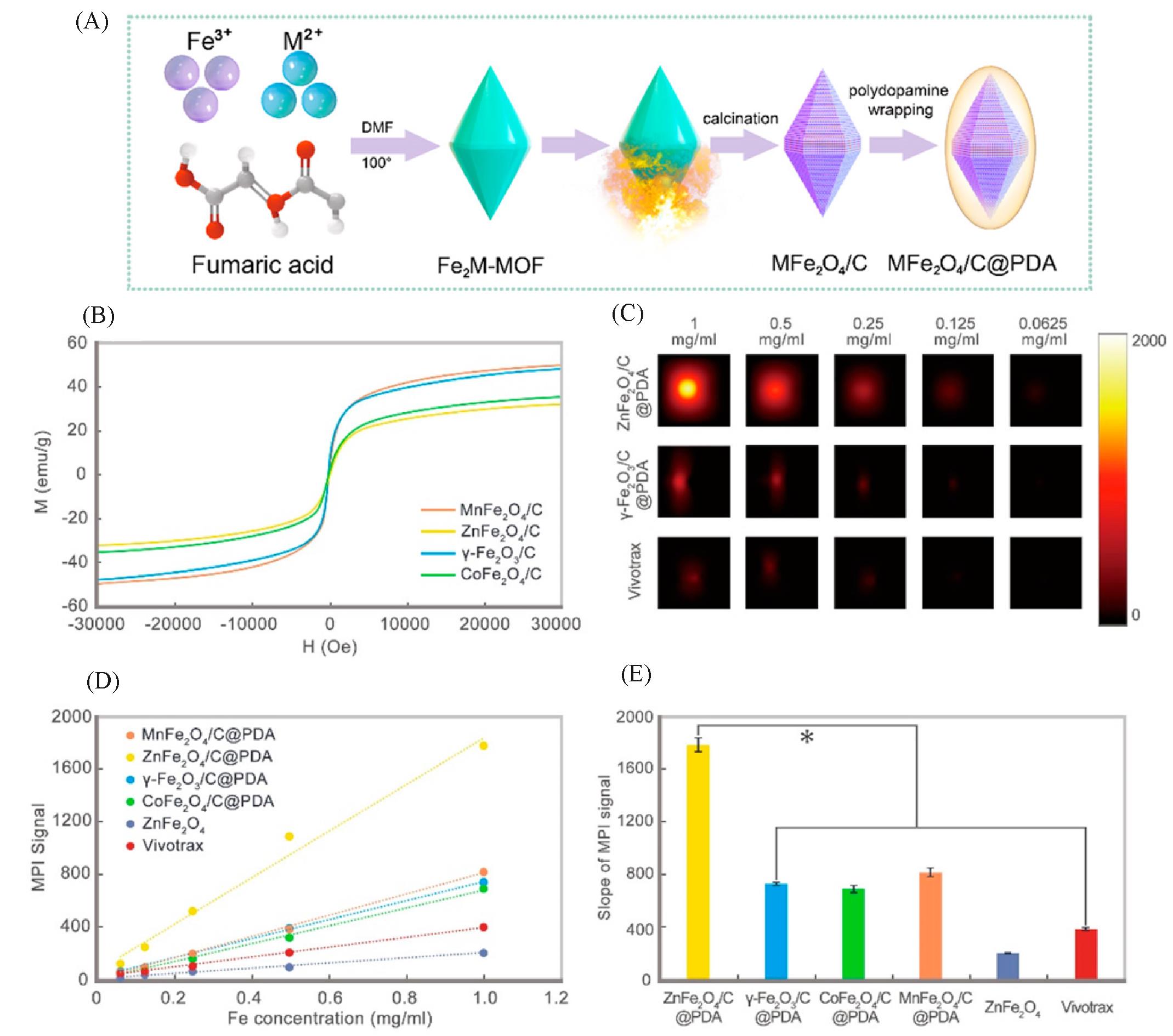
Fig.4 Carbon loading and metal doping improve the performance of MPI tracers[17](A) Schematic diagram of the synthesis progress of MFe2O4/C@PDA; (B) vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) measurement for all samples; (C) MPI images of γ-Fe2O3/C@PDA, ZnFe2O4/C@PDA, and Vivotrax at series concentrations; (D) the plot and (E) slope of MPI signals of all samples. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society.
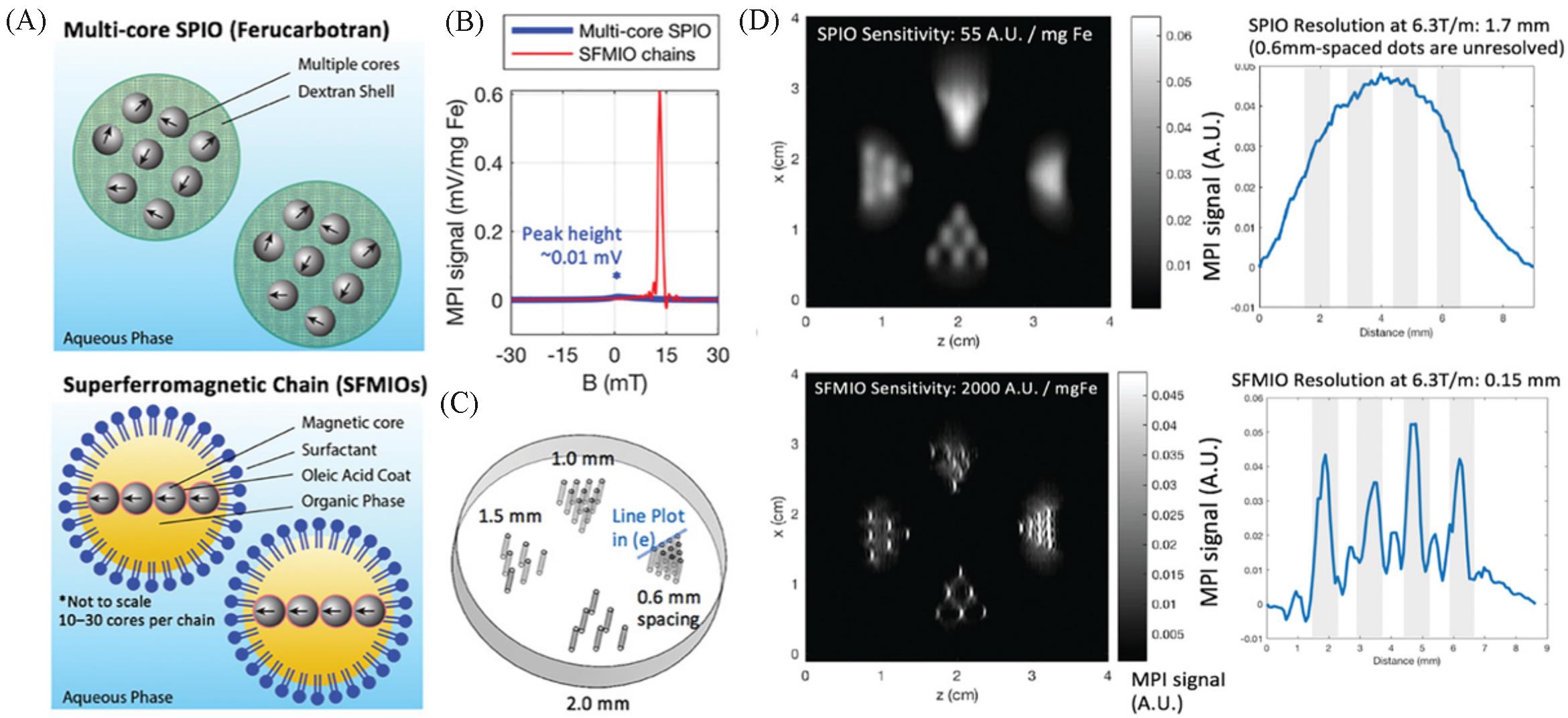
Fig.5 Order⁃of⁃magnitude mass sensitivity and resolution gains using superferro magnetic chains(SFMIOs)[25](A) Schematic of the SFMIO nanoparticle design compared to standard SPIOs; (B) MPI point spread function shows SFMIO signal peak is orders-of-magnitude taller and sharper than standard multi-core SPIO ferucarbotran; (C) imaging phantom of 0.3 mm radii wells with varying well-to-well spacing(mm); (D) MPI images of panel (C). Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH GmbH.
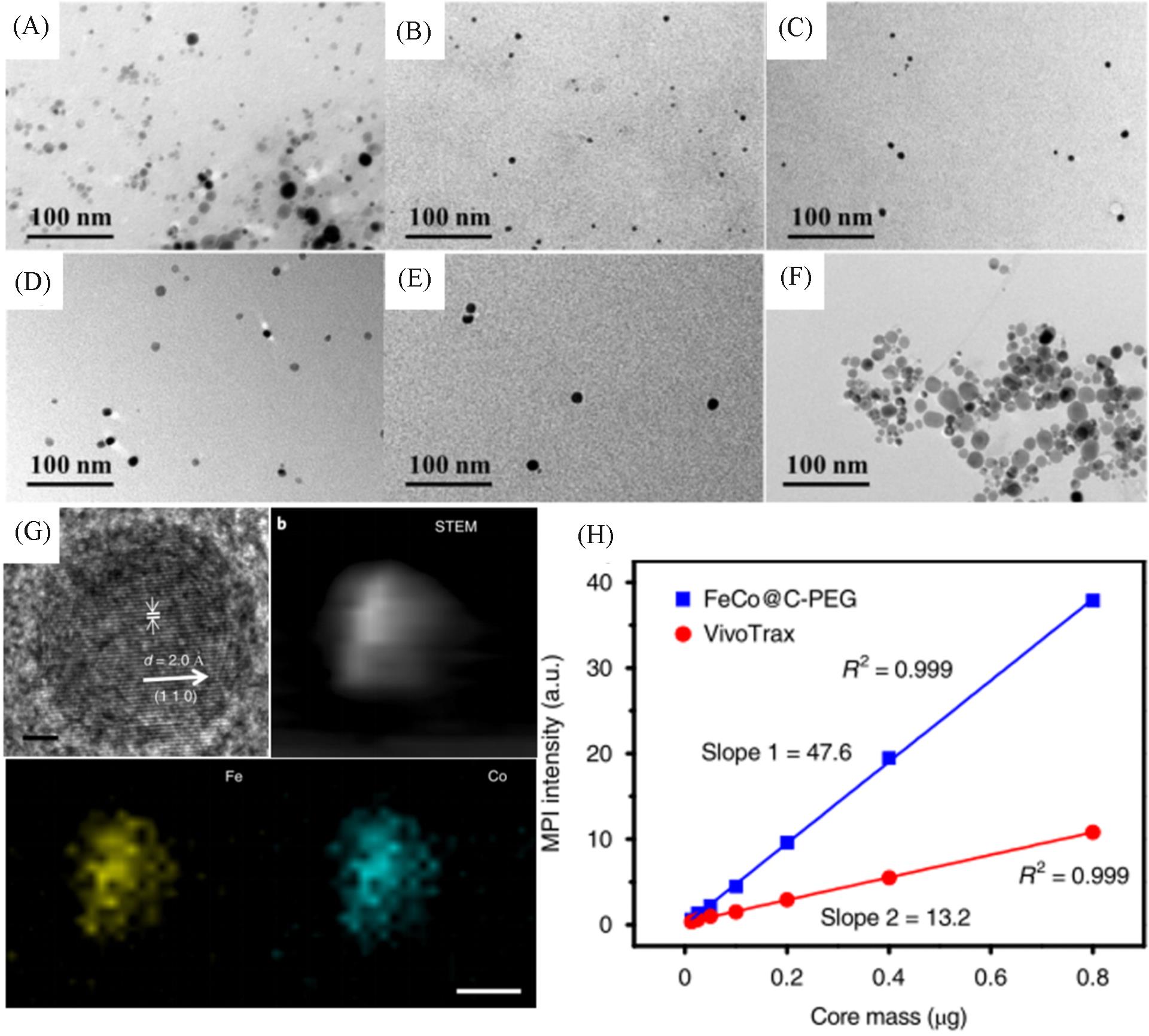
Fig.6 Representation and MPI performance of FeCo@C⁃PEG[19](A) TEM image of FeCo@C-PEG before density gradient separation; (B—F) TEM images of FeCo@C-PEG after density gradient separation; (G) HR-TEM and HAADF-STEM images of FeCo@C and element mapping; (H) MPI signals of FeCo@C-PEG and Vivotrax versus the nanoparticle core mass. Copyright 2020, the authors.
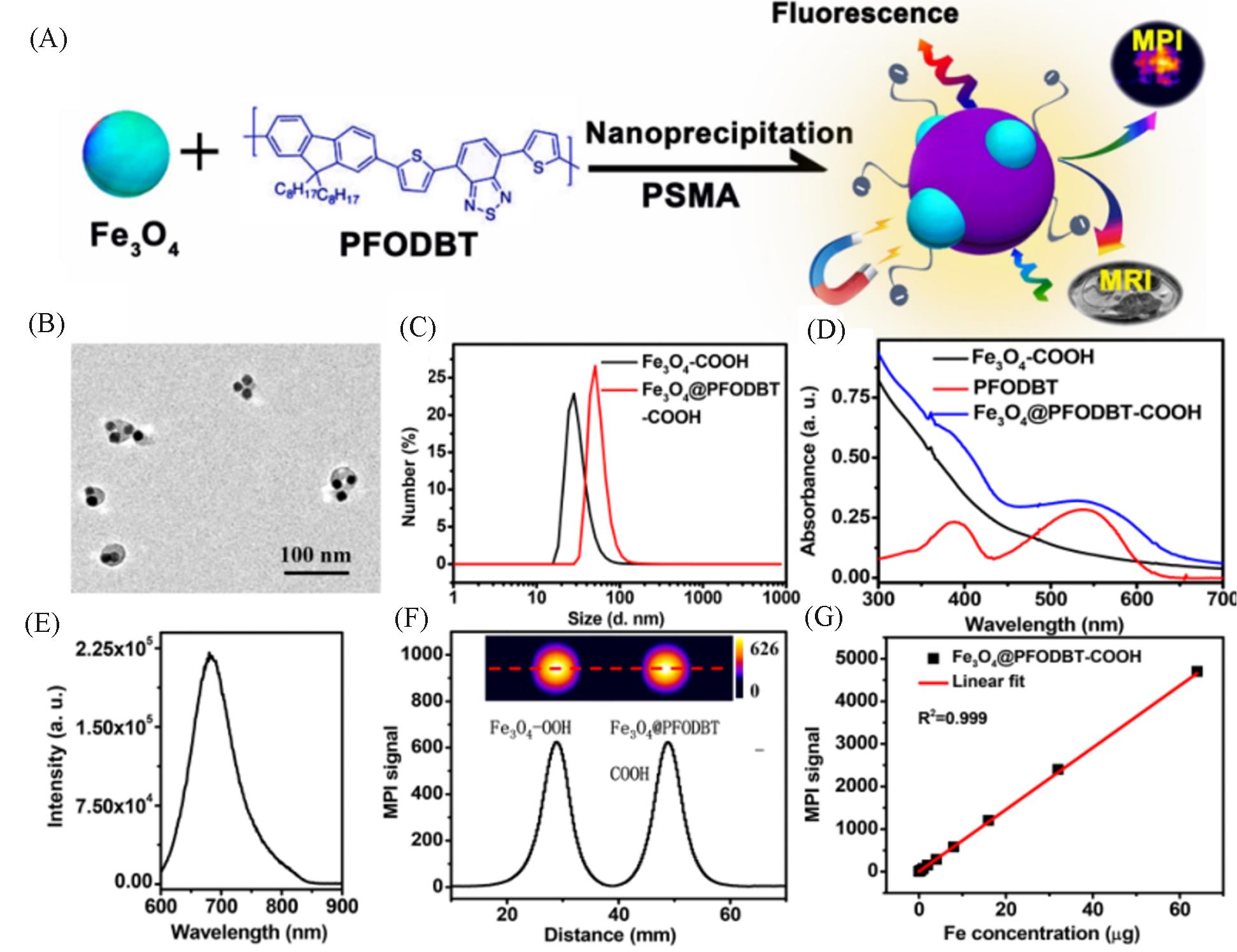
Fig.8 Synthesis and MPI performance of Janus MNPs[35](A) Schematic of the preparation of Fe3O4@PFODBT Janus nanoparticles through nanoprecipitation; (B) TEM image of Fe3O4@PFODBT Janus nanoparticles; (C) DLS size of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4@PFODBT in PBS; (D) UV-Vis absorption spectra of PFODBT in THF, and Fe3O4 and Fe3O4@PFODBT in PBS; (E) fluorescence spectrum of Fe3O4@PFODBT(excited at 540 nm); (F) two-dimensional projection MPI scanning of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4@PFODBT with the same amount of Fe(8 μg) in 200 μL of H2O, and their corresponding linear scanning MPI spectrum; (G) plot of MPI signals of Fe3O4@PFODBT versus amounts of Fe in 200 μL of H2O. Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society.
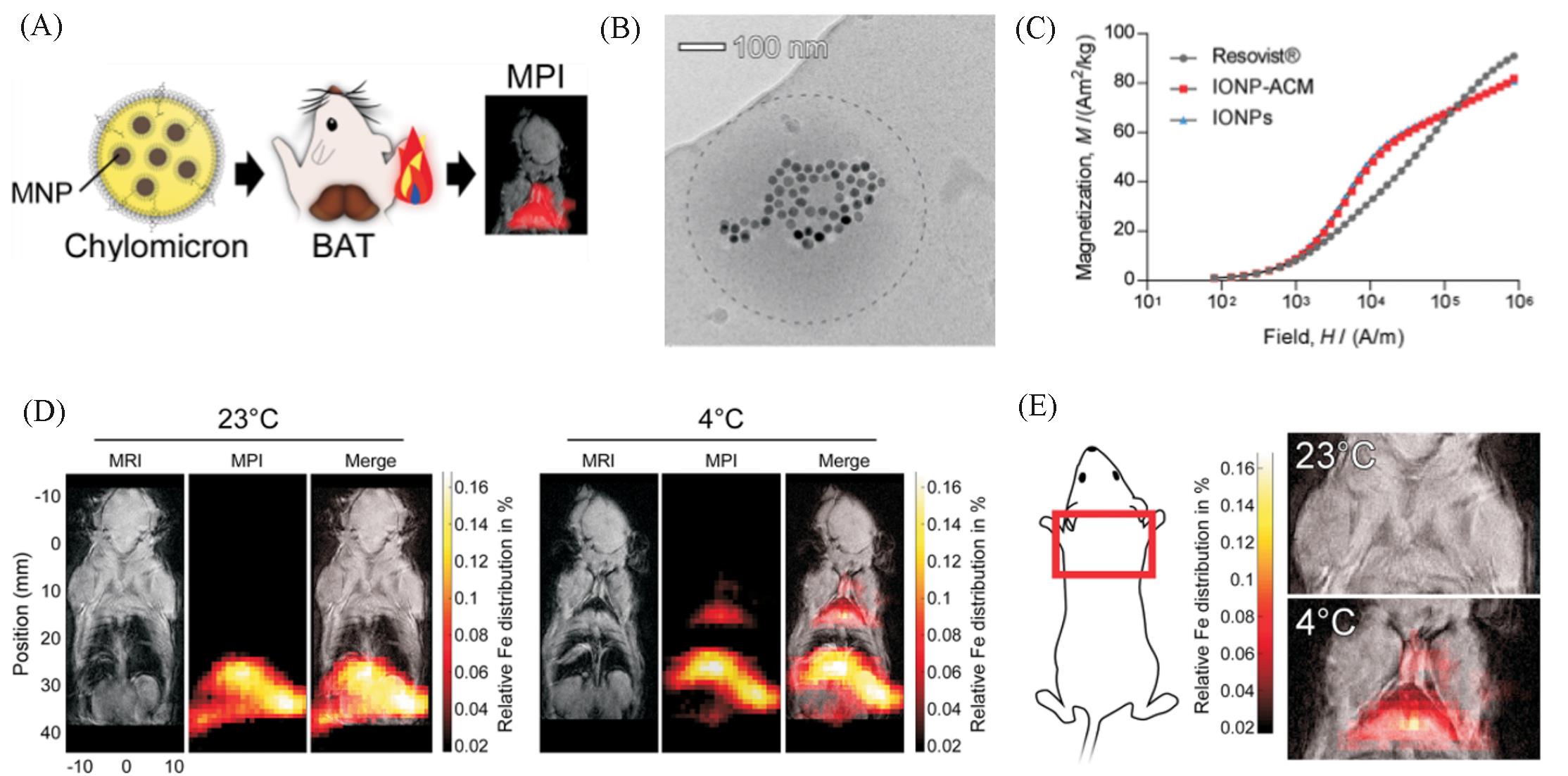
Fig.9 MPI tracers for quantification of lipoprotein uptake in vivo[37](A) Scheme shows quantification of lipoprotein uptake in vivo using MPI; (B) representative cryo-TEM image of IONP-loaded ACM. Dashed line outlines the circumference of the ACM. (C) Representative cryo-TEM image of IONP-loaded ACM. Dashed line outlines the circumference of the ACM. (D) Representative whole-body MRI and MPI images of mice injected with ZnMNP-ACM after exposure to either 23 or 4 ℃; (E) representative MPI images of the interscapular area(red box) with MRI overlay.Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society.
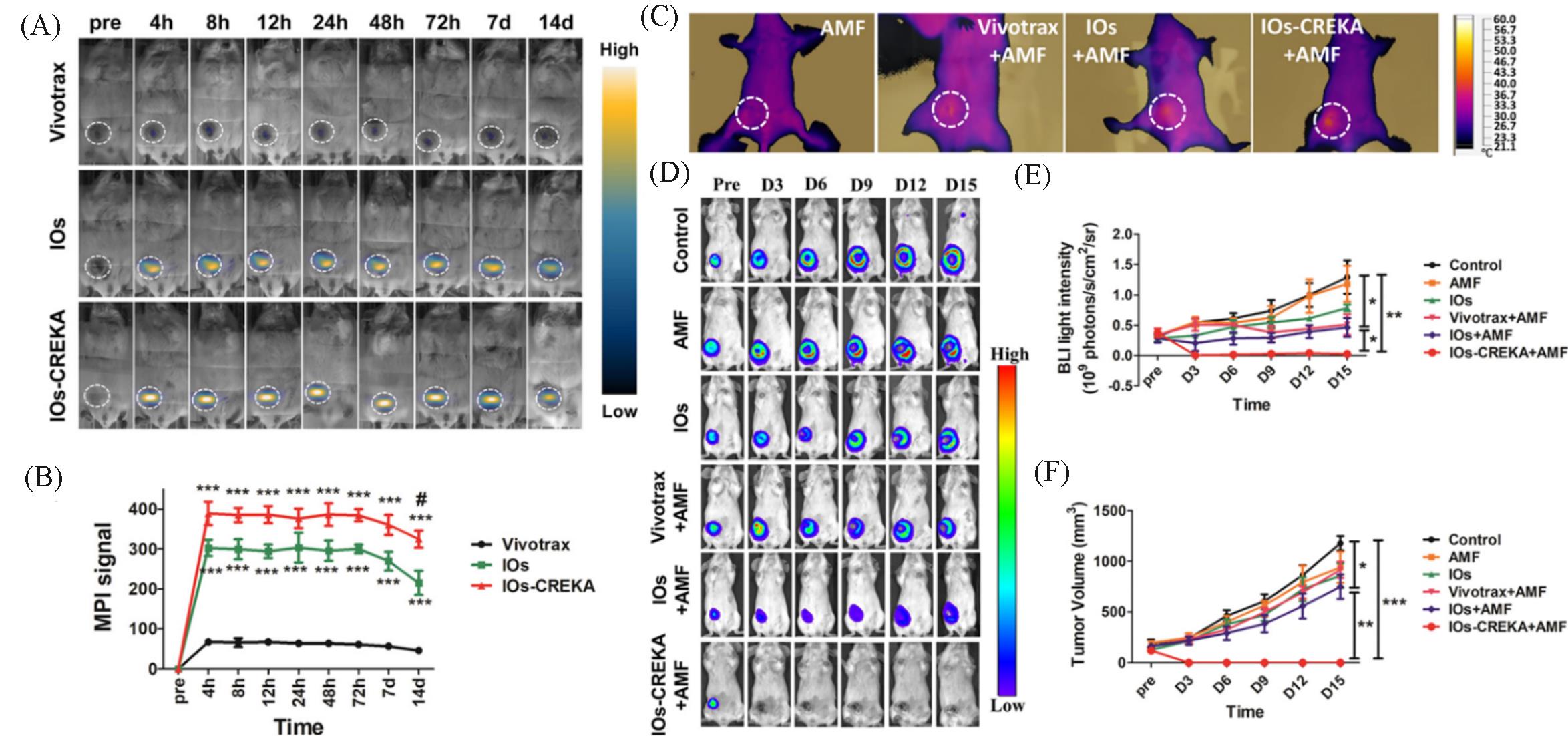
Fig.11 MPI tracers for cancer imaging and MHT[50](A) In vivo dynamic MPI of mice intratumorally injected with Vivotrax, IOs, and IOs-CREKA NPs, respectively; (B) MPI signal calculation and comparison between groups; (C) increase in the temperature induced by the MHT with different NPs treatment; (D) therapeutic efficacy of the magnetic hyperthermia dynamically monitored by BLI in different groups; (E, F) the calculation and comparison of the tumor bioluminescence intensity(E) and tumor volume changes(F). Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
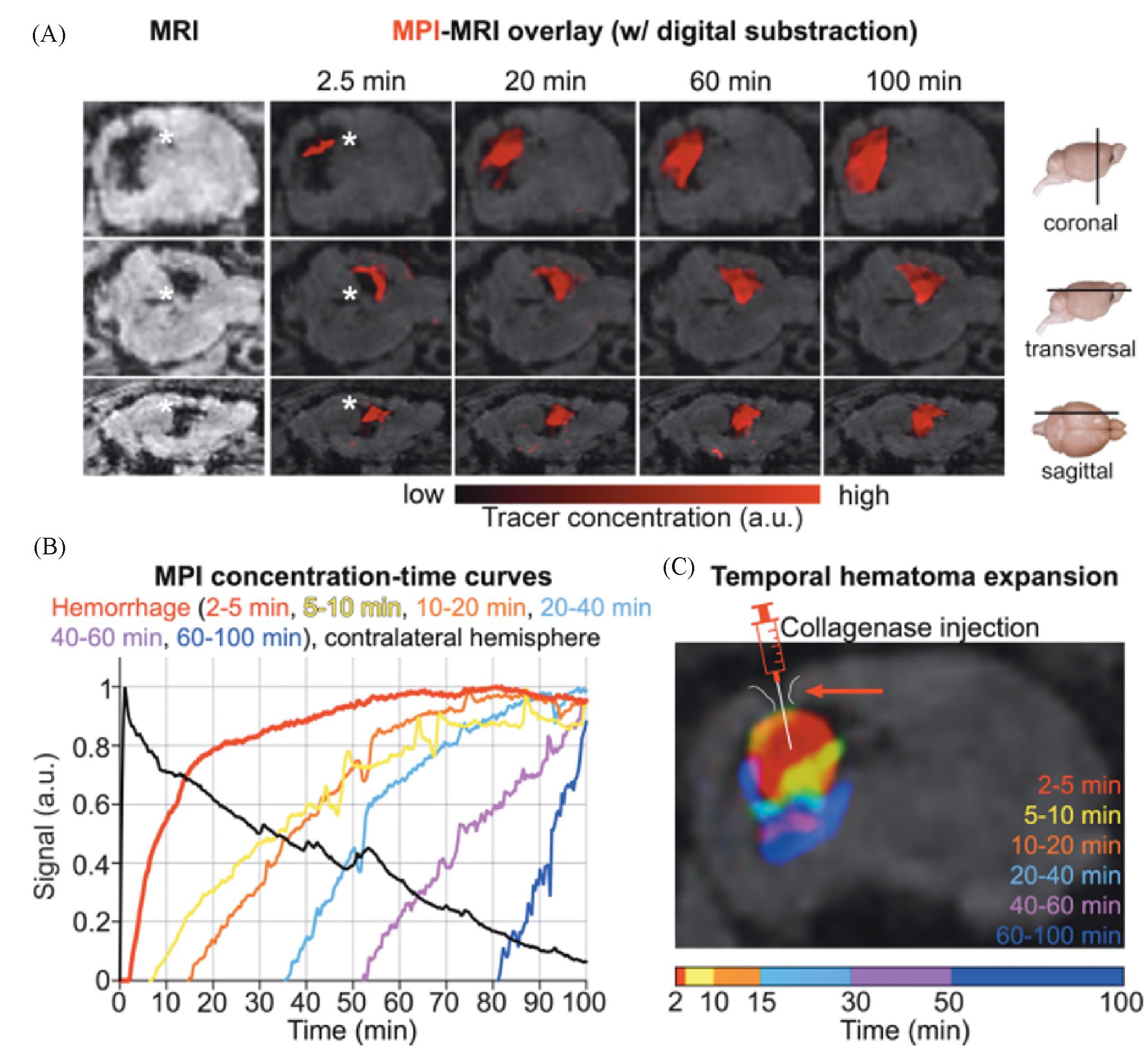
Fig.12 Rapid detection of intracranial hemorrhage with MPI[54](A) Early detection and expansion of the intracranial hemorrhage after the tracer injection at several time points on fused MPI/MRI slices(upper row: coronal sections; middle row: transversal sections; lower row: sagittal sections; the white asterisk indicates the hemorrhage in MRI and MPI; the signal information from these data sets was converted into a concentration⁃time curve on a voxel by pixel basis); (B) only (1.80±0.3) min passed between the tracer bolus arrival in the brain and the hemorrhage detection (bleeding continued up to 100 min; the extravasation of the tracer and expansion of the hemorrhage could be monitored in real time); (C) color coding the tracer arrival time allowed for the differentiation of bleeding areas of different age(the needle tip of the syringe marks the collagenase injection site for hemorrhage induction). Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
| 1 | Smith B. R., Gambhir S. S., Chem. Rev., 2017, 117(3), 901—986 |
| 2 | Rudin M., Weissleder R., Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 2003, 2(2), 123—131 |
| 3 | Chen F., Teng L., Lu C., Zhang C., Rong Q., Zhao Y., Yang Y., Wang Y., Song G., Zhang X., Anal. Chem., 2020, 92(19), 13452—13461 |
| 4 | Gleich B., Weizenecker J., Nature, 2005, 435(7046), 1214—1217 |
| 5 | Pablico⁃Lansigan M. H., Situ S. F., Samia A. C. S., Nanoscale, 2013, 5(10), 4040—4055 |
| 6 | Wu L. C., Zhang Y., Steinberg G., Qu H., Huang S., Cheng M., Bliss T., Du F., Rao J., Song G., Pisani L., Doyle T., Conolly S., Krishnan K., Grant G., Wintermark M., Am. J. Neuroradiol., 2019, 40(2), 206 |
| 7 | Bulte J. W. M., Adv. Drug Del. Rev., 2019, 138, 293—301 |
| 8 | Knopp T., Gdaniec N., Möddel M., Physics in Medicine & Biology, 2017, 62(14), R124—R178 |
| 9 | Sun C., Lee J. S. H., Zhang M., Adv. Drug Del. Rev., 2008, 60(11), 1252—1265 |
| 10 | Lu C., Han L., Wang J., Wan J., Song G., Rao J., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50(14), 8102—8146 |
| 11 | Yu E. Y., Chandrasekharan P., Berzon R., Tay Z. W., Zhou X. Y., Khandhar A. P., Ferguson R. M., Kemp S. J., Zheng B., Goodwill P. W., Wendland M. F., Krishnan K. M., Behr S., Carter J., Conolly S. M., ACS Nano, 2017, 11(12), 12067—12076 |
| 12 | Bauer L. M., Situ S. F., Griswold M. A., Samia A. C. S., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2015, 6(13), 2509—2517 |
| 13 | Borgert J., Schmidt J. D., Schmale I., Rahmer J., Bontus C., Gleich B., David B., Eckart R., Woywode O., Weizenecker J., Schnorr J., Taupitz M., Haegele J., Vogt F. M., Barkhausen J., J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr., 2012, 6(3), 149—153 |
| 14 | Biederer S., Knopp T., Sattel T. F., Lüdtke⁃Buzug K., Gleich B., Weizenecker J., Borgert J., Buzug T. M., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2009, 42(20), 205007 |
| 15 | Khandhar A. P., Ferguson R. M., Arami H., Krishnan K. M., Biomaterials, 2013, 34(15), 3837—3845 |
| 16 | Goodwill P. W., Saritas E. U., Croft L. R., Kim T. N., Krishnan K. M., Schaffer D. V., Conolly S. M., Adv. Mater., 2012, 24(28), 3870—3877 |
| 17 | Jiang Z., Han X., Du Y., Li Y., Li Y., Li J., Tian J., Wu A., Nano Lett., 2021, 21(7), 2730—2737 |
| 18 | Wang Q., Ma X., Liao H., Liang Z., Li F., Tian J., Ling D., ACS Nano, 2020, 14(2), 2053—2062 |
| 19 | Song G., Kenney M., Chen Y. S., Zheng X., Deng Y., Chen Z., Wang S. X., Gambhir S. S., Dai H., Rao J., Nat. Biomed. Eng., 2020, 4(3), 325—334 |
| 20 | Gloag L., Mehdipour M., Ulanova M., Mariandry K., Nichol M. A., Hernández⁃Castillo D. J., Gaudet J., Qiao R., Zhang J., Nelson M., Thierry B., Alvarez⁃Lemus M. A., Tan T. T., Gooding J. J., Braidy N., Sachdev P. S., Tilley R. D., Chem. Commun., 2020, 56(24), 3504—3507 |
| 21 | Kim D., Lee N., Park M., Kim B. H., An K., Hyeon T., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131(2), 454—455 |
| 22 | Wu L., Mendoza⁃Garcia A., Li Q., Sun S., Chem. Rev., 2016, 116(18), 10473—10512 |
| 23 | Ferguson R. M., Minard K. R., Khandhar A. P., Krishnan K. M., Med. Phys., 2011, 38(3), 1619—1626 |
| 24 | Ferguson R. M., Khandhar A. P., Krishnan K. M., J. Appl. Phys., 2012, 111(7), 07B318 |
| 25 | Tay Z. W., Savliwala S., Hensley D. W., Fung K. L. B., Colson C., Fellows B. D., Zhou X., Huynh Q., Lu Y., Zheng B., Chandrasekharan P., Rivera‐Jimenez S. M., Rinaldi‐Ramos C. M., Conolly S. M., Small Methods, 2021, 5(11), 2100796 |
| 26 | Seo W. S., Lee J. H., Sun X., Suzuki Y., Mann D., Liu Z., Terashima M., Yang P. C., Mcconnell M. V., Nishimura D. G., Dai H., Nat. Mater., 2006, 5(12), 971—976 |
| 27 | Yu J., Yang C., Li J., Ding Y., Zhang L., Yousaf M. Z., Lin J., Pang R., Wei L., Xu L., Sheng F., Li C., Li G., Zhao L., Hou Y., Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(24), 4114—4120 |
| 28 | Gao J., Liang G., Cheung J. S., Pan Y., Kuang Y., Zhao F., Zhang B., Zhang X., Wu E. X., Xu B., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130(35), 11828—11833 |
| 29 | Zeng J., Jing L., Hou Y., Jiao M., Qiao R., Jia Q., Liu C., Fang F., Lei H., Gao M., Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(17), 2694—2698 |
| 30 | Zeng H., Li J., Wang Z. L., Liu J. P., Sun S., Nano Lett., 2004, 4(1), 187—190 |
| 31 | Meiklejohn W. H., J. Appl. Phys., 1962, 33(3), 1328—1335 |
| 32 | Chai Y., Feng F., Li Q., Yu C., Feng X., Lu P., Yu X., Ge M., Wang X., Yao L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(8), 3366—3370 |
| 33 | Chien C. C., Chen H. H., Lai S. F., Wu K. C., Cai X., Hwu Y., Petibois C., Chu Y., Margaritondo G., J. Nanobiotechnol., 2012, 10(1), 10 |
| 34 | Landgraf L., Christner C., Storck W., Schick I., Krumbein I., Dähring H., Haedicke K., Heinz⁃Herrmann K., Teichgräber U., Reichenbach J. R., Tremel W., Tenzer S., Hilger I., Biomaterials, 2015, 68, 77—88 |
| 35 | Song G., Chen M., Zhang Y., Cui L., Qu H., Zheng X., Wintermark M., Liu Z., Rao J., Nano Lett., 2017, 18(1), 182—189 |
| 36 | Huang B., Law M. W. M., Khong P. L., Radiology, 2009, 251(1), 166—174 |
| 37 | Hildebrand S., Löwa N., Paysen H., Fratila R. M., Reverte⁃Salisa L., Trakoolwilaiwan T., Niu Z., Kasparis G., Preuss S. F., Kosch O., M. De La Fuente J., Thanh N. T. K., Wiekhorst F., Pfeifer A., ACS Nano, 2020, 15(1), 434—446 |
| 38 | Hong H., Yang Y., Zhang Y., Cai W., Curr. Top. Med. Chem., 2010, 10(12), 1237—1248 |
| 39 | Srinivas M., Aarntzen E. H. J. G., Bulte J. W. M., Oyen W. J., Heerschap A., de Vries I. J. M., Figdor C. G., Adv. Drug Del. Rev., 2010, 62(11), 1080—1093 |
| 40 | Gu E., Chen W. Y., Gu J., Burridge P., Wu J. C., Theranostics, 2012, 2(4), 335—345 |
| 41 | Hong G., Antaris A. L., Dai H., Nat. Biomed. Eng., 2017, 1(1), 0010 |
| 42 | Sutton E. J., Henning T. D., Pichler B. J., Bremer C., Daldrup⁃Link H. E., Eur. Radiol., 2008, 18(10), 2021—2032 |
| 43 | Bulte J. W. M., Am. J. Roentgenol., 2009, 193(2), 314—325 |
| 44 | Hong G., Lee J. C., Robinson J. T., Raaz U., Xie L., Huang N. F., Cooke J. P., Dai H., Nat. Med., 2012, 18(12), 1841—1846 |
| 45 | Liu X. L., Yang Y., Ng C. T., Zhao L. Y., Zhang Y., Bay B. H., Fan H. M., Ding J., Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(11), 1939—1944 |
| 46 | Carrey J., Mehdaoui B., Respaud M., J. Appl. Phys., 2011, 109(8), 083921 |
| 47 | Lee J. H., Jang J. T., Choi J. S., Moon S. H., Noh S. H., Kim J. W., Kim J. G., Kim I. S., Park K. I., Cheon J., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2011, 6(7), 418—422 |
| 48 | Kossatz S., Grandke J., Couleaud P., Latorre A., Aires A., Crosbie⁃Staunton K., Ludwig R., Dähring H., Ettelt V., Lazaro⁃Carrillo A., Calero M., Sader M., Courty J., Volkov Y., Prina⁃Mello A., Villanueva A., Somoza Á., Cortajarena A. L., Miranda R., Hilger I., Breast Cancer Res., 2015, 17(1), 66 |
| 49 | Moroz P., Jones S. K., Gray B. N., Int. J. Hyperth., 2002, 18(4), 267—284 |
| 50 | Du Y., Liu X., Liang Q., Liang X. J., Tian J., Nano Lett., 2019, 19(6), 3618—3626 |
| 51 | Ludewig P., Gdaniec N., Sedlacik J., Forkert N. D., Szwargulski P., Graeser M., Adam G., Kaul M. G., Krishnan K. M., Ferguson R. M., Khandhar A. P., Walczak P., Fiehler J., Thomalla G., Gerloff C., Knopp T., Magnus T., ACS Nano, 2017, 11(10), 10480—10488 |
| 52 | Möddel M., Meins C., Dieckhoff J., Knopp T., New J. Phys., 2018, 20(8), 083001 |
| 53 | Murase K., Song R., Hiratsuka S., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2014, 104(25), 252409 |
| 54 | Szwargulski P., Wilmes M., Javidi E., Thieben F., Graeser M., Koch M., Gruettner C., Adam G., Gerloff C., Magnus T., Knopp T., Ludewig P., ACS Nano, 2020, 14(10), 13913—13923 |
| [1] | SHA Meng, XU Weiqing, WU Zhichao, GU Wenling, ZHU Chengzhou. Recent Advances in Single-atom Materials for Enzyme-like Catalysis and Biomedical Applications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220077. |
| [2] | ZHANG Qian, LIU Yawei, WANG Fan, LIU Kai, ZHANG Hongjie. High-resolution in vivo Imaging, Diagnosis and Treatment Applications of Rare-earth-based Nanomaterials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(12): 20220552. |
| [3] | ZHANG Xiang, LI Shurun, ZHAI Wentao, CAO Yingze, QI Hongxu, JI Yan, WEI Yen. In Situ Encapsulation of Cellubiase Enzyme in Magnetic Mesoporous Silica via the Nonsurfactant-templated Sol-gel Method† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(11): 2349. |
| [4] | ZHANG Zhijie, GONG Jiang, TAN Haiying, YAO Kun, TANG Tao. Preparation and Characterization of PS-b-P2VP/Fe3O4 Nanocomposites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(5): 1080. |
| [5] | JIANG Ze-Quan, SONG Sheng, DOU Hong-Jing, SUN Kang, WANG Yi-Ming, HUANG Chao-Fan, WEI Zhen-Hua, QU Guan-Xiong. Synthesis of Polycarboxylic Ligand Capped Fe3O4 Nanoparticles with Excellent Water-dispersibility via a Ligand-exchange Approach [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(12): 2609. |
| [6] | FU Yu, YANG Min, LI Yan, ZHONG Chong-Bin, JIAO Yong-Hua, LIN Ao-Lei. Effect of Layer-by-layer Films of Natural Polymers on Drug Release of Magnetic Poly(lactic acid) Microspheres [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(12): 2779. |
| [7] | LIU Xue-Ping, OUYANG Xiang-Yuan, WU Hui-Wang, SHEN Guo-Li, YU Ru-Qin. Novel Fluorescent Technique for Detecting Adenosine Based on DNA Strand Displacement Induced by Target-aptamer Complex and Metal Deposition Catalyzed by Gold Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(08): 1692. |
| [8] | SU Peng-Fei, CHEN Guo*, ZHAO Jun. Convenient Preparation and Characterization of Surface Carboxyl-functioned Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(7): 1472. |
| [9] | GAO Qian, ZHANG Ji-Lin, HONG Guang-Yan*, NI Jia-Zuan. Solvothermal Synthesis of the Magnetite Micro-nano Particles(Fe3O4) with Different Morphologies [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(3): 552. |
| [10] | YANG Guo-Fu, LI Xiang-Hui, ZHAO Zhe, LIU Jia-Kun, WANG Wen-Bo*. Characterization and Tissue Pharmacokinetics in Mice of Arsenic Trioxide Magnetic Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(5): 892. |
| [11] | LI Zhong, ZHU Xin, DONG Chao-Qing, HUANG Xiang-Yi, CHEN Hong-Jin, REN Ji-Cun*. Aqueous Synthetic Approaches of Luminescent Quantum Dots and Their Applications in Chemical Assays and Bioassays [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(10): 1905. |
| [12] | TAO Lei, JIN Wei*, ZHANG Ying, YAN Fei, WANG Lin-Lin, MU Ying, ....... Different Materials Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles Studied by Home-made Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(5): 882. |
| [13] | LIU Hong-Na1, LI Song1,2*, WANG Zhi-Fei2, HE Nong-Yue2, HE Quan-Guo1*. High-throughput SNP Genotyping Method with PCR on Magnetic Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(6): 1035. |
| [14] | HE Xiao-Xiao, WANG Ke-Min, TAN Wei-Hong, LIU Bin, LI Du, HUANG Shan-Sheng . Concentration of Trace Amounts Oligonucleotide Using Super-paramagnetic DNA Nano-enricher [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2003, 24(1): 40. |
| [15] | HONG Xia, WEI Li, GUO Wei, LI Jun, SONG Wen-Long, BAI Yu-Bai, LI Tie-Jin. Direct Fabrication of Magnetite Nanoparticles Patterns via"Dip-Pen" Nanolithography [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2002, 23(9): 1778. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||