

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 20210640.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20210640
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHOU Ying, HE Peinan, FENG Haisong, ZHANG Xin( )
)
Received:2021-09-06
Online:2022-02-10
Published:2021-11-11
Contact:
ZHANG Xin
E-mail:zhangxin@mail.buct.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHOU Ying, HE Peinan, FENG Haisong, ZHANG Xin. Optimal Distribution of Active Sites of CO2 Reduction Reaction Catalyzed by Diatomic Site M-N-C[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210640.
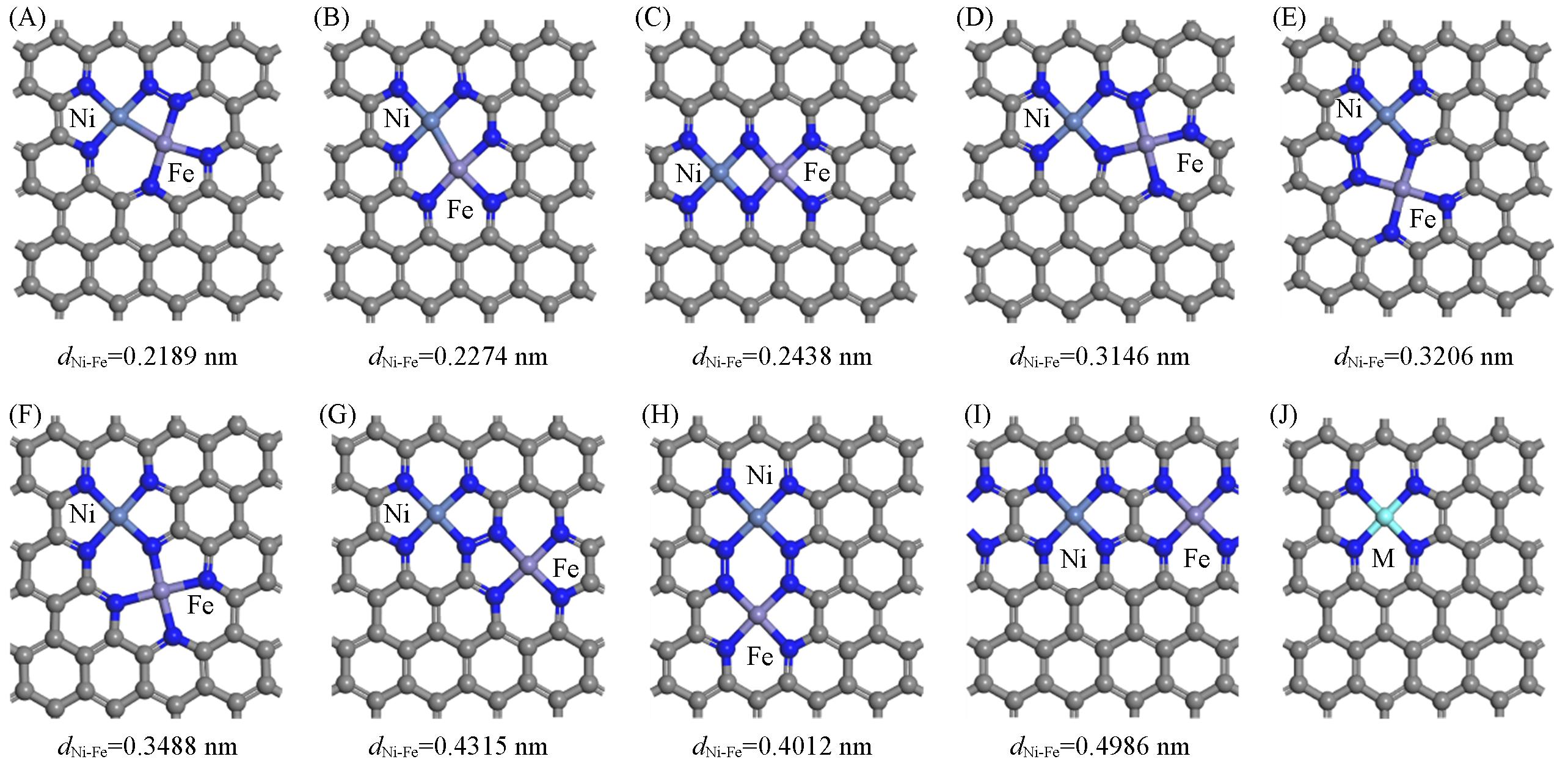
Fig.1 Structures of catalysts of NiFe?N?C catalysts(A―I) and M?N?C(M=Ni or Fe) catalysts(J)(A) Model 1; (B) model 2; (C) model 3; (D) model 4; (E) model 5; (F) model 6; (G) model 7; (H) model 8; (I) model 9.
| Catalyst | Bader charge/C | Valence | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Fe | Ni | Fe | |
| Ni?N?C | 9.16 | ― | 0.85 | ― |
| Fe?N?C | ― | 6.88 | ― | 1.12 |
| Model 1 | 9.45 | 7.10 | 0.55 | 0.90 |
| Model 2 | 9.42 | 7.07 | 0.58 | 0.93 |
| Model 3 | 9.15 | 6.89 | 0.85 | 1.11 |
| Model 4 | 9.14 | 6.94 | 0.86 | 1.06 |
| Model 5 | 9.20 | 6.94 | 0.80 | 1.06 |
| Model 6 | 9.19 | 6.90 | 0.81 | 1.10 |
| Model 7 | 9.13 | 6.92 | 0.87 | 1.08 |
| Model 8 | 9.23 | 6.95 | 0.77 | 1.05 |
| Model 9 | 9.18 | 6.93 | 0.82 | 1.07 |
Table 1 Bader charge and valence data of metal atoms in catalysts
| Catalyst | Bader charge/C | Valence | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Fe | Ni | Fe | |
| Ni?N?C | 9.16 | ― | 0.85 | ― |
| Fe?N?C | ― | 6.88 | ― | 1.12 |
| Model 1 | 9.45 | 7.10 | 0.55 | 0.90 |
| Model 2 | 9.42 | 7.07 | 0.58 | 0.93 |
| Model 3 | 9.15 | 6.89 | 0.85 | 1.11 |
| Model 4 | 9.14 | 6.94 | 0.86 | 1.06 |
| Model 5 | 9.20 | 6.94 | 0.80 | 1.06 |
| Model 6 | 9.19 | 6.90 | 0.81 | 1.10 |
| Model 7 | 9.13 | 6.92 | 0.87 | 1.08 |
| Model 8 | 9.23 | 6.95 | 0.77 | 1.05 |
| Model 9 | 9.18 | 6.93 | 0.82 | 1.07 |
| 1 | He L., Zhang W. Y., Liu S., Zhao Y., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2021, 298, 1―11 |
| 2 | Duan X. C., Xu J. T., Wei Z. X., Ma J. M., Guo S., Wang S., Liu H., Dou S., Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 170―178 |
| 3 | Li P. Y., Liu L., An W. J., Wang H., Liang Y., Cui W., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2020, 266, 118618―118626 |
| 4 | Jiang Y., Chu N., Qian D. K., Bioresour. Technol., 2020, 295, 122266―122274 |
| 5 | Liu Q. T., Qi J., Zhou Q. L., Li N., Appl. Chem. Ind., 2020, 49, 116―119(刘清田, 戚霁, 周屈兰, 李娜. 应用化工, 2020, 49, 116―119) |
| 6 | Lu Q., Jiao F., Nano Energ., 2016, 29, 439―456 |
| 7 | Guo C., Zhang T., Deng X., Liang X., Guo W., Lu X., Wu C. M., ChemSusChem, 2019,12, 5126―5132 |
| 8 | Varela A. S., Sahraie N. R., Steinberg J., Ju W., Oh P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 10758―10762 |
| 9 | Nielsen D. U., Hu X., Daasbjerg K., Skrydstrup T., Nature Catal., 2018, 1, 244―254 |
| 10 | Ilieva L., Ivanov I., Petrova P., Munteanu G., Tabakova T., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45, 26286―26299 |
| 11 | Mezzavilla S., Horch S., Stephens I. E., Seger B., Angew. Chem., 2019, 131, 3814―3818 |
| 12 | Lu Q., Rosen J., Jiao F., ChemCatChem, 2015, 7, 38―47 |
| 13 | Zhu W., Michalsky R., Metin Ö., Lv H., Guo S., Wright C. J., Sun A. A., Peterson A., Sun S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 16833―16836 |
| 14 | Rosen J., Hutchings G. S., Lu Q., Forest R. V., Moore F., ACS Catal., 2015, 5, 4586―4591 |
| 15 | Hall A. S., Yoon Y., Wuttig A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 14834―14837 |
| 16 | Zhang H. Y., Tian W. J., Duan X. G., Sun H. Q., Liu S. M., Wang S. B., Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, 1904037―1904045 |
| 17 | Jiao J., Lin R., Liu S., Cheong W., Zhang C., Chen Z., Pan Y., Tang J., Wu K., Hung S., Chen M., Zheng L., Lu Q., Yang X., Xu B., Xiao H., Li J., Wang D., Peng Q., Chen C., Li Y., Nat. Chem., 2019, 11, 222―228 |
| 18 | Ren W., Tan X., Yang W., Jia C., Xu S., Wang K., Smith S., Zhao C., Angew. Chem., 2019, 58, 6972―6976 |
| 19 | Hu R., Li Y., Zeng Q., Shang J., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 525, 146588―146592 |
| 20 | Li Y., Liu X., Zheng L., Shang J., Wan X., Hu R., Guo X., Hong S., Shui J., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 26147―26153 |
| 21 | Guo C., Zhang T., Liang X.Y., Deng X. X., Guo W. Y., Wang Z. J., Lu X. Q., Wu C. L., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 533, 147466―147475 |
| 22 | Kresse G., Furthmüller J., Phys. Rev. B, 1996, 54, 11169―11186 |
| 23 | Kresse G., Joubert D., Phys. Rev. B, 1999, 59, 1758―1775 |
| 24 | Perdew J. P., Burke K., Ernzerhof M., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1996, 77, 3865―3868 |
| 25 | Grimme S., J. Comput. Chem., 2006, 27, 1787―1799 |
| 26 | Monkhorst H. J., Pack J. D., Phys. Rev. B: Solid State, 1976, 13, 5188―5192 |
| 27 | Zhang X. L., Wang W. C., Yang Z. X., ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2020, 8, 6134―6141 |
| 28 | Liang Z., Luo M. M., Chen M. W., Qi X. P., Liu J., Liu C., Peera S., Liang T. X., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8, 20453―20462 |
| 29 | Nørskov J., Rossmeisl J., Logadottir A., Lindqvist L., Kitchin J., Bligaard T., J´onsson H., Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 17886―17892 |
| 30 | Peterson A. A., Abild⁃Pedersen F., Studt F., Osmiumsl J., Nerskov J. K., Energy Environ. Sci., 2010, 3, 1311―1315 |
| 31 | Miller S., Kitchin J., Surf. Sci., 2009, 603, 794―801 |
| 32 | Deng D., Chen X., Yu L., Wu X., Liu Q., Liu Y., Yang H., Tian H., Hu Y., Du P., Sci. Adv., 2015, 1, 1500462―1500468 |
| 33 | Hu R., Shang J., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 496, 143659―143662 |
| 34 | Wang X., Niu H., Liu Y., Shao C., Robertson J., Zhang Z., Guo Y., Cat. Sci. Technol., 2020, 10, 8465―8472 |
| 35 | Back S., Lim J., Kim N., Kimb Y., Jung Y., Chem. Sci., 2017, 8, 1090―1096 |
| 36 | Pan Y. A., DFT Study for Oxygen Reduction on Titanium Nitride and Cu⁃doped Titanium Nitride@Pt Core⁃shell Electrocatalysts, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, 2020(潘俞安. 氮化钛及铜掺杂氮化钛⁃铂核壳催化剂电催化氧还原反应的密度泛函理论研究, 广州: 华南理工大学, 2020) |
| 37 | Chen D. C., Chen Z. W., Lu Z. L., Tang J., Zhang X. X., Singh C. V., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8, 21241―21254 |
| 38 | Huang Q. L., Liu H M., An W., Wang Y. Q., Feng Y. H., Men Y., ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng.,2019, 7, 19113―19121 |
| 39 | Shen H., Li Y., Sun Q., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, 121, 3963―3969 |
| 40 | Peterson A. A., Abild⁃Pedersen F., Studt F., Rossmeisl J., Nørskov J. K., Energy Environ. Sci., 2010, 3, 1311―1315 |
| [1] | ZHANG Xiaoyu, XUE Dongping, DU Yu, JIANG Su, WEI Yifan, YAN Wenfu, XIA Huicong, ZHANG Jianan. MOF-derived Carbon-based Electrocatalysts Confinement Catalyst on O2 Reduction and CO2 Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210689. |
| [2] | YAN Xuan,XUE Bingchun,LIU Erbao. Synthesis of Urea Ammonium Halide Cocrystal and Theoretical Study of Its Influencing Factors in Water System† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(12): 2700. |
| [3] | YU Ao, WANG Hui-Kai, XUE Xiao-Song, CAI Yu, WANG Yong-Jian, HE Jia-Qi. Theoretical Study on the Thermodynamic Hydricity of Imidazole-based Organic Hydrides in Acetonitrile [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(02): 276. |
| [4] | WANG Feng, LI Wen-Hong*, LI Dong, YAN Sui-Hong, XU Kang-Zhen, SUN Xiao-Hong. Knoevenagel Reaction of 2-Aminothiophen-4-one [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(4): 903. |
| [5] | JI Chang-Chun, XU Zheng-Jiang, LI Jing, LIU Guang-Xiang, ZHENG He-Gen*. Syntheses, Structures of Four New Complexes Constructed by Flexible Pyridine Ligand and the Relationship Between Conformations and Structures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(5): 867. |
| [6] | YU Qing, CAO Jie*, ZHANG Cheng-Gen. Direct Experimental Evidence of Ternary Diastereomeric Complexes in Chiral Separations of Phenylglycine Enatiomers with Chiral Mobile Phase by RP-HPLC [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(5): 988. |
| [7] | HUANG Rong-Yi, CHEN Hong, YAN Juan, ZHU Kun, LIU Guang-Xiang*, REN Xiao-Ming. Syntheses, Structures and Theoretical Calculations of Three Novel Cu(Ⅱ) Complexes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(4): 655. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xin, HUANG Ting-Ting, TAN Kai, LIN Meng-Hai*, ZHANG Qian-Er. Theoretical Studies on Third-order Nonlinear Optical Property of (ZnS)6—12 Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(6): 1126. |
| [9] | MAO Hua-Ping1, YU You-Hai1, CHEN Liang1, LU Xiao-Feng1, ZHANG Wan-Jin1, ZHANG Hong-Xing2. Synthesis and Characterization of a Novel Azo Compound with ‘Dumbbell Shape’ [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(10): 1999. |
| [10] | HUANG Kun-Lin, LI Cai-Jin, LIU Qun, BAI Hong-Tao, MU Zhong-Cheng . Synthesis, Single Crystal Structure and 1H NMR Characterization of 3-(2-p-Methylphenylvinyl)-5(4H)-isoxazolone and Theoretical Study for Its Isomerization [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(7): 1264. |
| [11] | CHEN Yi-Qing, SUN Duo-Xian, SU Jing, YANG Jun . Theoretical Calculation and Experiments of Diameter of Calcium Alginate Gel Microspheres [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2003, 24(3): 481. |
| [12] | LIU YongDong, SUN RenAn, WANG ChangSheng . Theoretical Studies of the Chemisorption of CO on Supported-metal Catalysts of Ru, Rh, Pd(Ⅱ) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2001, 22(12): 2094. |
| [13] | MO Yi, LI Le-Min . Influence of the Computation Conditions on the Results in Density Functional Calculations [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2001, 22(1): 81. |
| [14] | TAI Xi-Shi, FANG Sheng-Qiang. Far Infrared Shift of Lithium Perchlorate Complex with4-tert-Butylbenzo-15-crown-5 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2000, 21(12): 1809. |
| [15] | WEI Jun-Hua, SHE Yi-Min, XU Wen-Guo, LIU Shu-Ying . Mass Spectrometry Study Combined with Theoretical Calculation on the Unimolecular Fragmentation of Tetrahydroimidazole-substituted Methyleneβ-Diketones [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1999, 20(1): 101. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||