

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (5): 996.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170601
Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Haidan, WANG Li, XU Mei, HUANG Lichen, SONG Xianliang*
Received:2017-09-04
Online:2018-04-21
Published:2018-04-21
Contact:
SONG Xianliang
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Haidan,WANG Li,XU Mei,HUANG Lichen,SONG Xianliang. Synthesis of Bi2WO6/TiO2 Nanocomposites for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Ethylene†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5): 996.
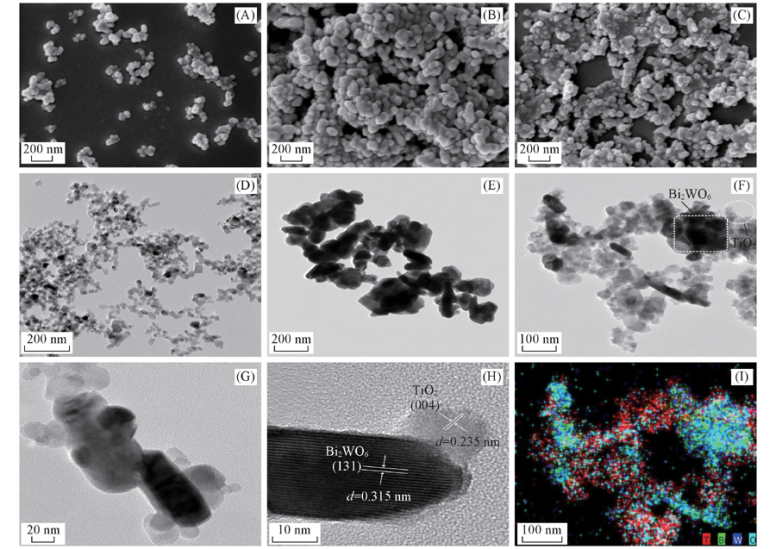
Fig.3 SEM, TEM and mapping images of nano Bi2WO6, TiO2 and Bi2WO6/TiO2 composites Note:(A) SEM images of TiO2; (B) SEM images of Bi2WO6; (C) SEM images of Bi2WO6/TiO2; (D) TEM images of TiO2; (E) TEM images of Bi2WO6; (F) and (G) TEM images of Bi2WO6/TiO2; (H) HRTEM image of Bi2WO6/TiO2; (I) mapping image of Bi2WO6/TiO2.
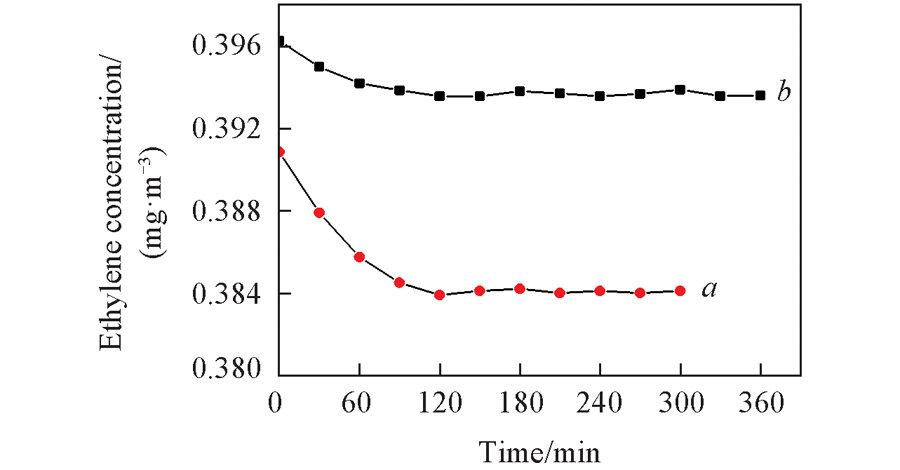
Fig.5 Adsorption equilibrium curve for ethylene with pure ACF film and simulated solar light illumination(a) and with Bi2WO6/TiO2/ACF film without illumination(b)
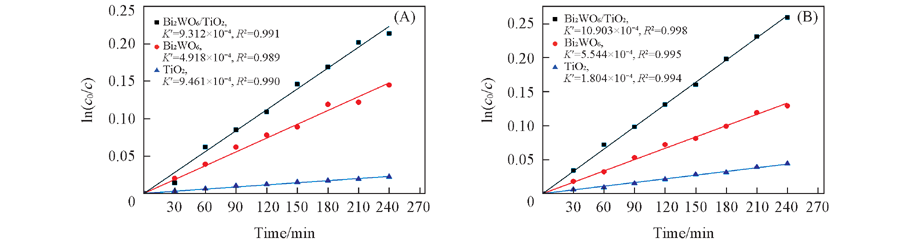
Fig.6 Kinetic curves of degradation of ethylene with different photocatalyts under visible light irradiation(A) and simulated solar light irradiation(B)
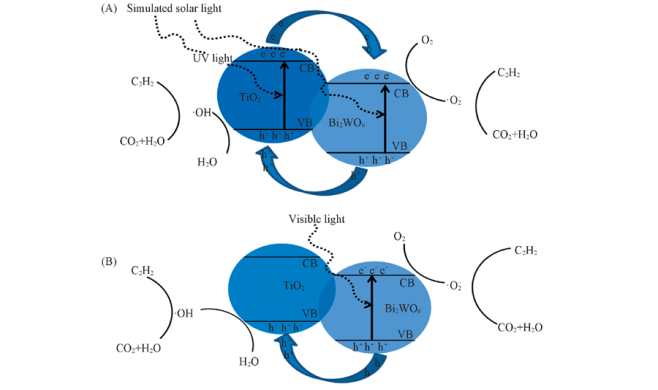
Scheme 1 Mechanism for the degradation of ethylene with Bi2WO6/TiO2 nano-heterostructure under simulated solar light(A) and visible light(B) irradiation
| [1] | Ansari M.W., Tuteja N., Protoplasma, 2015, 252(1), 21—32 |
| [2] | Chaves A.L. S., De Mello-Farias P. C., Genet. Mol. Biol., 2006, 29(3), 508—515 |
| [3] | Zheng S.H., Ye S. Y., Huang X., Shen S. W., Transactions of the CSAE, 2013, 29(20), 286—292 |
| (郑森鸿, 叶盛英, 黄迅, 沈生文. 农业工程学, 2013, 20(29), 286—292) | |
| [4] | Wang G., Wang H., Ling Y., Tang Y., Yang X., Fitzmorris R.C., Wang C., Zhang J. Z., Li Y., Nano Lett., 2011, 11, 3026—3033 |
| [5] | Schneider J., Matsuoka M., Takeuchi M., Zhang J., Horiuchi Y., Anpo M., Bahnemann D.W., Chem. Rev., 2014, 114(19), 9919—9986 |
| [6] | A S., Zheng J. W., Liu J. M., Bai J., Yang J. C., Zhang Q. C., Chem. [J]. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8), 1450—1457 |
| (阿山, 郑家威, 刘聚明, 白杰, 杨桔材, 张前程. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(8), 1450—1457) | |
| [7] | Ding S., Zhu G.W., Wang R. W., Zhang Z. T., Qiu S. L., Chem. [J]. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(5), 1016—1022 |
| (丁双, 朱国巍, 王润伟, 张宗弢, 裘式纶. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(05), 1016—1022) | |
| [8] | Song X.L., Li Y. Y., Wei Z. D., Ye S. Y., Dionysios D., Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 314, 443—452 |
| [9] | Xiao J., Dong W., Song C., Yu Y., Zhang L., Li C., Yin Y., Mater. Sci. Semicond.Process., 2015, 40, 463—467 |
| [10] | Yang A.M., Han Y., Li S. S., Xing H. W., Pan Y. H., Liu W. X., [J]. Alloys Compd., 2017, 695, 915—921 |
| [11] | Gui M., Zhang W., Chang Y., Yu Y., Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 197, 283—288 |
| [12] | Li J., Guo Z., Wang Y., Zhu Z., Micro & Nano Lett., 2014, 9(2), 65—68 |
| [13] | Xu Q.C., Wellia D. V., Ng Y. H., Amal R., Tan T. T. Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(15), 7419—7428 |
| [14] | Yang C., Huang Y., Li F., Li T., [J]. Mater. Sci., 2016, 51(2), 1032—1042 |
| [15] | Murcia-López S., Hidalgo M. C., Navío J. A., Appl Catal. A,2012, 423/424, 34—41 |
| [16] | Murcia-López S., Hidalgo M.C., Navío J. A., Photochem. Photobiol., 2013, 89(4), 832—840 |
| [17] | Liu Z., Liu X., Lu D., Fang P., Wang S., Mater. Lett., 2014, 130, 143—145 |
| [18] | Wang K.H., Tsai H. H., Hsieh Y. H., Appl. Catal. B, 1998, 17, 313—320 |
| [19] | Zhang X., Liu J.X., Wang Y. W., Fan C. M., Duan D. H., Wang Y. F., Chem. [J]. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(1), 88—93 |
| (张雪, 刘建新, 王雅文, 樊彩梅, 段东红, 王韵芳. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(1), 88—93) | |
| [20] | Zhang L., Wang H., Chen Z., Wong P.K., Liu J., Appl. Catal., B, 2011, 106, 1—13 |
| [21] | Lin H.X., In situ IR Study on the Surface Adsorption and Photocatalysis of TiO2, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, 2011 |
| (林华香. TiO2表面吸附与光催化作用的原位IR研究, 福州: 福州大学, 2011) | |
| [22] | Liu D.H., Study on Preparation, Structure and Photocatalytic Performance of Bi2WO6-C Composite Materials, Shanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, 2016 |
| (刘丁菡. Bi2WO6-C复合光傕化材料的制备、 结构及性能研究, 西安: 陕西科技大学, 2016) | |
| [23] | Balachandran V., Karpagam V., Santhi G., Revathi B., Ilango G., Kavimani M., Spectrochim. Acta A, 2015, 137, 165—175 |
| [24] | Luo S.X., Preparation, Characterization and Photocatalytic Activities of Bi2WO6 and TiO2 by Doping and Loading Photocatalysts, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 2010 |
| (罗善霞. Bi2WO6和掺杂与负载型 TiO2光催化剂的制备与表征及其活性评价, 天津: 天津大学, 2010) | |
| [25] | Zhang Y., Fei L., Jiang X., Pan C., Wang Y., Rapid Commun. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2011, 94(12), 4157—4161 |
| [26] | Sun X., Zhang H., Wei J., Yu Q., Yang P., Zhang F., Mater. Sci. Semicond.Process., 2016, 45, 51—56 |
| [1] | JIANG Shenghan, CAO Changlin, XIAO Liren, YANG Tang, QIAN Qingrong, CHEN Qinghua. Preparation of Composite Semiconductor Micro-sheets with UV Shielding Performance and Its Application in Polypropylene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220071. |
| [2] | HAO Honglei, MENG Fanyu, LI Ruoyu, LI Yingqiu, JIA Mingjun, ZHANG Wenxiang, YUAN Xiaoling. Biomass Derived Nitrogen Doped Porous Carbon Materials as Adsorbents for Removal of Methylene Blue in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220055. |
| [3] | ZHAO Sheng, HUO Zhipeng, ZHONG Guoqiang, ZHANG Hong, HU Liqun. Preparation of Modified Gadolinium/Boron/Polyethylene Nanocomposite and Its Radiation Shielding Performance for Neutron and Gamma-ray [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220039. |
| [4] | LIU Jiaxin, MIN Jie, XU Huajie, REN Haisheng, TAN Ningxin. Interaction Between Produced Radicals During Ethylene Combustion and Nitrogen Molecules Based on Reaxff Molecular Dynamics Simulation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210834. |
| [5] | JIA Hongjun, ZHANG Jiatao, MA Zhuoli, WANG Heng, YANG Xinyu, YANG Jiazhi. Preparation of PTFE/PAA/Nafion Composite Membrane by Aqueous Polymerization of Acrylic Acid and Its Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220350. |
| [6] | JIANG Shan, SHEN Qianqian, LI Qi, JIA Husheng, XUE Jinbo. Pd-loaded Defective TiO2 Nanotube Arrays for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220206. |
| [7] | ZHANG Lingyu, ZHANG Jilong, QU Zexing. Dynamics Study of Intramolecular Vibrational Energy Redistribution in RDX Molecule [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220393. |
| [8] | XU Xiaolong, FANG Lining, LIU Changyu, LIU Minchao, JIA Jianbo. Preparation of Z-type g-C3N4/Pt/TiO2 Nanotube Array Composite Electrode and Its Performance of Photoelectric Oxidation of Methanol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2926. |
| [9] | LIU Simei, LIU Weihua, LU Manli, ZHANG Wenli, SHEN Rongfang, WANG Mouhua. Evolution of the Radicals in γ-Rays Irradiated Medical Grade Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2602. |
| [10] | CHEN Shaoyun, ZHANG Xingying, LIU Ben, TIAN Du, LI Qi, CHEN Fang, HU Chenglong, CHEN Jian. Controllable Growth of Silver Nanoparticles on TiO2 Tetragonal Prism Nanarrays and Its SERS Effect [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2381. |
| [11] | WU Qiliang, MEI Jinghao, LI Zheng, FAN Haidong, ZHANG Yanwei. Photo-thermal Coupling Water Splitting over Fe-doped TiO2 with Various Nanostructures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1837. |
| [12] | ZHOU Shuai, WANG Juan. Carbon-doped Oxygen-deficient TiO2 Fibers Synthesized without Adding External Carbon Sources and Their Photocatalytic Activity [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1284. |
| [13] | LIU Aiqing, XU Wensheng, XU Xiaolei, CHEN Jizhong, AN Lijia. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Polymer/rod Nanocomposite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 875. |
| [14] | JIA Bingquan, YE Bin, ZHAO Wei, XU Fangfang, HUANG Fuqiang. Metallic 1T′ MoS2 Boosts Graphitic C3N4 for Efficient Visible-light Photocatalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 615. |
| [15] | HUANG Huilong, HUANG Hanxiong. Low-temperature Impact Behavior of Droplet on Injection-compression Molded Nanostructured PP/POE Blend Surfaces [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3195. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||