

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (10): 1737.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170160
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Tianxia1, ZHANG Zhengtao1, WANG Yong1,*( ), NI Yongnian1,2,*(
), NI Yongnian1,2,*( )
)
Received:2017-03-20
Online:2017-10-10
Published:2017-09-20
Contact:
WANG Yong,NI Yongnian
E-mail:wangyong@ncu.edu.cn;ynni@ncu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
CHEN Tianxia, ZHANG Zhengtao, WANG Yong, NI Yongnian. Cytidine-protected Copper Nanoclusters as a Novel Fluorescent Probe for the Detection of Dichromate Anion†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1737.
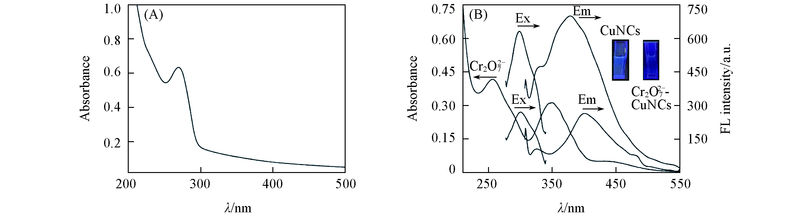
Fig.2 UV-Vis absorption spectrum of CuNCs(A) and fluorescence excitation(Ex) and emission(Em) spectra of CuNCs with and without 5.0 μmol/L Cr2O72- and UV-Vis absorption spectra of 5.0 μmol/L Cr2O72-(B)Insets of (B) are the optical images under 365 nm UV light.
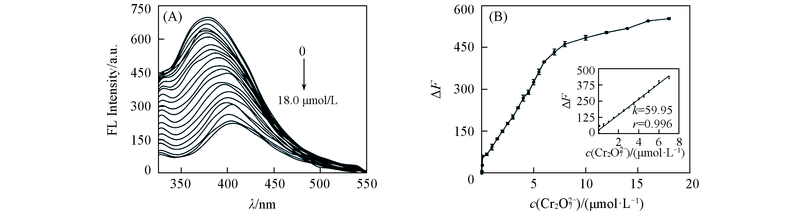
Fig.3 Fluorescence emission spectra of CuNCs in the presence of different concentrations of Cr2O72-(A) and the relationship between ΔF and the concentration of Cr2O72- (B)(A) Concentration of CuNCs from top to bottom/(μmol·L-1): 0, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 10.0, 12.0, 14.0, 16.0, 18.0. Inset of (B) shows the corresponding linear calibration plot.
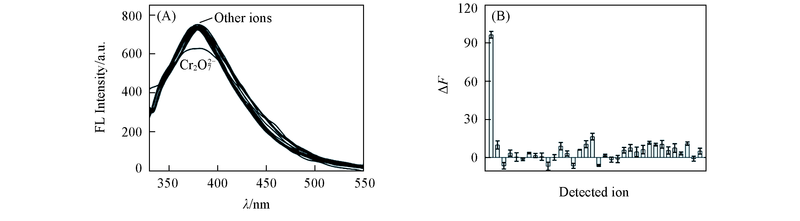
Fig.4 Fluorescence emission spectra of CuNCs in the presence or absence(blank) of each ion(A) and selectivity of CuNCs for Cr2O72-(B)(A) Concentration of Cr2O72- or any other ion is 1.0 μmol/L. Other ions include Blank, S2-, SCN-, S2O32-, Cl-, NO2-, F-, Br-, ClO3-, IO4-, BrO3-, PO43-, SO32-, H2PO4-, I-, Al3+, Pb3+, Fe3+, Mg2+, Cd2+, Cr3+, Co2+, Ba2+, Mn2+, Ca2+, Fe2+, Ni2+, Hg2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, NH4+, C15H34N+, C8H20N+. (B) ΔF=F0-F; F0 and F denote the fluorescence intensity without(blank) and with each ion, respectively. Ions from left to right: Cr2O72-, blank, S2-, SCN-, S2O32-, Cl-, NO2-, F-, Br-, ClO3-, IO4-, BrO3-, PO43-, SO32-, H2PO4-, I-, Al3+, Pb3+, Fe3+, Mg2+, Cd2+, Cr3+, Co2+, Ba2+, Mn2+, Ca2+, Fe2+, Ni2+, Hg2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, NH4+, C8H20N+, C15H34N+.
| Sample source | No. | Added/(μmol·L-1) | Mean found/(μmol·L-1) | Mean Recovery*(%) | RSD(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qingshan lake | 1 | 0.50 | 0.59 | 118 | 8.3 |
| 2 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 96 | 5.6 | |
| 3 | 1.50 | 1.48 | 99 | 2.9 | |
| Ganjiang river | 1 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 98 | 3.5 |
| 2 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 96 | 2.6 | |
| 3 | 1.50 | 1.62 | 108 | 3.9 |
Table 1 Determination of Cr2O72- in spiked water samples(n=3)
| Sample source | No. | Added/(μmol·L-1) | Mean found/(μmol·L-1) | Mean Recovery*(%) | RSD(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qingshan lake | 1 | 0.50 | 0.59 | 118 | 8.3 |
| 2 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 96 | 5.6 | |
| 3 | 1.50 | 1.48 | 99 | 2.9 | |
| Ganjiang river | 1 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 98 | 3.5 |
| 2 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 96 | 2.6 | |
| 3 | 1.50 | 1.62 | 108 | 3.9 |
| [1] | Kieber R. J., Willey J. D., Zvalaren S. D., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2002, 36(24), 5321—5327 |
| [2] | Ueno S., Kashimoto T., Susa N., Ueno S. J., Kashimoto T., Susa N., Furukawa Y., Ishii M., Yokoi K., Yasuno M., Sasaki Y. F., Ueda J., Nishimura Y., Sugiyama M., Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 2001, 170(1), 56—62 |
| [3] | Morris B. W., Griffiths H., Kemp G. J., Clin. Chem., 1988, 34(6), 1114—1116 |
| [4] | Daniels D. S., Tainer J. A., Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen., 2000, 460(3/4), 151—163 |
| [5] | Gunaratnam M., Grant M. H., Biochem. Soc. Trans., 2002, 30(4), 748—50 |
| [6] | Douglas G. R., Bell R. D., Grant C. E., Wytsma J. M., Bora K. C., Mutat. Res., 1980, 77(2), 157—163 |
| [7] | Holmes A. L, Wise S. S, Sr W. J., Indian J. Med. Res., 2008, 128(4), 353—72 |
| [8] | Cao C. S., Hu H. C., Xu H., Qiao W. Z., Zhao B., Cryst. Eng. Comm., 2016, 18(23), 4445—4451 |
| [9] | Arancibia V., Valderrama M., Silva K., Tapia T., J. Chromatogr. B,2003, 785(2), 303—309 |
| [10] | Xiang Y., Mei L., Li N., Tong A., Anal. Chim. Acta,2007, 581(1), 132—136 |
| [11] | Anthemidis A. N., Zachariadis G. A., Kougoulis J. S., Stratis J. A., Talanta,2002, 57(1), 15—22 |
| [12] | Yuan Y. H., Feng F., Tian M. Z., Meng S. M, Bai Y. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2011, 32(1), 62—66 |
| (袁跃华, 冯锋, 田茂忠, 孟双明, 白云峰. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(1), 62—66) | |
| [13] | Yan L. M., Zhou H., Wu C. Q., Wang L. D., Yang W., Jin M. Y., Zhao Y. X., Xu J. W., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2016, 32(6), 877—881 |
| [14] | Li T., Cao Z., Li P. P., He J. L., Xiao H.,Yang C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2016, 37(9), 1616—1621 |
| (李婷, 曹忠, 李盼盼, 何婧琳, 肖慧, 杨婵. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(9), 1616—1621) | |
| [15] | Yuan Y., He X. X., Shi H., Wang K. M., Wu X., Huo X. Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(11), 2167—2172 |
| (袁媛, 何晓晓, 石慧, 王柯敏, 伍旭, 霍希琴. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(11), 2167—2172) | |
| [16] | Lin C., Gong H., Fan L. Z., Li X. H., Acta Chim. Sinica,2014, 72(6), 704—708 |
| (蔺超, 宫贺, 范楼珍, 李晓宏. 化学学报, 2014, 72(6), 704—708) | |
| [17] | Zhang Y. Y., Jiang H., Ge W., Li Q. W., Wang X. M., Langmuir,2014, 30(36), 10910—10917 |
| [18] | Skoog D. A., Holler F. J., Crouch S. R., Principles of Instrumental Analysis, Thomson Brooks/Cole Publisher, Philadelphia, 2007 |
| [19] | Lakowicz J. R., Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, Springer, New York, 2006 |
| [20] | Ding B., Guo C., Liu S. X., Cheng Y., Wu X. X., Su X. M., Liu Y. Y., Li Y., RSC Adv., 2016, 6(40), 33888—33900 |
| [21] | Ahmed F., Khalid S., Shah K., Shah M. R., J. Chem. Soc. Pak., 2016, 38(1), 171—176 |
| [22] | Shi M., Yang J., Liu Y. Y., Ma J. F., Dyes Pigm., 2016, 129, 109—120 |
| [1] | A Li, WANG Yong. Fluorescent Peptide Sensor for Detection of Copper Ions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2736. |
| [2] | ZHOU Sihui, LI Qiong, ZHANG Ting, PANG Daiwen, TANG Hongwu. Luminescent Nanoswitch Based on Carbon Dots for Sensitive Detection of Cu(Ⅱ) Ions and Pyrophosphates [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1593. |
| [3] | ZHANG Chunyan,LUO Jianxin,LI Wenjun,OU Lijuan,YU Guipeng,PAN Chunyue. Preparation and Sensing Properties of Covalent-linked Europium Complex Monodisperse Polystyrene Microspheres† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 153. |
| [4] | LI Ting, CAO Zhong, LI Panpan, HE Jinglin, XIAO Hui, YANG Chan. High-sensitive Fluorescent Enhancement Detection of Hg(Ⅱ) Ions Based on Poly(thymine)-templated Copper Nanoclusters† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(9): 1616. |
| [5] | ZHUANG Qianfen, CAO Wei, WU Qi, NI Yongnian. Fluorescence Detection of Au(Ⅲ) Based on Carbon Nitride Nanoparticles† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(9): 1611. |
| [6] | SHEN Zhu-Ying1, WANG Bing-Xiang1*, SHEN Jian1,2, HU Hong-Wen1. Synthesis and Fluorescence Properties of 3-Pyridin-3-yl-indolizines [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(5): 916. |
| [7] | WANG Bing-Xiang, HU Hong-Wen . Reaction Between Pyridinium N-Ylides and 1,4,4a,8a-Tetrahydro-1,4- methanonaphthalene-5,8-dione in the Presence of Oxidant [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(2): 273. |
| [8] | WANG Bing Xiang, LIU Wei Wei, HU Hong Wen. A Novel Method for the Synthesis of 1,3,5-Triarylpyrazoles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2003, 24(4): 648. |
| [9] | WANG Bing-Xiang, HU Jia-Xin, HU Yue-Fei, HU Hong-Wen . A Facile Onestep Synthesis of 1-Acylindolizines by the Reaction of Pyridinium Salts with Mannich Bases in the Presence of TPCD [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1999, 20(3): 418. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||