

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (11): 2023.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170107
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Yuying, LI Dan, CHENG Longjiu, JIN Baokang*( )
)
Received:2017-02-25
Online:2017-11-10
Published:2017-10-30
Contact:
JIN Baokang
E-mail:bkjinhf@aliyun.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Yuying, LI Dan, CHENG Longjiu, JIN Baokang. Investigation on Redox Mechanism of p-Nitrophenol in Aprotic Media†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 2023.
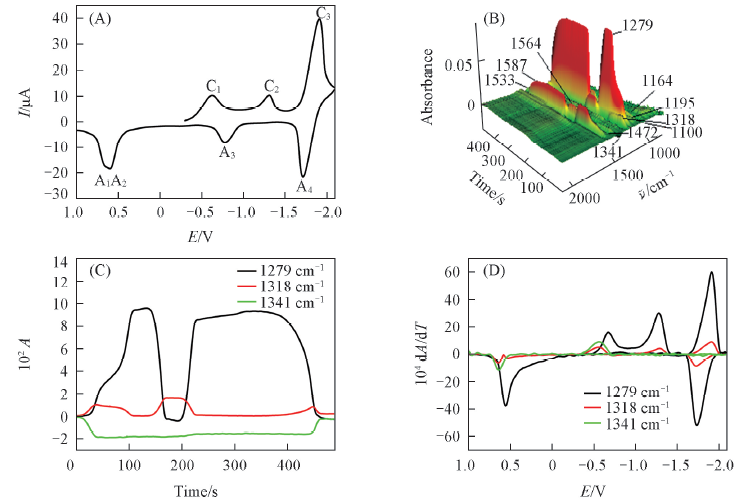
Fig.1 Cyclic voltammogram(A), the corresponding 3D IR spectrum(B), CVAs(C) and selected DCVAs(D) in acetonitrile containing 10 mmol/L PNP and 0.2 mol/L Bu4NClO4 as the supporting electrolyteTo make the DCVA data readily comparable to CV, the partial data in DCVA were multiplied by -1. Au electrode as working electrode, Ag/AgCl as reference electrode. The potential scan rate was 10 mV/s.
| Assignment | Assignment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1110 | Cl | 1318 | νN—O from -OC6H4NOOH· |
| 1156 | νC—N from -OC6H4NOOH·- | 1341 | |
| 1164 | νC—N from HOC6H4NOOH· | 1472[ | νN—O from -OC6H4NOOH· |
| 1195 | νC—N from -OC6H4NOOH· | 1533 | νN—O from HOC6H4NOOH· |
| 1272[ | νC—O from -OC6H4NOOH·- | 1564 | Benzene skeleton vibration from -OC6H4NOOH· |
| 1279 | νC—O from HOC6H4NOOH· | 1587 | Benzene skeleton vibration from HOC6H4NOOH· |
Table 1 Attribution of IR absorption peaks of PNP in acetonitrile
| Assignment | Assignment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1110 | Cl | 1318 | νN—O from -OC6H4NOOH· |
| 1156 | νC—N from -OC6H4NOOH·- | 1341 | |
| 1164 | νC—N from HOC6H4NOOH· | 1472[ | νN—O from -OC6H4NOOH· |
| 1195 | νC—N from -OC6H4NOOH· | 1533 | νN—O from HOC6H4NOOH· |
| 1272[ | νC—O from -OC6H4NOOH·- | 1564 | Benzene skeleton vibration from -OC6H4NOOH· |
| 1279 | νC—O from HOC6H4NOOH· | 1587 | Benzene skeleton vibration from HOC6H4NOOH· |
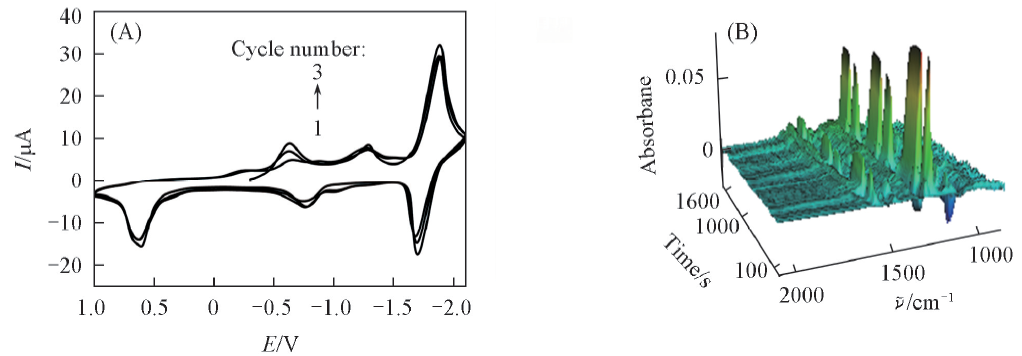
Fig.3 Consecutive CV(A) and the corresponding 3D IR spectra(B) in acetonitrile containing 10 mmol/L PNP The experimental conditions were the same as those of Fig.1.
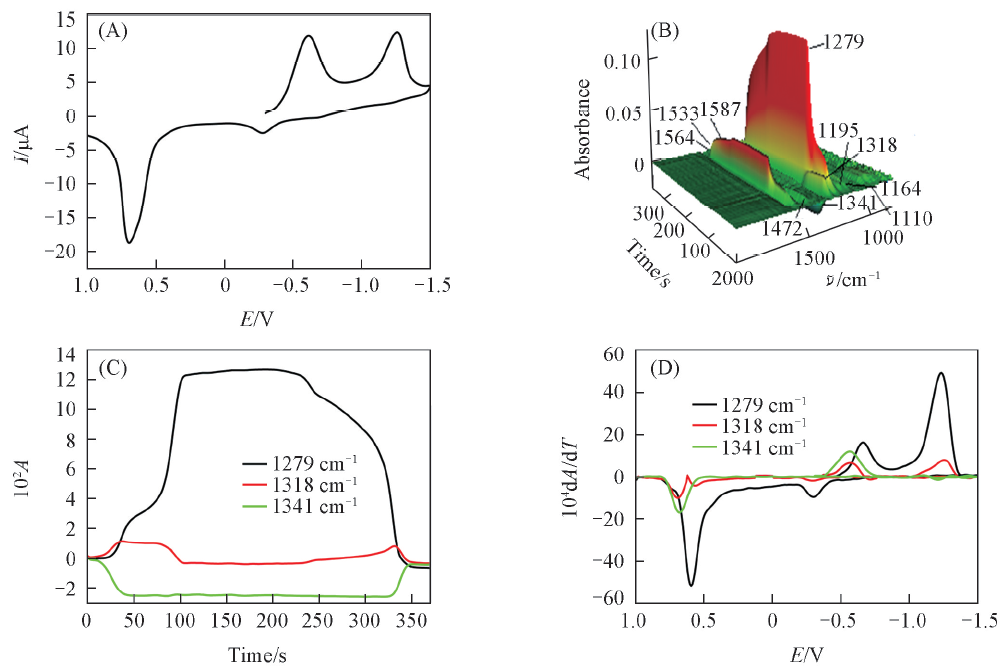
Fig.4 CV(A), the corresponding 3D IR spectra(B), CVAs(C) and selected DCVAs(D) in acetonitrile containing 10 mmol/L PNPThe scan range was -0.3—-1.5—1.0 V. Experimental conditions were the same as those of Fig.1.
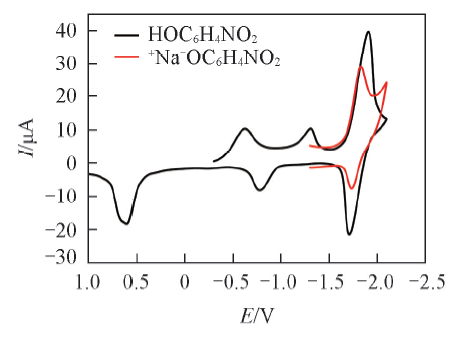
Fig.6 CV curves of PNP and +Na-OC6H4NO2 for comparisonAu electrode as working electrode, Ag/AgCl as reference electrode. The potential scan rate was 10 mV/s.
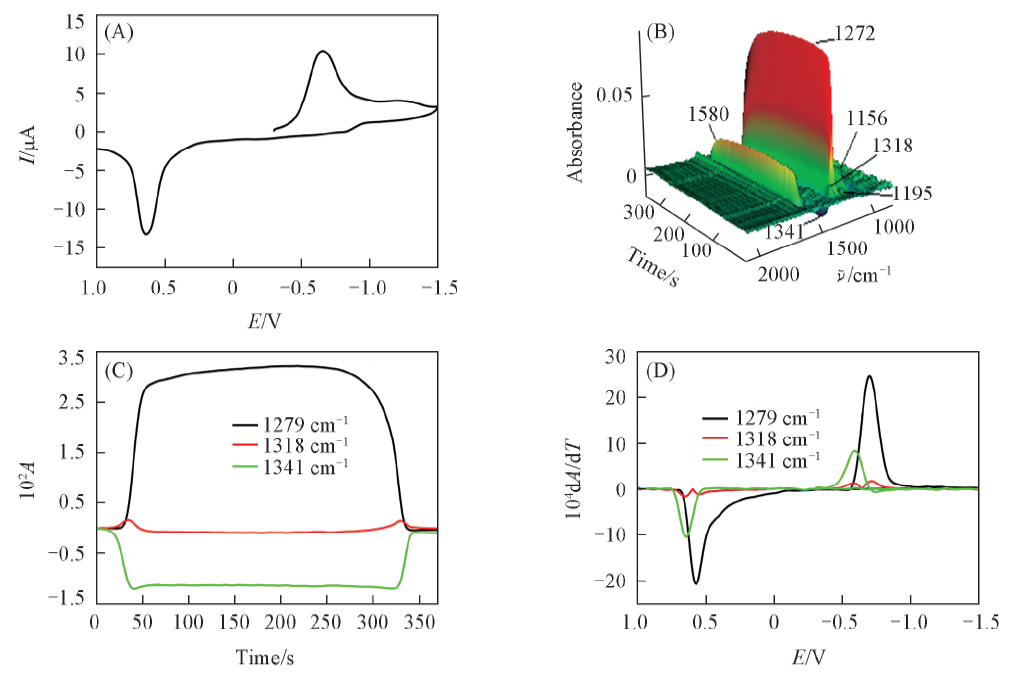
Fig.8 CV curve(A), 3D IR spectra(B), CVAs(C) and selected DCVAs(D) in acetonitrile containing 5 mmol/L PNPThe partial data in DCVA(D) were multiplied by -1 or divided by 2. Experimental conditions were the same as those of Fig.1.
| [1] | Nasima A., Kausar J. N., Safeer A., Yaseen K. A., Skibsted L. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(26), 6184-6189 |
| [2] | Álvarez-Lueje A., Pessoa H., Núñnez-Vergara L. J., Squella J. A., Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg., 1998, 46(1), 21-28 |
| [3] | Baeza A., Ortiz J. L.,González I., J. Electroanal. Chem., 1997, 429(1), 121-127 |
| [4] | Zhang H. L., Zheng L. X., Xu L., Nong J. Y., J. Wuhan Univ. Sci. Tech.(Nat. Sci. Ed.), 2007, 30(6), 632-635 |
| (张惠灵, 郑利祥, 徐亮, 农佳莹. 武汉科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 30(6), 632-635) | |
| [5] | Peng X. L., Chen C., Long J., Sun J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(5), 164-167 |
| (彭晓兰, 陈晨, 龙娟, 孙婧. 给水排水, 2007, 33(5), 164-167) | |
| [6] | Yuan S. H., Tian M., Lu X. H.,J. Hazard. Mater., 2006, 137(2), 573-580 |
| [7] | Honeychurch C. K., Hart J. P., Electroanalysis,2007, 19(21), 2176-2184 |
| [8] | Wan N. S., Gu J. D., Huang J. H., Gao C. D., Environmental Science., 2007, 28(2), 422-426 |
| (万年升, 顾继东, 黄锦辉, 高传德. 环境科学, 2007, 28(2), 422-426) | |
| [9] | Tian D. X., Jin B. K., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(25), 9144-9151 |
| [10] | Xie Y. L., Li D., Jin B. K., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2016, 774, 1-6 |
| [11] | Rappich J., Hinrichs K., Electrochem. Commun., 2009, 11(12), 2316-2319 |
| [12] | Li Y. P., Cao H. B., Liu C. M., Zhang Y., J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 148(1/2), 158-163 |
| [13] | Zhang Y. X., Mao X. B., Ren S. Y., Ma C. A., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(2), 293-296 |
| [14] | Andres T., Eckmann L., Smith D. K., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 257-268 |
| [15] | Prasad M. A., Sangaranarayanan M. V., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(2), 242-246 |
| [16] | Wang A. J., Cheng H. Y., Liang B., Ren N. Q., Cui D., Lin N., Kim B. H., Rabaey K., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2011, 45(23), 10186-10193 |
| [17] | Gard J. C., Lessard J., Mugnier Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(5), 677-680 |
| [18] | Cyr A., Huot P., Marcoux J. F., Belot G., Laviron E., Lessard J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(3), 439-445 |
| [19] | Wang W., Wang K., He J. J., Zhang X. T., Wang C., Zhao Z. W., Cui F. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(6), 1012-1017 |
| [20] | Wang H., Ye X. H., Chen L. M., Lu J. X., He M. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(2), 326-329 |
| (王欢, 叶小鹤, 陈黎明, 陆嘉星, 何鸣元. 高等学校化学学报, 2005, 26(2), 326-329) | |
| [21] | Amatore C., Copobianco G., Farnia G., Sandona G., Saveant J. M., Severin M. G., Vianello., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1985, 107(7), 1815-1824 |
| [22] | Forryan C. L., Lawrence N. S., Rees N. V., Compton R. G., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2004, 561(1/2), 53-65 |
| [23] | Debbie S. S., Andrew J. W., Aldous L., Hardacre C., Richard G. C.,J. Electroanal. Chem., 2006, 596(2), 131-140 |
| [24] | Li M. C., Wu H. F., Hu J. Q., Ma C. A., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2008, 24(10), 1937-1940 |
| (李美超, 吴海峰, 胡佳琦, 马淳安. 物理化学学报, 2008, 24(10), 1937-1940) | |
| [25] | Jin B. K., Huang J. L., Li L., Zhang S. Y., Tian Y. P., Yang J. Y., Anal. Chem., 2009, 81(11), 4476-4481 |
| [26] | Astuti Y., Topoglidis E., Briscoe P. B., Fantuzzi A., Gilardi G., Durrant J. R., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(25), 8001-8009 |
| [27] | Nekrasov A. A., Ivanov V. F., Gribkova O. L., Vannikov A. V., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(7), 1605-1613 |
| [28] | Li D., Jin B. K., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(8), 1959-1964 |
| (李丹, 金葆康. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(8), 1959-1964) | |
| [29] | Wang J., Jin B., Cheng L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 152-157 |
| [30] | Cheng W. X., Jin B. K., Huang P., Cheng L. J., Zhang S. Y., Tian Y. P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(8), 3940-3948 |
| [31] | House H. O., Feng E., Peet N. P., J. Org. Chem., 1971, 36(16), 2371-2375 |
| [32] | Fu D.Q., Jin B. K.,Chin. J. Inorg. Chem., 2010, 26(11), 2001-2005 |
| (傅东祺, 金葆康. 无机化学学报, 2010, 26(11), 2001-2005) | |
| [33] | Frisch M.J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Mennucci B., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Caricato M., Li X., Hratchian H. P., Izmaylov A. F., Bloino J., Zheng G., Sonnenberg J. L., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Vreven T. J., Montgomery J. A., Peralta J. E., Ogliaro F., Bearpark M., Heyd J. J., Brothers E., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N., Kobayashi R., Normand J., Raghavachari K., Rendell A., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Rega N., Millam J. M., Klene M., Knox J. E., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Gaussian 09, Revision B. 01, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, 2009 |
| [1] | WANG Nan,YAO Kaisheng,ZHAO Chenchen,LI Tianjin,LU Weiwei. Ionic Liquid-assisted Synthesis of AuPd Nanosponges and Their Catalytic Performance † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 62. |
| [2] | FAN Hui, JIN Baokang. Investigation on Electrochemical Capture of CO2 by Quinone Derivatives Based on in situ FTIR Spectroelectrochemistry † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1847. |
| [3] | HU Haixia, HU Shirong, DONG Peihui, TANG Yuanjun, HONG Kejun, WANG Songhua. Synthesis of New Type ZnO Nanomaterial and Its Application for Electrochemical Detection of p-Nitrophenol† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1171. |
| [4] | LUO Minghong, XIA Kejian, ZHOU Guanghua, GE Wen. Synthesis of Pd/PEI-GNs Composites as Electrocatalyst for Reduction of p-Nitrophenol† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(12): 2268. |
| [5] | LI Dan, JIN Bao-Kang. Study on the Electrochemical Redox Mechanism of 2-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(8): 1959. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||