

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 335.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160871
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Tao, CHENG Tiexin*( ), ZHOU Guangdong
), ZHOU Guangdong
Received:2016-12-02
Online:2017-03-10
Published:2017-02-22
Contact:
CHENG Tiexin
E-mail:ctx@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YANG Tao, CHENG Tiexin, ZHOU Guangdong. Effects of Ag or Yb Doping on Thermoelectric Properties of Ca3Co3.9Cu0.1
| Sample | a/nm | b1/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca3Co4O9-δ | 0.4837 | 0.4559 | 1.0733 | 0.2367 |
| Ca2.9Ag0.1Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4821 | 0.4501 | 1.1009 | 0.2389 |
| Ca2.85Ag0.15Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4819 | 0.4491 | 1.1047 | 0.2391 |
| Ca2.8Ag0.2Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4811 | 0.4482 | 1.1099 | 0.2393 |
| Ca2.7Ag0.3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4802 | 0.4475 | 1.1162 | 0.2399 |
| Ca2.7Ag0.3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ (bulk) | 0.4802 | 0.4463 | 1.1172 | 0.2394 |
Table 1 Lattice parameter and unit-cell volume of Ca3-xAgxCo3.9Cu0.1O9-δ
| Sample | a/nm | b1/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca3Co4O9-δ | 0.4837 | 0.4559 | 1.0733 | 0.2367 |
| Ca2.9Ag0.1Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4821 | 0.4501 | 1.1009 | 0.2389 |
| Ca2.85Ag0.15Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4819 | 0.4491 | 1.1047 | 0.2391 |
| Ca2.8Ag0.2Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4811 | 0.4482 | 1.1099 | 0.2393 |
| Ca2.7Ag0.3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4802 | 0.4475 | 1.1162 | 0.2399 |
| Ca2.7Ag0.3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ (bulk) | 0.4802 | 0.4463 | 1.1172 | 0.2394 |
| Sample | a/nm | b1/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca3Co4O9-δ | 0.4837 | 0.4559 | 1.0733 | 0.2367 |
| Ca2.95Yb0.05Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4841 | 0.4582 | 1.0599 | 0.2351 |
| Ca2.9Yb0.1Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4855 | 0.4632 | 1.0432 | 0.2345 |
| Ca2.8Yb0.2Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4863 | 0.4698 | 1.0185 | 0.2327 |
| Ca2.8Yb0.2Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ(bulk) | 0.4863 | 0.4691 | 1.0178 | 0.2322 |
| Ca2.7Yb0.3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4876 | 0.4719 | 1.0005 | 0.2302 |
Table 2 Lattice parameter and unit-cell volume of Ca3-yYbyCo3.9Cu0.1O9-δ
| Sample | a/nm | b1/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca3Co4O9-δ | 0.4837 | 0.4559 | 1.0733 | 0.2367 |
| Ca2.95Yb0.05Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4841 | 0.4582 | 1.0599 | 0.2351 |
| Ca2.9Yb0.1Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4855 | 0.4632 | 1.0432 | 0.2345 |
| Ca2.8Yb0.2Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4863 | 0.4698 | 1.0185 | 0.2327 |
| Ca2.8Yb0.2Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ(bulk) | 0.4863 | 0.4691 | 1.0178 | 0.2322 |
| Ca2.7Yb0.3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 0.4876 | 0.4719 | 1.0005 | 0.2302 |
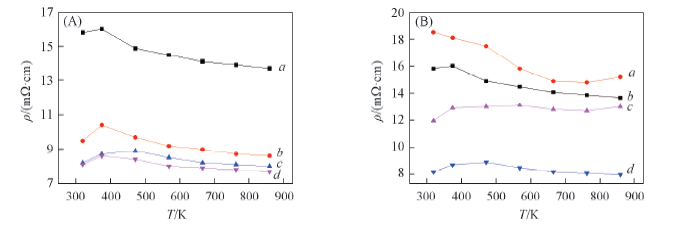
Fig.4 Temperature dependence of the electrical resistivity for dual-doped sample (A) a. Ca3Co4O9-δ; b. Ca2.8Ag0.2Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ; c. Ca3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ; d. Ca2.7Ag0.3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ; (B) a. Ca2.7Yb0.3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ; b. Ca3Co4O9-δ; c. Ca2.8Yb0.2Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ; d. Ca3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ.
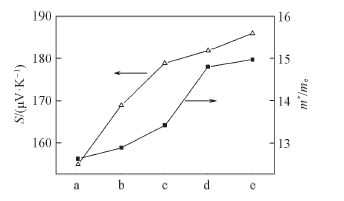
Fig.6 Different dual-doped sample of the Seebeck coefficient and effective mass a. Ca3Co4O9-δ; b. Ca2.8Ag0.2Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ; c. Ca2.7Ag0.2Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ; d. Ca2.8Yb0.2Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ; e. Ca2.7Yb0.3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ.
| Sample | P/(μW·mK-2) | Sample | P/(μW·mK-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ca2.7Ag0.3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 337 | Ca2.8Ag0.2Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 229 |
| Ca3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 316 | Ca2.7Yb0.3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 213 |
| Ca2.8Yb0.2Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 244 | Ca3Co4O9-δ | 189 |
Table 3 Power factor of dual-doped sample at 880 K
| Sample | P/(μW·mK-2) | Sample | P/(μW·mK-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ca2.7Ag0.3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 337 | Ca2.8Ag0.2Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 229 |
| Ca3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 316 | Ca2.7Yb0.3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 213 |
| Ca2.8Yb0.2Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ | 244 | Ca3Co4O9-δ | 189 |
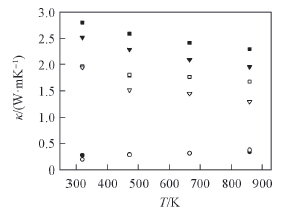
Fig.8 Temperature dependence of total κ(■□), phonon thermal conductivity κp(▼▽) and carrier thermal conductivity κc(●○) for Ca3Co4O9-δ(solid symbols) and Ca2.7Ag0.3Co3.9Cu0.1O9-δ(open symbols), respectively
| [1] | Zhang Q., Sun Y. M., Xu W., Zhu D. B., Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(40), 6829—6851 |
| [2] | Saleemi M., Toprak M. S., Li S. H., Johnsson M., Muhammed M., J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(2), 725—730 |
| [3] | Dong G. H., Zhu Y. J., Chen L. D., J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20(10), 1976—1981 |
| [4] | Yao Q., Chen L. D., Zhang W. Q., Liufu S. C., Chen X. H., ACS Nano, 2010, 4( 4), 2445—2451 |
| [5] | Poudel B., Hao Q., Science,2008, 320(5876), 634—642 |
| [6] | Fan X. A., Yang J. Y., Chen R. G., J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys.,2006, 39(4), 740—752 |
| [7] | Li Y. L., Jiang J., Xu G. J., Li W., Zhou L. M., Li Y., Cui P., J. Alloy. Compd., 2009, 480(2), 954—968 |
| [8] | Chen X. Z., Liu L. F., Dong Y., Ma S. T., Prog. Nat. Sci.-Mater., 2012, 22(3), 201—213 |
| [9] | Xie W. J., Tang X. F., Yan Y. G., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2009, 94(10), 1—13 |
| [10] | Chen H., Liu D. W., Zhang B. P., J. Electron. Mater., 2011, 40(8), 942—952 |
| [11] | Li D., Sun R. R., Qin X. Y., Prog. Nat. Sci.-Mater., 2011, 21(4), 336—348 |
| [12] | Ma X. Y., Zhang X., Lu Q., Zhang J. X., Rare Metal. Mat. Eng., 2012, 41(6), 1097—1109 |
| [13] | Xiu W. J., Ying P. Z., Cui J. L., Ma W. W., Shao D. Q., Rare Metal. Mat. Eng., 2008, 37(2), 334—345 |
| [14] | Yu F. R., Xu B., Zhang J. J., Yu D. L., He J. L., Liu Z. Y., Tian Y. J., Mater. Res. Bull., 2012, 47(6), 1432—1444 |
| [15] | Liang A. S., Li J. J., Pan C. J., Wang L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6), 1161—1167 |
| (梁安生, 李俊杰, 潘成军, 王雷. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(6), 1161—1167) | |
| [16] | Tang G. D., Yang W. C., He Y., Jiang S., Sun X. P., Ceram. Int., 2015, 41, 7115—7118 |
| [17] | Wu N. Y., Nong N. V., Pryds N., J. Alloy. Compd., 2015, 638, 127—132 |
| [18] | Butt S., Wei X., He W. Q., Wu J. H., J. Mater. Chem. A., 2014, 2, 19479—19487 |
| [19] | Constantinescu G., Madre M. A., Rasekh S., Torres M. A., Diez J. C., Sotelo A., Ceram. Int., 2014, 40(4), 6255—6260 |
| [20] | Liu Y., Li H. J., Chen H. M., J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2014, 75(5), 606—610 |
| [21] | Zhang D. W., Mi X. N., Wang Z. H., Tang G. D., Wu Q. S., Ceram. Int., 2014, 40(8), 12313—12318 |
| [22] | Demirel S., AltinE., OZ E., Altin S., Bayri A., J. Alloy. Compd., 2015, 627, 430—437 |
| [23] | Constantinescu G., RasekhS., Torres M. A., Madre M. A., Sotelo A., Diez J. C., J. Mater. Sci.-Marer. El., 2015, 26(6), 3466—3473 |
| [24] | Prasoetsopha N., PinitsoontornS., Kamanna T., Kurosaki K., Ohishi Y., Muta H., Yamanaka S., J. Eelectron. Mater., 2014, 43(6), 2064—2071 |
| [25] | LimeletteP., Hardy V., Auban-Senzier P., JéromeD., FlahautD., Hébert S., FrésardR., Simon C., NoudemJ., MaignanA., Phys. Rev. B, 2005, 71(23), 233108-233112 |
| [1] | JIANG Xiaokang, ZHOU Qi, ZHOU Hengwei. Synthesis and Luminescence Properties of Gd2ZnTiO6∶Dy3+, Eu3+ Single Phase White Light-emitting Phosphors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220029. |
| [2] | LI Yishan, GUO Liang, PENG Sifan, ZHANG Qingmao, ZHANG Yuhao, XU Shiqi. Cobalt Substitutions in Lanthanum Manganate Photocatalyst: First-principles and Visible-light Photocatalytic Ability Investigation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1881. |
| [3] | HAN Yandong, HAN Mingyong, YANG Wensheng. Sol-gel Construction of Mesoporous Silica Nanomicrostructures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 965. |
| [4] |
HAN Hongjing,GE Qin,CHEN Yanguang,WANG Haiying,ZHAO Hongzhi,WANG Yizhen,ZHANG Yanan,DENG Jitong,SONG Hua,ZHANG Mei.
Production of Phenolic Compounds from Bagasse Lignin via Catalytic Pyrolysis of Ca1-xPrxFe |
| [5] | WANG Yihan,YIN Qiang,DU Kai,YIN Qinjian. Polypyrrole/Polyaniline Nanocomposite Nanotubes with Enhanced Thermoelectric Properties † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 175. |
| [6] | DU Yifan, AI Chaoqian, ZHANG Yaoyao, WANG Wei. Preparation and Quasi-superhydrophobic Properties of the Surface of Mullite Whiskers/Cordierite † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1955. |
| [7] | ZHANG Shuming, LUO Jianhui, XIA Bibo, LI Yuanyang, HE Meiying, JIANG Bo. Sol-gel Preparation of Superhydrophilic Silica Coating-materials with Low Refractive Index† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(6): 1342. |
| [8] | LUO Jianhui,YANG Jie,LI Yuanyang,HE Lipeng,JIANG Bo. Synthesis of Amphiphilic Silica Nanoparticles with Double-sphere Morphology† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2170. |
| [9] | YANG Tao, CHENG Tiexin, ZHOU Guangdong. Effects of Ag+, Sr2+, Yb3+ Dual-doping on Thermoelectric Properties of Ca3Co4O9-δ [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8): 1309. |
| [10] | HE Meiying, LUO Jianhui, YANG Bowen, XIA Bibo, LI Yuanyang, ZHANG Shuming, JIANG Bo. Sol-gel Preparation of Hydrophobic Silica Coating-materials with Ultralow Refractive Index† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 2077. |
| [11] | XIA Yanyang, BU Tiantong, WANG Licheng, ZHU Wanchun, YANG Xuwei, BAO Qiang, HAO Mengmeng, CHENG Dongdong, WANG Zhenlü. Hydrodealkylation of Trimethylbenzene over Silicon-based Catalyst† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(12): 2215. |
| [12] | HE Yannan, YU Zhiqiang. Effect of Surface Organic Functional Modification of ZrB2 Nanosize Multiphase Ceramics on the Thermal Properties of Its Composites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1846. |
| [13] | YIN Hong, ZHOU Dan, CONG Lina, XIE Haiming, QIU Yongqing. MoO2/C Co-coated Si/graphite Composite as Anode Materials for Lithium Ion Batteries† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 1990. |
| [14] | XU Peng, LI Youji, LIU Chen, LI Ming, DENG Ruicheng. Preparation and Visible-light Photocatalytic Performance of Mesoporous Vanadium-doped Titania† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(9): 1954. |
| [15] | LIU Yun-Hong, LI Guang-Ji, LUO Xi-Wen, PENG Xin-Yan, WANG Li-Ying. Preparation of the Zwitteronic Hydrogel Layer by UV-initiated Surface Grafting and Its Antibacterial Adhesion Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(6): 1527. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||