

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (5): 989.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150950
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2015-12-14
Online:2016-05-10
Published:2016-04-12
Contact:
CHEN Kangcheng
E-mail:chenkc@bit.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
CHEN Kangcheng, JI Mengdie. High Tempreture Fuel Cell Performance and Anisotropy of Carbonyl and Sulfone Groups Co-crosslinked Sulfonated Polyimides Proton Exchange Membranes†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5): 989.
| Sample | IECa/(meq·g-1) | Δ | Δ | Δt/l | σ⊥/// | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 2.10 | 55 | 6.3 | 8.7 | 208 | 140 | 0.67 |
| M1C | 1.94 | 39 | 6.4 | 6.1 | 164 | 123 | 0.75 |
| M2 | 1.99 | 41 | 5.6 | 7.3 | 183 | 130 | 0.71 |
| M2C | 1.87 | 34 | 6.2 | 5.5 | 160 | 119 | 0.74 |
| R1 | 1.86 | 58 | 4.3 | 13 | 178 | 119 | 0.67 |
| R1C | 1.77 | 43 | 5.0 | 8.6 | 148 | 105 | 0.71 |
| NR212 | 0.89 | 16 | 14 | 1.1 | 141 | 136 | 0.98 |
Table 1 Anisotropic properties of SPIs and Nafion(NR212) membranes
| Sample | IECa/(meq·g-1) | Δ | Δ | Δt/l | σ⊥/// | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 2.10 | 55 | 6.3 | 8.7 | 208 | 140 | 0.67 |
| M1C | 1.94 | 39 | 6.4 | 6.1 | 164 | 123 | 0.75 |
| M2 | 1.99 | 41 | 5.6 | 7.3 | 183 | 130 | 0.71 |
| M2C | 1.87 | 34 | 6.2 | 5.5 | 160 | 119 | 0.74 |
| R1 | 1.86 | 58 | 4.3 | 13 | 178 | 119 | 0.67 |
| R1C | 1.77 | 43 | 5.0 | 8.6 | 148 | 105 | 0.71 |
| NR212 | 0.89 | 16 | 14 | 1.1 | 141 | 136 | 0.98 |
| Time/h | Ya/GPa | Sb/MPa | Ec(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.8 | 107 | 31 | |
| 200 | 2.1 | 76 | 19 |
| 500 | 2.0 | 77 | 18 |
Table 2 Physical properties of M1C before and after aging in water
| Time/h | Ya/GPa | Sb/MPa | Ec(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.8 | 107 | 31 | |
| 200 | 2.1 | 76 | 19 |
| 500 | 2.0 | 77 | 18 |
| Conditionsa(℃/MPa/%RH) | Code | OCV/V | V0.5/V | V1.0/V | Wmax/(W·cm-2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90/0.2/82 | M1C | 0.96 | 0.70 | 0.62 | 0.87 | 61 |
| R1C | 0.95 | 0.66 | 0.56 | 0.74 | 40 | |
| NR 212 | 0.93 | 0.69 | 0.61 | 0.86 | 90 | |
| 90/0.2/48 | M1C | 0.97 | 0.67 | 0.55 | 0.66 | 29 |
| R1C | 0.95 | 0.59 | 0.44 | 0.46 | 22 | |
| NR 212 | 0.94 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.75 | 70 | |
| 90/0.2/27 | M1C | 0.95 | 0.51 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 20 |
| R1C | 0.96 | 0.47 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 14 | |
| NR 212 | 0.93 | 0.66 | 0.64 | 0.57 | 58 | |
| 110/0.2/49 | M1C | 0.95 | 0.32 | 0.17 | 9 | |
| R1C | 0.92 | 0.23 | 0.14 | 6 | ||
| 110/0.3/49 | M1C | 0.96 | 0.62 | 0.38 | 17 | |
| R1C | 0.95 | 0.55 | 0.28 | 13 |
Table 3 PEFC performances of M1C, R1C and NR212 membranes
| Conditionsa(℃/MPa/%RH) | Code | OCV/V | V0.5/V | V1.0/V | Wmax/(W·cm-2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90/0.2/82 | M1C | 0.96 | 0.70 | 0.62 | 0.87 | 61 |
| R1C | 0.95 | 0.66 | 0.56 | 0.74 | 40 | |
| NR 212 | 0.93 | 0.69 | 0.61 | 0.86 | 90 | |
| 90/0.2/48 | M1C | 0.97 | 0.67 | 0.55 | 0.66 | 29 |
| R1C | 0.95 | 0.59 | 0.44 | 0.46 | 22 | |
| NR 212 | 0.94 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.75 | 70 | |
| 90/0.2/27 | M1C | 0.95 | 0.51 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 20 |
| R1C | 0.96 | 0.47 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 14 | |
| NR 212 | 0.93 | 0.66 | 0.64 | 0.57 | 58 | |
| 110/0.2/49 | M1C | 0.95 | 0.32 | 0.17 | 9 | |
| R1C | 0.92 | 0.23 | 0.14 | 6 | ||
| 110/0.3/49 | M1C | 0.96 | 0.62 | 0.38 | 17 | |
| R1C | 0.95 | 0.55 | 0.28 | 13 |
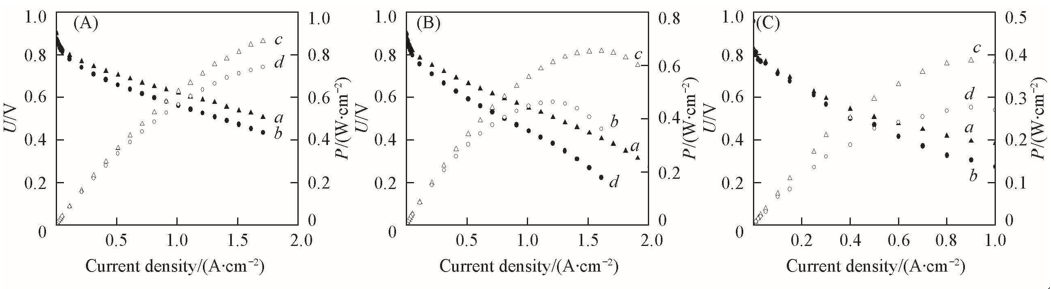
Fig.2 Cell volatage(a, b) and power output(c, d) of M1C(a, c) and R1C(b, d) membranes at 90 ℃ and gas pressure of 0.2 MPa under different relative humidities of 82%RH(A), 48%RH(B) and 27%RH(C)
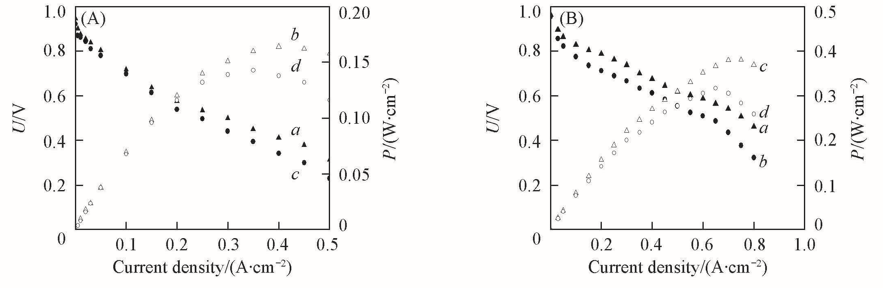
Fig.3 Cell volcotage(a, b) and power output(c, d) of M1C(a, c) and R1C(b, d) membranes at 110 ℃ under relative humidities of 49% and gas pressure of 0.2(A) and 0.3 MPa(B)
| Code No. | T/℃ | RH(%) | P/MPa | I/(A·cm-2) | Time/h | v/(μV·h-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI-8 | 80 | 100 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 5000 | 12 | [25] |
| M1A | 90 | 82 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1600 | 69 | [26] |
| BT2 | 90 | 50 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 283 | 106 | [27] |
| MX2 | 110 | 49 | 0.2 | 0* | 1000 | 180 | [28] |
| CMB2 | 110 | 50 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 200 | 133 | [29] |
| M1C | 110 | 49 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 330 | 91 | This paper |
Table 4 Durability of PEMFC
| Code No. | T/℃ | RH(%) | P/MPa | I/(A·cm-2) | Time/h | v/(μV·h-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI-8 | 80 | 100 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 5000 | 12 | [25] |
| M1A | 90 | 82 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1600 | 69 | [26] |
| BT2 | 90 | 50 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 283 | 106 | [27] |
| MX2 | 110 | 49 | 0.2 | 0* | 1000 | 180 | [28] |
| CMB2 | 110 | 50 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 200 | 133 | [29] |
| M1C | 110 | 49 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 330 | 91 | This paper |
| [1] | Yi B.L., Fuel Cell, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2000, 56—100 |
| (衣宝廉. 燃料电池, 北京:化学工业出版社, 2000, 56—100) | |
| [2] | Song Y., Jin Y. H., Liang Q. J., Li K. C., Zhang Y. H., Hu W., Jiang Z. H., Liu B., J. Power Sources,2013, 238, 236—244 |
| [3] | Tang W. F., Ling Y., Chen S. S., Hu Z. X., Chen S. W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(11), 2661—2666 |
| (唐卫芬, 凌瑛, 陈珊珊, 胡朝霞, 陈守文. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(11), 2661—2666) | |
| [4] | Elabd Y. A., Napadensky E., Walker C. W., Winey K. I., Macromol., 2006, 39(1), 399—407 |
| [5] | Chen K. C., Chen X. B., Yaguchi K., Endo N., Higa M., Okamoto K., Polym., 2009, 50(2), 510—518 |
| [6] | Yin Y., Fang J. H., Cui Y. F., Tanaka K., Kita H., Okamoto K., Polym., 2003, 44(16), 4509—4518 |
| [7] | Hu Z. X., Yin Y., Yaguchi K., Endo N., Higa M., Okamoto K., Polym., 2009, 50(13), 2933—2943 |
| [8] | Yamada O., Yin Y., Tanaka K., Kita H., Okamoto K., Electrochim.Acta,2005, 50(13), 2655—2659 |
| [9] | Mauriz K. A., Moore R. B., Chem. Rev., 2004, 104(10), 4535—4585 |
| [10] | Chen K. C., Bai W. X., Zhao Z. P., Liu W. F., Yang Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2015, 36(4), 781—787 |
| (陈康成, 白文馨, 赵之平, 刘文芳, 杨智. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(4), 781—787) | |
| [11] | Guo X. X., Fang J. H., Watari T., Tanaka K., Kita H., Okamoto K., Macromol., 2002, 35(17), 6707—6713 |
| [12] | Yin Y., Suto Y., Sakabe T., Chen S. W., Hayashi S., Mishima T., Yamada O., Tanaka K., Kita H., Kamoto K., Macromol., 2006, 39(3), 1189—1198 |
| [13] | Genies C., Mercier R., Sillion B., Petiaud R., Cornet N., Gebel G., Pineri M., Polym., 2001, 42(12), 5097—5105 |
| [14] | Chen X. B., Chen P., An Z. W., Chen K. C., Okamoto K., J. Power Sources,2011, 196, 1694—1703 |
| [15] | Yao H. Y., Feng P. J., Liu P., Liu B. J., Zhang Y. H., Guan S. W., Jiang Z. H., Polym. Chem, 2015, 6(14), 262—269 |
| [16] | Kreitmeier S., Schuler G. A., Wokaun A., Büchi F. N., J. Power Sources,2012, 212, 139—147 |
| [17] | Okamoto K., Yaguchi K., Yamamoto H., Chen K. C., Endo N., Higa M., Kita H., J. Power Sources,2010, 195, 5856—5861 |
| [18] | Cleghorn S. J., Mayfield D. K., Moore D. A., Moore J. C., Rusch G., Sherman T. W., Sisofo N. T., Beuscher U., J.Power Sources,2006, 158, 446—454 |
| [19] | Hu Z. X., Yin Y., Okamoto K., Moriyama Y., Morikawa A., J. Membrane Sci, 2009, 329(1), 146—152 |
| [20] | Samms S. R., Wasmus S., Savinell R. F., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1996, 143(5), 1498—1504 |
| [21] | Aoki M., Chikashige Y., Miyatake K., Uchida H., Watanabe M., Electrochem. Com, 2006, 8(9), 1412—1416 |
| [22] | Chen K.C., Han D. B., Zhao Z. P., Liu W. F.,Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2015, (6), 633—640 |
| (陈康成, 韩丁波, 赵之平, 刘文芳. 高分子学报, 2015, (6), 633—640) | |
| [23] | Aoki M., Asano N., Miyatake K., Uchida H., Watanabe M., J.Electrochem. Soc., 2006, 153(6), A1154—A1158 |
| [24] | Zhang X., Hua Z. X., Pu Y. L., Chen S. S., Ling J. N., Bi H. P., Chen S. W., Wang L. J., Okamoto K., J. Power Sources,2012, 216, 261—268 |
| [25] | Kabasawa A., Saito J., Miyatake K., Uchida H., Watanabe M., Electrochim. Acta,2009, 54(10), 2754—2760 |
| [26] | Endo N., Matsuda K., Yaguchi K., Hu Z. X., Chen K. C., Higa M., Okamoto K., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2009, 156(5), B628—633 |
| [27] | Chen S. W., Hara R., Chen K. C., Zhang X., Endo N., Higa M., Okamoto K., Wang L. J., J. Mater. Chem. A,2013, 1(28), 8178—8189 |
| [28] | Yaguchi K., Chen K. C., Endo N., Higa M., Okamoto K., J. Power Sources,2010, 195(15), 4676—4684 |
| [29] | Chen S. W., Zhang X., Chen K. C., Endo N., Higa M., Okamoto K., Wang L. J., J. Power Sources,2011, 196, 9946—9954 |
| [1] | QIU Xinsheng, WU Qin, SHI Daxin, ZHANG Yaoyuan, CHEN Kangcheng, LI Hansheng. Preparation and High Temperature Fuel Cell Performance of Ionic Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyimides for Proton Exchange Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220140. |
| [2] | JIA Hongjun, ZHANG Jiatao, MA Zhuoli, WANG Heng, YANG Xinyu, YANG Jiazhi. Preparation of PTFE/PAA/Nafion Composite Membrane by Aqueous Polymerization of Acrylic Acid and Its Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220350. |
| [3] | LIU Jie, LI Jinsheng, BAI Jingsen, JIN Zhao, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Constructing a Water-blocking Interlayer Containing Sulfonated Carbon Tubes to Reduce Concentration Polarization in Direct Methanol Fuel Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220420. |
| [4] | FU Zhinan, TAN Yunlong, XIAO Guyu, YAN Deyue. Synthesis and Properties of Sulfonated Poly(phthalazinone ether phosphine oxide)s with Perfluorobiphenyl Moieties for Proton Exchange Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2635. |
| [5] | CAO Kaiyue, PENG JinWu, LI Hongbin, SHI Chengying, WANG Peng, LIU Baijun. High-temperature Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Cross-linked Polybenzimidazole/hyperbranched-polymer Blends [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2049. |
| [6] | PU Yangyang, NING Cong, LU Yao, LIU Lili, LI Na, HU Zhaoxia, CHEN Shouwen. Preparation and Characterizations of Cross-linked Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone)/Partially Fluorinated Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether sulfone) Blend Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2002. |
| [7] | LIANG Minhui, WANG Peng, LI Hongbin, LI Tianyang, CAO Kaiyue, PENG Jinwu, LIU Zhenchao, LIU Baijun. Preparation of High-temperature Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Semi-interpenetrating Polymer Networks [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2845. |
| [8] | QIN Liulei,LIU Yang,GUAN Xiaoqin,ZHENG Xiaoyuan,ZHANG Ziyu,LIU Zunqi. Synthesis and Switchable Dielectric Properties of an Inorganic-organic Hybrid Complex [H2(DABCO)CuCl4]·H2O † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 70. |
| [9] | SONG Xipeng, LIU Jinyu, WANG Lihua, HAN Xutong, HUANG Qinglin. Preparation of Polybenzimidazole/Polyvinylpyrrolidone Proton Exchange Membranes for Vanadium Redox Flow Battery† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1543. |
| [10] | ZHU Yuxin,HARAGIRIMANA Alphonse,LU Yao,BUREGEYA Ingabire Providence,NING Cong,LI Na,HU Zhaoxia,CHEN Shouwen. Preparation and Properties of Filling-type Sulfonated Poly(arylene ether sulfone)/Poly(ether sulfone) Composite Membranes with Microporous Structures† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 1051. |
| [11] | REN Xiaorui,LIU Chao,LI Huanhuan,YANG Jingshuai,HE Ronghuan. Siloxane Crosslinked Imidazolium PPO/PTFE Membranes for High Temperature Proton Exchange Membranes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 1089. |
| [12] | LIU Jiaming,FU Kailin,ZHANG Ze,GUO Wei,PAN Mu. Ultra-low Pt Loading Cathodic Catalyst Layer Prepared on Textured Gas Diffusion Layer by Magnetron Sputtering Method for Hydrogen-oxygen Fuel Cells† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 542. |
| [13] | CHEN Yuhan,HUANG Xuehong. Preparation and Performance of the Self-crosslinking Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone) Proton Exchange Membrane† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 410. |
| [14] | LIU Bo,ZOU Nan,ZHANG Yuxia,SHI Haifeng. Structure and Properties of Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone)/Laponite Proton Exchange Membrane for All Vanadium Redox Flow Battery † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2186. |
| [15] | ZHU Xingye,QIAN Huidong,JIANG Jingjing,YUE Zhouying,XU Jianfeng,ZOU Zhiqing,YANG Hui. Cross-linking of Imidazole-grafted Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone) as Proton Exchange Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2046. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
