

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (2): 306.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150704
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YU Tao, HAN Yu*( ), WANG Hui, XIONG Shizhao, XIE Kai, GUO Qingpeng
), WANG Hui, XIONG Shizhao, XIE Kai, GUO Qingpeng
Received:2015-09-09
Online:2016-02-10
Published:2016-01-14
Contact:
HAN Yu
E-mail:yumihan1981@sina.com
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YU Tao, HAN Yu, WANG Hui, XIONG Shizhao, XIE Kai, GUO Qingpeng. Preparation and Lithium Ion Transport Behavior for Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 Based Solid Composite Electrolyte[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(2): 306.
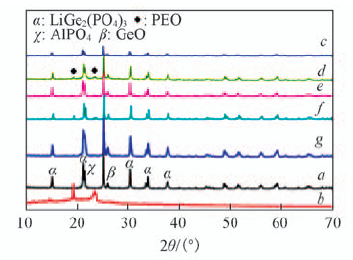
Fig.2 XRD patterns of LAGP(a), PEO(LiTFSI)(b) and LAGP-PEO(LiTFSI) solid composite electrolytes m(LAGP)/m(PEO): c. 5:5; d. 6:4; e. 7:3; f. 8:2; g. 9:1.
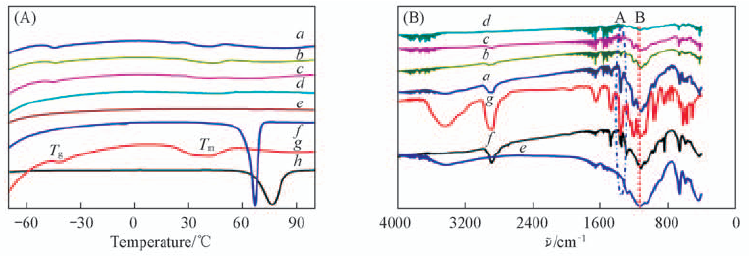
Fig.4 DSC curves(A) and FTIR spectra(B) of the LAGP-PEO(LiTFSI) solid composite electrolytes m(LAGP):m(PEO): a. 6:4; b. 7:3; c. 8:2; d. 9:1; e. LAGP; f. PEO(LAGP); g. PEO(LiTFSI); h. PEO. Peak A: CH2 rocking vibration absorption peak of PEO; peak B: C—O—C stretching vibration absorption peak of PEO.
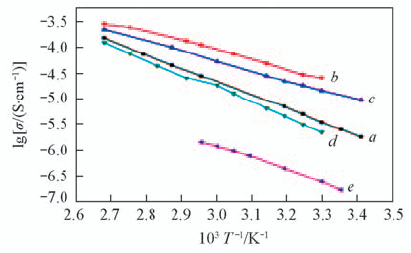
Fig.5 Ionic conductivity as a function of temperature for the LAGP-PEO(LiTFSI) solid composite electrolytes m(LAGP)/m(PEO): a. 6:4; b. 7:3; c. 8:2; d. 9:1.
| Mass ratio of LAGP to PEO | Tg/℃ | Tm/℃ | 105Conductivity/(S·cm-1) | Ea/(J·mol-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 ℃ | 60 ℃ | ||||
| Pure PEO(LiTFSI) | -33.84 | 52.56 | 0.23 | 1.74 | 92.74 |
| 6:4(without LiTFSI) | -43.81 | 66.61 | 0.07 | 1.10 | 76.55 |
| 5:5 | — | — | 0.34 | 2.07 | 50.22 |
| 6:4 | -44.43 | 42.35 | 2.57 | 8.96 | 33.61 |
| 7:3 | -45.10 | 39.94 | 1.44 | 5.30 | 36.31 |
| 8:2 | -45.77 | 36.53 | 0.22 | 1.81 | 53.38 |
| 9:1 | -48.17 | 29.65 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 57.25 |
Table 1 Thermal property and ionic conductivity of the LAGP-PEO(LiTFSI) solid composite electrolytes with various LAGP contents*
| Mass ratio of LAGP to PEO | Tg/℃ | Tm/℃ | 105Conductivity/(S·cm-1) | Ea/(J·mol-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 ℃ | 60 ℃ | ||||
| Pure PEO(LiTFSI) | -33.84 | 52.56 | 0.23 | 1.74 | 92.74 |
| 6:4(without LiTFSI) | -43.81 | 66.61 | 0.07 | 1.10 | 76.55 |
| 5:5 | — | — | 0.34 | 2.07 | 50.22 |
| 6:4 | -44.43 | 42.35 | 2.57 | 8.96 | 33.61 |
| 7:3 | -45.10 | 39.94 | 1.44 | 5.30 | 36.31 |
| 8:2 | -45.77 | 36.53 | 0.22 | 1.81 | 53.38 |
| 9:1 | -48.17 | 29.65 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 57.25 |
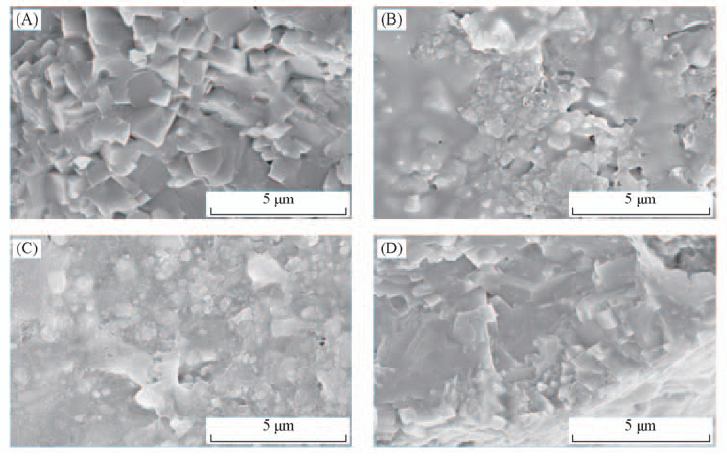
Fig.7 SEM images of the surface and cross-section of the LAGP from the PEO(LiTFSI)/LAGP/PEO(LiTFSI) cell (A) Surface morphology(initial state); (B) surface morphology(60 ℃ activation); (C) surface morphology after measurement; (D) cross-section morphology after measurement.
| Solid composite electrolyte | Tg/℃ | Tm/℃ | 105Conductivity/(S·cm-1) | Ea/(J·mol-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 ℃ | 60 ℃ | ||||
| Pure PEO(LiTFSI) | -33.84 | 52.56 | 0.23 | 1.74 | 92.74 |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-10%SiO2 | -39.8 | 45.37 | 0.40 | 7.85 | 70.84 |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-10%Al2O3 | -40.17 | 45.45 | 0.30 | 5.94 | 71.00 |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-10%LAGP | -40.37 | 46.17 | 0.62 | 10.14 | 64.94 |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-10%SiO2+10%LAGP | -41.50 | 39.67 | 0.29 | 5.09 | 74.36 |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-20%LAGP | -43.83 | 48.83 | 0.41 | 8.31 | 71.46 |
Table 2 Thermal property and ionic conductivity of the solid composite electrolyte with different cermatic fillers
| Solid composite electrolyte | Tg/℃ | Tm/℃ | 105Conductivity/(S·cm-1) | Ea/(J·mol-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 ℃ | 60 ℃ | ||||
| Pure PEO(LiTFSI) | -33.84 | 52.56 | 0.23 | 1.74 | 92.74 |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-10%SiO2 | -39.8 | 45.37 | 0.40 | 7.85 | 70.84 |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-10%Al2O3 | -40.17 | 45.45 | 0.30 | 5.94 | 71.00 |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-10%LAGP | -40.37 | 46.17 | 0.62 | 10.14 | 64.94 |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-10%SiO2+10%LAGP | -41.50 | 39.67 | 0.29 | 5.09 | 74.36 |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-20%LAGP | -43.83 | 48.83 | 0.41 | 8.31 | 71.46 |
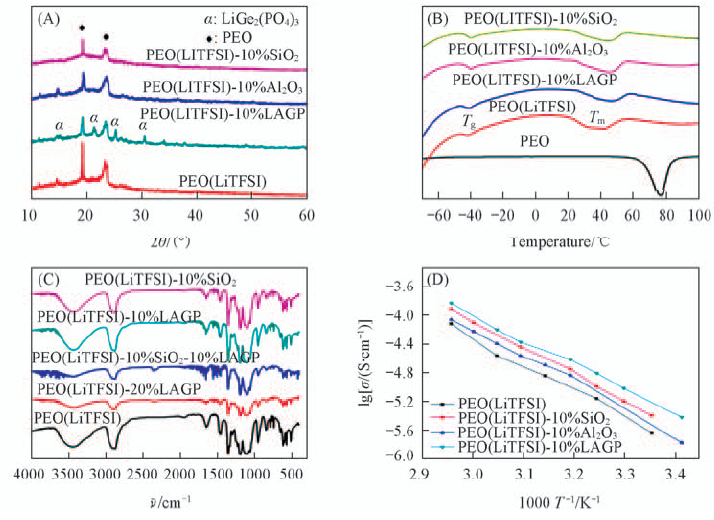
Fig.8 XRD patterns(A), DSC traces(B), FTIR spectra(C) and inoic conductivity as a function of temperature(D) of solid composite electrolyte with different ceramic fillers
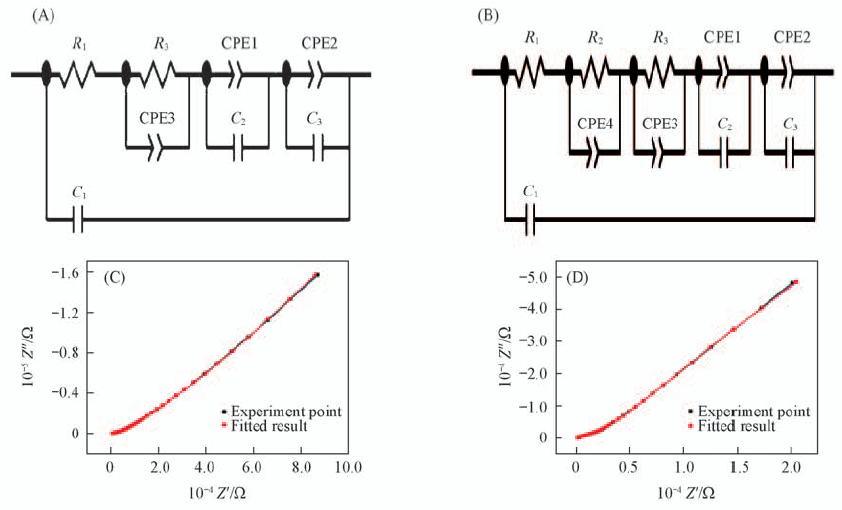
Fig.9 Equivalent circuit model(A, B) and fitted impedance results(C, D) of solid composite electrolytes PEO(LiTFSI)-10%inert filler at 30 ℃(A, C) and PEO(LiTFSI)-10%LAGP at 30 ℃(B, D) CPE1 and CPE2: diffusion element; CPE3 and CPE4: constant phase elements; Cl: the capacitance of double layer;C2 and C3: the capacitance of electrolyte.
| Ceramic filler | R1/Ω | R2/Ω | R3/Ω | 105Conductivity/(S·cm-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure PEO(LiTFSI) | 681.5 | 3638 | 0.23 | |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-10%SiO2 | 608.5 | 1159 | 0.40 | |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-10%Al2O3 | 628.5 | 1225 | 0.30 | |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-10%LAGP | 614.3 | 81.8 | 1224 | 0.62 |
Table 3 Fitted results of the solid composite electrolyte with different ceramic fillers
| Ceramic filler | R1/Ω | R2/Ω | R3/Ω | 105Conductivity/(S·cm-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure PEO(LiTFSI) | 681.5 | 3638 | 0.23 | |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-10%SiO2 | 608.5 | 1159 | 0.40 | |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-10%Al2O3 | 628.5 | 1225 | 0.30 | |
| PEO(LiTFSI)-10%LAGP | 614.3 | 81.8 | 1224 | 0.62 |
| [1] | Li Y. J., Cao T. P., Sun X. L., Shao C. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(1), 16—19 |
| (李跃军, 曹铁平, 孙新丽, 邵长路. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(1), 16—19) | |
| [2] | Liu J., Xu J. Y., Lin Y., Li J., Lai Y. Q., Yuan C. F., Zhang J., Zhu K., Acta Chim. Sin., 2013, 71, 869—878 |
| (刘晋, 徐俊毅, 林月, 李劼, 赖延清, 袁长福, 张锦, 朱凯. 化学学报, 2013, 71, 869—878) | |
| [3] | Young J. N., Sung J. C., Dae Y. O., Jun M. L., Sung Y. K., Jun H. S., Young G. L., Lee Y. S., Yoon S. J., Nano Letters, 2015, 15(5), 3317—3323 |
| [4] | Han F.D., Gao T., Zhu Y. J., Gaskell K. J., Wang C. S., Adv. Mater., 2015, 1—11 |
| [5] | Lin X. M., Zhu L. L., Han J., Liu X. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(1), 61—66 |
| (林晓敏, 朱丽丽, 韩健, 刘晓梅. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(1), 61—66) | |
| [6] | Arbi K., Bucheli W., Jiménez R., Sanz J., J. Eur. Ceramic Soc., 2015, 35, 1477—1484 |
| [7] | Brian E. F., Conrad R. S., Chem. Mater., 2014, 26, 4741—4749 |
| [8] | Kubansk A., Cast L., Torteta L., Schäf O., Dollé M., Bouchet R., Solid State Ionics, 2014, 266, 44—50 |
| [9] | Xu X. X., Qiu Z. J., Guan Y. B., Huang Z., Jin Y., Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2013, 2(4), 331—341 |
| (许晓雄, 邱志军, 官亦标, 黄祯, 金翼. 储能科学与技术, 2013, 2(4), 331—341) | |
| [10] | Goodenough B. J., Youngsik K., Chem. Mater., 2010, 22(3), 587—603 |
| [11] | Zhao X. D., Zhu W., Li J. R., Jia Y. B., Mater. Rev., 2014, 28(4), 13—17 |
| (赵旭东, 朱文, 李镜人, 贾迎宾. 材料导报, 2014, 28(4), 13—17) | |
| [12] | Angdl C. A., Liu C., Sanchez E., Nature, 1993, 362(6416), 137—139 |
| [13] | Xu K., Angell C. A., Electrochim. Acta, 1995, 40(13/14), 2401—2403 |
| [14] | Huang L. Z., Wen Z. Y., Jin J., Liu Y., J. Inorg. Mater., 2012, 27(3), 249—252 |
| (黄乐之, 温兆银, 靳俊, 刘宇. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(3), 249—252) | |
| [15] | Wang Y.J., Study on PEO Based Composite Polymer Electrolytes Using Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 as Main Component and Filler, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 2005 |
| (王严杰. Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3作主相和填料相的PEO基聚合物电解质的研究, 杭州: 浙江大学, 2005) | |
| [16] | Croce F., Persi L., Scrosati B., Serraino F., Plichta E., Hendricksonb M. A., Electrochim. Acta, 2001, 46, 2457—2461 |
| [17] | Appetecchi G. B., Zane D., Scrosati B., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2004, 151(9), A1369—A1374 |
| [18] | Marzantowicz M., Dygas J. R., Krok F., Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 53, 741—742 |
| [19] | Wieczorek W., RaduchaD., Zalewska A., Phys. Chem. B, 1998, 102(44), 8725—8731 |
| [20] | Wang Z. X., Gao W. D., Huang X. J., Mo Y. J., Chen L. Q., J. Raman Spectrosc., 2001, 32, 900—905 |
| [21] | Dany B., Donald E. I., Nicholas J. T., Ge'rald P., Marek O., Jacques E. D., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2002, 4, 6063—6071 |
| [22] | Shen C., Wang J. M., Tan Z., Wan H. J., Lia H. Q., Zhang J. Q., Cao C. N., Electrochim. Acta, 2009, 54, 3490—3494 |
| [23] | Wang C. S., Zhang X. W., John A., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2005, 152(1), A205—A209 |
| [24] | Capiglia C., Mustarelli P., Quartarone E., Tomasi C., Magistris A., Solid State Ionics, 1999, 118, 73—79 |
| [25] | Tan W. Q., Zang. D. Y., Li Y. F., Zhang Y. J., Lu C. J., Li Z. G., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(1), 85—91 |
| (谭伟强, 臧渡洋, 李云飞, 张永建, 陆晨君, 栗志广. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(1), 85—91) | |
| [26] | Qian X. M., Gu N. Y., Cheng Z. L., Yang X. R., Wang E. K., Dong S. J., Electrochim. Acta, 2001, 46, 1829—1836 |
| [1] | LUO Xinyan, JIA Ruonan, XIANG Yong, ZHANG Xiaokun. Progress on the Stretchable Composite Solid Polymer Electrolytes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220149. |
| [2] | LU Shanfu, LIU Yiyang, XIANG Yan. Preparation of PVP-based Iodine-iodide Gel-electrolyte and Its Application in DSSCs† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(6): 1293. |
| [3] | BAI Lian, JI Yan-Zhou, LI Ming, NAN Ce-Wen. Preparation and Performances of Polymer Electrolytes Based on the Random Copolymer of Epichlorohydrin and Ethylene Oxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(10): 2339. |
| [4] | NIU Li-Dan, FU Xiang-Kai*, LIU Su-Juan, DU Qiu-Liang. Polymer Electrolytes Based on PAMPSLi/P(MMA-VAc) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(2): 391. |
| [5] | JIN Lan-Ying, JIANG Yan-Xia*, LIAO Hong-Gang, ZENG Dong-Mei, SUN Shi-Gang. FTIR Spectroscopic Studies of PEO-based Polymer Electrolyte with Ionic Liquid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(4): 767. |
| [6] | BAI Ying1,2, PAN Chun-Hua1, WU Feng1,2, WU Chuan1,2*, YE Lin3, FENG Zeng-Guo3. Novel Hyperbranched PEU Polymer Electrolytes for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(9): 1796. |
| [7] | YANG Dao-Jun1,2, FU Xiang-Kai1,2,3*, JIANG Qing-Long1,2, GONG Yong-Feng1,2. Synthesis of Polymer Electrolyte Based on P(VAc-MA)/PMMA and Its Application in Electrochromic Devices [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(9): 1781. |
| [8] | WANG Cun-Guo*, HE Li-Xia, DONG Xian-Guo, WANG Yi-Zhen, ZHAO Shu-Gao, SUN Lin, LIN Lin, XIAO Hong-Jie. Preparation and Properties of Gel Polymer Electrolyte Used for Lithium Ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(12): 2373. |
| [9] | JIANG Jing; GAO De-Shu*; LI Zhao-Hui, SU Guang-Yao; WANG Cheng-Wei; LIU Li; DING Yan-Huai. Studies on Ionic Liquid/Polymer Electrolytes Prepared by in situ Polymerization [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(7): 1319. |
| [10] | XI Jing-Yu, MA Xiao-Mei, CUI Meng-Zhong, TANG Xiao-Zhen. PEO-LiClO4-ZSM-5 Composite Polymer Electrolyte——Effect of ZSM-5 on the Selective Transference of Lithium Ion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2005, 26(2): 330. |
| [11] | XIE Hong-Quan, HUANG Xu-Dong, GUO Jun-Shi . Complexes of Interpenetrating Polymer Networks Exhibiting Synergistic Effect of Ionic and Electronic Conductivities [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(5): 957. |
| [12] | LIANG Hong-Ying, WU Feng, CHEN Li-Quan, HUANG Xue-Jie . Comparative Studies on Thermal and Electrochemical Properties of Room-temperature Molten Salt Electrolytes Based on LiTFSI with Urea and Its Derivatives [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2003, 24(2): 305. |
| [13] | LI Zhao-Hui, SU Guang-Yao, WANG Xia-Yu, GAO De-Shu . Ionic Conductivity Study of PVF-HFP Composite Electrolyte Filled with Al2O3Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2003, 24(11): 2065. |
| [14] | WANG Zhi-Yin, HE Yun-Hua . Studies on New Polymeric Solid Electrolytes Based on Urea and Thiocyanate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2002, 23(12): 2375. |
| [15] | ZHAO Di-Shun, ZHANG Xing-Chen, ZHOU Qing-Ze, LI Hui-Yong, ZHANG Yue, XIONG Pei-Wen . Analysis of Conductive Process of the Solid Electrolyte Based on Urea and Thiourea [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2000, 21(5): 794. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||