

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (2): 373.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150627
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Xiaodan, ZHANG Zhiming( ), YU Liangmin*
), YU Liangmin*
Received:2015-08-07
Online:2016-02-10
Published:2015-12-26
Contact:
YU Liangmin
E-mail:zzmcyj@ouc.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
MA Xiaodan, ZHANG Zhiming, YU Liangmin. Antimicrobial Adhesion and Anticorrosion Properties of Polypyrrole Film in Natural Seawater†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(2): 373.
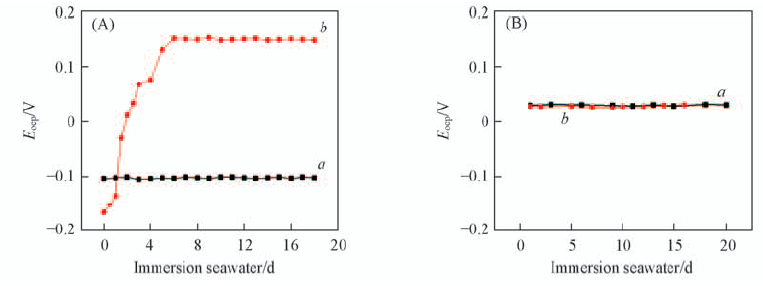
Fig.3 Open circuit potentials of 316L stainless steel(SS) electrode(A) and 316L SS electrode coated with polypyrrole(B) immersed in natural(a) and sterile seawater(b)
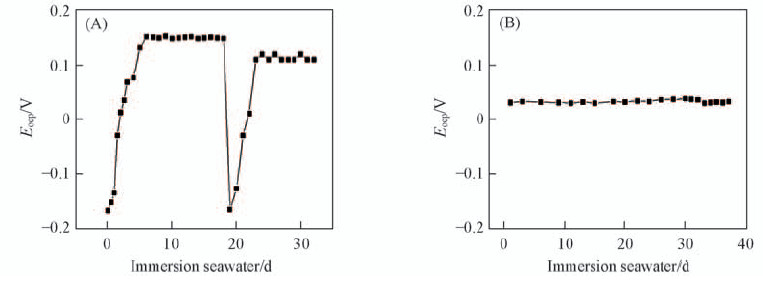
Fig.4 Open circuit potential of 316L SS electrode(A) and 316L SS electrode coated with polypyrrole(B) immersed in natural seawater after being treated under ultrasound
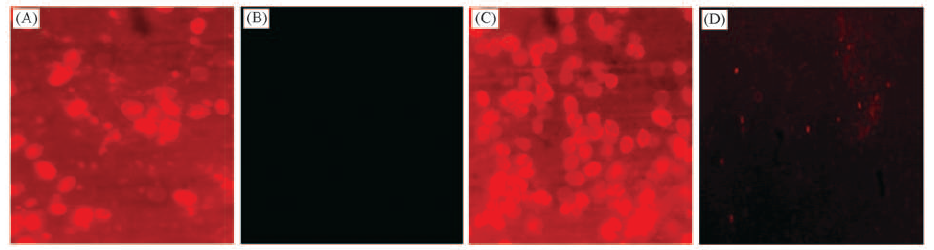
Fig.5 Biological microscope images of bare electrode(A, C) and sample electrode(B, D) after being immersed in natural seawater for 3 d(A, B) and 50 d(C, D)
| Time | Ecorr/V | icorr/(mA·cm-2) | η(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316L SS electrode | Sample electrode | 316L SS electrode | Sample electrode | 316L SS electrode | Sample electrode | |
| 2 h | -0.4447 | -0.3026 | 6.365×10-6 | 1.352×10-7 | 97.88 | |
| 5 d | -0.3113 | -0.3038 | 1.006×10-6 | 1.143×10-7 | 84.19 | 98.20 |
| 15 d | -0.3033 | -0.3065 | 3.422×10-7 | 1.351×10-7 | 94.62 | 97.88 |
| 25 d | -0.0411 | -0.3838 | 2.131×10-8 | 1.294×10-7 | 99.67 | 97.97 |
| 35 d | -0.5872 | -0.3762 | 3.651×10-6 | 1.681×10-7 | 42.64 | 97.36 |
| 50 d | -0.7713 | -0.3679 | 6.429×10-5 | 1.620×10-7 | Corroded | 97.45 |
Table 1 Fitting data of the 316 L SS electrode/316L SS electrode coated with polypyrrole immersed in natural seawater
| Time | Ecorr/V | icorr/(mA·cm-2) | η(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316L SS electrode | Sample electrode | 316L SS electrode | Sample electrode | 316L SS electrode | Sample electrode | |
| 2 h | -0.4447 | -0.3026 | 6.365×10-6 | 1.352×10-7 | 97.88 | |
| 5 d | -0.3113 | -0.3038 | 1.006×10-6 | 1.143×10-7 | 84.19 | 98.20 |
| 15 d | -0.3033 | -0.3065 | 3.422×10-7 | 1.351×10-7 | 94.62 | 97.88 |
| 25 d | -0.0411 | -0.3838 | 2.131×10-8 | 1.294×10-7 | 99.67 | 97.97 |
| 35 d | -0.5872 | -0.3762 | 3.651×10-6 | 1.681×10-7 | 42.64 | 97.36 |
| 50 d | -0.7713 | -0.3679 | 6.429×10-5 | 1.620×10-7 | Corroded | 97.45 |
| Time | Rs/(Ω·cm2) | Rp/(kΩ·cm2) | Qp/μF | 104W/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 h | 6.25 | 3.6 | 186 | — |
| 5 d | 6.02 | 28.5 | 163 | — |
| 15 d | 7.61 | 35.7 | 241 | — |
| 25 d | 14.90 | 12.0 | 129 | 3.72 |
| 35 d | 4.93 | 9.89 | 12.0 | 2.32 |
| 50 d | 7.31 | 6.50 | 21.5 | 5.45 |
Table 2 EIS fitting data of 316 L SS electrode immersed in natural seawater
| Time | Rs/(Ω·cm2) | Rp/(kΩ·cm2) | Qp/μF | 104W/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 h | 6.25 | 3.6 | 186 | — |
| 5 d | 6.02 | 28.5 | 163 | — |
| 15 d | 7.61 | 35.7 | 241 | — |
| 25 d | 14.90 | 12.0 | 129 | 3.72 |
| 35 d | 4.93 | 9.89 | 12.0 | 2.32 |
| 50 d | 7.31 | 6.50 | 21.5 | 5.45 |
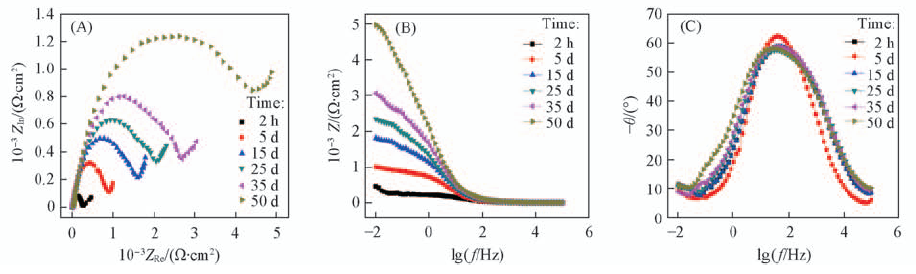
Fig.9 EIS of 316 L SS electrode coated with polypyrrole immersed in natural seawater for different time (A) Nyquist polts; (B) Bode magnitude polts; (C) Bode phase angle plots.
| Time | Rs/(Ω·cm2) | Rp/(kΩ·cm2) | Qp/μF | 106W/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 h | 6.04 | 0.82 | 38.8 | 18.2 |
| 5 d | 9.48 | 1.10 | 39.0 | 6.15 |
| 15 d | 9.78 | 1.80 | 27.3 | 1.74 |
| 25 d | 9.96 | 2.40 | 27.1 | 1.33 |
| 35 d | 9.97 | 3.10 | 27.0 | 1.08 |
| 50 d | 11.20 | 5.20 | 23.4 | 387 |
Table 3 EIS fitting data of 316 L SS electrode coated with polypyrrole immersed in natural seawater
| Time | Rs/(Ω·cm2) | Rp/(kΩ·cm2) | Qp/μF | 106W/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 h | 6.04 | 0.82 | 38.8 | 18.2 |
| 5 d | 9.48 | 1.10 | 39.0 | 6.15 |
| 15 d | 9.78 | 1.80 | 27.3 | 1.74 |
| 25 d | 9.96 | 2.40 | 27.1 | 1.33 |
| 35 d | 9.97 | 3.10 | 27.0 | 1.08 |
| 50 d | 11.20 | 5.20 | 23.4 | 387 |
| [1] | Wu J. X., Cheng S., Mao C. Y., Chang K. Y., Wei K., Corrosion Science, 2014, 88, 291—305 |
| [2] | Labena A., Hegazy M. A., Horn H., Müller E., Materials Science and Engineering, 2015, 47, 367—375 |
| [3] | Melchers R. E., Bioelectrochemistry, 2014, 97, 89—96 |
| [4] | Duan J., Wu S., Zhang X., Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 54(1), 22—28 |
| [5] | Sun C., Han E. H., Wang X., J. Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2003, 15(2), 104—106 |
| (刘斌, 韩思原, 王旭. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2003, 15(2), 104—106) | |
| [6] | Niu G. H., Yin Y. S., Chang X. T., J.Chemical Research, 2008, 19(3), 83—86 |
| [7] | Mahdi D., Zeinab H., Nathalie T., Sasha O., Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2014, 117, 152—157 |
| [8] | Wu J. Y., Chai K., Xiao W. L., En H., Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2010, 46(6), 775—760 |
| [9] | Moradi M., Duan J., Ashassi-Sorkhabi H., Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(12), 4282—4290 |
| [10] | Usher K. M., Kaksonen A. H., Cole I., Marney D., International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2014, 93, 84—106 |
| [11] | Wang J., Li X. B., Wang W., J. Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2004, 24(5), 262—266 |
| (王佳, 李相波, 王伟. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2004, 24(5), 262—266) | |
| [12] | Shirakawa H., Louis E.J., MacDiarmid A. G., Chiang C. K., Heeger A. J.,Chem. Commun., 1977, (16), 578—580 |
| [13] | Ignacio T. V., Marco A. A., Juan P. P., Gustavo A. J., Pablo A. P., Magdalena W., Gonzalo E. P., Bioelectrochemistry, 2014, 97, 15—22 |
| [14] | Chiang C. K., Fincher C. R. Jr., Physical Review Letters, 1997, 39, 1098—1101 |
| [15] | Wan M.X.,Chinese Journal of Polymer Bulletin, 1999, (3), 47—53 |
| (万梅香. 高分子通报, 1999, (3), 47—53) | |
| [16] | Troch-Nagels G., Winand R., Weymeersch A., Applied Electrochemistry, 1992, 22(8), 756—764 |
| [17] | Deronzier A. A., Moutet J. C., Accounts of Chemical Research, 1989, 22, 248—255 |
| [18] | Xing C. J., Yu L. M., Zhang Z. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(8), 1999—2004 |
| (邢翠娟, 于良民, 张志明. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(8), 1999—2004) | |
| [19] | Salanak W. R., Erlandssom R., Priza J., Lundatrom I., Inganas D., Synthetic Metals, 1983, 5(2), 125—139 |
| [20] | Cho G., Fung B. M., Glatzhofer D. T., Langmuir, 2001, 17(2), 456—461 |
| [21] | Zhong W., Liu S., Chen X., Macromolecules, 2006, 39(9), 3224—3230 |
| [22] | Jude O. I., Greg A. W., Composites Part B: Engineering, 1998, 29(2), 181—188 |
| [23] | Zhang Y., Su X., Zhou Y. T., Li J. J., Feng J. T., Yan W., Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2014, 33(9), 2886—2292 |
| (张瑜, 苏翔, 周远涛, 李晶晶, 冯江涛, 延卫. 化工进展, 2014, 33(9), 2886—2292) | |
| [24] | Wynne K. J., Street G. B., Macromolecules, 1985, 18(12), 2361—2368 |
| [25] | Li X.B., The Electrochemical Characteristics of Microbial Adhesion in the Marine Environment and the Detection and Control Methods, Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 2004, 47—50 |
| (李相波. 海洋环境中微生物附着的电化学特征及检测与控制方法研究, 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院, 2004, 47—50) | |
| [26] | Tunç T., Birgül Y., Mehmet E., Progress in Organic Coatings, 2004, 51(2), 152—160 |
| [27] | Tunç T., Surface & Coatings Technology, 2006, 200(16/17), 4713—4719 |
| [28] | Liu B., Duan J. Z., Hou B. R., J.Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2012, 32(1), 48—53 |
| (刘斌, 段继周, 候宝荣. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2012, 32(1), 48—53) | |
| [29] | Chen S.G., The Mechanism Research on the Anti-corrosion of Conducting Polymers for Metals, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, 2008, 21—25 |
| (陈世刚. 导电聚合物对金属腐蚀防护机理的研究, 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2008, 21—25) |
| [1] | WANG Yingnan, DAI Xueyan, XU Tianlu, QU Lijie, ZHANG Chunling. Preparation and Anticorrosion Properties of Silane Grafted Nano-silica/Epoxy Composite Coating† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1564. |
| [2] | XING Cui-Juan, YU Liang-Min, ZHANG Zhi-Ming. Superhydrophobic Polyaniline Micro/Nano Structures as Anticorrosion Coating [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(8): 1999. |
| [3] | GAN Meng-Yu, LI Zhi-Chun, MA Li, HAO Shao-Na, JIA Chun-Yue, LIU Xing-Min. Surface Modification and Anticorrosive Properties of Polyaniline [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(03): 630. |
| [4] | YOU Bo*, XING Wen-Tao, WU Li-Min. Preparation and Properties of Macromolecule Phytic Acid-Polysilsesquioxane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(12): 2408. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||