

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 134.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150389
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
JI Keming, MENG Fanhui, GAO Yuan, LI Zhong*( )
)
Received:2015-05-14
Online:2016-01-10
Published:2015-12-20
Contact:
LI Zhong
E-mail:lizhong@tyut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
JI Keming, MENG Fanhui, GAO Yuan, LI Zhong. Effect of Fuel on Structure and Catalytic Performance for Slurry Methanation over Ni-Al2O3 Catalysts Prepared by Combustion Method†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(1): 134.
| Sample | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | Average pore diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| γ-Al2O3 | 191 | 0.38 | 5.8 |
| NiAl-IU | 162 | 0.30 | 5.5 |
| NiAl-IG | 153 | 0.29 | 5.2 |
| NiAl-IE | 147 | 0.24 | 4.9 |
| NiAl-CU | 468 | 0.28 | 2.4 |
| NiAl-CG | 158 | 0.41 | 10.1 |
| NiAl-CE | 51 | 0.05 | 3.6 |
Table 1 Textural properties of Al2O3 support and the catalysts
| Sample | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | Average pore diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| γ-Al2O3 | 191 | 0.38 | 5.8 |
| NiAl-IU | 162 | 0.30 | 5.5 |
| NiAl-IG | 153 | 0.29 | 5.2 |
| NiAl-IE | 147 | 0.24 | 4.9 |
| NiAl-CU | 468 | 0.28 | 2.4 |
| NiAl-CG | 158 | 0.41 | 10.1 |
| NiAl-CE | 51 | 0.05 | 3.6 |
| Catalyst | Ni crystallite size/nm | Ni dispersion(%) | Metal surface area/(m2·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiAl-IU | 6.9 | 7.7 | 10.3 |
| NiAl-IG | 7.0 | 7.2 | 9.6 |
| NiAl-IE | 7.3 | 6.9 | 9.2 |
| NiAl-CU | 6.3 | 7.9 | 10.5 |
| NiAl-CG | 7.6 | 6.2 | 8.3 |
| NiAl-CE | 12.5 | 3.5 | 4.8 |
Table 2 XRD and H2 chemisorption analytic results for the catalysts
| Catalyst | Ni crystallite size/nm | Ni dispersion(%) | Metal surface area/(m2·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiAl-IU | 6.9 | 7.7 | 10.3 |
| NiAl-IG | 7.0 | 7.2 | 9.6 |
| NiAl-IE | 7.3 | 6.9 | 9.2 |
| NiAl-CU | 6.3 | 7.9 | 10.5 |
| NiAl-CG | 7.6 | 6.2 | 8.3 |
| NiAl-CE | 12.5 | 3.5 | 4.8 |
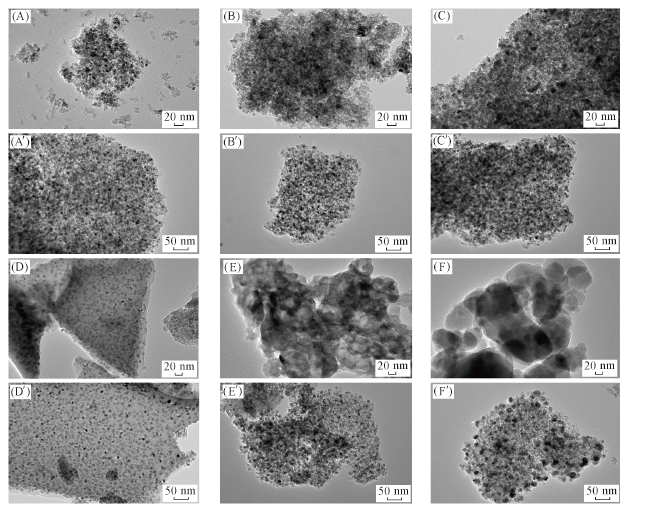
Fig.4 TEM images of NiAl-IU(A, A'), NiAl-IG(B, B'), NiAl-IE(C, C'), NiAl-CU(D, D'), NiAl-CG(E, E') and NiAl-CE(F, F') catalysts before(A—F) and after(A'—F') reduction
| Catalyst | Relative content, w(%)(reduction temperature/℃) | /(mmol·g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni2O3 | α-NiO | β1-NiO | β2-NiO | γ-NiO | ||
| NiAl-IU | 11(220) | 5(268) | 36(321) | 37(439) | 11(499) | 2.70 |
| NiAl-IG | 8(232) | 5(279) | 30(323) | 46(412) | 11(504) | 2.14 |
| NiAl-IE | 2(214) | 5(275) | 38(321) | 46(462) | 9(566) | 1.96 |
| NiAl-CU | ___ | 27(280) | 35(459) | 31(543) | 7(709) | 2.76 |
| NiAl-CG | ___ | 39(373) | 14(448) | 33(509) | 14(646) | 2.04 |
| NiAl-CE | ___ | 83(345) | 3(430) | 3(499) | 11(600) | 1.91 |
Table 3 Gaussian fitting analysis of H2-TPR profiles of the Ni-based catalysts
| Catalyst | Relative content, w(%)(reduction temperature/℃) | /(mmol·g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni2O3 | α-NiO | β1-NiO | β2-NiO | γ-NiO | ||
| NiAl-IU | 11(220) | 5(268) | 36(321) | 37(439) | 11(499) | 2.70 |
| NiAl-IG | 8(232) | 5(279) | 30(323) | 46(412) | 11(504) | 2.14 |
| NiAl-IE | 2(214) | 5(275) | 38(321) | 46(462) | 9(566) | 1.96 |
| NiAl-CU | ___ | 27(280) | 35(459) | 31(543) | 7(709) | 2.76 |
| NiAl-CG | ___ | 39(373) | 14(448) | 33(509) | 14(646) | 2.04 |
| NiAl-CE | ___ | 83(345) | 3(430) | 3(499) | 11(600) | 1.91 |
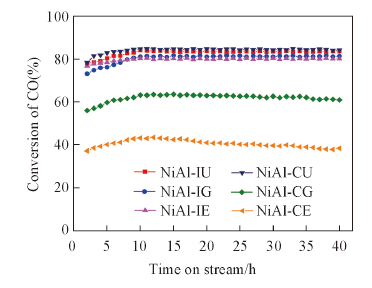
Fig.6 Catalytic stability of Ni-Al2O3 catalysts for slurry CO methanation ^Reaction conditions: 260 ℃, 1.0 MPa, V(H2)∶V(CO)=3∶1, space velocity: 3000 mL·g-1·h-1.
| Catalyst | Conversion of CO(%) | Selectivity(%) | Yield for CH4(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | C2—C4 | CO2 | |||
| NiAl-IU | 83.5 | 90.1 | 4.6 | 5.3 | 75.2 |
| NiAl-IG | 81.3 | 89.4 | 5.2 | 5.4 | 72.7 |
| NiAl-IE | 80.1 | 88.3 | 5.8 | 5.9 | 70.7 |
| NiAl-CU | 84.7 | 91.1 | 4.4 | 4.5 | 77.2 |
| NiAl-CG | 63.2 | 87.8 | 6.2 | 6.0 | 55.5 |
| NiAl-CE | 43.1 | 81.6 | 7.1 | 11.3 | 35.2 |
Table 4 Catalytic performance of Ni-Al2O3 catalysts for slurry CO methanation*
| Catalyst | Conversion of CO(%) | Selectivity(%) | Yield for CH4(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | C2—C4 | CO2 | |||
| NiAl-IU | 83.5 | 90.1 | 4.6 | 5.3 | 75.2 |
| NiAl-IG | 81.3 | 89.4 | 5.2 | 5.4 | 72.7 |
| NiAl-IE | 80.1 | 88.3 | 5.8 | 5.9 | 70.7 |
| NiAl-CU | 84.7 | 91.1 | 4.4 | 4.5 | 77.2 |
| NiAl-CG | 63.2 | 87.8 | 6.2 | 6.0 | 55.5 |
| NiAl-CE | 43.1 | 81.6 | 7.1 | 11.3 | 35.2 |
| [1] | Gao J., Liu Q., Gu F., Liu B., Zhong Z., Su F., RSC Adv., 2015, 5(29), 22759—22776 |
| [2] | Kopyscinski J., Schildhauer T. J., Biollaz S. M. A., Fuel,2010, 89(8), 1763—1783 |
| [3] | Cui X. X., Meng F. H., He Z., Li Z., Zheng H. Y., Chin. J. Inorg. Chem., 2013, 30(2), 277—283 |
| (崔晓曦, 孟凡会, 何忠, 李忠, 郑华艳. 无机化学学报,2013, 30(2), 277—283) | |
| [4] | Meng F., Li Z., Liu J., Cui X., Zheng H., J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng., 2015, 23, 250—258 |
| [5] | Meng F., Li Z., Ji F., Li M., Int. J. Hydrogen Energ., 2015, 40(29), 8833—8843 |
| [6] | Meng F. H., Chang H. R., Li Z., CIESC J., 2014, 65(8), 2997—3003 |
| (孟凡会, 常慧蓉, 李忠, 化工学报, 2014, 65(8), 2997—3003) | |
| [7] | Zhang J., Bai Y., Zhang Q., Wang X., Zhang T., Tan Y., Han Y., Fuel,2014, 132(15), 211—218 |
| [8] | Götz M., Ortloff F., Reimert R., Basha O., Morsi B. I., Kolb T., Energ. Fuel, 2013, 27(8), 4705—4716 |
| [9] | Meng F. H., Liu J., Li Z., Zhong P. Z., Zheng H. Y., J. Fuel Chem. Technol., 2014, 42(2), 231—237 |
| (孟凡会, 刘军, 李忠, 钟朋展, 郑华艳. 燃料化学学报,2014, 42(2), 231—237) | |
| [10] | Meng F., Zhong P., Li Z., Cui X., Zheng H., J. Chem., 2014, 2014, 1—7 |
| [11] | Piumetti M., Fino D., Russo N., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2015, 163, 277—287 |
| [12] | Cao Z., Qin M., Jia B., Gu Y., Chen P., Volinsky A. A., Qu X., Ceram. Int., 2015, 41(2), 2806—2812 |
| [13] | Ghose R., Hwang H. T., Varma A., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 2014, 472, 39—46 |
| [14] | Groven L. J., Pfeil T. L., Pourpoint T. L., Int. J. Hydrogen Energ., 2013, 38(15), 6377—6380 |
| [15] | González-Cortés S. L., Imbert F. E., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 2013, 452, 117—131 |
| [16] | Shi L., Jin Y., Xing C., Zeng C., Kawabata T., Imai K., Matsuda K., Tan Y., Tsubaki N., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 2012, 435/436, 217—224 |
| [17] | Yan C. F., Chen H., Hu R. R., Huang S., Luo W., Guo C., Li M., Li W., Int. J. Hydrogen Energ., 2014, 39(32), 18695—18701 |
| [18] | Colussi S., Gayen A., Llorca J., de Leitenburg C., Dolcetti G., Trovarelli A., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2012, 51(22), 7510—7517 |
| [19] | Liu Q., Ren J., Qin Z. F., Miao M. Q., Li Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(9), 2171—2177 |
| (刘泉, 任军, 秦志峰, 苗茂谦, 李忠. 高等学校化学学报,2013, 34(9), 2171—2177) | |
| [20] | Ji K. M., Meng F. H., Gao Y., Li Z., Chin. J. Inorg. Chem., 2015, 31(2), 267—274 |
| (吉可明, 孟凡会,高源, 李忠. 无机化学学报,2015, 31(2), 267—274) | |
| [21] | Jung C. H., Jalota S., Bhaduri S. B., Mater. Lett., 2005, 59(19/20), 2426—2432 |
| [22] | Sing K. S. W., Everett D. H., Haul R. A. W., Moscou L., Pierotti R. A., Rouquerol J., Siemieniewska T., Pure Appl. Chem., 1985, 57(4), 603—619 |
| [23] | Aziz M. A. A., Jalil A. A., Triwahyono S., Mukti R. R., Taufiq-Yap Y. H., Sazegar M. R., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2014, 147, 359—368 |
| [24] | Han S. J., Bang Y., Yoo J., Seo J. G., Song I. K., Int. J. Hydrogen Energ., 2013, 38(20), 8285—8292 |
| [25] | Li G., Hu L., Hill J. M., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 2006, 301(1), 16—24 |
| [26] | Xu Y., Yang J., Demura M., Hirano T., Matsushita Y., Tanaka M., Katsuya Y., Int. J. Hydrogen Energ., 2014, 39(25), 13156—13163 |
| [27] | Bai X., Wang S., Sun T., Wang S., React. Kinet. Mech. Catal., 2014, 112(2), 437—451 |
| [28] | Hardiman K. M., Hsu C. H., Ying T. T., Adesina A. A., J. Mol. Catal. A Chem., 2005, 239(1/2), 41—48 |
| [29] | Zhang J., Xu H., Jin X., Ge Q., Li W., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 2005, 290(1/2), 87—96 |
| [30] | Zhang Y. H., Xiong G. X., Sheng S. S., Liu S. L., Yang W. S., Acta Phys-Chim. Sin., 1999, 15(8), 735—741 |
| (张玉红, 熊国兴, 盛世善, 刘盛林, 杨维慎. 物理化学学报, 1999, 15(8), 735—741) | |
| [31] | Kumar A., Wolf E. E., Mukasyan A. S., AIChE J. 1999, 15(8), 735—741ource>, 2011, 57(8), 2207—2214 |
| [32] | Thyssen V. V., Maia T. A., Assaf E. M., Fuel,2013, 105, 358—363 |
| [1] | QIU Xinsheng, WU Qin, SHI Daxin, ZHANG Yaoyuan, CHEN Kangcheng, LI Hansheng. Preparation and High Temperature Fuel Cell Performance of Ionic Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyimides for Proton Exchange Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220140. |
| [2] | CHEN Changli, MI Wanliang, LI Yujing. Research Progress of Single Atom Catalysts in Electrochemical Hydrogen Cycling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220065. |
| [3] | LUO Bian, ZHOU Fen, PAN Mu. Study on Preparation and Accessibility of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Supported Platinum Catalyst [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210853. |
| [4] | LIU Jie, LI Jinsheng, BAI Jingsen, JIN Zhao, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Constructing a Water-blocking Interlayer Containing Sulfonated Carbon Tubes to Reduce Concentration Polarization in Direct Methanol Fuel Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220420. |
| [5] | CAO Kaiyue, PENG JinWu, LI Hongbin, SHI Chengying, WANG Peng, LIU Baijun. High-temperature Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Cross-linked Polybenzimidazole/hyperbranched-polymer Blends [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2049. |
| [6] | PU Yangyang, NING Cong, LU Yao, LIU Lili, LI Na, HU Zhaoxia, CHEN Shouwen. Preparation and Characterizations of Cross-linked Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone)/Partially Fluorinated Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether sulfone) Blend Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2002. |
| [7] | WANG Yuemin, MENG Qinglei, WANG Xian, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Enhancement of Performance of Fe-N-C Catalysts by Copper and Sulfur Doping for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1843. |
| [8] | LIANG Minhui, WANG Peng, LI Hongbin, LI Tianyang, CAO Kaiyue, PENG Jinwu, LIU Zhenchao, LIU Baijun. Preparation of High-temperature Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Semi-interpenetrating Polymer Networks [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2845. |
| [9] | HUA Tao, LI Shengnan, LI Fengxiang, WANG Haonan. Treatment of Naphthalene by Microbial Electrochemical System and the Analysis of Microbial Communities † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1964. |
| [10] | YU Yancun, WANG Xian, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Promoted Formic Acid Electrooxidation Using PdNx/C Catalyst Prepared with Hyperbranched Polymer† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1433. |
| [11] | ZHU Yuxin,HARAGIRIMANA Alphonse,LU Yao,BUREGEYA Ingabire Providence,NING Cong,LI Na,HU Zhaoxia,CHEN Shouwen. Preparation and Properties of Filling-type Sulfonated Poly(arylene ether sulfone)/Poly(ether sulfone) Composite Membranes with Microporous Structures† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 1051. |
| [12] | LIN Zhouchen,HUANG Qiaoxi,LEI Ming. Fabrication and Electrocatalytic Performance of Graphene-fullerene Ammonium Iodide Composite Supported Pd Nanocatalyst for Ethanol Oxidation† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 1013. |
| [13] | LIU Jiaming,FU Kailin,ZHANG Ze,GUO Wei,PAN Mu. Ultra-low Pt Loading Cathodic Catalyst Layer Prepared on Textured Gas Diffusion Layer by Magnetron Sputtering Method for Hydrogen-oxygen Fuel Cells† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 542. |
| [14] | SHI Yue,MAO Qing,XIAO Cheng,JING Weiyun,ZHANG Xueyuan. Nonlinear Spectroscopy Analysis for Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Methanol on PtRu/C Surface† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2017. |
| [15] | ZHU Xingye,QIAN Huidong,JIANG Jingjing,YUE Zhouying,XU Jianfeng,ZOU Zhiqing,YANG Hui. Cross-linking of Imidazole-grafted Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone) as Proton Exchange Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2046. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||