

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 864.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20141148
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Yongjun*( ), DING Jing, JIN Zhimei, TIE Zhenzhen, ZHOU Min
), DING Jing, JIN Zhimei, TIE Zhenzhen, ZHOU Min
Received:2014-12-31
Online:2015-05-10
Published:2015-04-16
Contact:
MA Yongjun
E-mail:mayj@nwnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
MA Yongjun, DING Jing, JIN Zhimei, TIE Zhenzhen, ZHOU Min. Inhibiting Effect of Chloride Ion for the Electro-oxidation Reaction of Four Organic Alcohols on a Chemically Modified Platinum Anode†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(5): 864.
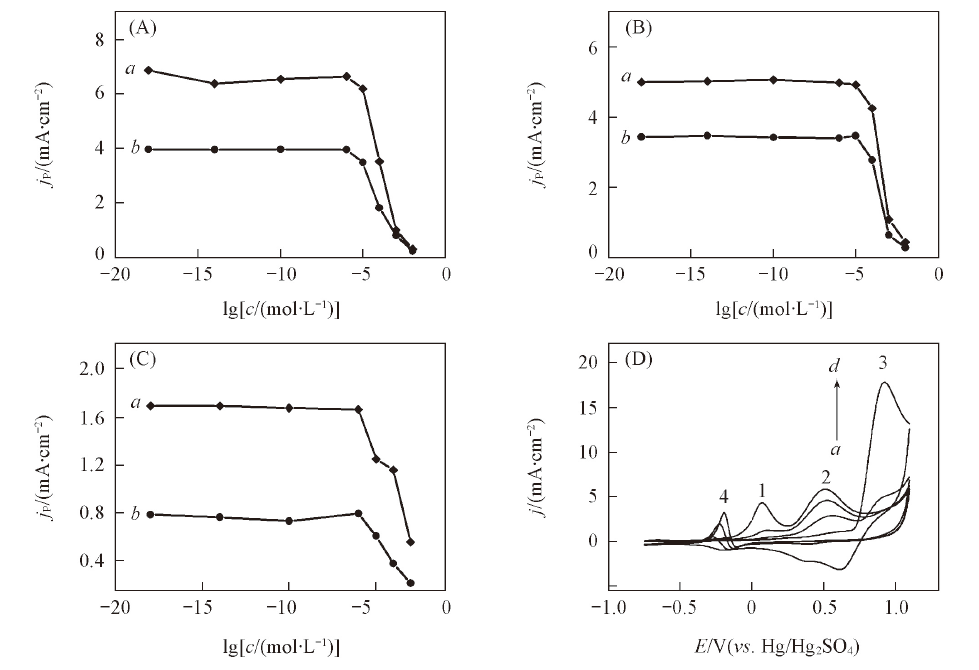
Fig.2 Influence of chloride ion on the oxidative peak currents of methanol(A), ethanol(B), n-propanol(C) on the modified platinum anode(a) and a bare platinum anode(b) and the CV curves of ethanol on the modified platinum anode with different concentrations of chloride ion(D)(D) c(Cl-)/(mol·L-1): a—d: 0.1, 0.01, 0.001, 0.0001.
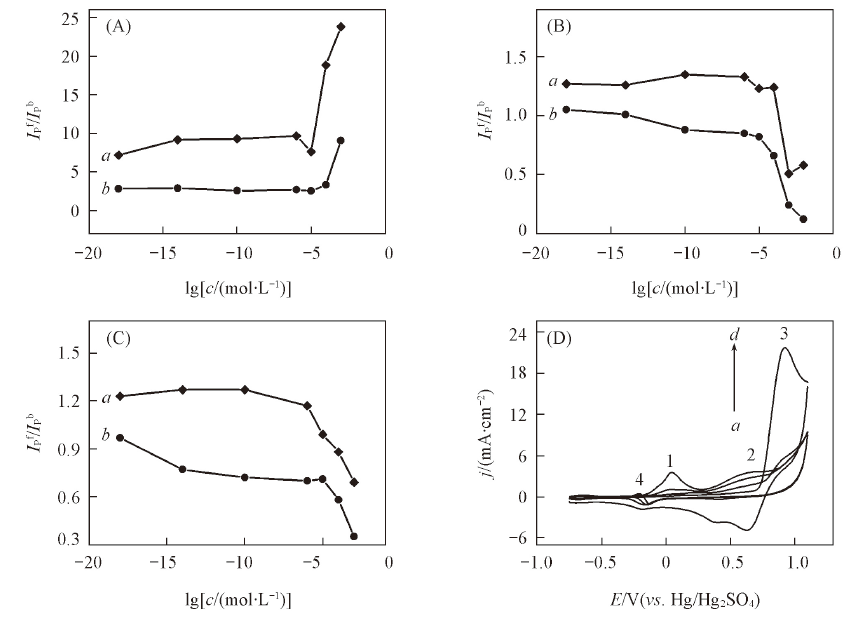
Fig.3 Influence of chloride ion on the oxidative peak current ratio(Ipf/Ipb) of methanol(A), ethanol(B), n-propanol(C) on the modified platinum anode(a) and a bare platinum anode(b) and the CV curves of methanol on the modified platinum anode with different concentrations of chloride ion(D)(D) c(Cl-)/(mol·L-1): a—d: 0.1, 0.01, 0.001, 0.0001.
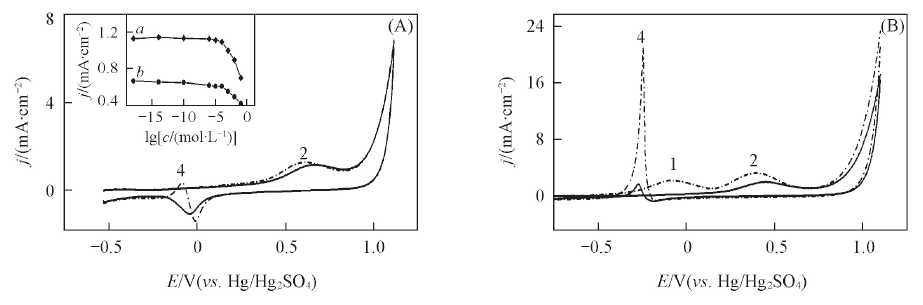
Fig.4 Influence of chloride ion on the cyclic voltammograms of iso-propanol on modified electrodes at 25 ℃(A) and 60 ℃(B)-˖-˖ [Cl-]=0; —[Cl-]=0.001 mol/L. Inset of (A) show the relationship between chloride ion concentration and the current density of oxidative peak 2 of iso-propanol on the modified platinum anode(a) and bare platinum anode(b).
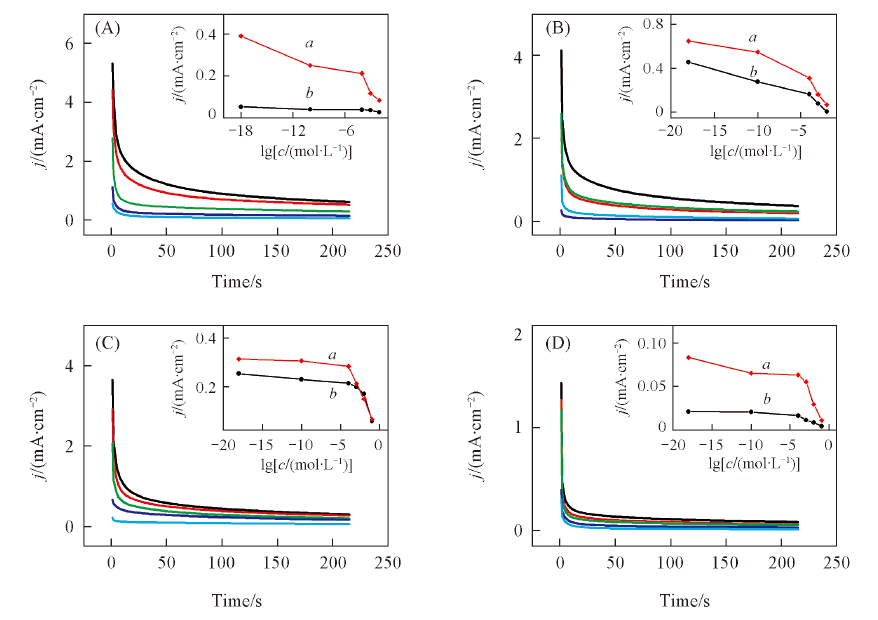
Fig.5 Influence of chloride ion on the chronoamperometric curves of methanol(A), ethanol(B), n-propanol(C) and iso-propanol(D) on the modified electrodeEapp/V: (A) 0.1; (B—D) 0.3. The insets show the relationship between chloride ion concentration and the chronoamperometric current density of four alcohols at 200 s on the modified platinum anode(a) and bare platinum anode(b), respectively.
| [1] | Borup, R. , Meyers, J. , Pivovar, B. , Kim Y., S. , Mukundan, R. , Garland, N. , Myers, D. , Wilson, M. , Garzon, F. , Wood, D. , Zelenay, P. , More, K. , Stroh, K. , Zawodzinski, T. , Boncella, J. , McGrath J., E. , Inaba, M. , Miyatake, K. , Hori, M. , Ota, K. , Ogumi, Z. , Miyata, S. , Nishikata, A. , Siroma, Z. , Uchimoto, Y. , Yasuda, K. , Kimijima K., I. , Iwashita, N. , Chem. Rev., 2007, 107, 3904- 3951 |
| [2] | Liu R., R. , Wang D., J. , Leng, J. , Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2013, 29( 4), 747- 750 |
| [3] | Matsuoka, K. , Sakamoto, S. , Nakato, K. , Hamada, A. , Itoh, Y. , J. Power Sources, 2008, 179, 560- 565 |
| [4] | Li, H. , Wang H., J. , Qian W., M. , Zhang S., S. , Wessel, S. , Cheng T. T., H. , Shen, J. , Wu S., H. , J. Power Sources, 2011, 196, 6249- 6255 |
| [5] | Lama, A. , Li, H. , Zhang S., S. , Wang H., J. , Wilkinson D., P. , Wessel, S. , Cheng T. T., H. , J. Power Sources, 2012, 205, 235- 238 |
| [6] | Yadav A., P. , Nishikata, A. , Tsuru, T. , Electrochim. Acta, 2007, 52, 7444- 7452 |
| [7] | Wang Z., Q. , Tada E., J. , Nishikata, A. , J. Electrochem. Soc., 2014, 161( 9), F845- F849 |
| [8] | Baturina O., A. , Epshteyn, A. , Northrup P., A. , Swider-Lyons K., E. , J. Electrochem. Soc., 2011, 158( 10), B1198- B1205 |
| [9] | Horá, nyi G. , J. Electroanal. Chem., 1978, 86, 215- 218 |
| [10] | Lamy, C. , Lima, A. , LeRhum, V. , Delime, F. , J. Power Sources, 2002, 105, 283- 296 |
| [11] | Iwasita, T. , Electrochim. Acta, 2002, 47, 3663- 3674 |
| [12] | Rousseau, S. , Coutanceau, C. , Lamy, C. , Lé, ger J. M. , J. Power Sources, 2006, 158, 18- 24 |
| [13] | Kim J., H. , Choi S., M. , Nam S., H. , Seo M., H. , Choi S., H. , Kim W., B. , Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2008, 82, 89- 102 |
| [14] | Qi Z., G. , Kaufman, A. , J. Power Sources, 2002, 112, 121- 129 |
| [15] | El-Nagar G., A. , Mohammad A., M. , El-Deab M., S. , El-Anadouli B., E. , Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2014, 9, 4523- 4534 |
| [16] | Thomas C., F. , Homma, H. , J. Catal., 1976, 42, 360- 366 |
| [17] | Sobkowski, J. , Franaszczuk, K. , Dobrowolska, K. , J. Electroanal. Chem., 1992, 330, 529- 540 |
| [18] | Conway B., E. , Mozota, J. , J. Chem. Soc. Faladay Trans. I, 1982, 78, 1717- 1732 |
| [19] | Snell K., D. , Keenan A., G. , Electrochim. Acta, 1981, 26( 9), 1339- 1344 |
| [20] | 马永钧, 杨梅霞, 王伟峰, 周敏. 化学学报, 2001, 69( 3), 262- 268 |
| Ma Y., Y. , Yang M., X. , Wang W., F. , Zhou, M. , Acta Chim. Sinica, 2001, 69( 3), 262- 268 | |
| [21] | Ma Y., J. , Du Y., L. , Ye W., C. , Su B., Q. , Yang M., X. , Wang C., M. , Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2012, 7, 2654- 2679 |
| [22] | 马永钧, 田玉秀, 刘婧, 周敏, 丁静, 金芝梅, 王向梅. 电化学, 2014, 20( 2), 150- 155 |
| Ma Y., J. , Tian Y., X. , Liu, J. , Zhou, M. , Ding, J. , Jin Z., M. , Wang X., M. , J. Electrochem., 2014, 20( 2), 150- 155 | |
| [23] | 马心英, 林宪杰. 应用化学, 2009, 26( 3), 287- 291 |
| Ma X., Y. , Lin X., J. , Chin. J. Appl. Chem., 2009, 26( 3), 287- 291 | |
| [24] | Katikawong, P. , Ratana T , Veerasai W., J. Chem. Sci., 2009 , 121( 3), 329- 337 |
| [25] | Wang M., Y. , Chen J., H. , Fan, Z. , Tang, H. , Deng G., H. , He D., L. , Kuang Y., F. , Carbon, 2004, 42, 3251- 3272 |
| [26] | Liu Z., L. , Ling X., Y. , Su X., D. , Lee J., Y. , J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 8234- 8240 |
| [27] | Pastor, E. , Gonzá, lez S. , Arvia A., J. , J. Electroanal. Chem., 1995, 395, 233- 242 |
| [1] | WANG Xuan, HUANG Wei-Min, LIU Xiao-Bo, LU Hai-Yan, LIN Hai-Bo*. Influence of Chloride Ion on Electrochemical Oxidation Degradation of Phenol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(2): 361. |
| [2] | SU Bi-Quan, ZHANG Yu-Zhen, DU Yong-Ling, WANG Chun-Ming*. Fabrication of a Silver Nanoparticle/polydopamine Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode and Its Electrocatalytic Reduction for p-Nitrophenol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(8): 1661. |
| [3] | YANG Shao-Ming*, WEI Zhi-Peng, HU Guang-Hui, JIANG Dan, HUANG Ai-Hua, .... Simultaneous Determination of Catechol and Hydroquinone at a Carbon Nanotubes Modified Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(2): 264. |
| [4] | ZHANG Dong-Mei1, ZHOU Nan-Di1, ZHOU Hui1, CHEN Ting2, LI Gen-Xi1*. Electrochemical Study of the Inhibitory Effect of Sinapic Acid and Its Derivatives on Tyrosinase Reactivity [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(2): 273. |
| [5] | WANG Xia-Yan, CUI Xing-Pin, CUI Yun-Mei, JIN Bao-Kang, LIN Xiang-Qin. Investigation of Electrochemical Oxidation of L-Ascorbic Acid at CoCuHCF/Pt Electrode in Neutral Solutions by In situ FTIRRAS [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2002, 23(8): 1498. |
| [6] | DAI Li-Zong, XU Yi-Ting, Jean-Yves-GAL, WU Hui-Huang . Effects of Ring-substituted Groups on the Properties of Metallized Polyaniline Membrane Modified Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2002, 23(7): 1404. |
| [7] | DAI Li-Zong, XU Yi-Ting, ZHOU Shan-Kang, WU Hui-Huang . Studies on Electrochemical and Catalytic Properties of Poly-m-chloraniline Modified Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2002, 23(6): 1174. |
| [8] | SUN Yan-Yi, WU Kang-Bing, HU Sheng-Shui . Selective Determination of Dopamine in the Presence of High Concentration Ascorbic Acid and Uric Acid Using Carbon Nanotube Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2002, 23(11): 2067. |
| [9] | SHI Sheng-Hua, GUO Yan-Li, SUO Zhi-Rong . A Study on Chloride Ion-selective Electrode Transient Potentiometry [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2001, 22(4): 556. |
| [10] | LUO Hong-Xia, SHI Zu-Jin, LI Nan-Qiang, GU Zhen-Nan, ZHUANG Qian-Kun . Investigation on the Electrochemical and Electrocatalytic Behavior of Chemically Modified Electrode of Single Wall Carbon Nanotube Functionalized with Carboxylic Acid Group [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2000, 21(9): 1372. |
| [11] | GONG Yi, YE Lei, JU Huang-Xian, CHEN Hong-Yuan. Electrocatalysis of Osmium Poly-vinylindole Complex Modified Glassy Carbon Electrodes to Epinephrine Oxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2000, 21(2): 202. |
| [12] | BAI Yan, MO Jin-Yuan, CHENG Qiang, ZHOU Yan-Hui . Studies on Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Catechols and Ascorbic acid on the Polymeric Heme Film Modified Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1998, 19(12): 1943. |
| [13] | ZHAO Jian-Wei, NIU Li, DONG Shao-Jun . Electrochemical Behavior of 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid in Self-Assembled Monolayer Electrode System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1998, 19(11): 1749. |
| [14] | WANG Yun, ZHOU Dong-Mei, CHEN Gang, CHEN Hong-Yuan . The Electrochemical Polymerization of Methylene Violet and Electrocatalytic Reduction of Nitrite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1997, 18(6): 864. |
| [15] | XU Jing-Juan, FANG Hui-Qun, CHEN Hong-Yuan. The Electrochemical Characteristics of Gold Electrode Modified by Thionine Covalently Bound to Self-assembled Cysteamine Monolayer and Its Electrocatalytic Oxidation for Ascorbic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1997, 18(5): 706. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||