

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (12): 2662.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140405
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Mei, LI Wei, HAN Wei*( ), ZHANG Milin, YAN Yongde
), ZHANG Milin, YAN Yongde
Received:2014-04-28
Online:2014-12-10
Published:2014-11-29
Contact:
HAN Wei
E-mail:weihan@hrbeu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Mei, LI Wei, HAN Wei, ZHANG Milin, YAN Yongde. Electrochemical Behavior of Pr(Ⅲ) in the LiCl-KCl Melt on a Ni Electrode†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(12): 2662.
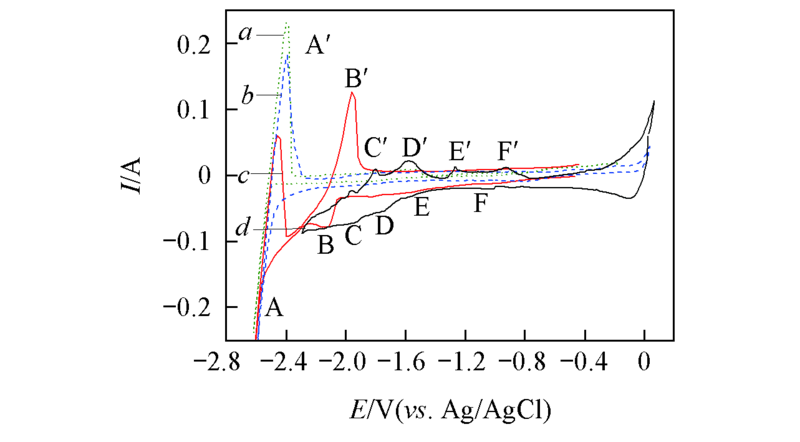
Fig.1 Cyclic voltammograms of LiCl-KCl melts before(a, b) and after(c, d) the addition of PrCl3(1.25×10-4 mol/L) at 873 K S=0.322 cm2, scan rate: 0.1 V/s. a. LiCl-KCl, Mo electrode; b. LiCl-KCl, Ni electrode; c. LiCl-KCl-PrCl3, Mo electrode; d. LiCl-KCl-PrCl3, Ni electrode.
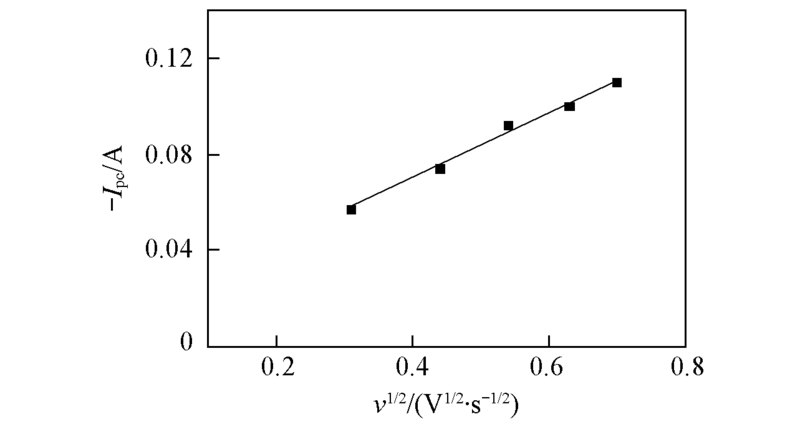
Fig.2 Variation of cathodic peak current as a function of the potential scan rate on a Mo electrode(S=0.322 cm2) in LiCl-KCl-PrCl3[c(PrCl3)=1.25×10-4 mol/L] melt at 873 K
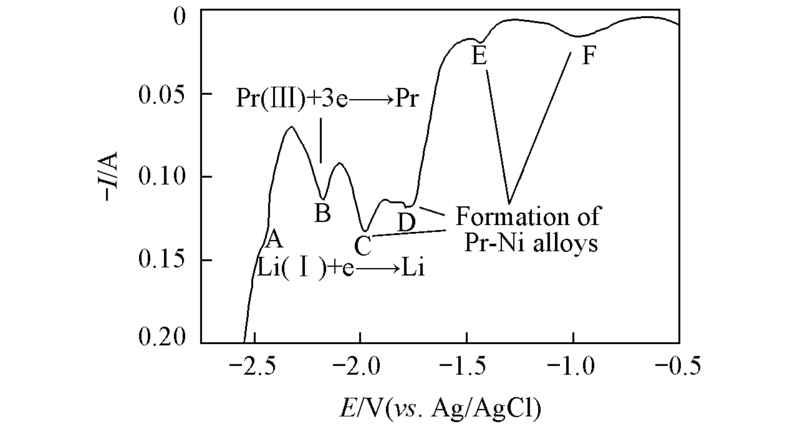
Fig.3 Square wave voltammogram on a Ni electrode in LiCl-KCl-PrCl3[c(PrCl3)=1.25×10-4 mol/L] melt(S=0.322 cm2) at 873 K Pulse height: 25 mV; potential step: 1 mV; frequency: 30 Hz.
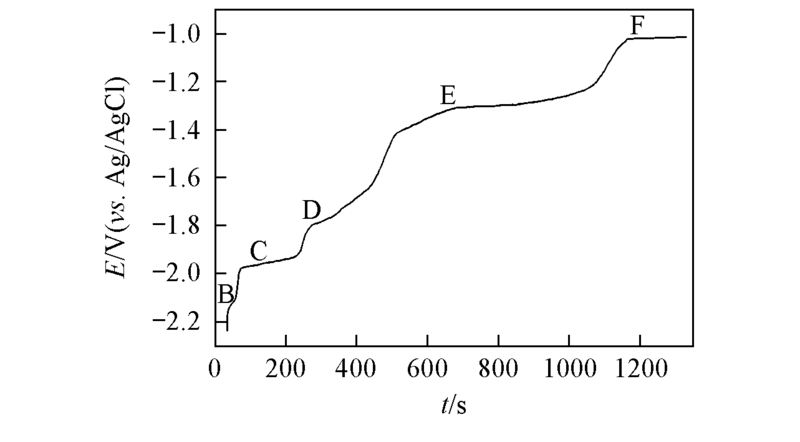
Fig.5 Open-circuit transient curve by potentiosta-tic electrolysis at -2.3 V(vs. Ag/AgCl) for 60 s on a Ni electrode(S=0.322 cm2) in LiCl-KCl-PrCl3[c(PrCl3)=1.25×10-4 mol/L] melt at 873 K
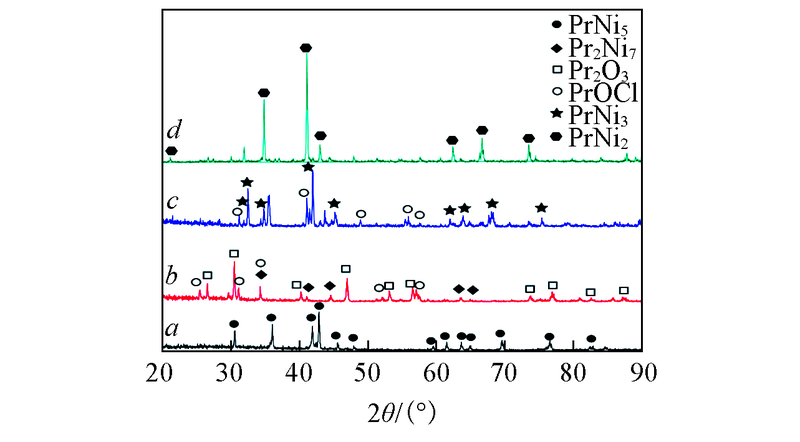
Fig.6 XRD patterns of Pr-Ni alloys by potentiostatic electrolysis on a Ni electrode(S=2.3 cm2) in LiCl-KCl-PrCl3[c(PrCl3)=1.25×10-4 mol/L] melt at 873 K a. -1.2 V for 10 h; b. -1.6 V for 8 h; c. -1.8 V for 6 h; d. -2.0 V for 2 h.
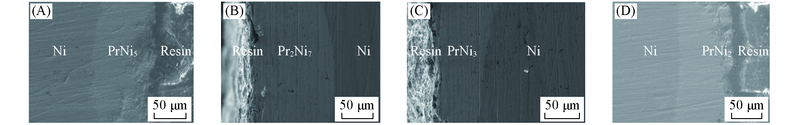
Fig.7 SEM images of Pr-Ni alloys by potentiostatic electrolysis on a Ni electrode(S=2.3 cm2) in LiCl-KCl-PrCl3[c(PrCl3)=1.25×10-4 mol/L] melt at 873 K (A) -1.2 V, 10 h; (B) -1.6 V, 8 h; (C) -1.8 V, 6 h; (D) -2.0 V, 2 h.
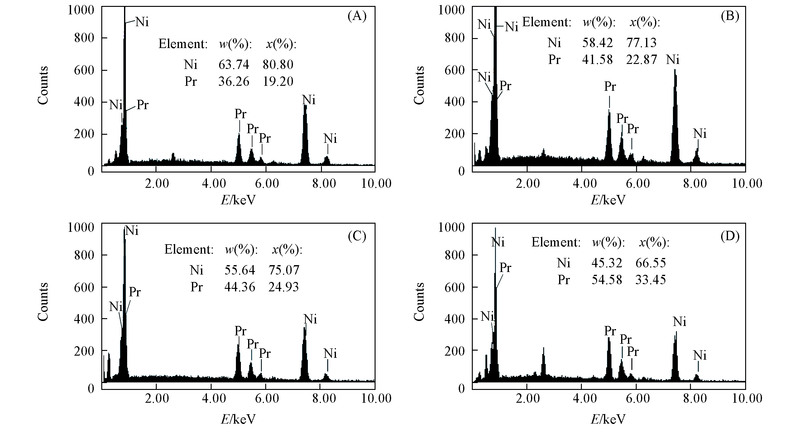
Fig.8 EDS analysis of Pr-Ni alloy by potentiostatic electrolysis on a Ni electrode(S=2.3 cm2) in the LiCl-KCl-PrCl3[c(PrCl3)=1.25×10-4 mol/L] melt at 873 K (A) -1.2 V, 10 h; (B) -1.6 V, 8 h; (C) -1.8 V, 6 h; (D) -2.0 V, 2 h.
| [1] | Yaropolov Y. L., Andreenko A. S., Nikitin S. A., Agafonov S. S., Glazkov V. P., Verbetsky V. N., J. Alloy Compd., 2011, 509(2), S830—S834 |
| [2] | Haraguchi T., Kogachi M., Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 329—331(1/2), 402—407 |
| [3] | Shahgaldi S., Yaakob Z., Jalil N. M., Tasirin S. M., J. Alloy Compd., 2012, 541, 335—337 |
| [4] | Prigent J., Toubert J. M., Gupta M., J. Solid State Chem., 2011, 184(1), 123—133 |
| [5] | Dhaou H., Askri F., Ben Salah M., Jemni A., Ben Nasrallah S., Lamloumi J., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32, 576—587 |
| [6] | Ao B. Y., Chen S. X., Jiang G. Q., J. Alloy Compd., 2005, 390(1/2), 122—126 |
| [7] | Bermejo M. R., Gomez J., Martinez A. M., Barrado E., Castrillejo Y., Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 53(16), 5106—5112 |
| [8] | Iida T., Nohira T., Ito Y., Electrochim. Acta, 2003, 48(11), 1531—1536 |
| [9] | Iida T., Nohira T., Ito Y., Electrochim. Acta, 2001, 46(16), 2537—2544 |
| [10] | Chamelot P., Massot L., Hamel C., Nourry C., Taxil P., J. Nucl. Mater., 2007, 360(1), 64—74 |
| [11] | Konishi H., Nohira T., Ito Y., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2001, 148(7), C506—C511 |
| [12] | Han W., Sheng Q. N., Zhang M. L., Li M., Sun T. T., Liu Y. C., Ye K., Yan Y. D., Wang Y. C., Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, 45(3), 929—935 |
| [13] | Hoshinoa H., Uchida H., Kimura H., Takamoto K., Hiraoka K., Matsumae Y., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2001, 26(8), 873—877 |
| [14] | Anantha M. V., Ganesan M., Renganathan N. G., Lakshmi S., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(1), 356—362 |
| [15] | Lucille L., Michel L., Bernard K., Patrick B., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(39), 19437—19444 |
| [16] | Nohira T., Kambara H., Amezawa K., Ito Y., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2005, 152(4), 183—189 |
| [17] | Tong Y. X., Yang Q. Q., Liu G. K., Wang X. B., J. Rare Earth, 1994, 18(6), 433—435 |
| (童叶翔, 杨绮琴, 刘冠昆, 王小波, 稀有金属, 1994, 18(6), 433—435) | |
| [18] | Yang Q. Q., Liu G. K., Tong Y. X., Liang G. C., Acta Metall. Sin., 1992, 28(3), B111—B114 |
| (杨绮琴, 刘冠昆, 童叶翔, 梁广超, 金属学报, 1992, 28(3), 111—114) | |
| [19] | Castrillejo Y., Hernández P., Rodriguez J. A., Vega M., Barrado E., Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 71, 166—172 |
| [20] | Tang H., Pesic B., Electrochim. Acta, 2014, 119, 120—130 |
| [21] | Vandarkuzhali S., Gogoi N., Ghosh S., Prabhakara Reddy B., Nagarajan K., Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 59, 245—255 |
| [22] | Kim S. H., Paek S., Kim T. J., Park D. Y., Ahn D. H., Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 85, 332—335 |
| [23] | Castrillejo Y., de la Fuente C., Vega M., de la Rosa F., Pardo R., Barrado E., Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 97, 120—131 |
| [24] | Caravaca C., de Córdoba G., Tomás M. J., Rosado M., J. Nucl. Mater., 2007, 360(1), 25—31 |
| [25] | Tang H., Pesic B., Electrochim. Acta, 2014, 133, 224—232 |
| [26] | Zhang M., Han W., Zhang M. L., Li Y. N., Zhu F. Y., Xue Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2014, 30(3), 489—494 |
| [27] | Chen L. J., Zhang M. L., Han W., Yan Y. D., Cao P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(2), 327—330 |
| (陈丽军, 张密林, 韩伟, 颜永得, 曹鹏, 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(2), 327—330) | |
| [28] | Yang Y. S., Zhang M. L., Han W., Sun P. Y., Liu B., Jiang H. L., Jiang T., Peng S. M., Li M., Ye K., Yan Y. D., Electrochim. Acta, 2014, 118, 150—156 |
| [29] | Hamel C., Chamelot P., Laplace A., Walle E., Dugne O., Taxil P., Electrochim. Acta, 2007, 52(12), 3995—4003 |
| [30] | Pan Y. Y., Nash P., Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams, 1989, 10(3), 253—257 |
| [1] | MA Jianxin, LIU Xiaodong, XU Na, LIU Guocheng, WANG Xiuli. A Multi-functional Zn(II) Coordination Polymer with Luminescence Sensing, Amperometric Sensing, and Dye Adsorption Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210585. |
| [2] | XIA Yan, CAO Fa-He, CHANG Lin-Rong, LIU Wen-Juan, ZHANG Jian-Qing. Corrosion Micro- and Macro-electrochemical Behavior of Rusted Carbon Steel and Weathering Steel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(5): 1246. |
| [3] | CHENG Jie, WEN Yue-Hua*, XU Yan, CAO Gao-Ping, YANG Yu-Sheng . Effects of Substrates on Deposition of Zinc from Flowing Alkaline Zincate Solutions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(11): 2640. |
| [4] | WANG Sui-Jun, ZHAO Yu-Juan, ZHAO Chun-Song, XIA Ding-Guo*. Synthesis and Electrochemical Behavior of Li-rich Cathode Materials Li[NixLi1/3-2x/3Mn2/3-x/3]O2(x=1/5, 1/4, 1/3) in the Lithium-ion Battery [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(12): 2358. |
| [5] | DONG She-Ying*, WANG Yuan, HUANG Ting-Lin, ZHOU Yuan-Zhen, ZHENG Jian-Bin. Electrochemical Behavior of Rutin in [bmim]BF4 Ionic Liquid and Influence Factors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(11): 2165. |
| [6] | XING Hai-Qing1,2, GUO Zhan-Cheng1,3*, WANG Zhi1, WANG Ming-Yong1. Electrochemical Behavior of Aqueous Electrochemical Reactions in Super Gravity Field [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(9): 1765. |
| [7] | ZHENG Jian-Bin, ZHANG Hong-Fang, ZHANG Xiu-Qi, GAO Hong. Electrochemical Behavior of Resveratrol and Its Interaction with DNA [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(9): 1635. |
| [8] | WEN Jing-Bang,ZHOU Hai-Hui,LUO Sheng-Lian,PANG Xin-Yu. Influences of Substrate Materials on Properties of Nano-fibrous Polyaniline Film Prepared by Pulse Galvanostatic Method [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(5): 948. |
| [9] | WANG Li, HUANG Bing-Qiang, XIE Zhao-Xiong. Preparation of Modified Electrode of Multilayer Films of Polyoxometalat K17[Ce(P2Mo17O61)2] and Its Electrochemical Behavior [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(3): 543. |
| [10] | TAN Xue-Cai, MAI Zhi-Bin, ZOU Xiao-Yong, QIU Jun-Ming, CAI Pei-Xiang. Electrochemical Behaviour of the Interaction Between Chitosan and Alizarin [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2005, 26(6): 1055. |
| [11] | SUN Zi-Jie, HU Jin-Bo, QIAN Yong-Gui, LU Yi-Qiang, LI Qi-Long. Studies on the Electrochemical Behavior of Methotrexate and Its Applicationat Co/GC Ion Implantation Modified Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2002, 23(4): 541. |
| [12] | YUAN Hua-Tang, CAO Jian-Sheng, WANG Yi-Jing, ZHOU Yong, Wu Xu-Li, LIU Jing-Wang. Study on Electrochemical Behavior of the Positive Electrode Mg1.2Mn1.8O4 in Magnesium Ion Battery [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2001, 22(S1): 16. |
| [13] | MAO Yan-Ning, HU Jing-Bo, LI Qi-Long, XUE Ping . Electrochemical Behavior and Application of Pirarubicin at Co Ion Implantation Modified Ultramicroelectrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2001, 22(8): 1310. |
| [14] | HU Jin-Bo, SHANG Jun, LI Qi-Long . Electrochemical Studies of Mitoxantrone Interaction with DNA at a Ni/GC Ion Implantation Modified Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2001, 22(5): 749. |
| [15] | CAO Ling-Hua, LIU Yu-Ting. The Oxidation of the Secondary Hydroxyl Group in Monosaccharides and Electrochemical Behavior of the Oxidants [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1996, 17(11): 1744. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||