

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (4): 717.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20130781
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Lingling, TIAN Ruixue, ZHAO Qing, CHANG Qing, HU Shengliang*( )
)
Received:2013-08-14
Online:2014-04-10
Published:2013-12-05
Contact:
HU Shengliang
E-mail:hsliang@yeah.net
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WU Lingling, TIAN Ruixue, ZHAO Qing, CHANG Qing, HU Shengliang. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Properties of the Composites Between Carbon Dots and Silver Nanostructures†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(4): 717.
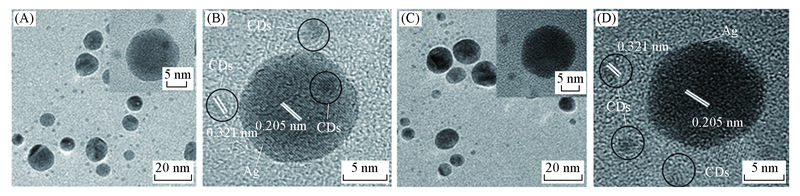
Fig.2 TEM(A, C) and HRTEM(B, D) images of CDs/Ag obtained by in-situ synthesis(A, B), by simple mixing(C, D) Insets in (A) and (C) are TEM images of typical single CDs/Ag obtained by in-situ synthesis and simple mixing.
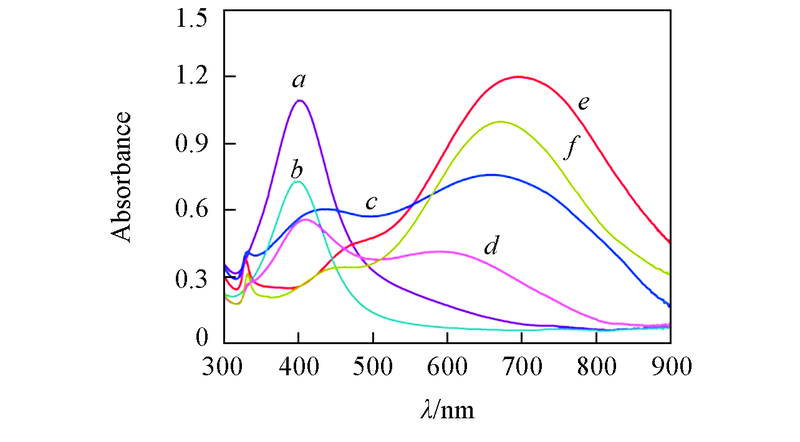
Fig.3 UV-Vis spectra of CDs/Ag obtained by in-situ synthesis and Aga. CDs/Ag(0 μL H2O2); b. Ag(0 μL H2O2); c. CDs/Ag(30 μL H2O2); d. Ag(30 μL H2O2); e. CDs/Ag(60 μL H2O2); f. Ag(60 μL H2O2).
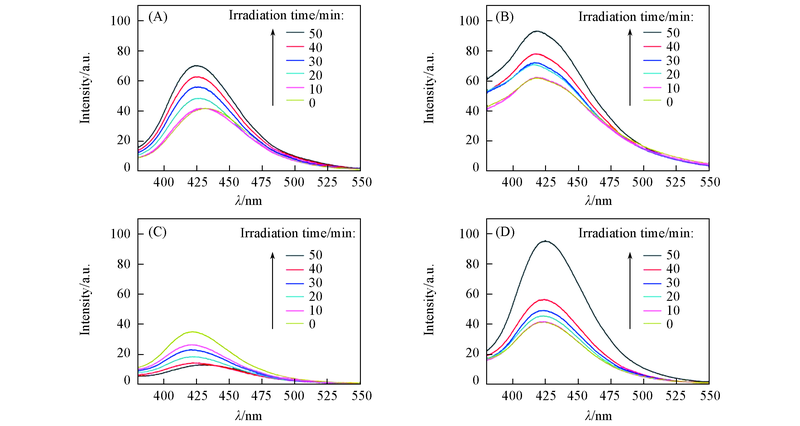
Fig.6 Fluorescence spectra of the visible-light irradiated CDs/Ag and Ag in TA at different irradiation time (A) Ag(0 μL H2O2); (B) Ag(60 μL H2O2); (C) CDs/Ag(0 μL H2O2); (D) CDs/Ag(60 μL H2O2).
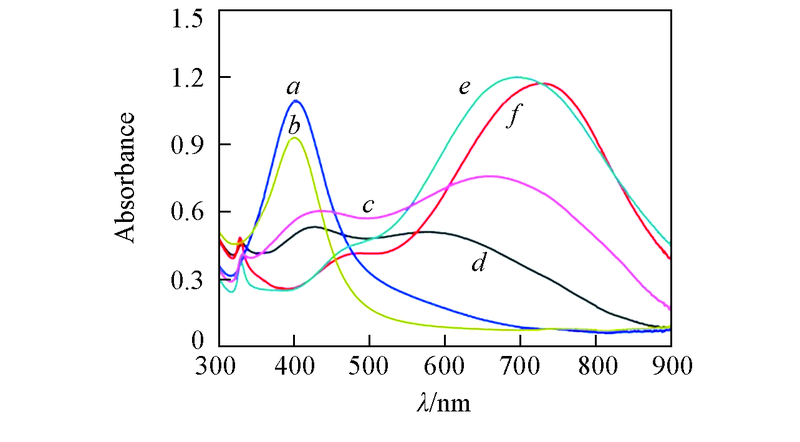
Fig.8 UV-Vis spectra of CDs-1/Ag(0 μL H2O2)(a), CDs-2/Ag(0 μL H2O2)(b), CDs-1/Ag(30 μL H2O2)(c), CDs-2/Ag(30 μL H2O2)(d), CDs-1/Ag(60 μL H2O2)(e), CDs-2/Ag(60 μL H2O2)(f)
| [1] | Baker S. N., Baker G. A., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49(38), 6726—6744 |
| [2] | Xu X., Ray R., Gu Y., Ploehn H. J., Gearheart L., Raker K., Scrivens W. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(40), 12736—12737 |
| [3] | Hu S. L., Bai P. K., Sun J., Cao S. R., Prog. Chem., 2010, 22(2/3), 345—351 |
| (胡胜亮, 白培康, 孙景, 曹士瑞. 化学进展, 2010, 22(2/3), 345—351) | |
| [4] | Sun Y. P., Zhou B., Lin Y., Wang W., Fernando K. A. S., Pathak P., Meziani M. J., Harruff B. A. , Wang X., Wang H. F., Luo P. G. , Yang H. , Kose M. E. , Chen B. L., Veca L. M., Xie S. Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128(24), 7756—7757 |
| [5] | Hu S. L., Bai P. K., Cao S. R., Sun J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2009, 30(8), 1497—1500 |
| (胡胜亮, 白培康, 曹士瑞, 孙景. 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30(8), 1497—1500) | |
| [6] | Ray S. C., Saha A., Jana N. R., Sarkar R., Phys. Chem. C,2009, 113, 18546—18551 |
| [7] | Cao L., Sahu S., Anilkumar P., Bunker C. E., Xu J., Fernando K. S., Wang P., Guliants E. A., Tackett K. N., Sun Y. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(13), 4754—4757 |
| [8] | Li H. T., He X. D., Kang Z. H., Huang H., Liu Y., Liu J. L., Lian S. Y., Tsang C. H., Yang X. B., Lee S. T., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 4430—4434 |
| [9] | Yu B. Y., Kwak S. Y., J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 8345—8353 |
| [10] | Xing Y. Y., Li Q. Y.,Yang J. J., J. Funct. Mater., 2012, 43(16), 2126—2130 |
| (邢阳阳, 李秋叶, 杨建军. 功能材料, 2012, 43(16), 2126—2130) | |
| [11] | Chan S. C., Barteau M. A., Langmuir,2005, 21(12), 5588—5595 |
| [12] | Chen Y.Y., Wang C. A., Liu H. Y., Qiu J. S., Bao X. H.,Chem.Commun., 2005, (42), 5298—5300 |
| [13] | Zheng Y. H., Zheng L. R., Zhan Y. Y., Lin X. Y., Zheng Q., Wei K. M., Inorg. Chem., 2007, 46(17), 6980—6986 |
| [14] | Li H. T., Kang Z. H., Liu Y., Lee S. T., J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 24230—24253 |
| [15] | Yu H., Zhang H. C., Huang H., Liu Y., Li H. T., Ming H., Kang Z. H., New J. Chem., 2012, 36, 1031—1035 |
| [16] | Guo Y., Tian R. X., Dong Y. G., Hu S. L., Chin. J. Lumin., 2012, 33(2), 155—160 |
| (郭艳, 田瑞雪, 董英鸽, 胡胜亮. 发光学报, 2012, 33(2), 155—160) | |
| [17] | Zhang Q., Li N., Goebl J., Lu Z., Yin Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(46), 18931—18939 |
| [18] | Liu G., Wang L. Z, , Sun C. H., Yan X. X., Wang X. W., Chen Z. G., Smith S. C., Cheng H. M., Lu G. Q., Chem. Mater., 2009, 21, 1266—1270 |
| [19] | Hirakawa T., Nosaka Y., Langmuir,2002, 18(8), 3247—3254 |
| [20] | Kowalska E., Mahaney O. O. P., Abe R., Ohtani B., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12, 2344—2355 |
| [21] | Tanaka A., Hashimoto K., Kominami H., Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 10446—10448 |
| [22] | Gao L., Zheng S., Zhang Q.H., Photocatalytic Nanomaterials of Titanium Dioxide and Their Applications, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2002, 44—52 |
| (高濂, 郑珊, 张青红. 纳米氧化钛光催化材料及应用, 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2002, 44—52) | |
| [23] | Subramanian V., Wolf E. E., Kamat P. V., J. Am.Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(15), 4943—4950 |
| [1] | YUAN Chunling, YAO Xiaotiao, XU Yuanjin, QIN Xiu, SHI Rui, CHENG Shiqi, WANG Yilin. Colorimetry/Ratio Fluorimetry Determination of Glucose with Bifunctional Carbon Dots [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2428. |
| [2] | DING Hui, ZHOU Xuanxuan, ZHANG Zihui, XIA Kunlin, ZHAO Yunpeng. Solvent-free and High-yielding Synthesis of Highly Efficient Red-emitting Carbon Dots and Their Application in White Light Devices [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2080. |
| [3] | SUN Haizhu, YANG Guoduo, YANG Bai. Synthesis, Structure Control and Applications of Carbon Dots [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 349. |
| [4] | XUE Yarong, LI Hongwei, WU Yuqing. Carbon Dots Based-on Polyethyleneimines as a Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensor of Morin† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1531. |
| [5] | ZHOU Sihui, LI Qiong, ZHANG Ting, PANG Daiwen, TANG Hongwu. Luminescent Nanoswitch Based on Carbon Dots for Sensitive Detection of Cu(Ⅱ) Ions and Pyrophosphates [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1593. |
| [6] | DONG Xiangyang,NIU Xiaoqing,WEI Jishi,XIONG Huanming. One-step Hydrothermal Synthesis of Copper Doped Carbon Dots and Their Application in White Light Devices† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1288. |
| [7] | ABUDUHEIREMU Awati,ZHANG Dedong,HALIDAN Maimaiti. Preparation and CO2 Reduction Performance of Composite Photocatalyst Based on Aminated Coal-based Carbon Dots† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 306. |
| [8] | ZHAO Zu, LI Rui, ZHANG Xiaochao, ZHANG Changming, LIU Jianxin, WANG Yawen, WANG Yunfang, FAN Caimei. Electrochemical In-situ Synthesis and Photocatalytic Properties of BiF3 Thin Films† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1775. |
| [9] | XU Yuan, CHEN Yanhua, DING Lan. One-pot Microwave-assisted Synthesis of Passivated Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Fe(Ⅲ) Detection† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1420. |
| [10] | DING Yanli, HU Shengliang, CHANG Qing. Preparation and Characterization of Composites of Amine-functionalized Carbon Dots and Zinc Phthalocyaine† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(4): 619. |
| [11] | HE Liwen, LIN Bizhou, ZHANG Guohua, YAO Qianru. Preparation and Photocatalytic Activity of Fe-Doped Hydroxyl-Zr Pillared Titanate† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 1984. |
| [12] | SHAO Kerang, LI Jianjiao, AN Xingcai, LEI Ziqiang, SU Bitao. Preparation and Visible-light Catalytic Property of Ag+/Ag/ZnOPorous Nano-structured Fiber Materials† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(7): 1523. |
| [13] | WANG Jin-Gang, JI Ping-Li, KONG Xiang-Zheng. Preparation of Ag/AgCl-TiO2 Hollow Nanoparticles by Co-precipitation and Their Photocatalytic Property [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(11): 2635. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||