

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (11): 2375.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190258
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Yapan,SUN Xiaogang( ),LI Rui,LIANG Guodong,WEI Chengcheng,HU Hao
),LI Rui,LIANG Guodong,WEI Chengcheng,HU Hao
Received:2019-05-06
Online:2019-11-10
Published:2019-07-15
Contact:
SUN Xiaogang
E-mail:xiaogangsun@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HUANG Yapan, SUN Xiaogang, LI Rui, LIANG Guodong, WEI Chengcheng, HU Hao. Suppression of Shuttle Effect of Lithium-sulfur Batteries by Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine Interlayer †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11): 2375.
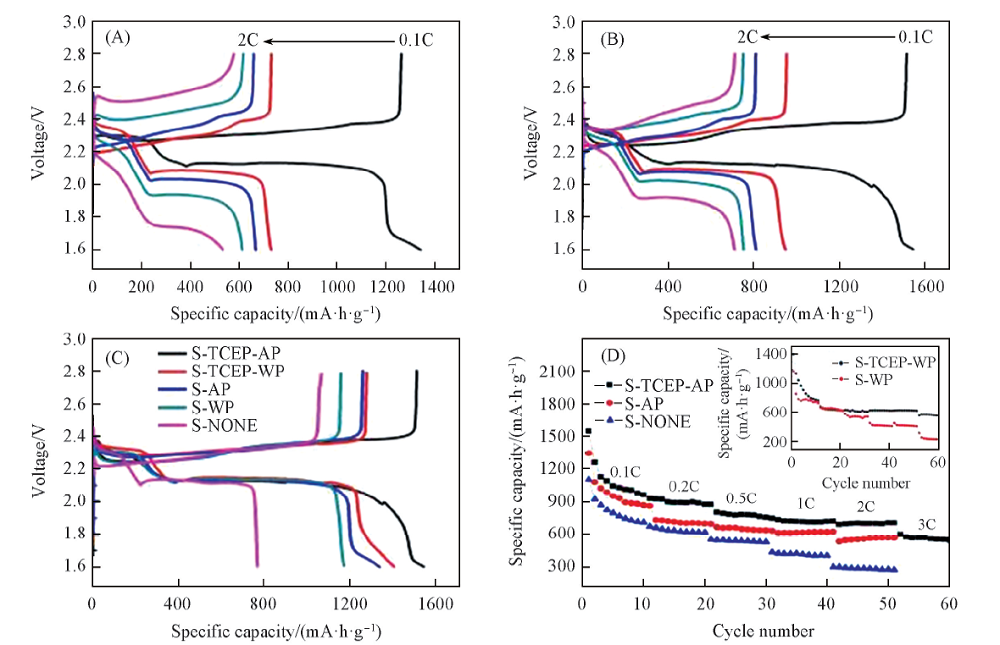
Fig.7 The first cycle charge/discharge curves at 0.1C, 0.2C, 0.5C, 1C, 2C of S-AP(A), S-TCEP-AP(B) lithium-sulfur batteries, the first cycle charge/discharge curves at 0.1C(C) and rate capability(D) of different lithium-sulfur batteries
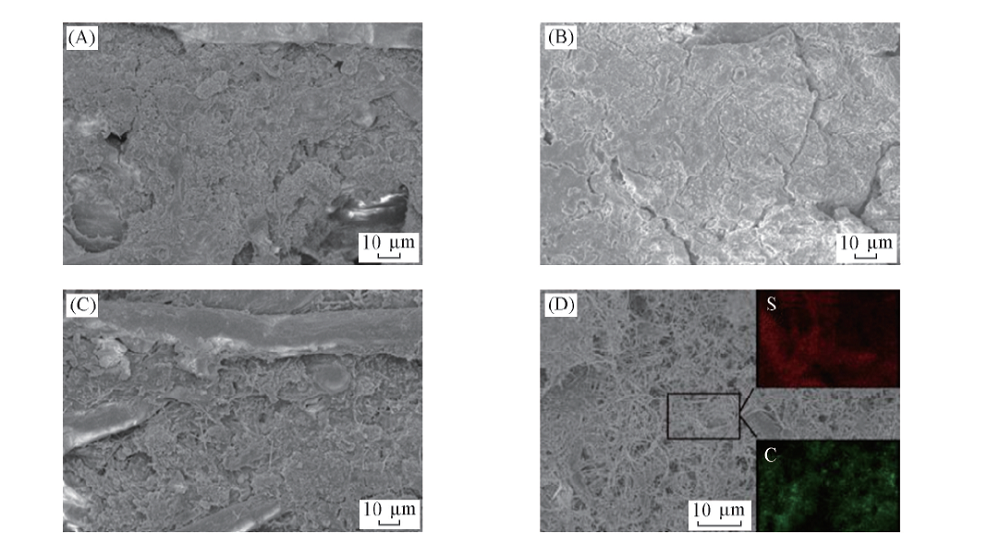
Fig.10 SEM images of cathodes of S-NONE(A), S-AP(B) and S-TCEP-AP(C) after 50 cycles and SEM(D) and element mapping(insets) images of TCEP-AP after 50 cycles
| [1] | Tarascon J. M., Armand M, Nature, 2001,414(6861), 359— 67 |
| [2] | Armand M., Tarascon J. M., Nature, 2008,451(7179), 652— 657 |
| [3] | Kang K ., Science, 2006,311(5763), 977— 980 |
| [4] | Huang J. Q., Peng H. J., Liu X. Y., Nie J. Q., Cheng X. B., Zhang, Q., Wei F., Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014,2(28), 10869— 10875 |
| [5] | Diao Y., Xie K., Xiong S., Hong X. J ., Journal of Power Sources, 2013,235(4), 181— 186 |
| [6] | Xiong S. Z., Xie K., Hong X. B., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011,32(11), 2645— 2649 |
| ( 熊仕昭, 谢凯, 洪晓斌 . 高等学校化学学报, 2011,32(11), 2645— 2649 | |
| [7] | Chen K ., Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2018,34(4), 377— 390 |
| [8] | Evers S., Nazar L. F., Accounts of Chemical Research, 2012,46(5), 1135— 1143 |
| [9] | Jayaprakash N., Shen J., Moganty S. S., Corona A., Archer L. A., Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011,123(96), 6026— 6030 |
| [10] | Suo L., Hu Y. S., Li H., Armand M., Chen L., Nature Communications, 2013,4(1), 1481— 1489 |
| [11] | Singhal R., Chung S. H., Manthiram A., Kalra V., Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015,3(8), 4530— 4538 |
| [12] | Zhou G. M, Li L., Wang D. W., Shan X. Y., Pei S. F., Li F., Advanced Materials, 2015,27(4), 641— 647 |
| [13] | Su Y. S., Manthiram A., Chemical Communications, 2012,48(70), 8817— 8822 |
| [14] | Zhou G., Pei S., Li L., Wang D. W., Wang S., Huang K., Advanced Materials, 2014,26(4), 625— 631 |
| [15] | Manthiram A., Chung S. H., Zu C., Advanced Materials, 2015,27(12), 1980— 2006 |
| [16] | Tao X., Wang J., Liu C., Wang H., Yao H., Zheng G ., Nature Communications, 2016,7(3), 11203— 11208 |
| [17] | Yuan Z., Peng H. J., Hou T. Z., Huang J. Q., Chen C. M., Wang D. W., Nano Letters, 16(1), 519— 527 |
| [18] | Pang Q., Kundu D., Cuisinier M., Nazar L. F., Nature Communications, 2014,5, 4759— 4767 |
| [19] | Seh Z. W., Yu J. H., Li W., Hsu P. C., Wang H., Sun Y., Nature Communications, 2014,5, 5017— 5025 |
| [20] | Pang Q., Kundu D., Nazar L. F., Materials Horizons, 2016,3(2), 130— 136 |
| [21] | Yuan Z., Peng H. J., Hou T. Z., Huang J. Q., Chen C. M., Wang D. W., Nano Letters, 2016,16(1), 519— 527 |
| [22] | Burns J. A., Butler J. C., Moran J., Whitesides G. M., Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1991,22(39), 2648— 2650 |
| [23] | Zhao M. Q., Zhang Q., Huang J. Q., Tian G. L., Nie J. Q., Peng H. J., Nature Communications, 2014,5(5), 3410— 3418 |
| [24] | Hesham A. S., Ganguli B., Rao C. V., Arava M. R., Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015,137(36), 11542— 11547 |
| [25] | Xiao Z., Yang Z., Wang L., Nie H. G., Zhong M., Lai Q. Q., Xu X. G., Zhang L. G., Huang S. M., Advanced Materials, 2015,27(18), 2891— 2898 |
| [26] | Cleland W. W., Biochemistry, 1964,3(4), 480— 482 |
| [27] | Chen W ., Acta Chimica Sinica, 1965,31(1), 29— 37 |
| [1] | HAN Fuchao, LI Fujin, CHEN Liang, HE Leiyi, JIANG Yunan, XU Shoudong, ZHANG Ding, QI Lu. Enhance of CoSe2/C Composites Modified Separator on Electrochemical Performance of Li-S Batteries at High Sulfur Loading [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220163. |
| [2] | ZHANG Shiyu, HE Runhe, LI Yongbing, WEI Shijun, ZHANG Xingxiang. Fabrication of Lithium-sulfur Battery Cathode with Radiation Crosslinked Low Molecular Weight of Polyacrylonitrile and the Mechanism of Sulfur Storage [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210632. |
| [3] | CHEN Mingsu, ZHANG Huiru, ZHANG Qi, LIU Jiaqin, WU Yucheng. First-principles Study on the Catalytic Effect of Co,P co-Doped MoS2 in Lithium-sulfur Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2540. |
| [4] | ZHUO Zengqing, PAN Feng. Progress of Key Electronic States in Lithium Ion Battery Materials Probed Through Soft X-ray Spectroscopy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2332. |
| [5] | GENG Chuannan, HUA Wuxing, LING Guowei, TAO Ying, ZHANG Chen, YANG Quanhong. Catalysis in Li-sulfur Battery: Materials and Characterization [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1331. |
| [6] | LI Rui, SUN Xiaogang, ZOU Jingyi, HE Qiang. High Performance Lithium-sulfur Battery with Hydroxyapatite Nanowire Composite Interlayer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1866. |
| [7] | WU Tong, CONG Lina, SUN Liqun, XIE Haiming. Application of Porous Black Titanium Dioxide with Oxygen Vacancy/Polyethylene as a Composite Separator for Lithium Sulfur Batteries† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1661. |
| [8] | WANG Jie, SUN Xiaogang, CHEN Wei, LI Xu, HUANG Yapan, WEI Chengcheng, HU Hao, LIANG Guodong. Electrochemical Performance of Hydroxylated Multi-walled Carbon Nanotube Sandwich Separator in Lithium-sulfur Battery† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1782. |
| [9] | LI Xiang,WANG Huiying,WANG Hongqiang,YE Jinting,QIU Yongqing. Theoretical Studies on the Second-order Nonlinear Optical Properties of RuⅡ/Ⅲ Complexes of Bipyridyl† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2221. |
| [10] | HUANG Xiao, GAN Hanlin, PENG Liang, GU Fenglong. Theoretical Study on the Selective Redox Mechanism of Benzaldehyde in Photo-catalyzed Reaction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(2): 297. |
| [11] | SUN Shuheng, WU Ying, ZHOU Weilong, CHEN Youchun, LI Fenghong. Fabrication and Performance of Organic Optoelectronic Devices with Alkali Metal Salts as a Cathode Interlayer† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(2): 349. |
| [12] | LUO Yanling, LIU Yajun. Role of Superoxide in Bioluminescence† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(1): 24. |
| [13] | LIANG Li-Zhi, WU Ying, SHI Jing-Long, KANG Bo-Nan*. New Buffer Interlayer for Improving Device Performances of Organic Photovoltaics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(8): 1661. |
| [14] | XIONG Shi-Zhao, XIE Kai*, HONG Xiao-Bin. Effect of LiNO3 as Additive on Electrochemical Properties of Lithium\|sulfur Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(11): 2645. |
| [15] | ZHU Xiao-Dong1, SUN Ke-Ning1*, ZHANG Nai-Qing1,2, CHEN Xin-Bing1, FU Qiang1, JIA De-Chang2. Investigation of Novel Anode NiO-La0.3Ce0.7O2-δ of IT-SOFC with LSGM-based Electrolyte [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(5): 824. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||