

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (9): 1832.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190256
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Nanxi,LV Jingwei,JIN Ping,LI Jingfeng,BIAN Xuefeng,ZHANG Hui( ),SUN Jiaming(
),SUN Jiaming( )
)
Received:2019-05-05
Online:2019-09-10
Published:2019-07-19
Contact:
ZHANG Hui,SUN Jiaming
E-mail:zhanghui_8080@163.com;sun_jiaming2000@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHANG Nanxi, LV Jingwei, JIN Ping, LI Jingfeng, BIAN Xuefeng, ZHANG Hui, SUN Jiaming. 1H NMR Metabonomic Investigations of N-Benzylhexadecanamide Induced Proliferation and Iestosterone Secretion of Mouse Testicular Leydig Cells†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1832.
| Group code | Concentration of NBH/(μg·mL-1) | Cell viablility rate(%) | Testosteron secretion/(nmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0 | 100±1.73** | 15.70±0.85** |
| NBH | 62.5 | 121.49±1.59** | 24.50±1.77** |
| NBH | 125.0 | 125.82±2.12* | 28.71±2.08** |
| NBH | 250.0 | 130.54±1.93** | 31.10±1.93** |
| Group code | Concentration of NBH/(μg·mL-1) | Cell viablility rate(%) | Testosteron secretion/(nmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0 | 100±1.73** | 15.70±0.85** |
| NBH | 62.5 | 121.49±1.59** | 24.50±1.77** |
| NBH | 125.0 | 125.82±2.12* | 28.71±2.08** |
| NBH | 250.0 | 130.54±1.93** | 31.10±1.93** |
| No. | Name | δ |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pantothenic acid | 0.90(s), 0.94(s), 3.96(s) |
| 2 | Leucine | 0.96(d), 0.97(d), 1.68(m), 3.74(m) |
| 3 | Valine | 0.99(d, 7.0), 1.01(d, 7.0), 1.04(d) |
| 4 | 3-Hydroxybutyrate | 1.15(d, 6.0) |
| 5 | Ethanol | 1.19(t, 7.2), 3.65(q) |
| 6 | Lipid | 1.27(m), 2.0(m), 4.24(m) |
| 7 | Lactate | 1.33(d), 4.11(q) |
| 8 | Alanine | 1.48(d, 7.2), 3.78(m) |
| 9 | Lysine | 1.72(m), 1.89(m), 3.04(t, J=7.57 Hz), 3.76(t, J=6.11 Hz) |
| 10 | Acetic acid | 1.92(s) |
| 11 | Pyroglutamate | 2.06(m), 2.35(m) |
| 12 | Glutamate | 2.09(m), 2.13(m), 2.36(m), 2.46(m) |
| 13 | Methionine | 2.14(s), 2.65(t) |
| 14 | Citrate | 2.53(d), 2.69(d) |
| 15 | Dimethylamine | 2.73(s) |
| 16 | Sarcosine | 2.76(s), 3.60(s) |
| 17 | Aspartate | 2.85(dd, 17.3, 3.7), 3.91(m) |
| No. | Name | δ |
| 18 | Glutathione | 2.16(m), 2.56(m), 2.94(m) |
| 19 | Creatine | 3.03s, 3.23(s), 3.93s |
| 20 | Ethanolamine | 3.12(t, 5.5 Hz), 3.15(t, J=7.2 Hz), 3.86(t) |
| 21 | Malonate | 3.15(s) |
| 22 | O-Phosphocholine | 3.21(s) |
| 23 | Phosphocholine | 3.22(s), 3.59(m), 4.17(m) |
| 24 | Histidine | 3.25(dd), 7.08(s), 7.82(s) |
| 25 | Betaine | 3.27(s) |
| 26 | Inositol | 3.28(t, J=9.0 Hz), 3.63(t, J=9.6 Hz), 4.07(t, J=3.0 Hz) |
| 27 | Scyllo-inositol | 3.37(s) |
| 28 | Taurine | 3.44(t) |
| 29 | Methyl phosphate | 3.47(d, 10.2) |
| 30 | Glycero | 3.55(dd, 4.2, 9.6), 3.66(dd, 4.2, 11.4) |
| 31 | Glycine | 3.57(s), 3.68(s) |
| 32 | Threonine | 1.33(d), 3.58(d), 4.25(m) |
| 33 | Hippurate | 3.97(d, 6.0), 7.54(t) |
| 34 | Adenosine monophosphate | 4.01(m), 4.37(m), 4.51(m), 6.14(d), 8.27(s), 8.61(s) |
| 35 | Adenosine | 4.30(dd), 8.24(s), 8.35(s) |
| 36 | Inosine | 4.28(m), 4.44(m), 6.11(d), 8.23(s), 8.34(s) |
| 37 | Lactose | 4.46(d), 4.66(d, J=7.8 Hz) |
| 38 | β-Glucose | 4.50(d, 7.9) |
| 39 | α-Glucose | 5.24(d, 3.6) |
| 40 | Urea | 5.81(s) |
| 41 | Uracil | 5.81(d, J=9.0 Hz) |
| 42 | Guanosine monophosphate | 5.94(d), 8.20(s) |
| 43 | Uridine monophosphate | 6.00(m), 8.11(d) |
| 44 | Cytidine | 6.08(d), 7.85(d) |
| 45 | Fumaric acid | 6.52(s) |
| 46 | Tyrosine | 6.89(d), 7.19(d) |
| 47 | Tryptophan | 7.33(d) |
| 48 | Phenylacetylglycine | 3.68(s), 7.37(m), 7.43(m) |
| 49 | Uridine | 7.92(d, 8.2) |
| 50 | Inosine monophosphate | 8.25(s), 8.58(s) |
| 51 | Formate | 8.46(s) |
| No. | Name | δ |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pantothenic acid | 0.90(s), 0.94(s), 3.96(s) |
| 2 | Leucine | 0.96(d), 0.97(d), 1.68(m), 3.74(m) |
| 3 | Valine | 0.99(d, 7.0), 1.01(d, 7.0), 1.04(d) |
| 4 | 3-Hydroxybutyrate | 1.15(d, 6.0) |
| 5 | Ethanol | 1.19(t, 7.2), 3.65(q) |
| 6 | Lipid | 1.27(m), 2.0(m), 4.24(m) |
| 7 | Lactate | 1.33(d), 4.11(q) |
| 8 | Alanine | 1.48(d, 7.2), 3.78(m) |
| 9 | Lysine | 1.72(m), 1.89(m), 3.04(t, J=7.57 Hz), 3.76(t, J=6.11 Hz) |
| 10 | Acetic acid | 1.92(s) |
| 11 | Pyroglutamate | 2.06(m), 2.35(m) |
| 12 | Glutamate | 2.09(m), 2.13(m), 2.36(m), 2.46(m) |
| 13 | Methionine | 2.14(s), 2.65(t) |
| 14 | Citrate | 2.53(d), 2.69(d) |
| 15 | Dimethylamine | 2.73(s) |
| 16 | Sarcosine | 2.76(s), 3.60(s) |
| 17 | Aspartate | 2.85(dd, 17.3, 3.7), 3.91(m) |
| No. | Name | δ |
| 18 | Glutathione | 2.16(m), 2.56(m), 2.94(m) |
| 19 | Creatine | 3.03s, 3.23(s), 3.93s |
| 20 | Ethanolamine | 3.12(t, 5.5 Hz), 3.15(t, J=7.2 Hz), 3.86(t) |
| 21 | Malonate | 3.15(s) |
| 22 | O-Phosphocholine | 3.21(s) |
| 23 | Phosphocholine | 3.22(s), 3.59(m), 4.17(m) |
| 24 | Histidine | 3.25(dd), 7.08(s), 7.82(s) |
| 25 | Betaine | 3.27(s) |
| 26 | Inositol | 3.28(t, J=9.0 Hz), 3.63(t, J=9.6 Hz), 4.07(t, J=3.0 Hz) |
| 27 | Scyllo-inositol | 3.37(s) |
| 28 | Taurine | 3.44(t) |
| 29 | Methyl phosphate | 3.47(d, 10.2) |
| 30 | Glycero | 3.55(dd, 4.2, 9.6), 3.66(dd, 4.2, 11.4) |
| 31 | Glycine | 3.57(s), 3.68(s) |
| 32 | Threonine | 1.33(d), 3.58(d), 4.25(m) |
| 33 | Hippurate | 3.97(d, 6.0), 7.54(t) |
| 34 | Adenosine monophosphate | 4.01(m), 4.37(m), 4.51(m), 6.14(d), 8.27(s), 8.61(s) |
| 35 | Adenosine | 4.30(dd), 8.24(s), 8.35(s) |
| 36 | Inosine | 4.28(m), 4.44(m), 6.11(d), 8.23(s), 8.34(s) |
| 37 | Lactose | 4.46(d), 4.66(d, J=7.8 Hz) |
| 38 | β-Glucose | 4.50(d, 7.9) |
| 39 | α-Glucose | 5.24(d, 3.6) |
| 40 | Urea | 5.81(s) |
| 41 | Uracil | 5.81(d, J=9.0 Hz) |
| 42 | Guanosine monophosphate | 5.94(d), 8.20(s) |
| 43 | Uridine monophosphate | 6.00(m), 8.11(d) |
| 44 | Cytidine | 6.08(d), 7.85(d) |
| 45 | Fumaric acid | 6.52(s) |
| 46 | Tyrosine | 6.89(d), 7.19(d) |
| 47 | Tryptophan | 7.33(d) |
| 48 | Phenylacetylglycine | 3.68(s), 7.37(m), 7.43(m) |
| 49 | Uridine | 7.92(d, 8.2) |
| 50 | Inosine monophosphate | 8.25(s), 8.58(s) |
| 51 | Formate | 8.46(s) |
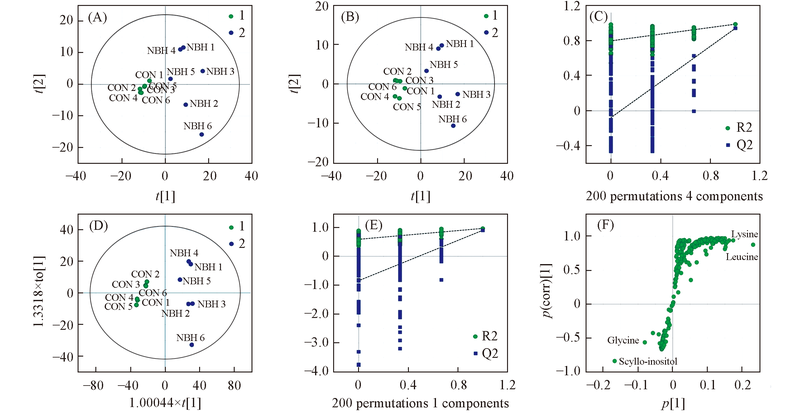
Fig.1 PCA score plot(A), PLS score plot(B), the PLS-DA permutation test(C), OPLS-DA score plots(D), the OPLS-DA permutation test(E) and S-plot(F) based on 1H NMR-metabolomics of cell from the control group() and NBH treatedgroup()
| No. | Metabolites | VIP | FC | P-value | Trenda | Related pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pantothenic acid | 1.70 | 4.20 | 3.65×10-5 | ↑** | Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis |
| 2 | Leucine | 3.36 | 9.11 | 3.57×10-4 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis |
| 3 | Valine | 2.27 | 9.52 | 1.89×10-3 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, pantothenate |
| and CoA biosynthesis | ||||||
| 6 | Lipid | 1.67 | 9.06 | 3.10×10-5 | ↑** | - |
| 7 | Lactate | 1.42 | 4.06 | 3.86×10-3 | ↑** | Pyruvate metabolism |
| 8 | Alanine | 2.25 | 9.68 | 1.14×10-3 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, alanine, aspar- |
| tate and glutamate metabolism | ||||||
| 9 | Lysine | 2.46 | 11.12 | 2.61×10-5 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis |
| Lysine degradation | ||||||
| 10 | Acetic acid | 2.21 | 12.07 | 2.37×10-4 | ↑** | Pyruvate metabolism |
| 11 | Pyroglutamate | 1.97 | 5.44 | 1.63×10-5 | ↑** | Glutathione metabolism |
| 12 | Glutamate | 1.78 | 6.95 | 1.04×10-5 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, glutathione metabolism, alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism, D-glutamine and D-glutamate metabolism |
| 13 | Methionine | 1.68 | 6.89 | 2.25×10-4 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis |
| 17 | Aspartate | 1.42 | 4.01 | 3.64×10-6 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism, pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism |
| 18 | Glutathione | 1.08 | 18.44 | 1.87×10-5 | ↑** | Glutathione metabolism |
| 20 | Ethanolamine | 1.09 | 4.45 | 1.08×10-5 | ↑** | Glycerophospholipid metabolism |
| 21 | Malonate | 1.64 | 3.84 | 1.21×10-3 | ↑** | - |
| 23 | Phosphocholine | 2.02 | 2.86 | 3.41×10-5 | ↑** | Glycerophospholipid metabolism |
| 26 | Inositol | 1.66 | 6.59 | 2.38×10-4 | ↑** | Inositol phosphate metabolism |
| 27 | Scyllo-inositol | 2.36 | 0.17 | 4.76×10-4 | ↓** | - |
| 31 | Glycine | 1.14 | 0.67 | 4.67×10-2 | ↓* | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, glutathione metabolism, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, lysine degradation |
| No. | Metabolites | VIP | FC | P-value | Trenda | Related pathway |
| 32 | Threonine | 1.42 | 4.06 | 3.86×10-3 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, glycine, serine |
| and threonine metabolism | ||||||
| 34 | Adenosine monophosphate | 1.16 | 4.30 | 2.00×10-5 | ↑** | |
| 35 | Adenosine | 1.23 | 4.37 | 2.27×10-5 | ↑** | |
| 36 | Inosine | 1.06 | 4.62 | 4.67×10-5 | ↑** | |
| 48 | Phenylacetylglycine | 1.14 | 0.67 | 4.67×10-2 | ↓* |
| No. | Metabolites | VIP | FC | P-value | Trenda | Related pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pantothenic acid | 1.70 | 4.20 | 3.65×10-5 | ↑** | Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis |
| 2 | Leucine | 3.36 | 9.11 | 3.57×10-4 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis |
| 3 | Valine | 2.27 | 9.52 | 1.89×10-3 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, pantothenate |
| and CoA biosynthesis | ||||||
| 6 | Lipid | 1.67 | 9.06 | 3.10×10-5 | ↑** | - |
| 7 | Lactate | 1.42 | 4.06 | 3.86×10-3 | ↑** | Pyruvate metabolism |
| 8 | Alanine | 2.25 | 9.68 | 1.14×10-3 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, alanine, aspar- |
| tate and glutamate metabolism | ||||||
| 9 | Lysine | 2.46 | 11.12 | 2.61×10-5 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis |
| Lysine degradation | ||||||
| 10 | Acetic acid | 2.21 | 12.07 | 2.37×10-4 | ↑** | Pyruvate metabolism |
| 11 | Pyroglutamate | 1.97 | 5.44 | 1.63×10-5 | ↑** | Glutathione metabolism |
| 12 | Glutamate | 1.78 | 6.95 | 1.04×10-5 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, glutathione metabolism, alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism, D-glutamine and D-glutamate metabolism |
| 13 | Methionine | 1.68 | 6.89 | 2.25×10-4 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis |
| 17 | Aspartate | 1.42 | 4.01 | 3.64×10-6 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism, pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism |
| 18 | Glutathione | 1.08 | 18.44 | 1.87×10-5 | ↑** | Glutathione metabolism |
| 20 | Ethanolamine | 1.09 | 4.45 | 1.08×10-5 | ↑** | Glycerophospholipid metabolism |
| 21 | Malonate | 1.64 | 3.84 | 1.21×10-3 | ↑** | - |
| 23 | Phosphocholine | 2.02 | 2.86 | 3.41×10-5 | ↑** | Glycerophospholipid metabolism |
| 26 | Inositol | 1.66 | 6.59 | 2.38×10-4 | ↑** | Inositol phosphate metabolism |
| 27 | Scyllo-inositol | 2.36 | 0.17 | 4.76×10-4 | ↓** | - |
| 31 | Glycine | 1.14 | 0.67 | 4.67×10-2 | ↓* | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, glutathione metabolism, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, lysine degradation |
| No. | Metabolites | VIP | FC | P-value | Trenda | Related pathway |
| 32 | Threonine | 1.42 | 4.06 | 3.86×10-3 | ↑** | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, glycine, serine |
| and threonine metabolism | ||||||
| 34 | Adenosine monophosphate | 1.16 | 4.30 | 2.00×10-5 | ↑** | |
| 35 | Adenosine | 1.23 | 4.37 | 2.27×10-5 | ↑** | |
| 36 | Inosine | 1.06 | 4.62 | 4.67×10-5 | ↑** | |
| 48 | Phenylacetylglycine | 1.14 | 0.67 | 4.67×10-2 | ↓* |
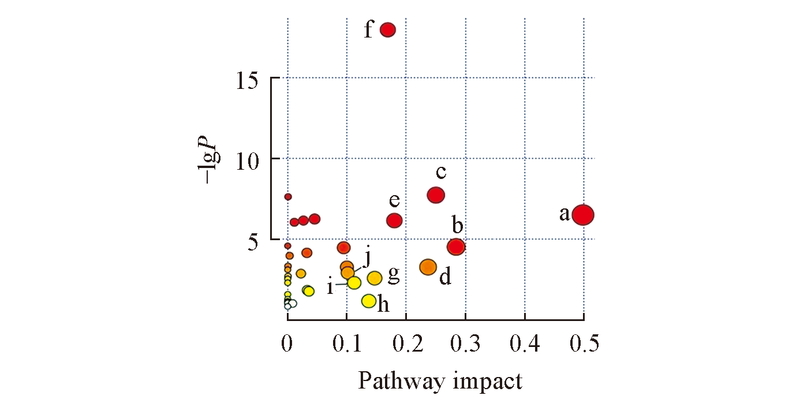
Fig.2 Themetabolome view of the NBH treated group and the control groupa. Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism; b. glycine, serine and threonine metabolism; c. glutathione metabolism; d. pyruvate metabolism; e. pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis; f. aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis; g. lysine degradation; h. inositol phosphate metabolism; i. D-glutamine and D-glutamate metabolism; j. glycerophospholipid metabolism.
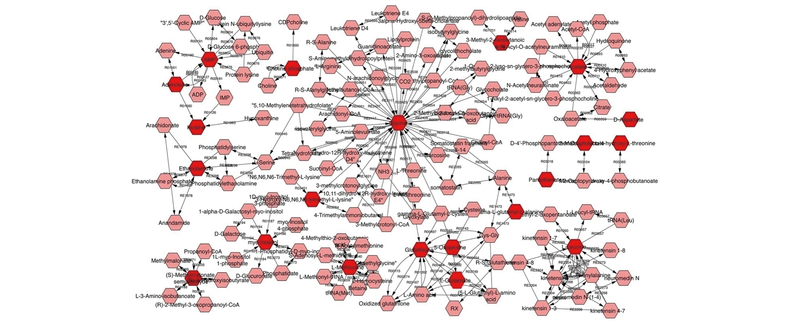
Fig.3 Network of potential biomarkers of the proliferation and testosterone secretion effects on mouse testicular Leydig cells treated by NBH using the metscape analysis
| [1] | Gonzales G. F., Leonidas V., Gasco M., Rubio J., Gonzales C., Rev. Peru. Med. Exp. Salud Publica., 2014, 31(1), 100-110 |
| [2] | Mccollom M. M., Villinski J. R., Mcphail K. L., Craker L. E., Gafner S., Phytochem.Anal.,2010, 16(6), 463-469 |
| [3] | Muhammad I., Zhao J., Dunbar D. C., Khan I. A., Phytochem.,2002, 59(1), 105-110 |
| [4] | Mccollom M. M., Villinski J. R., Mcphail K. L., Craker L. E., Gafner S., Phytochem.Anal.,2010, 16(6), 463-469 |
| [5] | Hajdu Z., Nicolussi S., Rau M.,L szl Lor ntfyForgo P., Hohmann J., Journal of Natural Products,2014, 77(7), 1663-1669 |
| [6] | Wu H., Kelley C. J., Pino-Figueroa A., Vu H. D., Maher T. J., Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry,2013, 21(17), 5188-5197 |
| [7] | Uchiyama F., Jikyo T., Takeda R., Ogata M., J.Ethnopharmacol.,2014, 151(2), 897-902 |
| [8] | Gonzales C., Rubio J., Gasco M., Nieto J., Yucra S., Gonzales G. F., J.Ethnopharmacol., 2006, 103(3), 448-454 |
| [9] | Choi E. H., Kang J. I., Cho J. Y., Lee S. H., Kim T. S., Yeo I. H., Journal of Functional Foods,2012, 4(2), 568-573 |
| [10] | Zhou Y., Wang H., Guo F., Si N., Brantner A., Yang J., Han L., Wei X., Zhao H., Bian B., Molecules,2018, 23(11), 2929 |
| [11] | Ganzera M., Zhao J. I., Khan I. A., Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin,2002, 50(7), 988-991 |
| [12] | Yang Q., Jin W., Lv X., Dai P., Yu L., Pharm Biol., 2016, 54(5), 827-834 |
| [13] | Zheng B. L., He K., Kim C. H., Rogers L., Shao Y., Huang Z. Y., Urology,2000, 55(4), 598-602 |
| [14] | Sun J. M., Tian L. L., He Z. M., Meng L. W., Sun H., Gan J. M., Zhang H., Chinese J. Anal.Chem.,2016, 44(11), 1735-1741 |
| (孙佳明, 田淋淋, 何忠梅, 孟令文, 孙慧, 阚俊明, 张辉. 分析化学, 2016, 44(11), 1735-1741) | |
| [15] | Podlasek C. A., Mulhall J., Davies K., Wingard C. J., Hannan J. L., Bivalacqua T. J., J. Sex Med., 2016, 13(8), 1183-1198 |
| [16] | Pomara C., Barone R., Marino Gammazza A., J. Cell Physiol., 2016, 231(6), 1385-1391 |
| [17] | Lenz E. M., Wilson I. D., Journal of Proteome Research,2007, 6(2), 443-458 |
| [18] | Henry C. M., Chemical & Engineering News, 2002, 80(48), 66-70 |
| [19] | Sun H., Li J. F., Zhao Z. J., Zhang H., Sun J. M., Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,2017, 28(11), 2656-2658 |
| (孙慧, 李晶峰, 赵子佳, 张辉, 孙佳明.时珍国医国药, 2017, 28(11), 2656-2658) | |
| [20] | Dona A. C., Kyriakides M., Scott F., Shephard E. A., Varshavi D., Veselkov K., Comput. Struct. Biotechnol.J.,2016, 14, 135-153 |
| [21] | Yang Y. X., Wang L. L., Zheng L. Y., Wang S. M., Huang R. B., Zhang L., Huang Y. T., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2014, 35(9), 1883-1888 |
| (杨永霞, 王琳琳, 郑凌云, 王淑美, 黄榕波, 张磊, 黄耀庭.高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(9), 1883-1888) | |
| [22] | Wishart D.S.,Feunang Y. D., Marcu A., Guo A. C., Liang K., Vázquezfresno R.,Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, D608-D617 |
| [23] | Roberts G.C. K., Encyclopedia of Biophysics, Springer,Berlin, 2013 |
| [24] | Miao H., Chen H., Zhang X., Yin L., Chen D Q., Cheng X. L.,J. Anal. Methods Chem., 2014, 1-9 |
| [25] | Lunt S. Y., Vander Heiden M. G., Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. ,2011, 27(1), 441-464 |
| [26] | Pang Y. L., Poruri K., Martinis S. A., Wiley Interdiscip Rev.RNA,2014, 5(4), 461-480 |
| [27] | Cai L., Sutter B. M., Li B., Tu B. P., Molecular Cell,2011, 42(4), 426-437 |
| [28] | Cai L., Tu B. P., Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. ,2012, 28(4), 59-87 |
| [29] | Agathocleous M., Harris W. A., Trends in Cell Biology,2013, 23(10), 484-492 |
| [30] | Abdul R.M., Shajahan B. P., Buddolla V., Senthilkumar R.,Oxid. Med. Cell Longev., 2017, 1-8 |
| [31] | Ahn S. Y., Jamshidi N., Mo M. L., Wu W., Eraly S. A., Dnyanmote A., J. Biol.Chem.,2011, 286(36), 31522-31531 |
| [1] | MENG Ling-Min, HUANG Qing-Rong, DENG Jing, WU Yi-Jie, SHI Tong-Fei. Micellization of PAA-F108-PAA Block Copolymer Using NMR Spectroscopy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(07): 1624. |
| [2] | JIANG Ping-Yue1, XUE Sai-Feng1,2*, WU Ming-Qiang1, XIAO Xin1, ZHU Qian-Jiang1,2, TAO Zhu1,2. Interaction of Cucurbituril with N,N’-Bisalkyl-1,3-(4,4’-bispyridyl)propanes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(8): 1573. |
| [3] | SHU Jie1, PENG Min1, YU Jia-Hui2*, LUO Shu-Fang2, YU Lei2, CHEN Qun1 . Synthesis and Characterization of Polyacetals and NMR Study on Its Degradation Kinetics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(7): 1398. |
| [4] | TU Chun-Lai, ZHENG Chao, CHEN Yan, SHU Mou-Hai*. Synthesis and Reversible Recognition for Organic Ammoniums of a Molecular Receptor Based on Calixarene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(10): 1917. |
| [5] | MOU Lan, XUE Sai-Feng, ZHU Qian-Jiang, TAO Zhu, ZENG Xi . Inclusion Complexing Behavior of Cucurbit[n] urils with Some Quinoline Derivatives [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2005, 26(10): 1835. |
| [6] | REN Qi-Zhi, ZHU Zhi-Ang, JIANG Dong-Qing, HUANG Jin-Wang, JI Liang-Nian, CHEN Yong-Ti. Molecular Recognition of Zinc Porphyrin Dimers to DABCO andCorresponding Thermodynamic Study [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2002, 23(4): 700. |
| [7] | DU Zhe-Wei, LIAN Yan-Qing, WANG Xiao-Gong, ZHOU Qi-Xiang, LIU De-Shan . Studies on Sequence Distribution of Copolyureas and Relationship of Diamines Reactivity Ratio [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2001, 22(9): 1587. |
| [8] | LIU Peng, CHEN Rong-Feng, CHANG Jun-Biao, XIE Jing-Xi . 1H NMR Studies on Synthetic Isoflavones with p-Substituents on B Ring [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2000, 21(11): 1671. |
| [9] | CHEN Bao-Wei, StellaS. G. E. VanBoom, JanReedljk. 1H NMR Study of Interaction of cis-[Pt (NH3)2 (4-methylpyridine) Cl]NO3 with S-methylglutathione [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1997, 18(6): 840. |
| [10] | WANG Qun, SHAO Zheng-Zhong, YU Tong-Yin. Synthesis and Structural Studies of Polyamide-46(Ⅱ)──Characterization and Structure of Polyamide-46 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1997, 18(4): 628. |
| [11] | HAN Mei, SHI Xu-Ling, YANG Zhen-Jun, CAI Meng-Shen, CHENG Tie-Ming. A Study of 1,2,4-Triazines (XX) ——Study on Structures of Products from a Series of Substituted Benzene Sulfonation of 3-Methylthio-5-hydroxy-1,2,4-triazine by Spectrum Analysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1993, 14(9): 1254. |
| [12] | WANG Jia-Xi, CHEN Shou-Shan, WANG Xu-Kun. Syntheses and Structure Analysis of Bulkier Substituted Titanocene,Zirconocene, Hafnocene Dichlorides and Ferrocenes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1993, 14(4): 495. |
| [13] | LIU Shi-Xiong, WANG Zhe-Min, ZHANG Bin. The Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Spectral Properties of 2,2'-Dihydro-2,2'-Bipyridinium Di(triiodide) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1992, 13(8): 1013. |
| [14] | ZHAO Da-qing, QIU Shi-lun, PANG Wen-qin, ZHANG Jian-guo, WU Yi-jie, PEI Feng-kui. Studies on the Synthesis of Molecular Sieves from TMAOH-P2O5-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O-HF System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1992, 13(6): 717. |
| [15] | LIU Zhi-jie, LI Wen-ge, ZHANG Jian-heng, GONG Yong . Syntheses and 1H NMR Studies of Substituted Styryl-10H-Pyrido [1,2-a]Indolium Perchlorates [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1992, 13(4): 470. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||