

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 950.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190038
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Xiaolei, WANG Changsheng*( )
)
Received:2019-01-14
Online:2019-04-17
Published:2019-04-17
Contact:
WANG Changsheng
E-mail:chwangcs@lnnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Xiaolei,WANG Changsheng. Rapid Calculation of the Three-body Interaction Energies in Water Clusters†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 950.
| No. | Cluster | Ref. | MP2/aug-cc-pVDZ | M06-2X/jul-cc-pVTZ | This work | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E3B | Δ | δ(%) | Δ | δ(%) | E3B | Δ | δ(%) | ||||
| 1 | 3w-1a | -5.82c | -5.77 | 0.05 | 0.86 | -5.65 | 0.17 | 2.92 | -5.77 | 0.05 | 0.86 |
| 2 | 3w-1b | 4.52c | 4.35 | -0.17 | 3.76 | 5.36 | 0.84 | 18.58 | 4.85 | 0.33 | 7.30 |
| 3 | 3w-1c | -10.13c | -10.29 | -0.16 | 1.58 | -11.34 | -1.21 | 11.94 | -10.00 | 0.13 | 1.28 |
| 4 | 4w-1 | -25.82d | -25.94 | -0.12 | 0.46 | -26.53 | -0.71 | 2.75 | -25.27 | 0.55 | 2.13 |
| 5 | 4w-2 | -24.73d | -24.85 | -0.12 | 0.49 | -25.23 | -0.50 | 2.02 | -24.60 | 0.13 | 0.53 |
| 6 | 4w-3 | -15.40d | -16.11 | -0.71 | 4.61 | -19.04 | -3.64 | 23.64 | -14.64 | 0.76 | 4.94 |
| 7 | 5w-1 | -37.95d | -37.87 | 0.08 | 0.21 | -36.90 | 1.05 | 2.77 | -38.41 | -0.46 | 1.21 |
| 8 | 5w-2 | -31.46d | -32.22 | -0.76 | 2.42 | -32.38 | -0.92 | 2.92 | -30.84 | 0.62 | 1.97 |
| 9 | 5w-3 | -26.57d | -27.82 | -1.25 | 4.70 | -29.71 | -3.14 | 11.82 | -27.07 | -0.50 | 1.88 |
| 10 | 5w-4 | -24.85d | -25.94 | -1.09 | 4.39 | -27.95 | -3.10 | 12.47 | -24.27 | 0.58 | 2.33 |
| 11 | 5w-5 | -24.18d | -25.31 | -1.13 | 4.67 | -26.07 | -1.89 | 7.82 | -23.30 | 0.88 | 3.64 |
| 12 | 5w-6 | -26.07d | -26.53 | -0.46 | 1.76 | -26.32 | -0.25 | 0.96 | -24.48 | 1.59 | 6.10 |
| 13 | 5w-7 | -25.94d | -26.36 | -0.42 | 1.62 | -26.48 | -0.54 | 2.08 | -25.06 | 0.88 | 3.39 |
| 14 | 6w-prism | -36.40d | -38.07 | -1.67 | 4.59 | -37.99 | -1.59 | 4.37 | -37.91 | -1.51 | 4.15 |
| 15 | 6w-cage | -37.53d | -38.99 | -1.46 | 3.89 | -40.29 | -2.76 | 7.35 | -38.07 | -0.54 | 1.44 |
| 16 | 6w-book1 | -43.43d | -43.76 | -0.33 | 0.76 | -42.97 | 0.46 | 1.06 | -43.22 | 0.21 | 0.48 |
| 17 | 6w-book2 | -42.30d | -42.84 | -0.54 | 1.28 | -41.21 | 1.09 | 2.58 | -41.80 | 0.50 | 1.18 |
| 18 | 6w-bag | -43.30d | -44.10 | -0.80 | 1.85 | -41.59 | 1.71 | 3.95 | -41.59 | 1.71 | 3.95 |
| 19 | 6w-chair | -49.29d | -49.08 | 0.21 | 0.43 | -48.53 | 0.76 | 1.54 | -51.13 | -1.84 | 3.73 |
| 20 | 6w-boat1 | -47.45d | -47.36 | 0.09 | 0.19 | -46.28 | 1.17 | 2.47 | -49.08 | -1.63 | 3.44 |
| 21 | 6w-boat2 | -47.45d | -47.40 | 0.05 | 0.11 | -46.32 | 1.13 | 2.38 | -49.41 | -1.96 | 4.13 |
| RMSD | 0.74 | 1.68 | 1.02 | ||||||||
| MAD | 1.67 | 3.64 | 1.96 | ||||||||
| MRD(%) | 2.12 | 6.11 | 2.86 | ||||||||
Table 1 Calculated total three-body interaction energies(E3B) of 21 small water clustersa
| No. | Cluster | Ref. | MP2/aug-cc-pVDZ | M06-2X/jul-cc-pVTZ | This work | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E3B | Δ | δ(%) | Δ | δ(%) | E3B | Δ | δ(%) | ||||
| 1 | 3w-1a | -5.82c | -5.77 | 0.05 | 0.86 | -5.65 | 0.17 | 2.92 | -5.77 | 0.05 | 0.86 |
| 2 | 3w-1b | 4.52c | 4.35 | -0.17 | 3.76 | 5.36 | 0.84 | 18.58 | 4.85 | 0.33 | 7.30 |
| 3 | 3w-1c | -10.13c | -10.29 | -0.16 | 1.58 | -11.34 | -1.21 | 11.94 | -10.00 | 0.13 | 1.28 |
| 4 | 4w-1 | -25.82d | -25.94 | -0.12 | 0.46 | -26.53 | -0.71 | 2.75 | -25.27 | 0.55 | 2.13 |
| 5 | 4w-2 | -24.73d | -24.85 | -0.12 | 0.49 | -25.23 | -0.50 | 2.02 | -24.60 | 0.13 | 0.53 |
| 6 | 4w-3 | -15.40d | -16.11 | -0.71 | 4.61 | -19.04 | -3.64 | 23.64 | -14.64 | 0.76 | 4.94 |
| 7 | 5w-1 | -37.95d | -37.87 | 0.08 | 0.21 | -36.90 | 1.05 | 2.77 | -38.41 | -0.46 | 1.21 |
| 8 | 5w-2 | -31.46d | -32.22 | -0.76 | 2.42 | -32.38 | -0.92 | 2.92 | -30.84 | 0.62 | 1.97 |
| 9 | 5w-3 | -26.57d | -27.82 | -1.25 | 4.70 | -29.71 | -3.14 | 11.82 | -27.07 | -0.50 | 1.88 |
| 10 | 5w-4 | -24.85d | -25.94 | -1.09 | 4.39 | -27.95 | -3.10 | 12.47 | -24.27 | 0.58 | 2.33 |
| 11 | 5w-5 | -24.18d | -25.31 | -1.13 | 4.67 | -26.07 | -1.89 | 7.82 | -23.30 | 0.88 | 3.64 |
| 12 | 5w-6 | -26.07d | -26.53 | -0.46 | 1.76 | -26.32 | -0.25 | 0.96 | -24.48 | 1.59 | 6.10 |
| 13 | 5w-7 | -25.94d | -26.36 | -0.42 | 1.62 | -26.48 | -0.54 | 2.08 | -25.06 | 0.88 | 3.39 |
| 14 | 6w-prism | -36.40d | -38.07 | -1.67 | 4.59 | -37.99 | -1.59 | 4.37 | -37.91 | -1.51 | 4.15 |
| 15 | 6w-cage | -37.53d | -38.99 | -1.46 | 3.89 | -40.29 | -2.76 | 7.35 | -38.07 | -0.54 | 1.44 |
| 16 | 6w-book1 | -43.43d | -43.76 | -0.33 | 0.76 | -42.97 | 0.46 | 1.06 | -43.22 | 0.21 | 0.48 |
| 17 | 6w-book2 | -42.30d | -42.84 | -0.54 | 1.28 | -41.21 | 1.09 | 2.58 | -41.80 | 0.50 | 1.18 |
| 18 | 6w-bag | -43.30d | -44.10 | -0.80 | 1.85 | -41.59 | 1.71 | 3.95 | -41.59 | 1.71 | 3.95 |
| 19 | 6w-chair | -49.29d | -49.08 | 0.21 | 0.43 | -48.53 | 0.76 | 1.54 | -51.13 | -1.84 | 3.73 |
| 20 | 6w-boat1 | -47.45d | -47.36 | 0.09 | 0.19 | -46.28 | 1.17 | 2.47 | -49.08 | -1.63 | 3.44 |
| 21 | 6w-boat2 | -47.45d | -47.40 | 0.05 | 0.11 | -46.32 | 1.13 | 2.38 | -49.41 | -1.96 | 4.13 |
| RMSD | 0.74 | 1.68 | 1.02 | ||||||||
| MAD | 1.67 | 3.64 | 1.96 | ||||||||
| MRD(%) | 2.12 | 6.11 | 2.86 | ||||||||
| No. | Cluster | CCSD(T) | MP2/aug-cc-pVDZ | M06-2X/jul-cc-pVTZ | This work | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δ | δ(%) | Δ | δ(%) | E3B | Δ | δ(%) | |||||
| 1 | 10w-1 | -70.58 | -73.64 | -3.06 | 4.34 | -61.63 | 8.95 | 12.68 | -70.63 | -0.05 | 0.07 |
| 2 | 10w-2 | -71.13 | -74.52 | -3.39 | 4.77 | -65.81 | 5.32 | 7.48 | -68.74 | 2.39 | 3.36 |
| 3 | 10w-3 | -66.94 | -70.84 | -3.90 | 5.83 | -61.09 | 5.85 | 8.74 | -66.40 | 0.54 | 0.81 |
| 4 | 10w-4 | -69.41 | -72.97 | -3.56 | 5.13 | -62.76 | 6.65 | 9.58 | -69.79 | -0.38 | 0.55 |
| 5 | 10w-5 | -70.84 | -73.30 | -2.46 | 3.47 | -61.04 | 9.80 | 13.83 | -75.02 | -4.18 | 5.90 |
| 6 | 10w-6 | -68.37 | -73.01 | -4.64 | 6.79 | -64.43 | 3.94 | 5.76 | -71.09 | -2.72 | 3.98 |
| No. | Cluster | CCSD(T) | MP2/aug-cc-pVDZ | M06-2X/jul-cc-pVTZ | This work | ||||||
| Δ | δ(%) | Δ | δ(%) | E3B | Δ | δ(%) | |||||
| 7 | 10w-7 | -70.42 | -72.59 | -2.17 | 3.08 | -61.67 | 8.75 | 12.43 | -75.27 | -4.85 | 6.89 |
| 8 | 10w-8 | -70.08 | -72.89 | -2.81 | 4.01 | -61.09 | 8.99 | 12.83 | -73.47 | -3.39 | 4.84 |
| 9 | 10w-9 | -69.45 | -71.84 | -2.39 | 3.44 | -59.20 | 10.25 | 14.76 | -72.01 | -2.56 | 3.69 |
| 10 | 10w-10 | -66.57 | -70.17 | -3.60 | 5.41 | -61.21 | 5.36 | 8.05 | -66.44 | 0.13 | 0.20 |
| 11 | 11w-1 | -79.54 | -82.09 | -2.55 | 3.21 | -70.00 | 9.54 | 11.99 | -82.01 | -2.47 | 3.11 |
| 12 | 11w-2 | -82.63 | -84.89 | -2.26 | 2.74 | -73.43 | 9.20 | 11.13 | -82.30 | 0.33 | 0.40 |
| 13 | 11w-3 | -78.87 | -81.80 | -2.93 | 3.71 | -69.54 | 9.33 | 11.83 | -79.54 | -0.67 | 0.85 |
| 14 | 11w-4 | -82.26 | -84.22 | -1.96 | 2.38 | -69.41 | 12.85 | 15.62 | -81.92 | 0.34 | 0.41 |
| 15 | 11w-5 | -81.76 | -83.60 | -1.84 | 2.25 | -71.84 | 9.92 | 12.13 | -82.09 | -0.33 | 0.40 |
| 16 | 12w-1 | -88.70 | -92.47 | -3.77 | 4.25 | -77.78 | 10.92 | 12.31 | -87.91 | 0.79 | 0.89 |
| 17 | 13w-1 | -99.87 | -103.51 | -3.64 | 3.64 | -85.77 | 14.10 | 14.12 | -99.54 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| 18 | 14w-1 | -111.55 | -115.48 | -3.93 | 3.52 | -95.10 | 16.45 | 14.75 | -108.95 | 2.60 | 2.33 |
| 19 | 15w-1 | -123.39 | -127.90 | -4.51 | 3.66 | -101.96 | 21.43 | 17.37 | -121.92 | 1.47 | 1.19 |
| 20 | 17w-1 | -142.05 | -148.36 | -6.31 | 4.44 | -117.32 | 24.73 | 17.41 | -138.87 | 3.18 | 2.24 |
| 21 | 17w-2 | -146.15 | -150.92 | -4.77 | 3.26 | -120.75 | 25.40 | 17.38 | -142.67 | 3.48 | 2.38 |
| 22 | 21w-1 | -182.17 | -190.54 | -8.37 | 4.59 | -141.46 | 40.71 | 22.35 | -181.71 | 0.46 | 0.25 |
| 23 | 21w-2 | -184.81 | -191.42 | -6.61 | 3.58 | -136.86 | 47.95 | 25.95 | -179.16 | 5.65 | 3.06 |
| RMSD | 4.04 | 17.91 | 2.50 | ||||||||
| MAD | 8.37 | 47.95 | 5.65 | ||||||||
| MRD(%) | 3.98 | 13.50 | 2.09 | ||||||||
Table 2 Calculated total three-body interaction energies of 23 medium-sized water clustersa
| No. | Cluster | CCSD(T) | MP2/aug-cc-pVDZ | M06-2X/jul-cc-pVTZ | This work | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δ | δ(%) | Δ | δ(%) | E3B | Δ | δ(%) | |||||
| 1 | 10w-1 | -70.58 | -73.64 | -3.06 | 4.34 | -61.63 | 8.95 | 12.68 | -70.63 | -0.05 | 0.07 |
| 2 | 10w-2 | -71.13 | -74.52 | -3.39 | 4.77 | -65.81 | 5.32 | 7.48 | -68.74 | 2.39 | 3.36 |
| 3 | 10w-3 | -66.94 | -70.84 | -3.90 | 5.83 | -61.09 | 5.85 | 8.74 | -66.40 | 0.54 | 0.81 |
| 4 | 10w-4 | -69.41 | -72.97 | -3.56 | 5.13 | -62.76 | 6.65 | 9.58 | -69.79 | -0.38 | 0.55 |
| 5 | 10w-5 | -70.84 | -73.30 | -2.46 | 3.47 | -61.04 | 9.80 | 13.83 | -75.02 | -4.18 | 5.90 |
| 6 | 10w-6 | -68.37 | -73.01 | -4.64 | 6.79 | -64.43 | 3.94 | 5.76 | -71.09 | -2.72 | 3.98 |
| No. | Cluster | CCSD(T) | MP2/aug-cc-pVDZ | M06-2X/jul-cc-pVTZ | This work | ||||||
| Δ | δ(%) | Δ | δ(%) | E3B | Δ | δ(%) | |||||
| 7 | 10w-7 | -70.42 | -72.59 | -2.17 | 3.08 | -61.67 | 8.75 | 12.43 | -75.27 | -4.85 | 6.89 |
| 8 | 10w-8 | -70.08 | -72.89 | -2.81 | 4.01 | -61.09 | 8.99 | 12.83 | -73.47 | -3.39 | 4.84 |
| 9 | 10w-9 | -69.45 | -71.84 | -2.39 | 3.44 | -59.20 | 10.25 | 14.76 | -72.01 | -2.56 | 3.69 |
| 10 | 10w-10 | -66.57 | -70.17 | -3.60 | 5.41 | -61.21 | 5.36 | 8.05 | -66.44 | 0.13 | 0.20 |
| 11 | 11w-1 | -79.54 | -82.09 | -2.55 | 3.21 | -70.00 | 9.54 | 11.99 | -82.01 | -2.47 | 3.11 |
| 12 | 11w-2 | -82.63 | -84.89 | -2.26 | 2.74 | -73.43 | 9.20 | 11.13 | -82.30 | 0.33 | 0.40 |
| 13 | 11w-3 | -78.87 | -81.80 | -2.93 | 3.71 | -69.54 | 9.33 | 11.83 | -79.54 | -0.67 | 0.85 |
| 14 | 11w-4 | -82.26 | -84.22 | -1.96 | 2.38 | -69.41 | 12.85 | 15.62 | -81.92 | 0.34 | 0.41 |
| 15 | 11w-5 | -81.76 | -83.60 | -1.84 | 2.25 | -71.84 | 9.92 | 12.13 | -82.09 | -0.33 | 0.40 |
| 16 | 12w-1 | -88.70 | -92.47 | -3.77 | 4.25 | -77.78 | 10.92 | 12.31 | -87.91 | 0.79 | 0.89 |
| 17 | 13w-1 | -99.87 | -103.51 | -3.64 | 3.64 | -85.77 | 14.10 | 14.12 | -99.54 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| 18 | 14w-1 | -111.55 | -115.48 | -3.93 | 3.52 | -95.10 | 16.45 | 14.75 | -108.95 | 2.60 | 2.33 |
| 19 | 15w-1 | -123.39 | -127.90 | -4.51 | 3.66 | -101.96 | 21.43 | 17.37 | -121.92 | 1.47 | 1.19 |
| 20 | 17w-1 | -142.05 | -148.36 | -6.31 | 4.44 | -117.32 | 24.73 | 17.41 | -138.87 | 3.18 | 2.24 |
| 21 | 17w-2 | -146.15 | -150.92 | -4.77 | 3.26 | -120.75 | 25.40 | 17.38 | -142.67 | 3.48 | 2.38 |
| 22 | 21w-1 | -182.17 | -190.54 | -8.37 | 4.59 | -141.46 | 40.71 | 22.35 | -181.71 | 0.46 | 0.25 |
| 23 | 21w-2 | -184.81 | -191.42 | -6.61 | 3.58 | -136.86 | 47.95 | 25.95 | -179.16 | 5.65 | 3.06 |
| RMSD | 4.04 | 17.91 | 2.50 | ||||||||
| MAD | 8.37 | 47.95 | 5.65 | ||||||||
| MRD(%) | 3.98 | 13.50 | 2.09 | ||||||||
| No. | Cluster | CCSD(T) | MP2/aug-cc-pVDZ | M06-2X/jul-cc-pVTZ | This work | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δ | δ(%) | Δ | δ(%) | E3B | Δ | δ(%) | |||||
| 1 | 16w-1 | -135.65 | -141.75 | -6.10 | 4.50 | -120.16 | 15.49 | 11.42 | -135.44 | 0.21 | 0.15 |
| 2 | 16w-2 | -141.00 | -147.70 | -6.70 | 4.75 | -125.69 | 15.31 | 10.86 | -139.58 | 1.42 | 1.01 |
| 3 | 16w-3 | -150.21 | -154.60 | -4.39 | 2.92 | -129.45 | 20.76 | 13.82 | -149.91 | 0.30 | 0.20 |
| 4 | 16w-4 | -150.21 | -154.60 | -4.39 | 2.92 | -130.46 | 19.75 | 13.15 | -150.79 | -0.58 | 0.39 |
| 5 | 16w-5 | -152.17 | -156.82 | -4.65 | 3.06 | -132.17 | 20.00 | 13.14 | -149.83 | 2.34 | 1.54 |
| 6 | 17w-3 | -132.59 | -137.90 | -5.31 | 4.00 | -111.67 | 20.92 | 15.78 | -128.24 | 4.35 | 3.28 |
| 7 | 17w-4 | -140.88 | -147.07 | -6.19 | 4.39 | -116.02 | 24.86 | 17.65 | -139.49 | 1.39 | 0.99 |
| 8 | 18w-1 | -147.07 | -152.80 | -5.73 | 3.90 | -123.30 | 23.77 | 16.16 | -141.21 | 5.86 | 3.98 |
| 9 | 19w-1 | -164.89 | -172.00 | -7.11 | 4.31 | -128.57 | 36.32 | 22.03 | -155.98 | 8.91 | 5.40 |
| 10 | 20w-1 | -173.05 | -180.54 | -7.49 | 4.33 | -140.50 | 32.55 | 18.81 | -179.24 | -6.19 | 3.58 |
| 11 | 20w-2 | -170.75 | -178.45 | -7.70 | 4.51 | -144.01 | 26.74 | 15.66 | -170.75 | 0 | 0 |
| 12 | 20w-3 | -166.23 | -173.22 | -6.99 | 4.21 | -140.25 | 25.98 | 15.63 | -173.34 | -7.11 | 4.28 |
| 13 | 20w-4 | -167.99 | -175.98 | -7.99 | 4.76 | -133.93 | 34.06 | 20.28 | -173.76 | -5.77 | 3.43 |
| 14 | 20w-5 | -170.87 | -178.49 | -7.62 | 4.46 | -143.30 | 27.57 | 16.14 | -175.60 | -4.73 | 2.77 |
| 15 | 20w-6 | -166.23 | -175.81 | -9.58 | 5.76 | -144.10 | 22.13 | 13.31 | -172.09 | -5.86 | 3.53 |
| 16 | 20w-7 | -166.65 | -175.39 | -8.74 | 5.24 | -136.02 | 30.63 | 18.38 | -167.86 | -1.21 | 0.73 |
| 17 | 20w-8 | -166.86 | -174.22 | -7.36 | 4.41 | -138.41 | 28.45 | 17.05 | -171.25 | -4.39 | 2.63 |
| 18 | 20w-9 | -168.49 | -176.19 | -7.70 | 4.57 | -133.97 | 34.52 | 20.49 | -167.44 | 1.05 | 0.62 |
| 19 | 20w-10 | -167.82 | -175.77 | -7.95 | 4.74 | -137.44 | 30.38 | 18.10 | -172.42 | -4.60 | 2.74 |
| 20 | 22w-1 | -164.81 | -173.43 | -8.62 | 5.23 | -124.73 | 40.08 | 24.32 | -154.64 | 10.17 | 6.17 |
| 21 | 30w-1 | -209.87 | -221.42 | -11.55 | 5.50 | -166.73 | 43.14 | 20.56 | -217.36 | -7.49 | 3.57 |
| 22 | 30w-2 | -196.77 | -211.88 | -15.11 | 7.68 | -157.19 | 39.58 | 20.11 | -203.64 | -6.87 | 3.49 |
| 23 | 30w-3 | -193.34 | -215.60 | -22.26 | 11.51 | -164.47 | 28.87 | 14.93 | -193.30 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| RMSD | 8.98 | 28.91 | 4.98 | ||||||||
| MAD | 22.26 | 43.14 | 10.17 | ||||||||
| MRD(%) | 4.85 | 16.86 | 2.37 | ||||||||
Table 3 Calculated total three-body interaction energies of 23 water nanoparticlesa
| No. | Cluster | CCSD(T) | MP2/aug-cc-pVDZ | M06-2X/jul-cc-pVTZ | This work | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δ | δ(%) | Δ | δ(%) | E3B | Δ | δ(%) | |||||
| 1 | 16w-1 | -135.65 | -141.75 | -6.10 | 4.50 | -120.16 | 15.49 | 11.42 | -135.44 | 0.21 | 0.15 |
| 2 | 16w-2 | -141.00 | -147.70 | -6.70 | 4.75 | -125.69 | 15.31 | 10.86 | -139.58 | 1.42 | 1.01 |
| 3 | 16w-3 | -150.21 | -154.60 | -4.39 | 2.92 | -129.45 | 20.76 | 13.82 | -149.91 | 0.30 | 0.20 |
| 4 | 16w-4 | -150.21 | -154.60 | -4.39 | 2.92 | -130.46 | 19.75 | 13.15 | -150.79 | -0.58 | 0.39 |
| 5 | 16w-5 | -152.17 | -156.82 | -4.65 | 3.06 | -132.17 | 20.00 | 13.14 | -149.83 | 2.34 | 1.54 |
| 6 | 17w-3 | -132.59 | -137.90 | -5.31 | 4.00 | -111.67 | 20.92 | 15.78 | -128.24 | 4.35 | 3.28 |
| 7 | 17w-4 | -140.88 | -147.07 | -6.19 | 4.39 | -116.02 | 24.86 | 17.65 | -139.49 | 1.39 | 0.99 |
| 8 | 18w-1 | -147.07 | -152.80 | -5.73 | 3.90 | -123.30 | 23.77 | 16.16 | -141.21 | 5.86 | 3.98 |
| 9 | 19w-1 | -164.89 | -172.00 | -7.11 | 4.31 | -128.57 | 36.32 | 22.03 | -155.98 | 8.91 | 5.40 |
| 10 | 20w-1 | -173.05 | -180.54 | -7.49 | 4.33 | -140.50 | 32.55 | 18.81 | -179.24 | -6.19 | 3.58 |
| 11 | 20w-2 | -170.75 | -178.45 | -7.70 | 4.51 | -144.01 | 26.74 | 15.66 | -170.75 | 0 | 0 |
| 12 | 20w-3 | -166.23 | -173.22 | -6.99 | 4.21 | -140.25 | 25.98 | 15.63 | -173.34 | -7.11 | 4.28 |
| 13 | 20w-4 | -167.99 | -175.98 | -7.99 | 4.76 | -133.93 | 34.06 | 20.28 | -173.76 | -5.77 | 3.43 |
| 14 | 20w-5 | -170.87 | -178.49 | -7.62 | 4.46 | -143.30 | 27.57 | 16.14 | -175.60 | -4.73 | 2.77 |
| 15 | 20w-6 | -166.23 | -175.81 | -9.58 | 5.76 | -144.10 | 22.13 | 13.31 | -172.09 | -5.86 | 3.53 |
| 16 | 20w-7 | -166.65 | -175.39 | -8.74 | 5.24 | -136.02 | 30.63 | 18.38 | -167.86 | -1.21 | 0.73 |
| 17 | 20w-8 | -166.86 | -174.22 | -7.36 | 4.41 | -138.41 | 28.45 | 17.05 | -171.25 | -4.39 | 2.63 |
| 18 | 20w-9 | -168.49 | -176.19 | -7.70 | 4.57 | -133.97 | 34.52 | 20.49 | -167.44 | 1.05 | 0.62 |
| 19 | 20w-10 | -167.82 | -175.77 | -7.95 | 4.74 | -137.44 | 30.38 | 18.10 | -172.42 | -4.60 | 2.74 |
| 20 | 22w-1 | -164.81 | -173.43 | -8.62 | 5.23 | -124.73 | 40.08 | 24.32 | -154.64 | 10.17 | 6.17 |
| 21 | 30w-1 | -209.87 | -221.42 | -11.55 | 5.50 | -166.73 | 43.14 | 20.56 | -217.36 | -7.49 | 3.57 |
| 22 | 30w-2 | -196.77 | -211.88 | -15.11 | 7.68 | -157.19 | 39.58 | 20.11 | -203.64 | -6.87 | 3.49 |
| 23 | 30w-3 | -193.34 | -215.60 | -22.26 | 11.51 | -164.47 | 28.87 | 14.93 | -193.30 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| RMSD | 8.98 | 28.91 | 4.98 | ||||||||
| MAD | 22.26 | 43.14 | 10.17 | ||||||||
| MRD(%) | 4.85 | 16.86 | 2.37 | ||||||||
| No. | Cluster | CCSD(T) | WHBB | This work | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E3B/(kJ·mol-1) | Δ/(kJ·mol-1) | δ(%) | E3B/(kJ·mol-1) | Δ/(kJ·mol-1) | δ(%) | |||
| 1 | 11w-1 | -79.54 | -81.17 | -1.63 | 2.05 | -82.01 | -2.47 | 3.11 |
| 2 | 11w-2 | -82.63 | -82.84 | -0.21 | 0.25 | -82.30 | 0.33 | 0.40 |
| 3 | 11w-3 | -78.87 | -81.59 | -2.72 | 3.45 | -79.54 | -0.67 | 0.85 |
| 4 | 11w-4 | -82.26 | -83.68 | -1.42 | 1.73 | -81.92 | 0.34 | 0.41 |
| 5 | 11w-5 | -81.76 | -83.26 | -1.50 | 1.83 | -82.09 | -0.33 | 0.40 |
| 6 | 12w-1 | -88.70 | -93.30 | -4.60 | 5.19 | -87.91 | 0.79 | 0.89 |
| 7 | 13w-1 | -99.87 | -103.76 | -3.89 | 3.90 | -99.54 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| 8 | 14w-1 | -111.55 | -115.06 | -3.51 | 3.15 | -108.95 | 2.60 | 2.33 |
| 9 | 15w-1 | -123.39 | -123.01 | 0.38 | 0.31 | -121.92 | 1.47 | 1.19 |
| 10 | 17w-1 | -142.05 | -148.95 | -6.90 | 4.86 | -138.87 | 3.18 | 2.24 |
| 11 | 17w-2 | -146.15 | -144.77 | 1.38 | 0.94 | -142.67 | 3.48 | 2.38 |
| 12 | 17w-3 | -132.59 | -140.16 | -7.57 | 5.71 | -128.24 | 4.35 | 3.28 |
| 13 | 17w-4 | -140.88 | -141.84 | -0.96 | 0.68 | -139.49 | 1.39 | 0.99 |
| 14 | 18w-1 | -147.07 | -153.97 | -6.90 | 4.69 | -141.21 | 5.86 | 3.98 |
| 15 | 19w-1 | -164.89 | -169.03 | -4.14 | 2.51 | -155.98 | 8.91 | 5.40 |
| 16 | 21w-1 | -182.17 | -193.30 | -11.13 | 6.11 | -181.71 | 0.46 | 0.25 |
| 17 | 21w-2 | -184.81 | -190.37 | -5.56 | 3.01 | -179.16 | 5.65 | 3.06 |
| 18 | 22w-1 | -164.81 | -190.37 | -25.56 | 15.51 | -154.64 | 10.17 | 6.17 |
| RMSD/(kJ·mol-1) | 7.61 | 4.14 | ||||||
| MAD/(kJ·mol-1) | 25.56 | 10.17 | ||||||
| MRD(%) | 3.66 | 2.09 | ||||||
Table 4 Calculated total three-body interaction energies of 18 water clusters
| No. | Cluster | CCSD(T) | WHBB | This work | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E3B/(kJ·mol-1) | Δ/(kJ·mol-1) | δ(%) | E3B/(kJ·mol-1) | Δ/(kJ·mol-1) | δ(%) | |||
| 1 | 11w-1 | -79.54 | -81.17 | -1.63 | 2.05 | -82.01 | -2.47 | 3.11 |
| 2 | 11w-2 | -82.63 | -82.84 | -0.21 | 0.25 | -82.30 | 0.33 | 0.40 |
| 3 | 11w-3 | -78.87 | -81.59 | -2.72 | 3.45 | -79.54 | -0.67 | 0.85 |
| 4 | 11w-4 | -82.26 | -83.68 | -1.42 | 1.73 | -81.92 | 0.34 | 0.41 |
| 5 | 11w-5 | -81.76 | -83.26 | -1.50 | 1.83 | -82.09 | -0.33 | 0.40 |
| 6 | 12w-1 | -88.70 | -93.30 | -4.60 | 5.19 | -87.91 | 0.79 | 0.89 |
| 7 | 13w-1 | -99.87 | -103.76 | -3.89 | 3.90 | -99.54 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| 8 | 14w-1 | -111.55 | -115.06 | -3.51 | 3.15 | -108.95 | 2.60 | 2.33 |
| 9 | 15w-1 | -123.39 | -123.01 | 0.38 | 0.31 | -121.92 | 1.47 | 1.19 |
| 10 | 17w-1 | -142.05 | -148.95 | -6.90 | 4.86 | -138.87 | 3.18 | 2.24 |
| 11 | 17w-2 | -146.15 | -144.77 | 1.38 | 0.94 | -142.67 | 3.48 | 2.38 |
| 12 | 17w-3 | -132.59 | -140.16 | -7.57 | 5.71 | -128.24 | 4.35 | 3.28 |
| 13 | 17w-4 | -140.88 | -141.84 | -0.96 | 0.68 | -139.49 | 1.39 | 0.99 |
| 14 | 18w-1 | -147.07 | -153.97 | -6.90 | 4.69 | -141.21 | 5.86 | 3.98 |
| 15 | 19w-1 | -164.89 | -169.03 | -4.14 | 2.51 | -155.98 | 8.91 | 5.40 |
| 16 | 21w-1 | -182.17 | -193.30 | -11.13 | 6.11 | -181.71 | 0.46 | 0.25 |
| 17 | 21w-2 | -184.81 | -190.37 | -5.56 | 3.01 | -179.16 | 5.65 | 3.06 |
| 18 | 22w-1 | -164.81 | -190.37 | -25.56 | 15.51 | -154.64 | 10.17 | 6.17 |
| RMSD/(kJ·mol-1) | 7.61 | 4.14 | ||||||
| MAD/(kJ·mol-1) | 25.56 | 10.17 | ||||||
| MRD(%) | 3.66 | 2.09 | ||||||
| Method | RMSD/(kJ·mol-1) | MAD/(kJ·mol-1) | MRD(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MP2 | 5.78 | 22.26 | 3.70 |
| M06-2X | 19.95 | 47.95 | 12.34 |
| This work | 3.32 | 10.17 | 2.43 |
Table 5 Deviations of different methods with respect to the CCSD(T) three-body interaction energies of 67 water clusters
| Method | RMSD/(kJ·mol-1) | MAD/(kJ·mol-1) | MRD(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MP2 | 5.78 | 22.26 | 3.70 |
| M06-2X | 19.95 | 47.95 | 12.34 |
| This work | 3.32 | 10.17 | 2.43 |
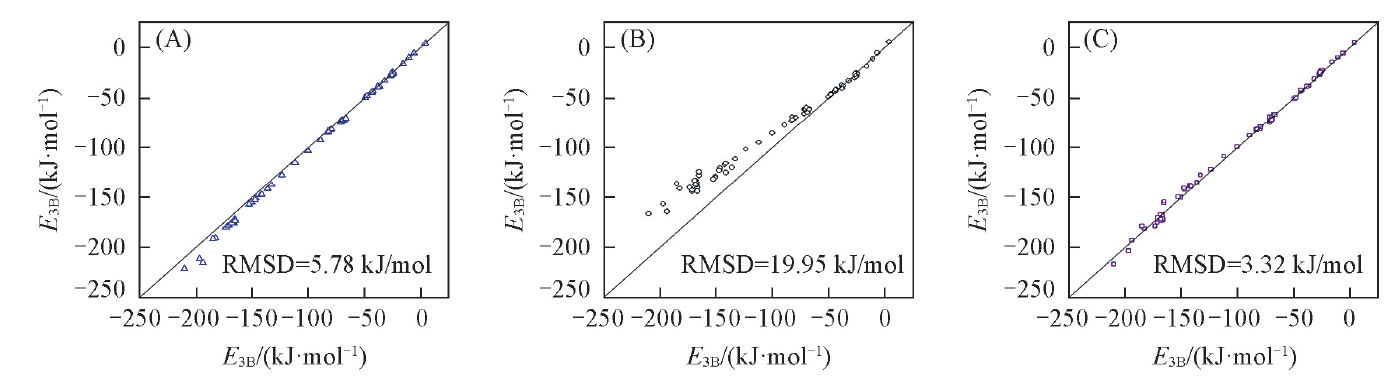
Fig.1 Correlation plots for the total three-body interaction energies of the 67 water clusters (A) MP2/aug-cc-pVDZ; (B) M06-2X/jul-cc-pVTZ; (C) this work.
| [1] | Xantheas S. S., Chem. Phys., 2000, 258, 225—231 |
| [2] | Milet A., Moszynski R., Wormer P. E. S., Avoird A. V. D., J. Phys. Chem. A,1999, 103(34), 6811—6819 |
| [3] | Li S. S., Jiang X. N., Wang C. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2014, 35(11), 2403—2409 |
| (李书实, 姜笑楠, 王长生. 高等学校化学学报,2014, 35(11), 2403—2409) | |
| [4] | Yang W., Li X. L., Wang C. S., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin.,2015, 31(12), 2285—2293 |
| (杨微, 李晓蕾, 王长生. 物理化学学报,2015, 31(12), 2285—2293) | |
| [5] | Babin V., Medders G. R., Paesani F., J. Chem. Theory Comput.,2014, 10(4), 1599—1607 |
| [6] | Ouyang J. F., Bettens R. P. A., J. Chem. Theory Comput.,2015, 11(11), 5132—5143 |
| [7] | Stone A.J., The Theory of Intermolecular Forces, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2013, 3 |
| [8] | Thole B. T., Chem. Phys., 1981, 59, 341—350 |
| [9] | Kumar R., Wang F. F., Jenness G. R., Jordan K. D., J. Chem. Phys.,2010, 132, 014309 |
| [10] | Burnham C. J., Li J., Xantheas S. S., Leslie M., J. Chem. Phys.,1999, 110(9), 4566—4581 |
| [11] | Burnham C. J., Anick D. J., Mankoo P. K., Reiter G. F., J. Chem. Phys.,2008, 128(15), 154519 |
| [12] | Ren P., Ponder J. W., J. Phys. Chem. B,2003, 107(24), 5933—5947 |
| [13] | Conte R., Qu C., Bowman J. M., J. Chem. Theory Comput.,2015, 11(4), 1631—1638 |
| [14] | Sun C. L., Jiang X. N., Wang C. S., J. Comput. Chem.,2009, 30(15), 2567—2575 |
| [15] | Jiang X. N., Sun C. L., Wang C. S., J. Comput. Chem.,2010, 31(7), 1410—1420 |
| [16] | Li Y., Jiang X. N., Wang C. S., J. Comput. Chem.,2011, 32(5), 953—966 |
| [17] | Li Y., Wang C. S., J. Comput. Chem.,2011, 32(13), 2765—2773 |
| [18] | Li S. S., Huang C. Y., Hao J. J., Wang C. S., J. Comput. Chem.,2014, 35(6), 415—426 |
| [19] | Hao J. J., Wang C. S., RSC Adv.,2015, 5, 6452—6461 |
| [20] | Gao X. C., Hao. Q., Wang C. S., J. Chem. Theory Comput.,2017, 13(6), 2730—2741 |
| [21] | Huang C., Hao Q., Wang C., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2017, 33(1), 94—99 |
| [22] | Dean J.A., Lange's Handbook of Chemistry, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1999 |
| [23] | Chen G. D., Weng J., Song G., Li Z. H., J. Chem. Theory Comput.,2017, 13(5), 2010—2020 |
| [24] | Leverentz H. R., Qi H. W., Truhlar D. G., J. Chem. Theory Comput.,2013, 9(2), 995—1006 |
| [25] | Frisch M.J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Mennucci B., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Caricato M., Li X., Hratchian H. P., Izmaylov A. F., Bloino J., Zheng G., Sonnenberg J. L., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Vreven T., Montgomery J. A. Jr., Peralta J. E., Ogliaro F., Bearpark M., Heyd J. J., Brothers E., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N., Keith T., Kobayashi R., Normand J., Raghavachari K., Rendell A., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Rega N., Millam J. M., Klene M., Knox J. E., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Martin R. L., Morokuma K., Zakrzewski V. G., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Farkas O., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cioslowski J., Fox D. J., Gaussian 09, Revision D. 01, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2013 |
| [26] | R$\check{e}$zá$\check{c}$ J., Huang Y., Hobza P., Beran G. J. O., J. Chem. Theory Comput.,2015, 11(7), 3065—3079 |
| [27] | Reddy S. K., Straight S. C., Bajaj P., Pham C. H., Riera M., Moberg D. R., Morales M. A., Knight C., Götz A. W., Paesani F., J. Chem. Phys.,2016, 145(19), 194504 |
| [28] | Yuan D., Shen X., Li W., Li S., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.,2016, 18(24), 16491—16500 |
| [29] | Wang Y., Huang X., Shepler B. C., Braams B. J., Bowman J. M., J. Chem. Phys.,2011, 134, 094509 |
| [30] | Ouyang J. F., Bettens R. P. A., J. Chem. Theory Comput.,2016, 12(12), 5860—5867 |
| [1] | LI Xiaolei, SUN Yunjiao, TANG Ying, WANG Changsheng. Rapid and Accurate Calculation of the Three⁃body Interaction Strength in the Hydrogen⁃bonded Complexes of Alcohols or Deoxyribose with Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3664. |
| [2] | SUN Xiao-Ying, WANG Qin, LI Zhi-Ru*, WU Di, SUN Chia-Chung, TANG Au-Chin. Intermolecular Interaction Potential Surface of the He2F- Complex [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(5): 960. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||