

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (10): 1813.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170202
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHOU Chao, SHI Ting, ZHAO Yilei, WANG Xiaolei*( )
)
Received:2017-04-01
Online:2017-10-10
Published:2017-09-22
Contact:
WANG Xiaolei
E-mail:thundawner@sjtu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHOU Chao, SHI Ting, ZHAO Yilei, WANG Xiaolei. Theoretical Analysis of Oxygen Diffusion in the Micro-channels of Quinoline Oxygenase†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1813.
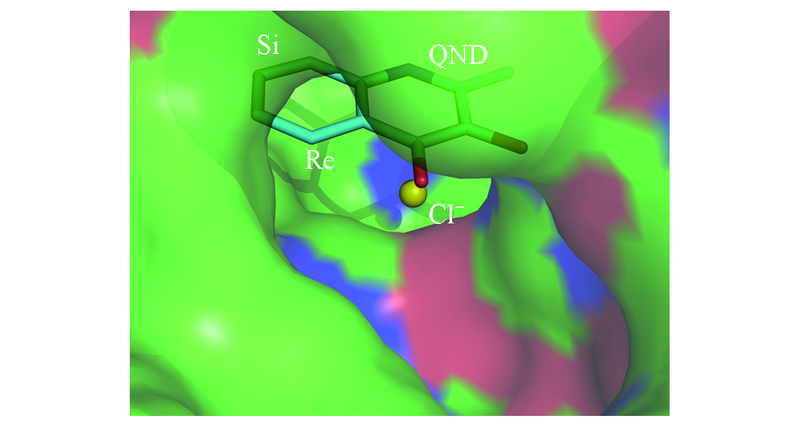
Fig.1 Location of Cl- in the crystal structure of HODCl- is buried deeper inside the active pocket, beneath the substrate QND, which is also the putative binding site of O2. Re face and Si face of QND are labelled according to the carbonyl group.
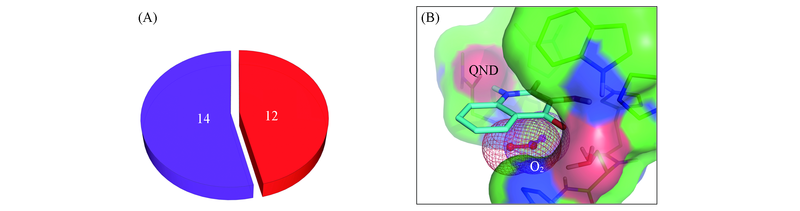
Fig.3 Proportion of the two pre-reaction oxygen orientations(red and purple) in total 26 optimizations(A) and their 3D structure in the active site of HOD(B)
| ID | Bottleneck radius/nm | Length/nm | Curvature | Priority | ID | Bottleneck radius/nm | Length/nm | Curvature | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.095 | 1.674 | 1.38 | 0.42 | 14 | 0.074 | 3.365 | 1.35 | 0.07 |
| 2 | 0.070 | 2.213 | 1.52 | 0.30 | 15 | 0.077 | 4.507 | 3.28 | 0.06 |
| 3 | 0.079 | 2.624 | 1.34 | 0.18 | 16 | 0.061 | 3.293 | 2.09 | 0.06 |
| 4 | 0.070 | 2.419 | 1.36 | 0.14 | 17 | 0.067 | 3.664 | 1.52 | 0.05 |
| 5 | 0.064 | 2.705 | 1.56 | 0.14 | 18 | 0.066 | 3.852 | 2.32 | 0.05 |
| 6 | 0.062 | 2.054 | 1.70 | 0.13 | 19 | 0.063 | 3.437 | 2.21 | 0.05 |
| 7 | 0.077 | 3.221 | 1.42 | 0.13 | 20 | 0.064 | 3.517 | 2.30 | 0.05 |
| 8 | 0.074 | 2.875 | 1.41 | 0.12 | 21 | 0.064 | 4.117 | 1.73 | 0.04 |
| 9 | 0.077 | 3.380 | 3.34 | 0.12 | 22 | 0.062 | 3.565 | 2.22 | 0.04 |
| 10 | 0.064 | 2.353 | 1.31 | 0.12 | 23 | 0.064 | 3.962 | 1.58 | 0.04 |
| 11 | 0.064 | 2.712 | 1.38 | 0.11 | 24 | 0.061 | 4.564 | 2.44 | 0.04 |
| 12 | 0.064 | 2.524 | 1.55 | 0.09 | 25 | 0.064 | 4.137 | 1.86 | 0.02 |
| 13 | 0.066 | 2.970 | 1.73 | 0.09 |
Table 1 25 Predicted oxygen tunnels and their bottleneck radius, length, curvature and priority
| ID | Bottleneck radius/nm | Length/nm | Curvature | Priority | ID | Bottleneck radius/nm | Length/nm | Curvature | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.095 | 1.674 | 1.38 | 0.42 | 14 | 0.074 | 3.365 | 1.35 | 0.07 |
| 2 | 0.070 | 2.213 | 1.52 | 0.30 | 15 | 0.077 | 4.507 | 3.28 | 0.06 |
| 3 | 0.079 | 2.624 | 1.34 | 0.18 | 16 | 0.061 | 3.293 | 2.09 | 0.06 |
| 4 | 0.070 | 2.419 | 1.36 | 0.14 | 17 | 0.067 | 3.664 | 1.52 | 0.05 |
| 5 | 0.064 | 2.705 | 1.56 | 0.14 | 18 | 0.066 | 3.852 | 2.32 | 0.05 |
| 6 | 0.062 | 2.054 | 1.70 | 0.13 | 19 | 0.063 | 3.437 | 2.21 | 0.05 |
| 7 | 0.077 | 3.221 | 1.42 | 0.13 | 20 | 0.064 | 3.517 | 2.30 | 0.05 |
| 8 | 0.074 | 2.875 | 1.41 | 0.12 | 21 | 0.064 | 4.117 | 1.73 | 0.04 |
| 9 | 0.077 | 3.380 | 3.34 | 0.12 | 22 | 0.062 | 3.565 | 2.22 | 0.04 |
| 10 | 0.064 | 2.353 | 1.31 | 0.12 | 23 | 0.064 | 3.962 | 1.58 | 0.04 |
| 11 | 0.064 | 2.712 | 1.38 | 0.11 | 24 | 0.061 | 4.564 | 2.44 | 0.04 |
| 12 | 0.064 | 2.524 | 1.55 | 0.09 | 25 | 0.064 | 4.137 | 1.86 | 0.02 |
| 13 | 0.066 | 2.970 | 1.73 | 0.09 |
| Tunnel | Time step | Sum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 30 | 50 | ||
| 1 | 9 | 8 | 11 | 28 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| 5 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 4 |
| 8 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 10 |
| Others | 1 | 1 | 8 | 10 |
| Sum | 20 | 20 | 20 | 60 |
Table 2 Results of the RAMD simulation
| Tunnel | Time step | Sum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 30 | 50 | ||
| 1 | 9 | 8 | 11 | 28 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| 5 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 4 |
| 8 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 10 |
| Others | 1 | 1 | 8 | 10 |
| Sum | 20 | 20 | 20 | 60 |
| [1] | Wang L., Li Y., Yang D., Process Biochem., 2010, 45(6), 919—928 |
| [2] | Neuwoehner J., Reineke A. K., Hollender J., Eisentraeger A., Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2009, 72(3), 819—827 |
| [3] | Sideropoulos A. S., Specht S. M., Curr. Microbiol., 1984, 11(2), 59—65 |
| [4] | Hirao K., Shinohara Y., Tsuda H., Fukushima S., Takahashi M., Cancer Res., 1976, 36(2 Part 1), 329—335 |
| [5] | Betz A., Facey S. J., Hauer B., Tshisuaka B., Lingens F., J. Basic Microbiol., 2000, 40(1), 7—23 |
| [6] | Fetzner S., Tshisuaka B., Lingens F., Kappl R., Hüttermann J., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 1998, 37(5), 576—597 |
| [7] | Hernandez-Ortega A., Quesne M. G., Bui S., Heuts D. P., Steiner R. A., Heyes D. J., de Visser S. P., Scrutton N. S., J. Biol. Chem., 2014, 289(12), 8620—8632 |
| [8] | Steiner R. A., Janssen H. J., Roversi P., Oakley A. J., Fetzner S., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2010, 107(2), 657—662 |
| [9] | Fischer F., Künne S., Fetzner S., J. Bacteriol., 1999, 181(18), 5725—5733 |
| [10] | Baas B. J., Poddar H., Geertsema E. M., Rozeboom H. J., de Vries M. P., Permentier H. P., Thunnissen A. M., Poelarends G. J., Biochemistry,2015, 54(5), 1219—1232 |
| [11] | Fetzner S., Steiner R. A., Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2010, 86(3), 791—804 |
| [12] | Frerichs-Deeken U., Fetzner S., Curr. Biol., 2005, 51(5), 344—352 |
| [13] | Calhoun D. B., Vanderkooi J. M., Englander S. W., Biochemistry,1983, 22(7), 1533—1539 |
| [14] | Oliveira A. S. F., Damas J. M., Baptista A. M., Soares C. M., PLoS Comput. Biol., 2014, 10(12), e1004010 |
| [15] | Shadrina M. S., English A. M., Peslherbe G. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(27), 11177—11184 |
| [16] | Saam J., Rosini E., Molla G., Schulten K., Pollegioni L., Ghisla S., J. Biol. Chem., 2010, 285(32), 24439—24446 |
| [17] | Baron R., Riley C., Chenprakhon P., Thotsaporn K., Winter R. T., Alfieri A., Forneris F., van Berkel W. J., Chaiyen P., Fraaije M. W., Mattevi A., McCammon J. A., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2009, 106(26), 10603—10608 |
| [18] | Saam J., Ivanov I., Walther M., Holzhütter H. G., Kuhn H., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2007, 104(33), 13319—13324 |
| [19] | Klinman J. P., Acc. Chem. Res., 2007, 40(5), 325—333 |
| [20] | Cohen J., Schulten K., Biophys. J., 2007, 93(10), 3591—3600 |
| [21] | Pesce A., Nardini M., LaBarre M., Richard C., Wittenberg J. B., Wittenberg B. A., Guertin M., Bolognesi M., BBA-Proteins and Proteomics., 2011, 1814(6), 810—816 |
| [22] | Milani M., Pesce A., Ouellet Y., Dewilde S., Friedman J., Ascenzi P., Guertin M., Bolognesi M., J. Biol. Chem., 2004, 279(20), 21520—21525 |
| [23] | Colloc’h N., Gabison L., Monard G., Altarsha M., Chiadmi M., Marassio G., Sopkova-de O. S. J., El H. M., Castro B., Abraini J. H., Prangé T., Biophys. J., 2008, 95(5), 2415—2422 |
| [24] | Boechi L., Arrar M., Martí M. A., Olson J. S., Roitberg A. E., Estrin D. A., J. Biol. Chem., 2013, 288(9), 6754—6762 |
| [25] | Vassiliev S., Zaraiskaya T., Bruce D., BBA-Bioenergetics., 2013, 1827(10), 1148—1155 |
| [26] | Frisch M. J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Mennucci B., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Caricato M., Li X., Hratchian H. P., Izmaylov A. F., Bloino J., Zheng G., Sonnenberg J. L., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Vreven T., Montgomery J. A. Jr., Peralta J. E., Ogliaro F., Bearpark M., Heyd J. J., Brothers E., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N., Kobayashi R., Normand J., Raghavachari K., Rendell A., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Rega N., Millam N. J., Klene M., Knox J. E., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Martin R. L., Morokuma K., Zakrzewski V. G., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Farkas Ö., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cioslowski J., Fox D. J., Gaussian 09, Revision A. 1, Gaussian Inc.,Wallingford CT, 2009 |
| [27] | Chovancova E., Pavelka A., Benes P., Strnad O., Brezovsky J., Kozlikova B., Gora A., Sustr V., Klvana M., Medek P., Biedermannova L., Sochor J., Damborsky J., PLoS Comput. Biol., 2012, 8(10), e1002708 |
| [28] | Schmidtke P., Bidon-Chanal A., Luque F. J., Barril X., Bioinformatics,2011, 27(23), 3276—3285 |
| [29] | Durrant J. D., Votapka L., Sørensen J., Amaro R. E., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2014, 10(11), 5047—5056 |
| [30] | Hamelberg D., Mongan J., McCammon J. A., J. Chem. Phys., 2004, 120(24), 11919—11929 |
| [31] | Burendahl S., Danciulescu C., Nilsson L., Proteins: Struct., Funct., Bioinf., 2009, 77(4), 842—856 |
| [32] | Vashisth H., Abrams C. F., Biophys. J., 2008, 95(9), 4193—4204 |
| [33] | Schleinkofer K., Sudarko Winn P. J., Lüdemann S. K., Wade R. C., EMBO Rep., 2005, 6(6), 584—589 |
| [34] | Case D. A., Darden T. A., Cheatham III T. E., Simmerling C. L., Wang J., Duke R. E., Luo R., Walker R. C., Zhang W., Merz K. M., Roberts B., Hayik S., Roitberg A., Seabra G., Swails J., Götz A. W., Kolossváry I., Wong K. F., Paesani F., Vanicek J., Wolf R. M., Liu J., Wu X., Brozell S. R., Steinbrecher T., Gohlke H., Cai Q., Ye X., Wang J., Hsieh M. J., Cui G., Roe D. R., Mathews D. H., Seetin M. G., Salomon-Ferrer R., Sagui C., Babin V., Luchko T., Gusarov S., Kovalenko A., Kollman P. A., AMBER 12, University of California, San Francisco, 2012 |
| [35] | Phillips J. C., Braun R., Wang W., Gumbart J., Tajkhorshid E., Villa E., Chipot C., Skeel R. D., Kale L., Schulten K., J. Comput. Chem., 2005, 26, 1781—1802 |
| [36] | Grossfield A., WHAM: the Weighted Histogram Analysis Method, Version 2.0.9, |
| [37] | Pap J. S., Matuz A., Baráth G., Kripli B., Giorgi M., Speier G., Kaizer J., J. Inorg. Biochem., 2012, 108, 15—21 |
| [1] | ZHANG Luge, XUE Zexu, ZHANG Chong, YAN Hui. Molecular Dynamics Studies on the Selective Deposition of 3(5)-(9-Anthryl) Pyrazole onto Self-assembled Monolayers† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(3): 505. |
| [2] | PAN Qi, LI Daixi, GUO Baisong, YANG Chunsheng, YANG Zhi. Active Structure Protection of Monoclonal Antibody Fusion Protein Etanercept† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(2): 274. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||