

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 1939.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160471
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
TONG Laga*( ), REN Guangsheng, DANG Xiaofeng, LIN Shijing, RONG Hua
), REN Guangsheng, DANG Xiaofeng, LIN Shijing, RONG Hua
Received:2016-07-04
Online:2016-11-10
Published:2016-10-20
Contact:
TONG Laga
E-mail:tonglaga@bipt.edu.cn
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
TONG Laga, REN Guangsheng, DANG Xiaofeng, LIN Shijing, RONG Hua. Induced Growth of Micro/nano ZnO Powder via Glu-BF4 Ionic Liquid Aqueous Solution†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(11): 1939.
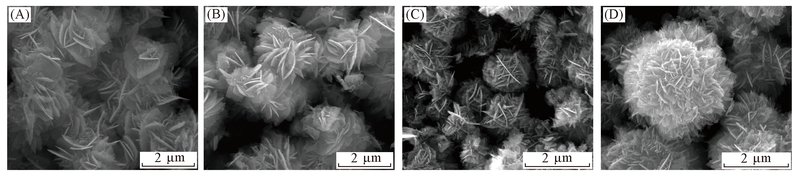
Fig.7 SEM images of ZnO nanostructures obtained using different concentrations of Glu-BF4 ionic liquid (A) 0.5 g(0.02 mol/L); (B) 1.0 g(0.04 mol/L); (C) 2.0 g(0.08 mol/L); (D) 3.0 g(0.12 mol/L).
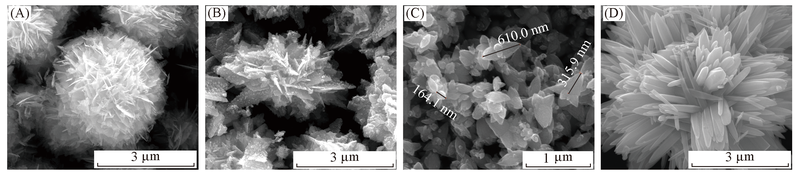
Fig.8 SEM images of ZnO nanostructures obtained with different concentrations of reactants(A) c(NaOH)=0.75 mol/L, c[Zn(OAc)2·2H2O]=0.125 mol/L; (B) c(NaOH)=0.5 mol/L, c[Zn(OAc)2·2H2O]=0.083 mol/L; (C) c(NaOH)=0.38 mol/L, c[Zn(OAc)2·2H2O]=0.063 mol/L; (D) c(NaOH)=3.0 mol/L, c[Zn(OAc)2·2H2O]=0.5 mol/L.
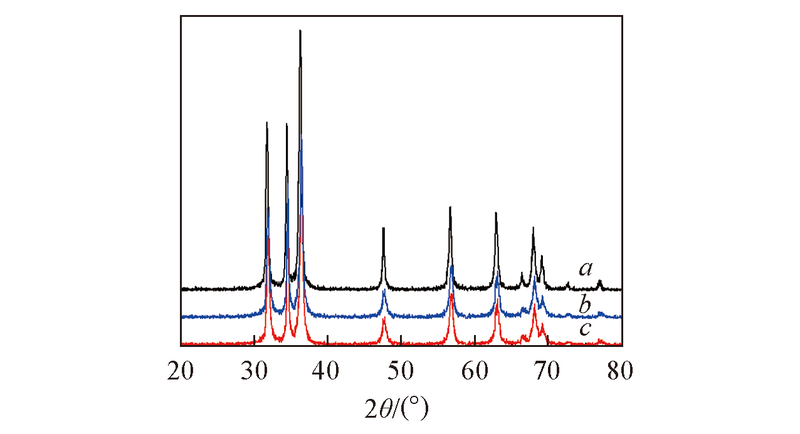
Fig.9 XRD patterns of the products obtained with different concentrations of reactantsa. c(NaOH)=0.75 mol/L, c[Zn(OAc)2·2H2O]=0.125 mol/L; b. c(NaOH)=0.5 mol/L, c[Zn(OAc)2·2H2O]=0.083 mol/L; c. c(NaOH)=0.38 mol/L, c[Zn(OAc)2·2H2O]=0.063 mol/L.
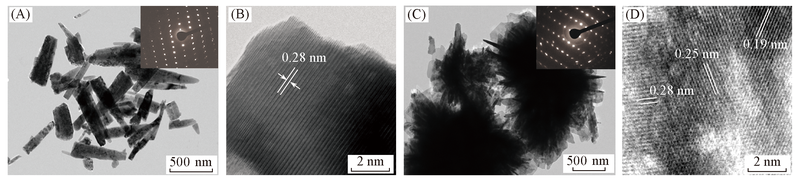
Fig.10 TEM(A, C) and HRTEM(B, D) images of nano-ZnO needles(A, B) and nano-ZnO pompons(C, D)Insets of (A) and (C): SAED images of nano-ZnO needles and nano-ZnO pompons, respectively.
| [1] | Motaung D., E. , Mhlongo G., H. , Nkosi S., S. , Malgas G., F. , Mwakikunga B., W. , Coetsee, E. , Swart H., C. , Abdallah H. M., I. , Moyo, T. , Ray S., S. , ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 8981- 8995 |
| [2] | Zhang Y., C. , Deng J., X. , Chen, J. , Yu R., B. , Xing X., R. , Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 2014, 43, 138- 141 |
| [3] | Wang H., Q. , Li C., H. , Zhao H., G. , Li, R. , Liu J., R. , Powder Technology, 2013, 239, 266- 271 |
| [4] | 王志芳, 李密, 张红霞. 无机化学学报, 2012, 28( 4), 715- 720 |
| Wang Z., F. , Li, M. , Zhang H. X, . , Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2012, 28( 4), 715- 720 ( | |
| [5] | Lang J., H. , Wang J., Y. , Zhang, Q. , Xu S., S. , Han, Q. , Zhang, Y. , Zhai H., J. , Cao, J. , Yan Y., S. , Yang J., H. , Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2014, 30( 4), 538- 542 |
| [6] | Xu S., G. , Guo W., H. , Du S., W. , Loy M. M., T. , Wang, N. , Nano Lett., 2012, 12, 5802- 5807 |
| [7] | Omar F., M. , Aziz H., A. , Stoll, S. , Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 468/469, 195- 201 |
| [8] | Ren, X. , Jiang C., H. , Li D., D. , He, L. , Mater. Lett., 2008, 62, 3114- 3116 |
| [9] | Razali, R. , Zak K., A. , Majid W. H., A. , Darroudi, M. , Ceramics International, 2011, 37, 3657- 3663 |
| [10] | Wang, F. , Qin X., F. , Guo Z., L. , Meng Y., F. , Yang L., X. , Ming Y., F. , Ceramics International, 2013, 39, 8969- 8973 |
| [11] | Shi R., X. , Yang, P. , Dong X., B. , Ma, Q. , Zhang A., Y. , Applied Surface Science, 2013, 264, 162- 170 |
| [12] | Hamedani N., F. , Mahjoub A., R. , Khodadadi A., A. , Mortazavi, Y. , Sensors and Actuators B, 2011, 156, 737- 742 |
| [13] | 李奡麒, 陈玉娟, 胡晓宇, 卓克垒. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36( 1), 165- 170 |
| Li A., Q. , Chen Y., J. , Hu X., Y. , Zhuo K., L. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36( 1), 165- 170 ( | |
| [14] | Goharshadi E., K. , Ding Y., L. , Nancarrow, P. , Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2008, 69, 2057- 2060 |
| [15] | Yu H., W. , Fan H., Q. , Wang, X. , Wang, J. , Optik., 2014, 125, 1461- 1464 |
| [16] | 胡晓宇, 刘千阁, 卓克垒, 王键吉. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34( 2), 324- 330 |
| Hu X., Y. , Liu Q., G. , Zhuo K. L, . , Wang J., J. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34( 2), 324- 330 ( | |
| [17] | Movahedi, M. , Kowsari, E. , Mahjoub A., R. , Yavari, I. , Mater. Lett., 2008, 62, 3856- 3858 |
| [18] | Sanes, J. , Carrion F., J. , Bermudez M., D. , Applied Surface Science, 2009, 255, 4859- 4862 |
| [19] | Chen C., Y. , Li, Q. , Nie, M. , Lin, H. , Li, Y. , Wu H., J. , Wang Y., Y. , Materials Research Bulletin, 2011, 46, 888- 893 |
| [20] | Wang, L. , Xu S., Z. , Li H., J. , Chang L., X. , Su, Z. , Zeng M., H. , Wang L., N. , Huang Y., N. , Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2011, 184, 720- 724 |
| [21] | Lee K., M. , Chiu W., H. , Hsu C., Y. , Cheng H., M. , Lee C., H. , Wu C., G. , Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 216, 330- 336 |
| [22] | Min Y., L. , Zhang, K. , Chen L., H. , Chen Y., C. , Zhang Y., G. , Diamond & Related Materials, 2012, 26, 32- 38 |
| [23] | Sabbaghan, M. , Shahvelayati A., S. , Bashtani S., E. , Solid State Sciences, 2012, 14, 1191- 1195 |
| [24] | Rong, H. , Li, W. , Chen Z., Y. , Wu X., M. , J. Phys. Chem. B, 2008, 112, 1451- 1455 |
| [25] | Tong L., G. , Liu, Y. , Rong, H. , Gong L., F. , Mater. Lett., 2013, 112, 5- 7 |
| [26] | 佟拉嘎, 刘金艳, 王岑晨, 荣华, 李巍. 物理化学学报, 2015, 31( 8), 1615- 1620 |
| Tong L., G. , Liu J., Y. , Wang C., C. , Rong, H. , Li, W. , Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin., 2015, 31( 8), 1615- 1620 ( | |
| [27] | 佟拉嘎, 欧阳萍, 马小丽, 荣华. 功能材料, 2015, 46( 6), 06020- 06025 |
| Tong L., G. , Ouyang, P. , Ma X., L. , Rong, H. , Journal of Functional Materials, 2015, 46( 6), 06020- 06025 ( | |
| [28] | Zhang, Y. , Jia H., B. , Wang R., M. , Chen C., P. , Luo X., H. , Yu D., P. , Appl. Phys. Lett., 2003, 83, 4631- 4633 |
| [29] | 管秋梅, 张辉朝, 叶永红, 崔一平, 张家雨. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33( 10), 2315- 2319 |
| Guan Q., M. , Zhang H., C. , Ye Y., H. , Cui Y., P. , Zhang J., Y. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33( 10), 2315- 2319 ( | |
| [30] | Fré, déric D. , Romain, P. , Fré, déric B. , Crystal Growth & Design, 2014, 14, 5388- 5396 |
| [31] | Cho, S. , Jung S., H. , Lee K., H. , J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 12769- 12776 |
| [1] | SONG Chao, DONG Xiang-Ting*, WANG Jin-Xian, LIU Gui-Xia. Synthesis and Formation Mechanism of NiO@Al2O3@TiO2 Coaxial Trilayered Submicrocables by Electrospinning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(8): 1673. |
| [2] | WANG Lu-De, HUANG Zai-Yin*, GUO Yun-Xiao, WANG Teng-Hui. In-situ Growth and Mechanism of the Octahedron BaMoO4 Nanostructures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(12): 2838. |
| [3] | WU Mian-Li, LI Jie*, LIU Fang-Yang, LIU Jun, LAI Yan-Qing, ZHANG Zhi-An, LIU Ye-. Electrodeposition of CuInSe2 and Its Formation Mechanism [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(2): 330. |
| [4] | ZHENG Yi-Fan*, LIU Hua-Zhang*, LI Xiao-Nian. In situ X-ray Diffraction Investigation on Reduction Process of Ammonia-synthesis Fused-iron Catalysts and the Formation Mechanism of Its Active Phase [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(6): 1177. |
| [5] | ZHANG Mao-Gen, WENG Zhi-Xue, HUANG Zhi-Ming, PAN Zu-Ren . Particle Formation Mechanism in the Emulsifier-free Emulsion Polymerization of MMA/BA/Sodium Polyethylene Glycol Maleate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1999, 20(11): 1800. |
| [6] | LUO Ying-Wu, WENG Zhi-Xue, HUANG Zhi-Ming, PAN Zu-Ren. Gel Point and Mechanism of Gel Formation in Copolymers from Free-Radical Crosslinking Polymerization of Vinyl/Divinyl Monomers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1997, 18(6): 968. |
| [7] | XU Shi-Ai, JIANG Ming, SHEN Jing-Shu. TEM Studies on Deformation Mechanisms of PS/LDPE Blends [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1995, 16(3): 489. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||