

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (10): 20220264.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220264
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2022-04-19
Online:2022-10-10
Published:2022-05-18
Contact:
ZHANG Hao
E-mail:hao_zhang@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
XU Wenzhe, ZHANG Hao. Supramolecular Interactions-mediated Nanodrug Nucleation[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220264.
| Abbreviation | Full name | Abbreviation | Full name | Abbreviation | Full name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAs | Amino acids | CPT | Camptothecin | ICG | Indocyanine green |
| ATO | Atovaquone | Cur | Curcumin | Ir | Irinotecan |
| BBR | Berberine | DOX | Doxorubicin | MTX | Methotrexate |
| BC | Betulonic acid | FA | Folic acid | PAAs | Polyamino acids |
| CA | Cinnamic acid | FZ | Phenylsulfonylfuroxan | PTX | Paclitaxel |
| Cb | Chlorambucil | GA | Gambogic acid | UA | Ursolic acid |
| Ce6 | Chlorin e6 | HCPT | 10?Hydroxycamptothecin |
Table 1 Abbreviations and full names of the drugs in this review
| Abbreviation | Full name | Abbreviation | Full name | Abbreviation | Full name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAs | Amino acids | CPT | Camptothecin | ICG | Indocyanine green |
| ATO | Atovaquone | Cur | Curcumin | Ir | Irinotecan |
| BBR | Berberine | DOX | Doxorubicin | MTX | Methotrexate |
| BC | Betulonic acid | FA | Folic acid | PAAs | Polyamino acids |
| CA | Cinnamic acid | FZ | Phenylsulfonylfuroxan | PTX | Paclitaxel |
| Cb | Chlorambucil | GA | Gambogic acid | UA | Ursolic acid |
| Ce6 | Chlorin e6 | HCPT | 10?Hydroxycamptothecin |
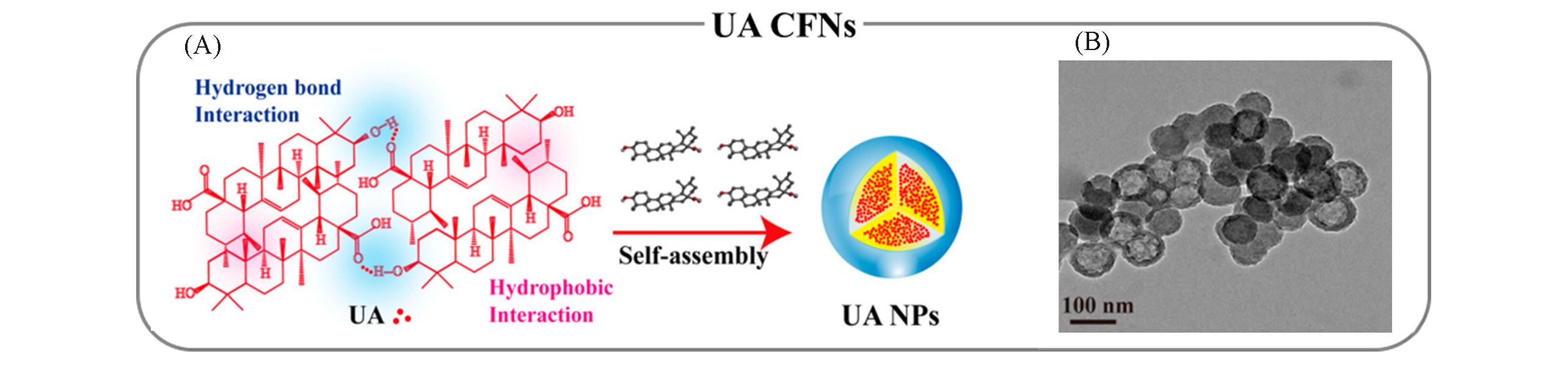
Fig.2 Representative natural drug?based self?assembled CFNs through predominant supramolecular interactions[34](A) Schematic illustration of the nanoprecipitation process of UA CFNs and the involved supramolecular interactions; (B) transmission electron microscope(TEM) image of UA CFNs. Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society.
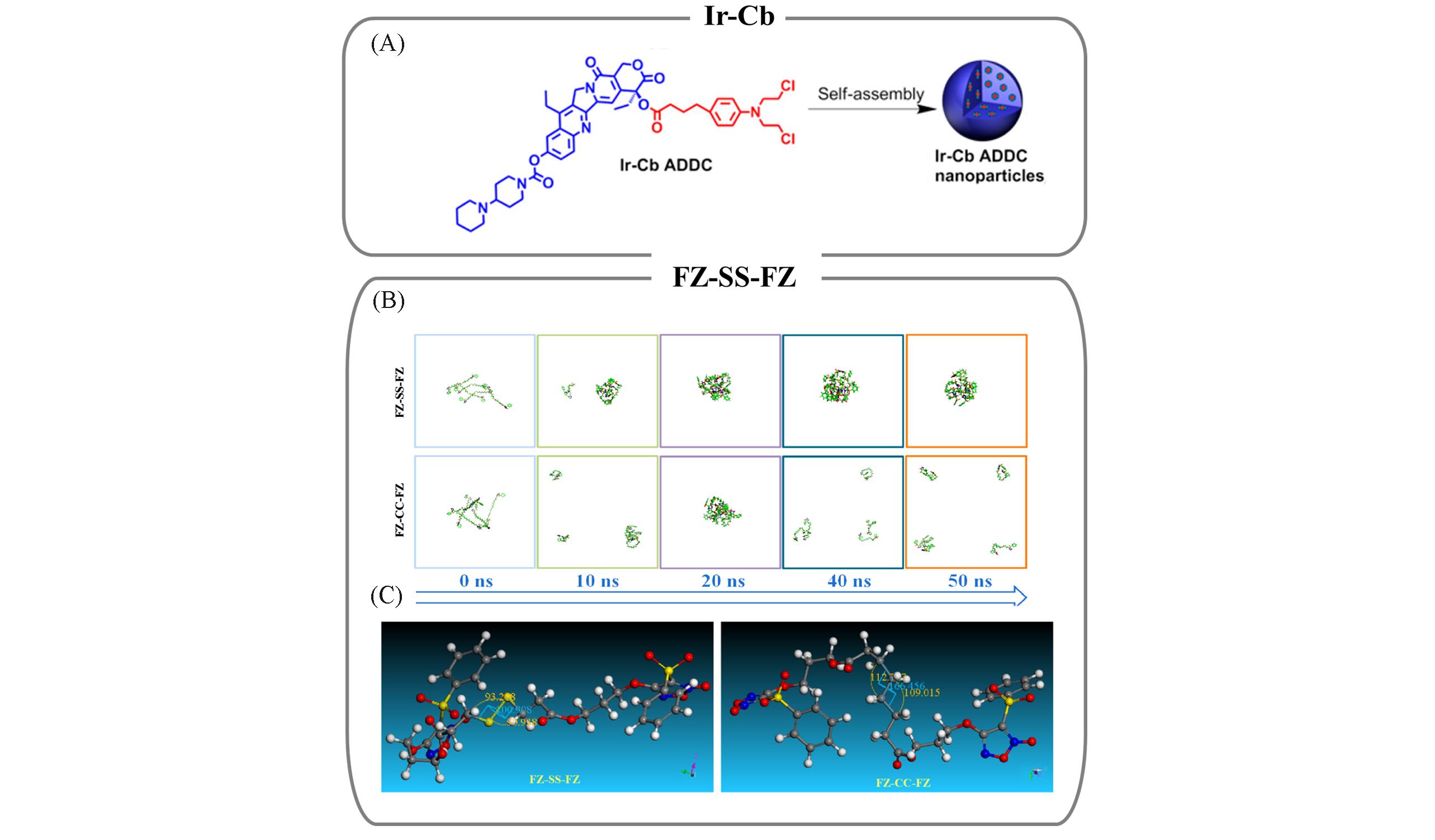
Fig.3 CFNs from drugs conjugated with complementary hydrophobic drugs and representative mechanism(A) Constitutional formula of Ir-Cb prodrugs and the preparation of Ir-Cb CFNs[40]; (B) self-assembly evolution of FZ-SS-FZ and FZ-CC-FZ CFNs studied by MD simulations; (C) Materials Studio simulation results of bond angles and dihedral angles of FZ-SS-FZ and FZ-CC-FZ prodrugs. When the bond angle and dihedral angle are closer to 90°, the CFNs is more stable. The bond angles of —SS— and —CC— are 93.2°/90.9° and 112.7°/109.0°, respectively. The dihedral angles of C—SS—C and C—CC—C are 100.9° and 166.4°, respectively[43].(A) Copyright 2014, American Chemical Society; (B, C) Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society.
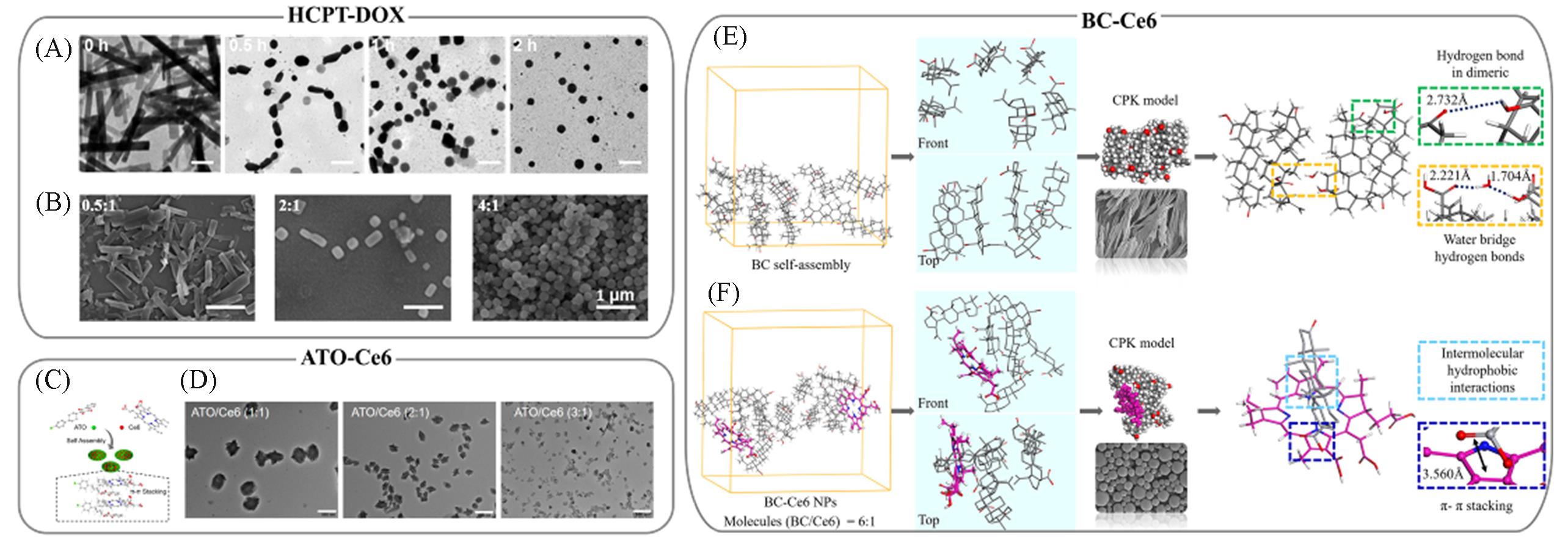
Fig.5 Representative π?system multidrug co?assembled CFNs with controllable size and morphology(A) Morphology evolution of HCPT-DOX CFNs characterized by TEM at different time points, the scale bar is 500 nm; (B) TEM images of HCPT-DOX CFNs at different DOX-to-HCPT molar ratios[54]; (C) schematic illustration of co-assembly between ATO and Ce6 through π?π stacking; (D) TEM images of ATO-Ce6 CFNs at different ATO-to-Ce6 molar ratios, the scale bar is 500 nm[56]; MD simulation results of BC self-assembled(E) and BC-Ce6 co-assembled CFNs(F)[29].(A, B) Copyright 2015, American Chemical Society; (C, D) Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society; (E, F) Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
| CFNs | Hydrodynamic diameter/nm | Zeta potential/mV | Stability duration/d | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coniferyl ferulate?Ce6 | 159.1 | Negative | 5 | [ |
| NLG919?Ce6 | — | Negative | 5 | [ |
| α?Tocopherol succinate?DOX | 199.9 | Negative | 7 | [ |
| ICG?PTX | 112±1.06 | -34.5 | 7(buffer solution) | [ |
| ICG@UA/PTX | ca. 130.8 | -30.8 | 8 | [ |
| Ce6?gambogic acid | 142.2±14.9 | -27.5±4.6 | 9 | [ |
| ATO?Ce6 | 193.5 | -23.31 | 9(water, PBS, or cell culture medium) | [ |
| BC?Ce6 | 231.4±8.4 | -5.2±2.23 | 10 | [ |
| UA?lactobionic acid?ICG | 116.4±2.4 | -30.6±1.8 | 30 | [ |
| PTX?ICG | 140±1.4 | -36±2.2 | Over 30 | [ |
Table 2 Summary of hydrodynamic diameter, zeta potential, and stability duration of CFNs
| CFNs | Hydrodynamic diameter/nm | Zeta potential/mV | Stability duration/d | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coniferyl ferulate?Ce6 | 159.1 | Negative | 5 | [ |
| NLG919?Ce6 | — | Negative | 5 | [ |
| α?Tocopherol succinate?DOX | 199.9 | Negative | 7 | [ |
| ICG?PTX | 112±1.06 | -34.5 | 7(buffer solution) | [ |
| ICG@UA/PTX | ca. 130.8 | -30.8 | 8 | [ |
| Ce6?gambogic acid | 142.2±14.9 | -27.5±4.6 | 9 | [ |
| ATO?Ce6 | 193.5 | -23.31 | 9(water, PBS, or cell culture medium) | [ |
| BC?Ce6 | 231.4±8.4 | -5.2±2.23 | 10 | [ |
| UA?lactobionic acid?ICG | 116.4±2.4 | -30.6±1.8 | 30 | [ |
| PTX?ICG | 140±1.4 | -36±2.2 | Over 30 | [ |
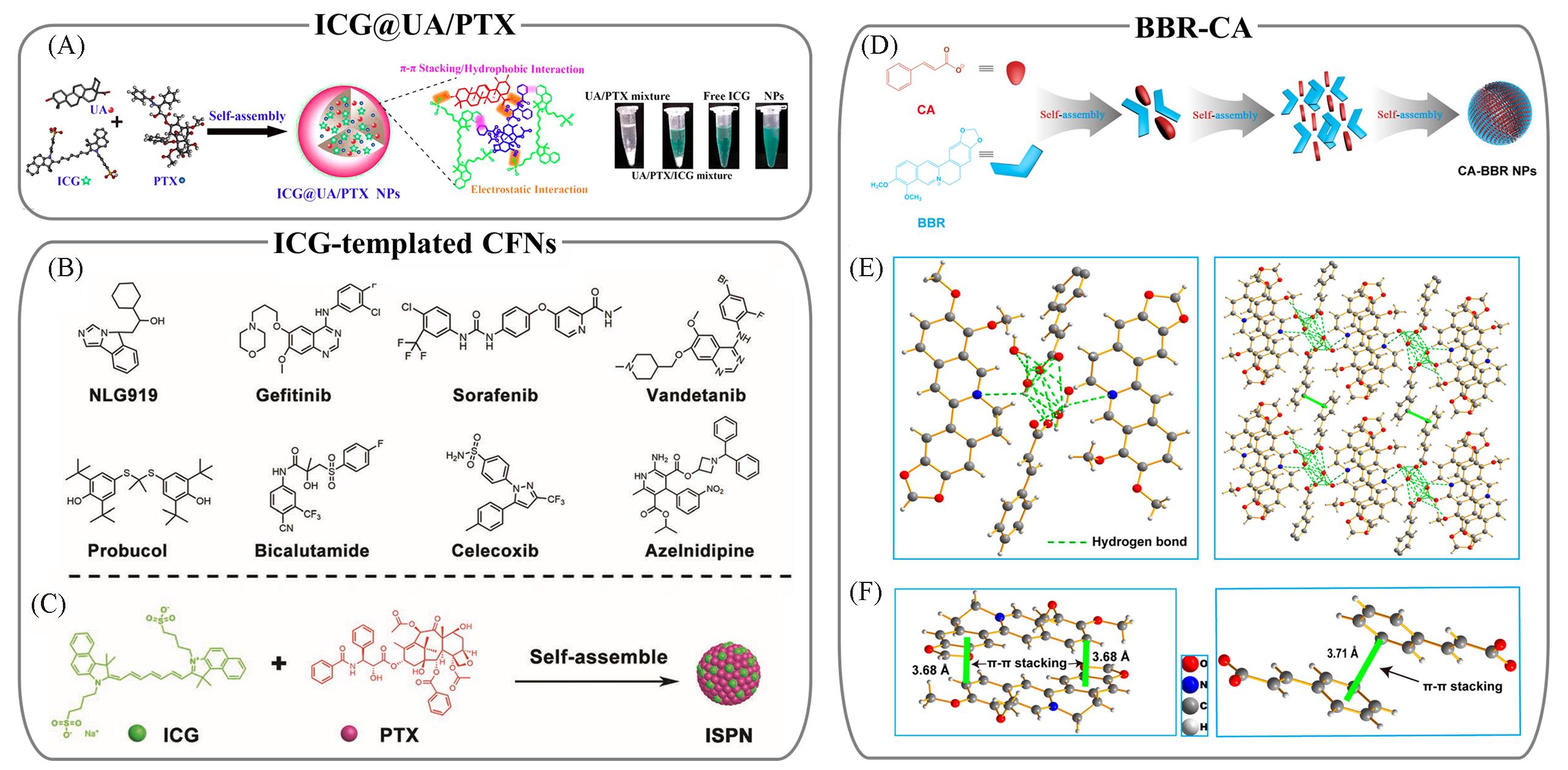
Fig.6 Representative π?system multidrug co?assembled CFNs characterized with function integration and type enrichment(A) Schematic illustration of co-assembled ICG@UA/PTX CFNs through π?π stacking, hydrophobic interaction and electrostatic interaction, and optical images of the corresponding constitutions[60]; (B) a library of small molecule drugs for ICG-templated CFNs; (C) schematic illustration of co-assembled ICG/PTX CFNs by adding PTX-contained organic solution into ICG-predissolved aqueous media[62]; (D) self-assembly process of BBR-CA CFNs; (E) formation of BBR-CA nucleus by hydrogen bonding(left) and 3D stacking of BBR-CA nucleus through π?π stacking (right); (F) inter-BBR(left) and inter-CA(right) π?π stacking[72].(A) Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society; (B, C) Copyright 2019, Wiley Online Library; (D—F) Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
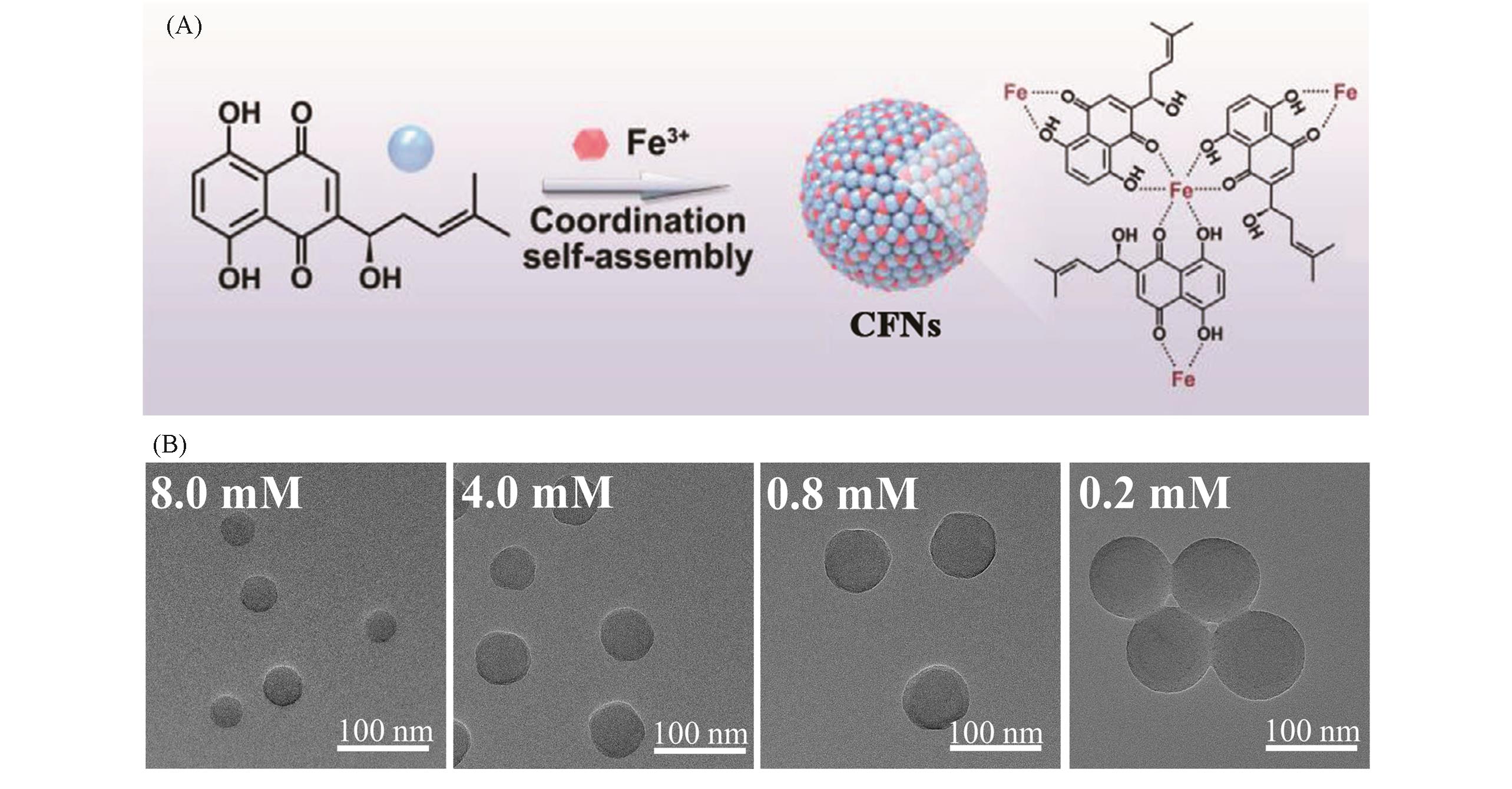
Fig.7 Schematic illustration of the formation of Fe(Ⅲ)?shikonin CFNs driven by coordination interaction(A) and TEM images of Fe(Ⅲ)?shikonin CFNs prepared with different Fe(Ⅲ) concentrations(B)[76]Copyright 2021, Wiley Online Library.
| 1 | Salvioni L., Rizzuto M. A., Bertolini J. A., Pandolfi L., Colombo M., Prosperi D., Cancers, 2019, 11, 1855 |
| 2 | US Food and Drug Administration, https://www.fda.gov/regulatory⁃information/search⁃fda⁃guidance⁃documents/considering⁃whether⁃fda⁃regulated⁃product⁃involves⁃application⁃nanotechnology |
| 3 | Zhao Y., Cao W. Q., Liu Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5), 909—923 |
| 4 | Sun Q. R., Zhao N., Liu S. W., Xin H., Zhang H., Zhang L. N., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10),3225—3232 |
| 5 | Edis Z., Wang J., Waqas M. K., Ijaz M., Ijaz M., Int. J. Nanomedicine, 2021, 16, 1313—1330 |
| 6 | Barenholz Y., J. Control. Release, 2012, 160, 117—134 |
| 7 | Shi J., Kantoff P. W., Wooster R., Farokhzad O. C., Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2017, 17, 20—37 |
| 8 | Qin S. Y., Zhang A. Q., Cheng S. X., Rong L., Zhang X. Z., Biomaterials, 2017, 112, 234—247 |
| 9 | Mei H., Cai S., Huang D., Gao H., Cao J., He B., Bioact. Mater., 2022, 8, 220—240 |
| 10 | Karaosmanoglu S., Zhou M., Shi B., Zhang X., Williams G. R., Chen X., J. Control. Release, 2021, 329, 805—832 |
| 11 | Jiang S., Fu Y., Zhang X., Yu T., Lu B., Du J., Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 2021, 9, 799806 |
| 12 | Ge W., Wang L., Zhang J., Ou C., Si W., Wang W., Zhang Q., Dong X., Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 8, 2001602 |
| 13 | Qiao Y., Wei Z., Qin T., Song R., Yu Z., Yuan Q., Du J., Zeng Q., Zong L., Duan S., Pu X., Chin. Chem. Lett., 2021, 32, 2877—2881 |
| 14 | Zhang J., Li Y., An F. F., Zhang X., Chen X., Lee C. S., Nano Lett., 2015, 15, 313—318 |
| 15 | Malamatari M., Taylor K. M. G., Malamataris S., Douroumis D., Kachrimanis K., Drug Discov. Today, 2018, 23, 534—547 |
| 16 | D'Addio S. M., Prud'homme R. K., Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev., 2011, 63, 417—426 |
| 17 | Lepeltier E., Bourgaux C., Couvreur P., Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev., 2014, 71, 86—97 |
| 18 | Martinez R. C. J., Tarhini M., Badri W., Miladi K., Greige⁃Gerges H., Nazari Q. A., Galindo R. S. A., Roman R. A., Fessi H., Elaissari A., Int. J. Pharm., 2017, 532, 66—81 |
| 19 | Prabagar B., Yang Y., Shi Z., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50, 11249—11269 |
| 20 | Li G., Sun B., Li Y., Luo C., He Z., Sun J., Small, 2021, 17, e2101460 |
| 21 | Zhang Y., Fang F., Li L., Zhang J., ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng., 2020, 6, 4816—4833 |
| 22 | Zhang X., Li N., Zhang S., Sun B., Chen Q., He Z., Luo C., Sun J., Med. Res. Rev., 2020, 40, 1754—1775 |
| 23 | Azadbakht R., Hakimi M., Khanabadi J., Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc., 2021, 250, 119236 |
| 24 | Lee J. H., Kim T. M., Choi I. G., Choi J. W., Nanomaterials, 2021, 11, 1790 |
| 25 | Mora⁃Huertas C. E., Fessi H., Elaissari A., Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2011, 163, 90—122 |
| 26 | Beck⁃Broichsitter M., Colloids and Surfaces A, 2021, 625, 126928 |
| 27 | Li X., Shen J., Wang B., Feng X., Mao Z., Sui X., ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2021, 9, 5470—5480 |
| 28 | Nikoubashman A., Lee V. E., Sosa C., Prud'homme R. K., Priestley R. D., Panagiotopoulos A. Z., ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 1425—1433 |
| 29 | Cheng J., Zhao H., Wang J., Han Y., Yang X., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 43488—43500 |
| 30 | Yan X., Bernard J., Ganachaud F., Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2021, 294, 102474 |
| 31 | Hicham F., Packiarajan M., Kenrick L. V., Debra M. S., Klaas H., Karl V. W., Joseph G. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, 123, 3854—3855 |
| 32 | Chen Z., Farag M. A., Zhong Z., Zhang C., Yang Y., Wang S., Wang Y., Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 2021, 176, 113870 |
| 33 | Shao J., Fang Y., Zhao R., Chen F., Yang M., Jiang J., Chen Z., Yuan X., Jia L., Asian J. Pharm. Sci., 2020, 15, 685—700 |
| 34 | Fan L., Zhang B., Xu A., Shen Z., Guo Y., Zhao R., Yao H., Shao J. W., Mol. Pharm., 2018, 15, 2466—2478 |
| 35 | Li W., Yang Y., Wang C., Liu Z., Zhang X., An F., Diao X., Hao X., Zhang X., Chem. Commun.(Camb.), 2012, 48, 8120—8122 |
| 36 | Zhang J., Li S., An F. F., Liu J., Jin S., Zhang J. C., Wang P. C., Zhang X., Lee C. S., Liang X. J., Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 13503—13510 |
| 37 | He D., Zhang W., Deng H., Huo S., Wang Y. F., Gong N., Deng L., Liang X. J., Dong A., Chem. Commun.(Camb.), 2016, 52, 14145—14148 |
| 38 | Hou M., Xue P., Gao Y. E., Ma X., Bai S., Kang Y., Xu Z., Biomater. Sci., 2017, 5, 1889—1897 |
| 39 | Huang L., Wan J., Wu H., Chen X., Bian Q., Shi L., Jiang X., Yuan A., Gao J., Wang H., Nano Today, 2021, 36, 101030 |
| 40 | Huang P., Wang D., Su Y., Huang W., Zhou Y., Cui D., Zhu X., Yan D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 11748—11756 |
| 41 | Zhang T., Huang P., Shi L., Su Y., Zhou L., Zhu X., Yan D., Mol. Pharm., 2015, 12, 2328—2336 |
| 42 | Cheng C., Sui B., Wang M., Hu X., Shi S., Xu P., Adv. Healthc. Mater., 2020, 9, e2001128 |
| 43 | Gu G., Chen C., Zhang S., Yin B., Wang J., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 50682—50694 |
| 44 | Onoue S., Yamada S., Chan H. K., Int. J. Nanomedicine, 2014, 9, 1025—1037 |
| 45 | Faul C. F. J., Antonietti M., Adv. Mater., 2003, 15, 673—683 |
| 46 | Wang Z., Wang L., Liu S., Zhang M., Li Y., Rong L., Liu Y., Zhang H., Nanoscale, 2022, 14, 2186—2198 |
| 47 | Xu Z., Hou M., Shi X., Gao Y. E., Xue P., Liu S., Kang Y., Biomater. Sci., 2017, 5, 444—454 |
| 48 | Xu Z., Shi X., Hou M., Xue P., Gao Y. E., Liu S., Kang Y., Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces, 2017, 150, 50—58 |
| 49 | Shen Y., Jin E., Zhang B., Murphy C. J., Sui M., Zhao J., Wang J., Tang J., Fan M., Kirk E. V., Murdoch W. J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 4259—4265 |
| 50 | Sun T., Lin W., Zhang W., Xie Z., Chem Asian J., 2016, 11, 3174—3177 |
| 51 | Kinnear C., Moore T. L., Rodriguez⁃Lorenzo L., Rothen⁃Rutishauser B., Petri⁃Fink A., Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 11476—11521 |
| 52 | Chen F., Zhao Y., Pan Y., Xue X., Zhang X., Kumar A., Liang X. J., Mol. Pharm., 2015, 12, 2237—2244 |
| 53 | Li Y., Lin J., Cai Z., Wang P., Luo Q., Yao C., Zhang Y., Hou Z., Liu J., Liu X., J. Control. Release, 2020, 321, 222—235 |
| 54 | Zhao Y., Chen F., Pan Y., Li Z., Xue X., Okeke C. I., Wang Y., Li C., Peng L., Wang P. C., Ma X., Liang X. J., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7, 19295—19305 |
| 55 | Wen Y., Zhang W., Gong N., Wang Y. F., Guo H. B., Guo W., Wang P. C., Liang X. J., Nanoscale, 2017, 9, 14347—14356 |
| 56 | Zhao L. P., Zheng R. R., Chen H. Q., Liu L. S., Zhao X. Y., Liu H. H., Qiu X. Z., Yu X. Y., Cheng H., Li S. Y., Nano Lett., 2020, 20, 2062—2071 |
| 57 | Li X., Kong R., Li Y., Huang J., Zhou X., Li S., Cheng H., Chem. Commun.(Camb.), 2022, 58, 3917—3920 |
| 58 | Zhao L. P., Zheng R. R., Huang J. Q., Chen X. Y., Deng F. A., Liu Y. B., Huang C. Y., Yu X. Y., Cheng H., Li S. Y., ACS Nano, 2020, 14, 17100—17113 |
| 59 | Zheng R. R., Zhao L. P., Liu L. S., Deng F. A., Chen X. Y., Jiang X. Y., Wang C., Yu X. Y., Cheng H., Li S. Y., Biomater. Sci., 2021, 9, 3445—3452 |
| 60 | Guo Y., Jiang K., Shen Z., Zheng G., Fan L., Zhao R., Shao J., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 43508—43519 |
| 61 | Lan J. S., Liu L., Zeng R. F., Qin Y. H., Hou J. W., Xie S. S., Yue S., Yang J., Ho R. J. Y., Ding Y., Zhang T., Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 407, 127212 |
| 62 | Feng B., Niu Z., Hou B., Zhou L., Li Y., Yu H., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 30, 1906605 |
| 63 | Zhao R., Zheng G., Fan L., Shen Z., Jiang K., Guo Y., Shao J. W., Acta Biomater., 2018, 70, 197—210 |
| 64 | Lin J., Li C., Guo Y., Zou J., Wu P., Liao Y., Zhang B., Le J., Zhao R., Shao J. W., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2019, 7, 6914—6923 |
| 65 | Zhang Z., Wang Y., Ma Q., Zhang S., Liu H., Zhao B., Liu R., Wang W., Du B., Zhong Y., Kong D., Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 406, 126801 |
| 66 | Lin H., Chen Y., Shi J., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47, 1938—1958 |
| 67 | Yu C., Zhou M., Zhang X., Wei W., Chen X., Zhang X., Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 5683—5690 |
| 68 | Jiang K., Han L., Guo Y., Zheng G., Fan L., Shen Z., Zhao R., Shao J., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017, 5, 9121—9129 |
| 69 | Liu C., Liu Q., Chen L., Li M., Yin J., Zhu X., Chen D., Adv. Healthc. Mater., 2020, 9, e2000899 |
| 70 | Wang X. L., Wang Z. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10), 2185—2191 |
| 71 | Yang B., Wang K., Zhang D., Sun B., Ji B., Wei L., Li Z., Wang M., Zhang X., Zhang H., Kan Q., Luo C., Wang Y., He Z., Sun J., Biomater. Sci., 2018, 6, 2965—2975 |
| 72 | Huang X., Wang P., Li T., Tian X., Guo W., Xu B., Huang G., Cai D., Zhou F., Zhang H., Lei H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 227—237 |
| 73 | Shan L., Gao G., Wang W., Tang W., Wang Z., Yang Z., Fan W., Zhu G., Zhai K., Jacobson O., Dai Y., Chen X., Biomaterials, 2019, 210, 62—69 |
| 74 | Liu T., Feng J., Zhang X. Z., Journal of Functional Polymers, 2019, 32, 421—433 |
| 75 | Xu C., Wang Y., Yu H., Tian H., Chen X., ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 8255—8265 |
| 76 | Feng W., Shi W., Liu S., Liu H., Liu Y., Ge P., Zhang H., Adv. Healthc. Mater., 2022, 11, e2101926 |
| 77 | Yang G. G., Zhou D. J., Pan Z. Y., Yang J., Zhang D. Y., Cao Q., Ji L. N., Mao Z. W., Biomaterials, 2019, 216, 119280 |
| 78 | Pucci C., Martinelli C., De Pasquale D., Battaglini M., di Leo N., Degl'Innocenti A., Belenli Gumus M., Drago F., Ciofani G., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14, 15927—15941 |
| 79 | Wang Y., Xu C., Meng M., Lin L., Hu Y., Hao K., Sheng S., Zhang S., Wu J., Liu F., Jiang X., Tian H., Chen X., Nano Today, 2021, 40, 101266 |
| 80 | Tu L., Fan Z., Zhu F., Zhang Q., Zeng S., Chen Z., Ren L., Hou Z., Ye S., Li Y., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2020, 8, 5667—5681 |
| 81 | Zhao L., Zheng R., Liu L., Chen X., Guan R., Yang N., Chen A., Yu X., Cheng H., Li S., Biomaterials, 2021, 275, 120970 |
| 82 | Liu J., Zuo W., Jin Q., Liu C., Liu N., Tian H., Zhu X., Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl., 2021, 129, 112351 |
| 83 | Thi T. T. H., Suys E. J. A., Lee J. S., Nguyen D. H., Park K. D., Truong N. P., Vaccines(Basel), 2021, 9, 359 |
| 84 | Scalise M., Pochini L., Galluccio M., Console L., Indiveri C., Front. Oncol., 2017, 7, 306 |
| 85 | Li Y., Jiang Y., Zheng Z., Du N., Guan S., Guo W., Tang X., Cui J., Zhang L., Liu K., Yu Q., Gan Z., Adv. Mater., 2022, 34, e2110490 |
| [1] | LI Lin, XU Xinru, LI Yingqi, ZHANG Caifeng. Preparation of Targeting Nanodiamond-metaminopterone Drug System and Its Interaction with MCF-7 Cells † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1998. |
| [2] |
YANG Bing, MA Yu-Guang*, SHEN Jia-Cong*.
Stacking Mode, Optoelectronic Property and Supramolecular Control Method in π\|Conjugated Organic Molecules [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(12): 2643. |
| [3] | HAN Shu-Bo, ZHU Min, YUAN Zhuo-Bin . An Amperometric Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor Based on Supramolecular Inclusion Complex of β-CD Polymer as Immobilization Matrix [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1999, 20(7): 1036. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
