

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 41.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160643
• Organic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Benguo1, LIU Jiangwei1, LI Jiaqi2, GENG Sheng1, MO Haizhen1, LIANG Guizhao2,*( )
)
Received:2016-09-14
Online:2017-01-10
Published:2016-12-20
Contact:
LIANG Guizhao
E-mail:gzliang@cqu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Benguo, LIU Jiangwei, LI Jiaqi, GENG Sheng, MO Haizhen, LIANG Guizhao. 3D-QSAR and Interaction Mechanism of Flavonoids s P-glycoprotein Inhibitors†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(1): 41.
| Compd. | Type | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 2' | 3' | 4' | 5' | 6' | KD/ (μmol·L-1) | Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ⅰ | —H | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 34.900 | Training | |
| 2 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —H | 10.100 | Training | |
| 3 | Ⅰ | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 10.100 | Training | |
| 4 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 8.900 | Test | |
| 5 | Ⅰ | —CH3 | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 8.900 | Training | |
| 6 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —OH | —OH | —H | —H | 7.000 | Training | |
| 7 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —F | —H | —H | 6.800 | Training | |
| 8 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —H | 6.700 | Test | |
| 9 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —F | —F | —H | —H | 6.300 | Training | |
| 10 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OCH3 | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 6.300 | Training | |
| 11 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 5.300 | Training | |
| 12 | Ⅱ | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | 4.800 | Test | ||
| 13 | Ⅱ | —H | —H | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | 4.600 | Training | ||
| 14 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —OCH3 | —H | —H | 4.500 | Training | |
| 15 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —Cl | —H | —Cl | —H | —H | 4.000 | Training | |
| 16 | Ⅱ | —H | —F | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | 3.600 | Test | ||
| 17 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —CH3 | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 3.100 | Training | |
| 18 | Ⅱ | —H | —OCH3 | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | 2.300 | Training | ||
| 19 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —I | —H | —H | 2.200 | Training | |
| 20 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —CH3 | —CH3 | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 1.300 | Test | |
| 21 | Ⅱ | —H | —Cl | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | 1.300 | Training | ||
| 22 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | Isopropyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 1.300 | Training | |
| 23 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —I | —H | —H | 1.100 | Training | |
| 24 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | Benzyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.990 | Test | |
| 25 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | Dimethylallyl | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —H | 0.700 | Training | |
| 26 | Ⅱ | —H | —Br | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | 0.570 | Training | ||
| 27 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | Dimethylallyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.450 | Training | |
| 28 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | Benzyl | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.340 | Test | |
| 29 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | Prenyl | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.300 | Training | |
| 30 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | Prenyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.280 | Training | |
| 31 | Ⅱ | —H | —I | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | 0.250 | Training | ||
| 32 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | Prenyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.220 | Test | |
| 33 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | Prenyl | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.210 | Training | |
| 34 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | Dimethylallyl | —H | —H | —OCH3 | —H | —H | 0.200 | Training | |
| 35 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | Dimethylallyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.200 | Training | |
| 36 | Ⅰ | —CH3 | —OH | —H | —CH3 | Dimethylallyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.150 | Test | |
| 37 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | n-C8H17 | —H | —H | 0.060 | Training | |
| 38 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | Geranyl | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.045 | Training | |
| 39 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | Geranyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.025 | Training |
Table 1 Bioactivity data of 3a flavonoids
| Compd. | Type | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 2' | 3' | 4' | 5' | 6' | KD/ (μmol·L-1) | Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ⅰ | —H | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 34.900 | Training | |
| 2 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —H | 10.100 | Training | |
| 3 | Ⅰ | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 10.100 | Training | |
| 4 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 8.900 | Test | |
| 5 | Ⅰ | —CH3 | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 8.900 | Training | |
| 6 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —OH | —OH | —H | —H | 7.000 | Training | |
| 7 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —F | —H | —H | 6.800 | Training | |
| 8 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —H | 6.700 | Test | |
| 9 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —F | —F | —H | —H | 6.300 | Training | |
| 10 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OCH3 | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 6.300 | Training | |
| 11 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 5.300 | Training | |
| 12 | Ⅱ | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | 4.800 | Test | ||
| 13 | Ⅱ | —H | —H | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | 4.600 | Training | ||
| 14 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —OCH3 | —H | —H | 4.500 | Training | |
| 15 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —Cl | —H | —Cl | —H | —H | 4.000 | Training | |
| 16 | Ⅱ | —H | —F | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | 3.600 | Test | ||
| 17 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —CH3 | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 3.100 | Training | |
| 18 | Ⅱ | —H | —OCH3 | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | 2.300 | Training | ||
| 19 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —I | —H | —H | 2.200 | Training | |
| 20 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —CH3 | —CH3 | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 1.300 | Test | |
| 21 | Ⅱ | —H | —Cl | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | 1.300 | Training | ||
| 22 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | Isopropyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 1.300 | Training | |
| 23 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —I | —H | —H | 1.100 | Training | |
| 24 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | Benzyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.990 | Test | |
| 25 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | Dimethylallyl | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —H | 0.700 | Training | |
| 26 | Ⅱ | —H | —Br | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | 0.570 | Training | ||
| 27 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | Dimethylallyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.450 | Training | |
| 28 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | Benzyl | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.340 | Test | |
| 29 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | Prenyl | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.300 | Training | |
| 30 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | Prenyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.280 | Training | |
| 31 | Ⅱ | —H | —I | —H | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | 0.250 | Training | ||
| 32 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | Prenyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.220 | Test | |
| 33 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | Prenyl | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.210 | Training | |
| 34 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | Dimethylallyl | —H | —H | —OCH3 | —H | —H | 0.200 | Training | |
| 35 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | Dimethylallyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.200 | Training | |
| 36 | Ⅰ | —CH3 | —OH | —H | —CH3 | Dimethylallyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.150 | Test | |
| 37 | Ⅰ | —OH | —OH | —H | —OH | —H | —H | —H | n-C8H17 | —H | —H | 0.060 | Training | |
| 38 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | Geranyl | —OH | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.045 | Training | |
| 39 | Ⅰ | —H | —OH | —H | —OH | Geranyl | —H | —H | —H | —H | —H | 0.025 | Training |
| No. | Modeling method | Training set size | Test set size | r2 | q2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2D-QSAR[ | 46 | 0 | 0.912 | 0.800 | |
| 2 | 2D-QSAR[ | 43 | 14 | 0.826 | 0.721 | 0.679 |
| 3 | Ligand based CoMFA[ | 32 | 9 | 0.747 | 0.639 | 0.802 |
| 4 | Ligand based CoMSIA[ | 32 | 9 | 0.810 | 0.676 | 0.785 |
| 5 | Receptor guided CoMFA[ | 32 | 9 | 0.712 | 0.497 | 0.841 |
| 6 | Receptor guided CoMSIA[ | 32 | 9 | 0.805 | 0.589 | 0.937 |
| 7 | Topomer CoMFA | 30 | 9 | 0.971 | 0.728 | 0.816 |
Table 2 Comparison of QSAR modeling of flavonoids as P-glycoprotein inhibitors
| No. | Modeling method | Training set size | Test set size | r2 | q2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2D-QSAR[ | 46 | 0 | 0.912 | 0.800 | |
| 2 | 2D-QSAR[ | 43 | 14 | 0.826 | 0.721 | 0.679 |
| 3 | Ligand based CoMFA[ | 32 | 9 | 0.747 | 0.639 | 0.802 |
| 4 | Ligand based CoMSIA[ | 32 | 9 | 0.810 | 0.676 | 0.785 |
| 5 | Receptor guided CoMFA[ | 32 | 9 | 0.712 | 0.497 | 0.841 |
| 6 | Receptor guided CoMSIA[ | 32 | 9 | 0.805 | 0.589 | 0.937 |
| 7 | Topomer CoMFA | 30 | 9 | 0.971 | 0.728 | 0.816 |
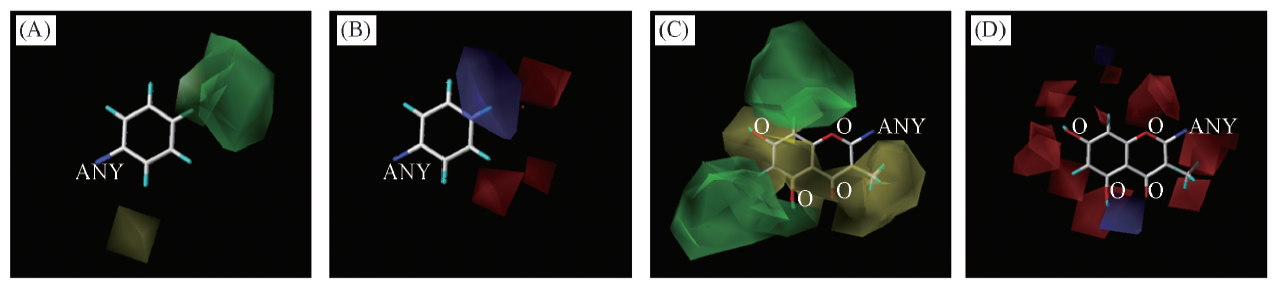
Fig.3 3D contour plots of the Topomer CoMFA modelThe reference molecule used was sample 4(Chrysin). (A) Steric field map of R1-group; (B) electrostatic field map of R1-group;(C) steric field map of R2-group; (D) electrostatic field map of R2-group.
| Molecules | Compd. | Total score | ClogP | H-donor | H-acceptor | Mw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chrysin | 4 | 2.69 | 3.56 | 2 | 4 | 254.24 |
| 6-Prenyl-chrysin | 29 | 3.87 | 5.46 | 2 | 4 | 322.36 |
| 8-Prenyl-chrysin | 30 | 4.06 | 5.51 | 2 | 4 | 322.36 |
| 6-Geranyl-chrysin | 38 | 6.66 | 7.49 | 2 | 4 | 390.48 |
| 8-Geranyl-chrysin | 39 | 7.47 | 7.54 | 2 | 4 | 390.48 |
Table 3 Total score and ClogP values of chrysin and its prenylated derivatives
| Molecules | Compd. | Total score | ClogP | H-donor | H-acceptor | Mw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chrysin | 4 | 2.69 | 3.56 | 2 | 4 | 254.24 |
| 6-Prenyl-chrysin | 29 | 3.87 | 5.46 | 2 | 4 | 322.36 |
| 8-Prenyl-chrysin | 30 | 4.06 | 5.51 | 2 | 4 | 322.36 |
| 6-Geranyl-chrysin | 38 | 6.66 | 7.49 | 2 | 4 | 390.48 |
| 8-Geranyl-chrysin | 39 | 7.47 | 7.54 | 2 | 4 | 390.48 |
| [1] | Tomono T., Kajita M., Yano K., Ogihara T., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2016, 476(4), 183—187 |
| [2] | Chen C. Y., Liu N. Y., Liu H. C., Lee C. Y., Hung C. C., Chang C. S., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2016, 118, 219—229 |
| [3] | Pan X., Mei H., Qu S., Huang S., Sun J., Yang L., Chen H., Int. J. Pharmaceut., 2016, 502(1/2), 61—69 |
| [4] | Leveille-Webster C. R., Arias I. M., J. Membrane. Biol., 1995, 143(2), 89—102 |
| [5] | Wu Y., Pan M., Dai Y., Liu B., Cui J., Shi W., Qiu Q., Huang W., Qian H., Bioorgan. Med. Chem., 2016, 24(10), 2287—2297 |
| [6] | Comte G., Daskiewicz J. B., Bayet C., Conseil G., Viornery-Vanier A., Dumontet C., di Pietro A., Barron D., J. Med. Chem., 2001, 44(5), 763—768 |
| [7] | Barron D., Ibrahim R. K., Phytochem., 1996, 43(5), 921—982 |
| [8] | Karelson M., Lobanov V. S., Katritzky A. R., Chem. Rev., 1996, 96(3), 1027—1044 |
| [9] | Wang J. X., Yang Y., Ma J. H., Zhang L., Guo Q. L., You Q. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities., 2010, 31(6), 1172—1178 |
| (王进欣, 杨燕, 马俊海, 张磊, 郭青龙, 尤启冬. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(6), 1172—1178) | |
| [10] | Zhang L., Ren Z., Lu A., Zhao Z., Xu W., Bao Q., Ding W., Yang C., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2015, 31(2), 228—234 |
| [11] | Li Y., Wang Y. H., Yang L., Zhang S. W., Jiang D., Liu C. H., Yang S. L., J. Dalian Univ. Techno., 2007, 47(1), 15—20 |
| (李燕, 王永华, 杨凌, 张述伟, 蒋达, 刘长厚, 杨胜利. 大连理工大学学报, 2007, 47(1), 15—20) | |
| [12] | Wang Y. H., Li Y., Yang S. L., Yang L., J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des., 2005, 19(3), 137—147 |
| [13] | Wang M. Y., Ma Y., Wang H. Y., Cao G., Li Z. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities., 2016, 37(9), 1636—1642 |
| (王美怡, 马翼, 王海英, 曹刚, 李正名. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(9), 1636—1642) | |
| [14] | Zhang L., Lin Y., Zhou Z. Z., Acta Chim. Sinica,2011, 69(2), 231—238 |
| (张莉, 林云, 周中振. 化学学报, 2011, 69(2), 231—238) | |
| [15] | Tong J., Wu Y., Bai M., Zhan P., J. Mol. Struct., 2017, 1129, 17—22 |
| [16] | Phosrithong N., Ungwitayatorn J., Bioorg. Chem., 2013, 49(6), 9—15 |
| [17] | Xu Z., Chen Y., Qiu Y., Gu W., Li Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2016, 32(6), 348—356 |
| [18] | Subramanian G., Rao S. N., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2012, 20(2), 851—858 |
| [19] | Cramer R. D., J. Med. Chem., 2003, 46(3), 374—388 |
| [20] | di Pietro A., Conseil G., Pérez-Victoria J. M., Dayan G., Baubichon-Cortay H., Trompier D., Steinfels E., Jault J. M., de Wet H., Maitrejean M., Comte G., Boumendjel A., Mariotte A. M., Dumontet C., McIntosh D. B., Goffeau A., Castanys S., Gamarro F., Barron D., Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 2002, 59(2), 307—322 |
| [21] | Kothandan G., Gadhe C. G., Madhavan T., Choi C. H., Cho S. J., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2011, 46(9), 4078—4088 |
| [22] | Huang D. D., Liu Y. L., Shi B. Z., Li Y. T., Wang G. X., Liang G. Z., J. Mol. Graph. Model,2013, 45, 65—83 |
| [23] | Miao X., Liang G. Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities., 2012, 33(10), 2263—2268 |
| (苗霞, 梁桂兆. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(10), 2263—2268) |
| [1] | TANG Guanghui, ZHANG Ya, ZHANG Yuping, ZHOU Pengpeng, LIN Zhihua, WANG Yuanqiang. Molecular Docking, QSAR and Molecular Dynamics Simulation on Phosphorus Containing Pyrimidines as CDK9 Inhibitors† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 2061. |
| [2] | MIAO Xia, LIANG Gui-Zhao. Molecular Design of PTH Derivatives as Tau Protein Inhibitors Using R-Group Search Technology [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(10): 2263. |
| [3] | ZHANG Xi, CHEN Xuan, BAI Xiao-Hong*. Determination of Partition Coefficient and Contents of Flavonoids Compounds Based on Solidification of Floating Organic Drop Liquid-Phase Microextraction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(2): 269. |
| [4] |
LU Juan1, LI Xu-Wen1, GUI Ming-Yu1, LIU Gui-Ying1, ZHU Na1, YU Ai-Min1, OKUYAMA Toru2, MASAKI Baba2, JIN Yong-Ri1* . Studies on Chemical Constituents of Leaves of Actinidia kolomikta Planch(Ⅱ) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(3): 468. |
| [5] | ZHANG Liang, XIANG Yu-Hong, Zhang Zhuo-Yong*. Studies on Hydroxamic Acid Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors(HDACI) by Molecular Docking and CoMFA [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(11(1)): 52. |
| [6] | JIA Shu-Yan1, JI Hai-Tao2, FANG Xue-Xun2, WU Yu-Qing1*. Spectroscopic Study on the Recognition Mechanism Between Matrix Metalloproteinase-16 and Natural Flavonoids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(4): 710. |
| [7] | LIU Zhong-Ying1,2, HU Xiu-Li1,2, BU Feng-Quan2, DING Lan1, ZHANG Han-Qi1. Studies on the Chemical Change in the Process of Microwave-assisted Extraction of Flavonoids from Acanthopanax Senticosus Harms [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(3): 431. |
| [8] | JIN Yong-Ri1, GUI Ming-Yu1, LI Xu-Wen1, LU Juan1, Masaki Baba2, Toru Okuyama2, XU Ji-Qing1*. Studies on Chemical Constituents of Leaves of Actinidia kolomikta [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(11): 2060. |
| [9] | MA Guang-Li1, ZHAO Xiao-Ping2, CHENG Yi-Yu1*. Identification of P-gp Substrates Using a Random Forest Method Based on Chemistry Development Kit Descriptors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(10): 1885. |
| [10] | LI Min-Jing, YOU Jing-Yan, LIU Zhong-Ying, ZHANG Han-Qi. Microwave-assisted Dynamic Extraction of Flavonoids from Flos Sophaoae [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(5): 850. |
| [11] | RUAN Ji-Wu, FU Li-Wu, HUANG Zhi-Shu, CHEN Li-Ming, MA Lin, GU Lian-Quan. Studies on Synthesis of Multiaryl-substituted Imidazoles and Reversal Activity on the Multidrug Resistance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(5): 870. |
| [12] | BAI Yu, GUO Ming-Quan, SONG Feng-Rui, LIU Zhi-Qiang, LIU Shu-Ying . Studies on Flavonoids from Sophora Flavescens Ait Using ESI-MS~n [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(2): 284. |
| [13] | LI Wen-Kui, XIAO Pei-Gen, LIAO Mao-Chuan, ZHANG Ru-Yi. Caohuoside-C from the Aerial Parts of Epimedium Koreanum Nakai [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1995, 16(2): 230. |
| [14] | LI Wen-Kui, XIAO Pei-Gen, LIAO Mao-Chuan, PAN Jing-Qi, Lü Mu-Jian, ZHANG Ru-Yi. Caohuoside-E from the Aerial Parts of Epimedium Koreanum Nakai [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1995, 16(12): 1892. |
| [15] | ZHANG Bao-Lin, WANG Wen-Qing, BAI Feng-Lian. Studies on the Binding of Anthraquinones and Flavonoids to Human Serum Albumin [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1994, 15(3): 373. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||